# nerf_pl
**Repository Path**: feed69/nerf_pl
## Basic Information
- **Project Name**: nerf_pl
- **Description**: No description available
- **Primary Language**: Unknown
- **License**: MIT
- **Default Branch**: master
- **Homepage**: None
- **GVP Project**: No
## Statistics
- **Stars**: 0
- **Forks**: 1
- **Created**: 2023-10-31
- **Last Updated**: 2024-06-01
## Categories & Tags
**Categories**: Uncategorized
**Tags**: None
## README
# nerf_pl
### Update: NVIDIA open-sourced a lightning-fast version of NeRF: [NGP](https://github.com/NVlabs/instant-ngp). I re-implemented in pytorch [here](https://github.com/kwea123/ngp_pl). This version is ~100x faster than this repo with also better quality!
### Update: an improved [NSFF](https://www.cs.cornell.edu/~zl548/NSFF/) implementation to handle dynamic scene is [open](https://github.com/kwea123/nsff_pl)!
### Update: [NeRF-W](https://nerf-w.github.io/) (NeRF in the Wild) implementation is added to [nerfw](https://github.com/kwea123/nerf_pl/tree/nerfw) branch!
### Update: The lastest code (using the latest libraries) will be updated to [dev](https://github.com/kwea123/nerf_pl/tree/dev) branch. The master branch remains to support the colab files. If you don't use colab, it is recommended to switch to dev branch. Only issues of the dev and nerfw branch will be considered currently.
### :gem: [**Project page**](https://kwea123.github.io/nerf_pl/) (live demo!)
Unofficial implementation of [NeRF](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2003.08934.pdf) (Neural Radiance Fields) using pytorch ([pytorch-lightning](https://github.com/PyTorchLightning/pytorch-lightning)). This repo doesn't aim at reproducibility, but aim at providing a simpler and faster training procedure (also simpler code with detailed comments to help to understand the work). Moreover, I try to extend much more opportunities by integrating this algorithm into game engine like Unity.
Official implementation: [nerf](https://github.com/bmild/nerf) .. Reference pytorch implementation: [nerf-pytorch](https://github.com/yenchenlin/nerf-pytorch)
### Recommend to read: A detailed NeRF extension list: [awesome-NeRF](https://github.com/yenchenlin/awesome-NeRF)
## :milky_way: Features
* Multi-gpu training: Training on 8 GPUs finishes within 1 hour for the synthetic dataset!
* [Colab](#mortar_board-colab) notebooks to allow easy usage!
* [Reconstruct](#ribbon-mesh) **colored** mesh!
* [Mixed Reality](https://youtu.be/S5phWFTs2iM) in Unity!
* [REAL TIME volume rendering](https://youtu.be/w9qTbVzCdWk) in Unity!
* [Portable Scenes](#portable-scenes) to let you play with other people's scenes!
### You can find the Unity project including mesh, mixed reality and volume rendering [here](https://github.com/kwea123/nerf_Unity)! See [README_Unity](README_Unity.md) for generating your own data for Unity rendering!
## :beginner: Tutorial
### What can NeRF do?
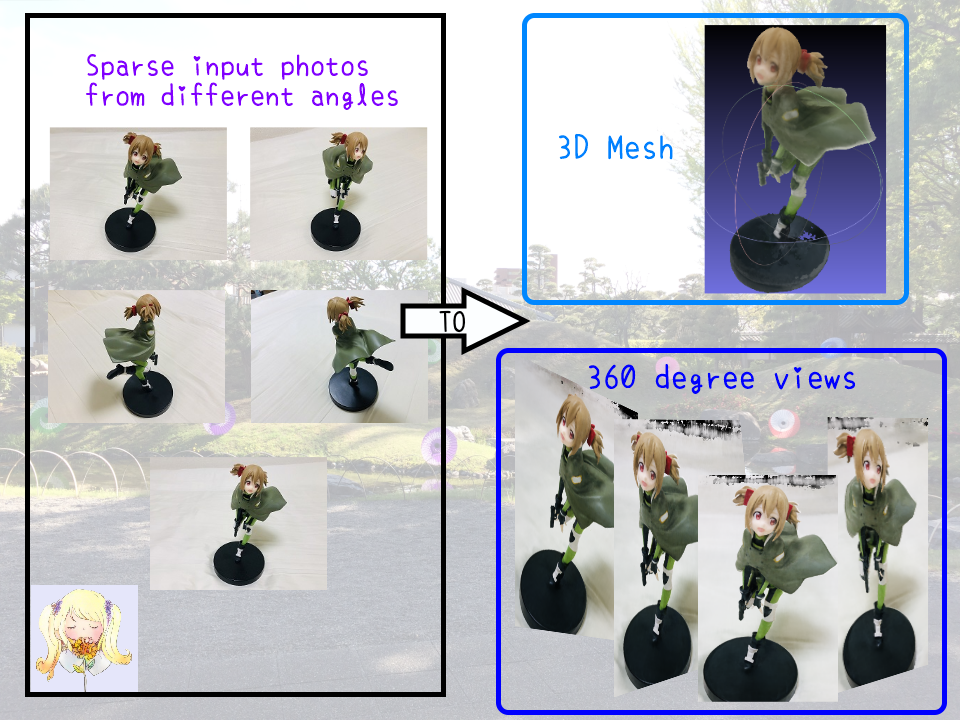 ### Tutorial videos
### Tutorial videos
 # :computer: Installation
## Hardware
* OS: Ubuntu 18.04
* NVIDIA GPU with **CUDA>=10.1** (tested with 1 RTX2080Ti)
## Software
* Clone this repo by `git clone --recursive https://github.com/kwea123/nerf_pl`
* Python>=3.6 (installation via [anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/distribution/) is recommended, use `conda create -n nerf_pl python=3.6` to create a conda environment and activate it by `conda activate nerf_pl`)
* Python libraries
* Install core requirements by `pip install -r requirements.txt`
* Install `torchsearchsorted` by `cd torchsearchsorted` then `pip install .`
# :key: Training
Please see each subsection for training on different datasets. Available training datasets:
* [Blender](#blender) (Realistic Synthetic 360)
* [LLFF](#llff) (Real Forward-Facing)
* [Your own data](#your-own-data) (Forward-Facing/360 inward-facing)
## Blender
# :computer: Installation
## Hardware
* OS: Ubuntu 18.04
* NVIDIA GPU with **CUDA>=10.1** (tested with 1 RTX2080Ti)
## Software
* Clone this repo by `git clone --recursive https://github.com/kwea123/nerf_pl`
* Python>=3.6 (installation via [anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/distribution/) is recommended, use `conda create -n nerf_pl python=3.6` to create a conda environment and activate it by `conda activate nerf_pl`)
* Python libraries
* Install core requirements by `pip install -r requirements.txt`
* Install `torchsearchsorted` by `cd torchsearchsorted` then `pip install .`
# :key: Training
Please see each subsection for training on different datasets. Available training datasets:
* [Blender](#blender) (Realistic Synthetic 360)
* [LLFF](#llff) (Real Forward-Facing)
* [Your own data](#your-own-data) (Forward-Facing/360 inward-facing)
## Blender
Steps
### Data download
Download `nerf_synthetic.zip` from [here](https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/128yBriW1IG_3NJ5Rp7APSTZsJqdJdfc1)
### Training model
Run (example)
```
python train.py \
--dataset_name blender \
--root_dir $BLENDER_DIR \
--N_importance 64 --img_wh 400 400 --noise_std 0 \
--num_epochs 16 --batch_size 1024 \
--optimizer adam --lr 5e-4 \
--lr_scheduler steplr --decay_step 2 4 8 --decay_gamma 0.5 \
--exp_name exp
```
These parameters are chosen to best mimic the training settings in the original repo. See [opt.py](opt.py) for all configurations.
NOTE: the above configuration doesn't work for some scenes like `drums`, `ship`. In that case, consider increasing the `batch_size` or change the `optimizer` to `radam`. I managed to train on all scenes with these modifications.
You can monitor the training process by `tensorboard --logdir logs/` and go to `localhost:6006` in your browser.
## LLFF
Steps
### Data download
Download `nerf_llff_data.zip` from [here](https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/128yBriW1IG_3NJ5Rp7APSTZsJqdJdfc1)
### Training model
Run (example)
```
python train.py \
--dataset_name llff \
--root_dir $LLFF_DIR \
--N_importance 64 --img_wh 504 378 \
--num_epochs 30 --batch_size 1024 \
--optimizer adam --lr 5e-4 \
--lr_scheduler steplr --decay_step 10 20 --decay_gamma 0.5 \
--exp_name exp
```
These parameters are chosen to best mimic the training settings in the original repo. See [opt.py](opt.py) for all configurations.
You can monitor the training process by `tensorboard --logdir logs/` and go to `localhost:6006` in your browser.
## Your own data
Steps
1. Install [COLMAP](https://github.com/colmap/colmap) following [installation guide](https://colmap.github.io/install.html)
2. Prepare your images in a folder (around 20 to 30 for forward facing, and 40 to 50 for 360 inward-facing)
3. Clone [LLFF](https://github.com/Fyusion/LLFF) and run `python img2poses.py $your-images-folder`
4. Train the model using the same command as in [LLFF](#llff). If the scene is captured in a 360 inward-facing manner, add `--spheric` argument.
For more details of training a good model, please see the video [here](#colab).
## Pretrained models and logs
Download the pretrained models and training logs in [release](https://github.com/kwea123/nerf_pl/releases).
## Comparison with other repos
| | training GPU memory in GB | Speed (1 step) |
| :---: | :---: | :---: |
| [Original](https://github.com/bmild/nerf) | 8.5 | 0.177s |
| [Ref pytorch](https://github.com/yenchenlin/nerf-pytorch) | 6.0 | 0.147s |
| This repo | 3.2 | 0.12s |
The speed is measured on 1 RTX2080Ti. Detailed profile can be found in [release](https://github.com/kwea123/nerf_pl/releases).
Training memory is largely reduced, since the original repo loads the whole data to GPU at the beginning, while we only pass batches to GPU every step.
# :mag_right: Testing
See [test.ipynb](test.ipynb) for a simple view synthesis and depth prediction on 1 image.
Use [eval.py](eval.py) to create the whole sequence of moving views.
E.g.
```
python eval.py \
--root_dir $BLENDER \
--dataset_name blender --scene_name lego \
--img_wh 400 400 --N_importance 64 --ckpt_path $CKPT_PATH
```
**IMPORTANT** : Don't forget to add `--spheric_poses` if the model is trained under `--spheric` setting!
It will create folder `results/{dataset_name}/{scene_name}` and run inference on all test data, finally create a gif out of them.
Example of lego scene using pretrained model and the reconstructed **colored** mesh: (PSNR=31.39, paper=32.54)
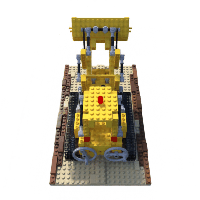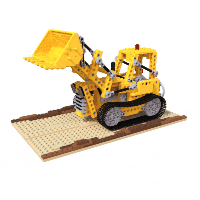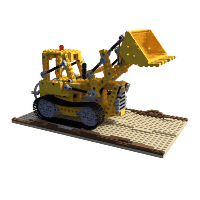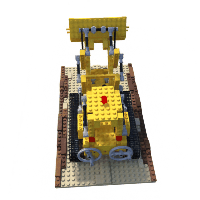

Example of fern scene using pretrained model:

Example of own scene ([Silica GGO figure](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hVQIvEq_Av0)) and the reconstructed **colored** mesh. Click to link to youtube video.


## Portable scenes
The concept of NeRF is that the whole scene is compressed into a NeRF model, then we can render from any pose we want. To render from plausible poses, we can leverage the training poses; therefore, you can generate video with **only** the trained model and the poses (hence the name of portable scenes). I provided my silica model in [release](https://github.com/kwea123/nerf_pl/releases), feel free to play around with it!
If you trained some interesting scenes, you are also welcomed to share the model (and the `poses_bounds.npy`) by sending me an email, or post in issues! After all, a model is just around **5MB**! Please run `python utils/save_weights_only.py --ckpt_path $YOUR_MODEL_PATH` to extract the final model.
# :ribbon: Mesh
See [README_mesh](README_mesh.md) for reconstruction of **colored** mesh. Only supported for blender dataset and 360 inward-facing data!
# :warning: Notes on differences with the original repo
* The learning rate decay in the original repo is **by step**, which means it decreases every step, here I use learning rate decay **by epoch**, which means it changes only at the end of 1 epoch.
* The validation image for LLFF dataset is chosen as the most centered image here, whereas the original repo chooses every 8th image.
* The rendering spiral path is slightly different from the original repo (I use approximate values to simplify the code).
# :mortar_board: COLAB
I also prepared colab notebooks that allow you to run the algorithm on any machine without GPU requirement.
* [colmap](https://gist.github.com/kwea123/f0e8f38ff2aa94495dbfe7ae9219f75c) to prepare camera poses for your own training data
* [nerf](https://gist.github.com/kwea123/a3c541a325e895ef79ecbc0d2e6d7221) to train on your data
* [extract_mesh](https://gist.github.com/kwea123/77ed1640f9bc9550136dc13a6a419e88) to extract colored mesh
Please see [this playlist](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLDV2CyUo4q-K02pNEyDr7DYpTQuka3mbV) for the detailed tutorials.
# :jack_o_lantern: SHOWOFF
We can incorporate *ray tracing* techniques into the volume rendering pipeline, and realize realistic scene editing (following is the `materials` scene with an object removed, and a mesh is inserted and rendered with ray tracing). The code **will not** be released.


With my integration in Unity, I can realize realistic mixed reality photos (note my character casts shadow on the scene, **zero** post- image editing required):


BTW, I would like to visit the museum one day...
# :book: Citation
If you use (part of) my code or find my work helpful, please consider citing
```
@misc{queianchen_nerf,
author={Quei-An, Chen},
title={Nerf_pl: a pytorch-lightning implementation of NeRF},
url={https://github.com/kwea123/nerf_pl/},
year={2020},
}
```

 ### Tutorial videos
### Tutorial videos
 # :computer: Installation
## Hardware
* OS: Ubuntu 18.04
* NVIDIA GPU with **CUDA>=10.1** (tested with 1 RTX2080Ti)
## Software
* Clone this repo by `git clone --recursive https://github.com/kwea123/nerf_pl`
* Python>=3.6 (installation via [anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/distribution/) is recommended, use `conda create -n nerf_pl python=3.6` to create a conda environment and activate it by `conda activate nerf_pl`)
* Python libraries
* Install core requirements by `pip install -r requirements.txt`
* Install `torchsearchsorted` by `cd torchsearchsorted` then `pip install .`
# :key: Training
Please see each subsection for training on different datasets. Available training datasets:
* [Blender](#blender) (Realistic Synthetic 360)
* [LLFF](#llff) (Real Forward-Facing)
* [Your own data](#your-own-data) (Forward-Facing/360 inward-facing)
## Blender
# :computer: Installation
## Hardware
* OS: Ubuntu 18.04
* NVIDIA GPU with **CUDA>=10.1** (tested with 1 RTX2080Ti)
## Software
* Clone this repo by `git clone --recursive https://github.com/kwea123/nerf_pl`
* Python>=3.6 (installation via [anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/distribution/) is recommended, use `conda create -n nerf_pl python=3.6` to create a conda environment and activate it by `conda activate nerf_pl`)
* Python libraries
* Install core requirements by `pip install -r requirements.txt`
* Install `torchsearchsorted` by `cd torchsearchsorted` then `pip install .`
# :key: Training
Please see each subsection for training on different datasets. Available training datasets:
* [Blender](#blender) (Realistic Synthetic 360)
* [LLFF](#llff) (Real Forward-Facing)
* [Your own data](#your-own-data) (Forward-Facing/360 inward-facing)
## Blender

