 -
-  -
- -
-我可以通过表格或者图片报告我的实验结果
-
-Algo | Acc |
------| ---- |
-KNN | 0.94 |
-
-## 代码使用方法
-
-```bash
-python source.py g # 生成数据集
-python source.py d # 展示数据集
-python source.py # 训练和测试
-```
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/15307130115/img/test.png b/assignment-1/submission/15307130115/img/test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 91eb7f4d19ce5d49a18e16441f824b8190ea4b1a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/15307130115/img/test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/15307130115/img/train.png b/assignment-1/submission/15307130115/img/train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index b33f36f126e616f1ade524bbd1c814355f2d518f..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/15307130115/img/train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/15307130115/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/15307130115/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 4717ab4ea92c73cd07d43101822c360cac8c2014..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/15307130115/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,96 +0,0 @@
-import sys
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
-
-class KNN:
-
- def __init__(self):
- pass
-
- def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- N = train_data.shape[0]
- cut = N//5*4
-
- train_data, dev_data = train_data[:cut,], train_data[cut:,]
- train_label, dev_label = train_label[:cut,], train_label[cut:,]
-
- max_score = 0
- max_score_K = 0
- for k in range(2,6):
- clf = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=k)
- clf.fit(train_data, train_label)
- score = clf.score(dev_data, dev_label)
- if score > max_score:
- max_score, max_score_K = score, k
-
- self.clf = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=max_score_K)
- self.clf.fit(
- np.concatenate([train_data,dev_data]),
- np.concatenate([train_label, dev_label])
- )
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- return self.clf.predict(test_data)
-
-
-def generate():
- mean = (1, 2)
- cov = np.array([[73, 0], [0, 22]])
- x = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (800,))
-
- mean = (16, -5)
- cov = np.array([[21.2, 0], [0, 32.1]])
- y = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (200,))
-
- mean = (10, 22)
- cov = np.array([[10,5],[5,10]])
- z = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (1000,))
-
- idx = np.arange(2000)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- data = np.concatenate([x,y,z])
- label = np.concatenate([
- np.zeros((800,),dtype=int),
- np.ones((200,),dtype=int),
- np.ones((1000,),dtype=int)*2
- ])
- data = data[idx]
- label = label[idx]
-
- train_data, test_data = data[:1600,], data[1600:,]
- train_label, test_label = label[:1600,], label[1600:,]
- np.save("data.npy",(
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
- ))
-
-
-def read():
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = np.load("data.npy",allow_pickle=True)
- return (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
-
-def display(data, label, name):
- datas =[[],[],[]]
- for i in range(len(data)):
- datas[label[i]].append(data[i])
-
- for each in datas:
- each = np.array(each)
- plt.scatter(each[:, 0], each[:, 1])
- plt.savefig(f'img/{name}')
- plt.show()
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "g":
- generate()
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "d":
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
- display(train_data, train_label, 'train')
- display(test_data, test_label, 'test')
- else:
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
-
- model = KNN()
- model.fit(train_data, train_label)
- res = model.predict(test_data)
- print("acc =",np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label)))
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index e204f9885f8172a6e79721a5f17d14f2ca9f51e4..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,343 +0,0 @@
-# 课程报告
-
-这是一个有关KNN模型的实验报告,我的代码保存在source.py中。本次实验使用了**numpy**库作为数据分析的工具,基于**matplotlib**库进行数据展示。
-
-## 一、数据集的生成与划分
-
-笔者采用以下参数产生四个不同的二维高斯分布数据集,每类使用不同的标签标记,这四组数据集分别是:
-
-+ 第一类数据,数量为400个,标签为0:
-
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-35 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 23
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-13 & 4
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-+ 第二类数据,数量为800个,标签为1:
-
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-12 & 1 \\\\
-1 & 35
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-1 & 14
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-+ 第三类数据,数量为1200个,标签为2:
-
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-33 & 5 \\\\
-5 & 9
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
--8 & -3
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-+ 第四类数据,数量为1600个,标签为3:
-
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-25 & 6 \\\\
-6 & 18
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
--15 & 10
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-将这四类数据集混合后打乱次序,将其中的80%(3200个)划分为训练集,20%(800个)划分为测试集,可以形成以下图像
-
-这是我生成的训练集:
-
-
-
-我可以通过表格或者图片报告我的实验结果
-
-Algo | Acc |
------| ---- |
-KNN | 0.94 |
-
-## 代码使用方法
-
-```bash
-python source.py g # 生成数据集
-python source.py d # 展示数据集
-python source.py # 训练和测试
-```
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/15307130115/img/test.png b/assignment-1/submission/15307130115/img/test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 91eb7f4d19ce5d49a18e16441f824b8190ea4b1a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/15307130115/img/test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/15307130115/img/train.png b/assignment-1/submission/15307130115/img/train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index b33f36f126e616f1ade524bbd1c814355f2d518f..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/15307130115/img/train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/15307130115/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/15307130115/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 4717ab4ea92c73cd07d43101822c360cac8c2014..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/15307130115/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,96 +0,0 @@
-import sys
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
-
-class KNN:
-
- def __init__(self):
- pass
-
- def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- N = train_data.shape[0]
- cut = N//5*4
-
- train_data, dev_data = train_data[:cut,], train_data[cut:,]
- train_label, dev_label = train_label[:cut,], train_label[cut:,]
-
- max_score = 0
- max_score_K = 0
- for k in range(2,6):
- clf = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=k)
- clf.fit(train_data, train_label)
- score = clf.score(dev_data, dev_label)
- if score > max_score:
- max_score, max_score_K = score, k
-
- self.clf = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=max_score_K)
- self.clf.fit(
- np.concatenate([train_data,dev_data]),
- np.concatenate([train_label, dev_label])
- )
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- return self.clf.predict(test_data)
-
-
-def generate():
- mean = (1, 2)
- cov = np.array([[73, 0], [0, 22]])
- x = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (800,))
-
- mean = (16, -5)
- cov = np.array([[21.2, 0], [0, 32.1]])
- y = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (200,))
-
- mean = (10, 22)
- cov = np.array([[10,5],[5,10]])
- z = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (1000,))
-
- idx = np.arange(2000)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- data = np.concatenate([x,y,z])
- label = np.concatenate([
- np.zeros((800,),dtype=int),
- np.ones((200,),dtype=int),
- np.ones((1000,),dtype=int)*2
- ])
- data = data[idx]
- label = label[idx]
-
- train_data, test_data = data[:1600,], data[1600:,]
- train_label, test_label = label[:1600,], label[1600:,]
- np.save("data.npy",(
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
- ))
-
-
-def read():
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = np.load("data.npy",allow_pickle=True)
- return (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
-
-def display(data, label, name):
- datas =[[],[],[]]
- for i in range(len(data)):
- datas[label[i]].append(data[i])
-
- for each in datas:
- each = np.array(each)
- plt.scatter(each[:, 0], each[:, 1])
- plt.savefig(f'img/{name}')
- plt.show()
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "g":
- generate()
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "d":
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
- display(train_data, train_label, 'train')
- display(test_data, test_label, 'test')
- else:
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
-
- model = KNN()
- model.fit(train_data, train_label)
- res = model.predict(test_data)
- print("acc =",np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label)))
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index e204f9885f8172a6e79721a5f17d14f2ca9f51e4..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,343 +0,0 @@
-# 课程报告
-
-这是一个有关KNN模型的实验报告,我的代码保存在source.py中。本次实验使用了**numpy**库作为数据分析的工具,基于**matplotlib**库进行数据展示。
-
-## 一、数据集的生成与划分
-
-笔者采用以下参数产生四个不同的二维高斯分布数据集,每类使用不同的标签标记,这四组数据集分别是:
-
-+ 第一类数据,数量为400个,标签为0:
-
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-35 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 23
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-13 & 4
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-+ 第二类数据,数量为800个,标签为1:
-
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-12 & 1 \\\\
-1 & 35
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-1 & 14
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-+ 第三类数据,数量为1200个,标签为2:
-
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-33 & 5 \\\\
-5 & 9
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
--8 & -3
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-+ 第四类数据,数量为1600个,标签为3:
-
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-25 & 6 \\\\
-6 & 18
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
--15 & 10
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-将这四类数据集混合后打乱次序,将其中的80%(3200个)划分为训练集,20%(800个)划分为测试集,可以形成以下图像
-
-这是我生成的训练集:
-
- -
-这是我生成的测试集:
-
-
-
-这是我生成的测试集:
-
- -
-## 二、KNN模型
-
-笔者的KNN模型包含5个属性和2个方法。
-
-三个属性分别为*k、data、label、mean、std*,其中*k*用来记录模型选择的近邻个数,*data*用来保存训练集的输入,*label*保存训练集的标签,*mean*记录训练集的均值,*std*记录训练集的标准差。
-
-两个方法分别是`model.fit()`与`model.predict()`。`model.fit()`方法主要包含以下步骤:
-
-1. 进行标准化处理:
- $$
- \bar{X}=\frac{X-\mu}{\sigma}
- $$
- 其中$ \mu $是训练集的均值,$\sigma$是训练集的标准差。
-
-2. 采用k折交叉验证方式,将训练集分割为k个子集(这里k取5),将其中一个作为验证集,其余的作为训练集。
-
-3. 对KNN的参数k,从1开始逐步增大,寻找到在验证集上准确率最高的k,作为测试时使用的参数。其中k增大的步长为2,上限为`min(30, int(n * .8))`即取30与训练集数量乘以0.8以后较小的那一个值。
-
-`model.predict()`方法用来预测新数据的类别,主要是先对数据进行标准化处理,再逐一进行预测,距离上采用欧氏距离作为度量,计算样本$X_{new}$与训练集中每一个样本之间的距离,从中选出最小的k个样本,采用投票的方式决定$X_{new}$的类别。
-
-## 三、实验结果分析
-
-笔者进行了十次实验,采用了不同的随机数种子产生不同的二维正态分布集合,这十次的实验结果如下:
-
-| 序号 | K | Acc |
-| :------- | :------- | ---------- |
-| 1 | 5 | 93.63% |
-| 2 | 29 | 95.00% |
-| 3 | 25 | 94.13% |
-| 4 | 19 | 96.38% |
-| 5 | 23 | 94.63% |
-| 6 | 9 | 94.75% |
-| 7 | 9 | 93.50% |
-| 8 | 21 | 93.13% |
-| 9 | 9 | 94.75% |
-| 10 | 19 | 92.63% |
-| **均值** | **16.8** | **94.23%** |
-
-可以看出,k取值存在选取大值的倾向,10次实验中仅有一次k值小于等于5,共计4次小于10,其余实验k取值都在19以上;准确率能够达到92%以上,比较高,说明KNN分类器模型的确能够对数据集进行正确分类,而分类错误的样本主要集中于不同*label*数据集间的交叉地带。
-
-## 四、修改数据集进行实验探究
-
-下面,笔者将通过修改生成数据集之间的距离、方差、数量以及计算样本距离的方式和归一化与否来对KNN模型进行探究。
-
-### 1、数据集间的距离
-
-在保持前文生成数据集方差不变的情况下,笔者修改了$\mu$的取值,从而可以控制分布之间的远近关系。
-
-1. #### 缩小分布之间的相对距离
-
- 笔者将原定的$\mu$参数缩小为原来的$1/10$,分布之间的距离更近,如下图所示:
-
- 训练集:
-
-
-
-## 二、KNN模型
-
-笔者的KNN模型包含5个属性和2个方法。
-
-三个属性分别为*k、data、label、mean、std*,其中*k*用来记录模型选择的近邻个数,*data*用来保存训练集的输入,*label*保存训练集的标签,*mean*记录训练集的均值,*std*记录训练集的标准差。
-
-两个方法分别是`model.fit()`与`model.predict()`。`model.fit()`方法主要包含以下步骤:
-
-1. 进行标准化处理:
- $$
- \bar{X}=\frac{X-\mu}{\sigma}
- $$
- 其中$ \mu $是训练集的均值,$\sigma$是训练集的标准差。
-
-2. 采用k折交叉验证方式,将训练集分割为k个子集(这里k取5),将其中一个作为验证集,其余的作为训练集。
-
-3. 对KNN的参数k,从1开始逐步增大,寻找到在验证集上准确率最高的k,作为测试时使用的参数。其中k增大的步长为2,上限为`min(30, int(n * .8))`即取30与训练集数量乘以0.8以后较小的那一个值。
-
-`model.predict()`方法用来预测新数据的类别,主要是先对数据进行标准化处理,再逐一进行预测,距离上采用欧氏距离作为度量,计算样本$X_{new}$与训练集中每一个样本之间的距离,从中选出最小的k个样本,采用投票的方式决定$X_{new}$的类别。
-
-## 三、实验结果分析
-
-笔者进行了十次实验,采用了不同的随机数种子产生不同的二维正态分布集合,这十次的实验结果如下:
-
-| 序号 | K | Acc |
-| :------- | :------- | ---------- |
-| 1 | 5 | 93.63% |
-| 2 | 29 | 95.00% |
-| 3 | 25 | 94.13% |
-| 4 | 19 | 96.38% |
-| 5 | 23 | 94.63% |
-| 6 | 9 | 94.75% |
-| 7 | 9 | 93.50% |
-| 8 | 21 | 93.13% |
-| 9 | 9 | 94.75% |
-| 10 | 19 | 92.63% |
-| **均值** | **16.8** | **94.23%** |
-
-可以看出,k取值存在选取大值的倾向,10次实验中仅有一次k值小于等于5,共计4次小于10,其余实验k取值都在19以上;准确率能够达到92%以上,比较高,说明KNN分类器模型的确能够对数据集进行正确分类,而分类错误的样本主要集中于不同*label*数据集间的交叉地带。
-
-## 四、修改数据集进行实验探究
-
-下面,笔者将通过修改生成数据集之间的距离、方差、数量以及计算样本距离的方式和归一化与否来对KNN模型进行探究。
-
-### 1、数据集间的距离
-
-在保持前文生成数据集方差不变的情况下,笔者修改了$\mu$的取值,从而可以控制分布之间的远近关系。
-
-1. #### 缩小分布之间的相对距离
-
- 笔者将原定的$\mu$参数缩小为原来的$1/10$,分布之间的距离更近,如下图所示:
-
- 训练集:
-
-  -
- 训练集:
-
-
-
- 训练集:
-
-  -
- 距离拉近后,不同分布已经重合到了一起,同样进行十次训练,其结果如下
-
- | 序号 | K | Acc |
- | :------- | :------- | ---------- |
- | 1 | 27 | 43.50% |
- | 2 | 27 | 42.25% |
- | 3 | 21 | 41.86% |
- | 4 | 29 | 43.25% |
- | 5 | 17 | 43.63% |
- | 6 | 29 | 42.75% |
- | 7 | 27 | 41.38% |
- | 8 | 29 | 40.00% |
- | 9 | 23 | 44.13% |
- | 10 | 27 | 41.88% |
- | **均值** | **25.6** | **42.46%** |
-
- 可见,这十次训练所取的K值更大,仅有一次小于20;准确率最高不超过45%,说明分布之间的距离较近会降低分类器的准确率。
-
-
-
-2. #### 扩大分布之间的相对距离
-
- 笔者将原定的$\mu$参数扩大为原来的2倍,分布之间的距离更远,如下图所示:
-
- 训练集:
-
-
-
- 距离拉近后,不同分布已经重合到了一起,同样进行十次训练,其结果如下
-
- | 序号 | K | Acc |
- | :------- | :------- | ---------- |
- | 1 | 27 | 43.50% |
- | 2 | 27 | 42.25% |
- | 3 | 21 | 41.86% |
- | 4 | 29 | 43.25% |
- | 5 | 17 | 43.63% |
- | 6 | 29 | 42.75% |
- | 7 | 27 | 41.38% |
- | 8 | 29 | 40.00% |
- | 9 | 23 | 44.13% |
- | 10 | 27 | 41.88% |
- | **均值** | **25.6** | **42.46%** |
-
- 可见,这十次训练所取的K值更大,仅有一次小于20;准确率最高不超过45%,说明分布之间的距离较近会降低分类器的准确率。
-
-
-
-2. #### 扩大分布之间的相对距离
-
- 笔者将原定的$\mu$参数扩大为原来的2倍,分布之间的距离更远,如下图所示:
-
- 训练集:
-
-  -
- 测试集:
-
-
-
- 测试集:
-
-  -
- 距离放大后,不同分布之间没有重合,实验结果显示分类正确率为100%,k值均取1
-
-
-由此可知,在方差不变的情况下,分布之间距离越近KNN分类器的准确率越低,距离越远准确率越高。这与KNN分类器的分类原理是分不开的,当分布之间距离较大时,待检测样本的周围只有同类样本,所以分类正确率较高,反之则会受到其他分布样本的干扰,从而降低准确率。
-
-### 2、分布的方差
-在保持原分布$\mu$不变的情况下,笔者修改了分布的方差进行实验。
-1. #### 缩小方差
- 将方差缩小为原来的1/2,同一标签下内的样本分布得更加紧密,如下图所示:
- 训练集:
-
-
-
- 距离放大后,不同分布之间没有重合,实验结果显示分类正确率为100%,k值均取1
-
-
-由此可知,在方差不变的情况下,分布之间距离越近KNN分类器的准确率越低,距离越远准确率越高。这与KNN分类器的分类原理是分不开的,当分布之间距离较大时,待检测样本的周围只有同类样本,所以分类正确率较高,反之则会受到其他分布样本的干扰,从而降低准确率。
-
-### 2、分布的方差
-在保持原分布$\mu$不变的情况下,笔者修改了分布的方差进行实验。
-1. #### 缩小方差
- 将方差缩小为原来的1/2,同一标签下内的样本分布得更加紧密,如下图所示:
- 训练集:
-
-  -
- 测试集:
-
-
-
- 测试集:
-
-  -
- 同样进行十次实验,结果如下:
- | 序号 | K | Acc |
- | :------- | :------- | ---------- |
- | 1 | 13 | 99.63% |
- | 2 | 9 | 99.50% |
- | 3 | 3 | 99.50% |
- | 4 | 9 | 100.00% |
- | 5 | 5 | 99.38% |
- | 6 | 19 | 99.00% |
- | 7 | 7 | 99.38% |
- | 8 | 3 | 98.75% |
- | 9 | 17 | 99.75% |
- | 10 | 9 | 98.63% |
- | **均值** | **9.4** | **99.35%** |
-
- 这十次实验的k取值更小,仅有三次超过10,准确率更高,表明方差减小有可能提升KNN分类器的准确率。
-2. #### 增大方差
-
- 笔者将原定的$\mu$参数扩大为原来的2倍,分布之间的距离更远,如下图所示:
- 训练集:
-
-
-
- 同样进行十次实验,结果如下:
- | 序号 | K | Acc |
- | :------- | :------- | ---------- |
- | 1 | 13 | 99.63% |
- | 2 | 9 | 99.50% |
- | 3 | 3 | 99.50% |
- | 4 | 9 | 100.00% |
- | 5 | 5 | 99.38% |
- | 6 | 19 | 99.00% |
- | 7 | 7 | 99.38% |
- | 8 | 3 | 98.75% |
- | 9 | 17 | 99.75% |
- | 10 | 9 | 98.63% |
- | **均值** | **9.4** | **99.35%** |
-
- 这十次实验的k取值更小,仅有三次超过10,准确率更高,表明方差减小有可能提升KNN分类器的准确率。
-2. #### 增大方差
-
- 笔者将原定的$\mu$参数扩大为原来的2倍,分布之间的距离更远,如下图所示:
- 训练集:
-
-  -
- 测试集:
-
-
-
- 测试集:
-
-  -
- 同样进行十次实验,结果如下:
- | 序号 | K | Acc |
- | :------- | :------- | ---------- |
- | 1 | 17 | 84.50% |
- | 2 | 19 | 82.50% |
- | 3 | 21 | 83.50% |
- | 4 | 19 | 84.63% |
- | 5 | 15 | 85.88% |
- | 6 | 7 | 81.13% |
- | 7 | 15 | 83.38% |
- | 8 | 13 | 82.63% |
- | 9 | 23 | 84.75% |
- | 10 | 29 | 83.50% |
- | **均值** | **17.8** | **83.64%** |
-
- 这十次实验的k取值变大,准确率降低,表明方差增大有可能降低KNN分类器的准确率。
-
-
-总而言之,数据集分布的离散程度会影响分类器的准确率,同一分布的数据越集中,分类准确率越高,反之越低。数据越分散,相当于不同的数据之间重合的可能性越高,因此更难进行准确地分类。
-### 3、数据的数量
-将每个标签下数据的数量降低为原来的1/10、扩大为原来的2倍,分别进行10次实验,实验结果如下:
-
-| 序号 | k(数量减少) | Acc(数量减少) | k(数量增大) | Acc(数量增大) |
-| -------- | ------------- | --------------- | ------------- | --------------- |
-| 1 | 15 | 95.00% | 5 | 94.69% |
-| 2 | 1 | 95.00% | 25 | 94.50% |
-| 3 | 5 | 92.50% | 13 | 93.88% |
-| 4 | 3 | 93.75% | 21 | 93.56% |
-| 5 | 27 | 98.75% | 15 | 94.88% |
-| 6 | 19 | 93.75% | 23 | 94.06% |
-| 7 | 3 | 96.25% | 29 | 94.50% |
-| 8 | 5 | 93.75% | 13 | 94.63% |
-| 9 | 3 | 90.00% | 17 | 93.63% |
-| 10 | 11 | 98.75% | 15 | 95.19% |
-| **均值** | **9.2** | **94.75%** | **17.6** | **94.35%** |
-
-可见,在一定范围内,数量的改变并不能影响模型的准确率,但是通过实验发现当样本数量增大时,KNN模型的速度会变慢。
-
-### 4、样本距离计算方式
-
-下面,笔者分别采用以下距离进行实验:
-
-曼哈顿距离(L1范数):
-
-$$
-L_ 1(x_ i,x_ j) = \sum^{n}_ {l=1} |x^{(l)}_ {i} - x^{(l)}_ {j}|
-\tag{1}
-$$
-
-欧氏距离(L2范数):
-
-$$
-L_2(x_i,x_j) =
-(\sum^{n}_ {l=1} |x^{(l)}_ i-x^{(l)}_ {j}|^2 )^{\frac{1}{2}}
-\tag{2}$$
-
-切比雪夫距离(L∞范数):
-$$
-L_{\infty}(x_i,x_j) = max_l|x^{(l)}_i-x^{(l)}_j|
-\tag{3}
-$$
-
-此外,笔者还引入了高斯核函数$K(x_i,x_j)$,将原始样本$x_i$映射入新的特征空间变为$\phi(x_i)$,在新的空间内进行距离计算。实际上,通过核函数,可以不用直接转换样本的坐标而隐式地计算样本在新特征空间内的距离,因为在新的特征空间中,两个样本点之间的距离$D(x_i,x_j)$可以通过核函数隐式地获得:
-$$
-\begin{align}
-D^2(x_i,x_j)&=||\phi(x_i)-\phi(x_j)||^2\\\\
-&=K(x_i, x_i) - 2K(x_i,x_j) + K(x_j,x_j)
-\end{align}
-$$
-这三种距离的控制主要通过`dis_function()`函数实现:
-
-```python
-def dis_function(x, y, mode='L2'):
- d = y.shape[1]
- x = x.reshape(1, -1)
- y = y.reshape(-1, d)
- if mode == 'L2':
- return np.linalg.norm(x - y, axis=1)
- elif mode == 'L1':
- return np.linalg.norm(x - y, axis=1, ord=1)
- elif mode == 'L_inf':
- return np.linalg.norm(x - y, axis=1, ord=np.inf)
- elif mode == 'Gaussian':
- gamma = 1e-3
- var = lambda x_i, x_j: np.exp(- gamma * np.square(np.linalg.norm(x_i - x_j, axis=1)))
- return np.sqrt(var(x, x) - 2 * var(x, y) + var(y, y))
-```
-
-为了使采用不同距离的分类器具有区别性,笔者将原数据集的参数$\Sigma$扩大为原来的两倍,实验结果如下:
-
-| 序号 | k_L1 | Acc_L1 | k_L2 | Acc_L2 | k_L∞ | Acc_L∞ | k_Gaussian | Acc_Gaussian |
-| -------- | -------- | ---------- | -------- | ---------- | -------- | ---------- | ---------- | ------------ |
-| 1 | 23 | 84.25% | 17 | 84.50% | 15 | 83.88% | 17 | 84.50% |
-| 2 | 19 | 82.63% | 19 | 82.50% | 15 | 82.38% | 19 | 82.50% |
-| 3 | 21 | 83.23% | 21 | 83.50% | 15 | 83.63% | 21 | 83.50% |
-| 4 | 19 | 85.25% | 19 | 84.63% | 21 | 85.00% | 19 | 84.63% |
-| 5 | 13 | 85.50% | 15 | 85.88% | 23 | 85.88% | 15 | 85.88% |
-| 6 | 21 | 82.75% | 7 | 81.13% | 13 | 83.13% | 7 | 81.13% |
-| 7 | 13 | 83.38% | 15 | 83.38% | 19 | 84.13% | 15 | 83.38% |
-| 8 | 11 | 82.87% | 13 | 82.63% | 17 | 82.26% | 13 | 82.63% |
-| 9 | 21 | 84.63% | 23 | 84.75% | 9 | 83.63% | 23 | 84.75% |
-| 10 | 27 | 84.00% | 29 | 83.50% | 23 | 83.38% | 29 | 83.50% |
-| **均值** | **18.8** | **83.89%** | **17.8** | **83.64%** | **17.0** | **83.72%** | **17.8** | **83.64%** |
-
-可以看出,在此数据分布下,不同的距离计算方式并没有产生较大的影响。此外,采用高斯核函数映射原数据所得到的结果并无不同,可见此情景下,高斯核函数也没有产生促进分类的作用。
-
-### 5、标准化
-
-下面是分别是在原数据集上进行的实验结果,区别是是否执行了标准化:
-
-| 序号 | k_without_normalization | Acc_without_normalization | k_with_normalization | Acc_with_normalization |
-| -------- | ----------------------- | ------------------------- | -------------------- | ---------------------- |
-| 1 | 5 | 93.50% | 5 | 93.63% |
-| 2 | 25 | 94.63% | 29 | 95.00% |
-| 3 | 27 | 94.50% | 25 | 94.13% |
-| 4 | 9 | 95.50% | 19 | 96.38% |
-| 5 | 25 | 94.50% | 23 | 94.63% |
-| 6 | 9 | 94.88% | 9 | 94.75% |
-| 7 | 9 | 93.13% | 9 | 93.50% |
-| 8 | 19 | 93.25% | 21 | 93.13% |
-| 9 | 5 | 95.50% | 9 | 94.75% |
-| 10 | 17 | 93.25% | 19 | 92.63% |
-| **均值** | **18.8** | **94.26%** | **16.8** | **94.23%** |
-
-从现有的实验结果来看,标准化并不能明显地提升KNN分类器的准确率,其是否有效还需要进一步的探究。
-
-## 五、代码使用方式
-
-```bash
-python source.py g # 生成数据集
-python source.py d # 展示数据集
-python source.py # 训练和测试
-```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test.png b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index d134664a436ac258eae767ab0245d0a6af0753fe..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_close.png b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_close.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 5dc3292a77d8176c8446cfab2fc11726dd1a8ee7..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_close.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_divide.png b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_divide.png
deleted file mode 100644
index d019e98a5c41530e60920e67a903277f088d6ee6..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_divide.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_far.png b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_far.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 1fed8f774e5b48753f86fa7336be29ad407fa70c..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_far.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_gather.png b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_gather.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 34733b975ead375a61abfbb15b59e16f1ea182b4..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_gather.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train.png b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index f083fb235fba9f5e34175a9708fe5ac6979b423d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_close.png b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_close.png
deleted file mode 100644
index efce494fc03a80b7d587ea1dae9f7c8dfb20f56a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_close.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_divide.png b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_divide.png
deleted file mode 100644
index bea982d45d81519fbaa9b1dbb10c89fb3949d224..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_divide.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_far.png b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_far.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 80e7c6dd3a3d62ae39533f32ea0b29b52833e96a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_far.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_gather.png b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_gather.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 6860b6113ea0c0ee832491ea37e9d5b136e7869a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_gather.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 712d25173c94b0c8107c7808267ed8482c464af1..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,244 +0,0 @@
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import random
-import sys
-
-NUM_OF_LABELS = 4
-DIMENSION = 2
-# 用来控制数据集的样本个数
-NUM_BASIS = 200
-
-
-
-def set_random_seed(seed):
- np.random.seed(seed)
- random.seed(seed)
-
-
-def dis_function(x, y, mode='L2'):
- d = y.shape[1]
- x = x.reshape(1, -1)
- y = y.reshape(-1, d)
- if mode == 'L2':
- return np.linalg.norm(x - y, axis=1)
- elif mode == 'L1':
- return np.linalg.norm(x - y, axis=1, ord=1)
- elif mode == 'L_inf':
- return np.linalg.norm(x - y, axis=1, ord=np.inf)
- elif mode == 'Gaussian':
- gamma = 1e-3
- var = lambda x_i, x_j: np.exp(- gamma * np.square(np.linalg.norm(x_i - x_j, axis=1)))
- return np.sqrt(var(x, x) - 2 * var(x, y) + var(y, y))
-
-
-
-class KNN:
-
- def __init__(self):
- self.k = 1
- self.data = None
- self.label = None
- self.mean = 0
- self.std = 0
-
- def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- n, d = train_data.shape
- acc_best = 0
- k_best = self.k
- k_max = min(30, int(n * 0.8))
-
- # 归一化
- self.mean = np.mean(train_data, axis=0)
- self.std = np.std(train_data, axis=0)
- train_data = (train_data - self.mean) / self.std
-
- idx = np.arange(n)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
-
- train_data = train_data[idx]
- train_label = train_label[idx]
-
- acc_best = 0
- k_best = 0
-
- for j in range(5):
- val_start_point = int(n * j * .2)
- val_end_point = int(n * (j + 1) * .2)
-
- temp_val_data = train_data[
- val_start_point: val_end_point, :
- ]
- temp_val_label = train_label[
- val_start_point: val_end_point
- ]
-
- temp_train_data = np.vstack(
- [
- train_data[:val_start_point, :],
- train_data[val_end_point:, :]
- ]
- )
-
- temp_train_label = np.concatenate(
- [
- train_label[:val_start_point],
- train_label[val_end_point:]
- ]
- )
-
- # temp_train_data, temp_val_data = train_data[:int(
- # n * 0.8), :], train_data[int(n * 0.8):, :]
- # temp_train_label, temp_val_label = train_label[:int(
- # n * 0.8)], train_label[int(n * 0.8):]
- self.data = temp_train_data
- self.label = temp_train_label
-
- for i in range(1, k_max, 2):
- self.k = i
- res = self.predict(temp_val_data, normalization=False)
- acc = np.mean(np.equal(res, temp_val_label))
- # print(i, acc)
- if acc > acc_best:
- acc_best = acc
- k_best = i
- # print(acc_best, k_best)
- self.k = k_best
- # print(f'j={j}')
- self.data = train_data
- self.label = train_label
-
- def predict(self, test_data, normalization=True, mode='Gaussian'):
- n, d = test_data.shape
- if normalization:
- test_data = (test_data - self.mean) / self.std
- res = []
- for i in range(n):
- temp = test_data[i, :]
- # dis = np.linalg.norm(temp - self.data, axis=1) # 使用欧式距离
- # 使用核函数
- dis = dis_function(temp, self.data, mode=mode)
- idx = np.argpartition(dis, self.k)[:self.k]
- # print(self.data[idx], self.label[idx], np.argmax(np.bincount(self.label[idx])))
- res.append(np.argmax(np.bincount(self.label[idx])))
- return np.array(res)
-
-
-def generate_cov(dimension):
- # 用于生成随机的数据集
- A = np.abs(np.random.randn(dimension, dimension))
- B = np.dot(A, A.T)
- return B
-
-
-def generate():
- global NUM_OF_LABELS
- global DIMENSION
- # 通过控制系数调整mean和cov
- mean = [(13 * 1, 4 * 1), (1 * 1, 14 * 1), (-8 * 1, -3 * 1), (-15 * 1, 10 * 1)]
- # mean = [tuple(np.random.randn(DIMENSION,) * mean_factor)
- # for i in range(NUM_OF_LABELS)]
-
- cov = [
- np.array([[35, 0], [0, 23]]) * 1,
- np.array([[12, 1], [1, 35]]) * 1,
- np.array([[33, 5], [5, 9]]) * 1,
- np.array([[25, 6], [6, 18]]) * 1,
- ]
- # cov = [
- # generate_cov(DIMENSION) * cov_factor for i in range(NUM_OF_LABELS)
- # ]
- dataset = [None] * NUM_OF_LABELS
- data_num = []
- num_of_examples = 0
- for i in range(NUM_OF_LABELS):
- data_num.append((i + 1) * 2 * NUM_BASIS)
- num_of_examples += (i + 1) * 2 * NUM_BASIS
- dataset[i] = np.random.multivariate_normal(
- mean[i], cov[i], ((i + 1) * 2 * NUM_BASIS, ))
- # print(data_num)
- idx = np.arange(num_of_examples)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- data = np.concatenate([item for item in dataset])
- label = np.concatenate(
- # [
- # np.zeros((data_num[0],), dtype=int),
- # np.ones((data_num[1],), dtype=int),
- # np.ones((data_num[2],), dtype=int) * 2,
- # np.ones((data_num[3],), dtype=int) * 3
- # ]
- [np.ones((data_num[i],), dtype=int) * i for i in range(NUM_OF_LABELS)]
- )
-
- data = data[idx]
- label = label[idx]
-
- train_data, test_data = data[:int(
- num_of_examples * 0.8), :], data[int(num_of_examples * 0.8):, :]
- train_label, test_label = label[:int(
- num_of_examples * 0.8)], label[int(num_of_examples * 0.8):]
-
- np.save(
- 'data.npy',
- (
- (train_data, train_label),
- (test_data, test_label)
- )
- )
-
-
-def read():
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = np.load(
- 'data.npy', allow_pickle=True)
- return (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
-
-
-def display(data, label, name):
- global NUM_OF_LABELS
- datas = [[] for i in range(NUM_OF_LABELS)]
- for i in range(len(data)):
- datas[label[i]].append(data[i])
-
- for each in datas:
- each = np.array(each)
- plt.scatter(each[:, 0], each[:, 1])
- plt.savefig(f'img/{name}')
- plt.show()
-
-def experiment():
- generate()
- data = read()
- train_data, train_label = data[0][0], data[0][1]
- test_data, test_label = data[1][0], data[1][1]
- # display(train_data, train_label, 'train_divide')
- # display(test_data, test_label, 'test_divide')
- model = KNN()
- model.fit(train_data, train_label)
- res = model.predict(test_data, normalization=True)
- acc = np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label))
- print(model.k)
- print("acc =", acc)
- return model.k, acc, compute_index(res, test_label)
-
-def compute_index(res, label):
- res_bin = np.bincount(res)
- label_bin = np.bincount(label)
- return res_bin, label_bin
-
-
-if __name__ == '__main__':
-
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "g":
- generate()
- elif len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "d":
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
- display(train_data, train_label, 'train')
- display(test_data, test_label, 'test')
- else:
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
-
- model = KNN()
- model.fit(train_data, train_label)
- res = model.predict(test_data)
- print("acc =",np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label)))
-
-
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/.keep b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/.keep
deleted file mode 100644
index e69de29bb2d1d6434b8b29ae775ad8c2e48c5391..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 06a0098602e802319c84db26985360e4c9e99cfb..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,214 +0,0 @@
-# KNN实验探索
-
-## 一.KNN算法代码实现
-
-首先定义KNN类,KNN类中包括三个方法:
-
-```python
-import numpy as np
-from collections import Counter #用于计数
-def __init__(self,k):
- #输入超参k,并赋给内部变量self._k;定义另外内部三个重要变量
- #self._train_data,self._train_label,self._test_data
- self._k = k
- self._train_data=None
- self._train_label = None
- self._test_data=None
-```
-
-```python
-def fit(self,train_data,train_label):
- #输入train_data,train_label并赋给内部变量
- self._train_data=train_data
- self._train_label=train_label
-```
-
-```python
-def predict(self,test_data):
- #输入test_data并赋给内部变量
- self._test_data=test_data
- predicts_ =[]
- #遍历测试集
- for i in self._test_data:
- #对测试集中的数据求与每一个训练集中数据的欧氏距离
- distances_ = [np.sum((i-x)**2)**0.5 for x in self._train_data]
- distances = np.array(distances_)
- #用Counter函数求距离前k个中0-1的个数
- sorted_distances = np.argsort(distances)
- topK = [self._train_label[j] for j in sorted_distances[0:self._k]]
- votes = Counter(topK)
- #预测结果为距离前k个中0-1数量多的种类
- predict = votes.most_common(1)[0][0]
- predicts_.append(predict)
- predicts = np.array(predicts_)
- return predicts
-```
-
-
-
-## 二.试验探究
-
-### 1.二维随机正态分布的简单分类实验
-
-(1)两维之间完全不相关
-
-```python
-import numpy as np
-from source import KNN
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-#每一维均值为0,方差为10,并且两维独立,创建1000个数据
-cov = [[10,0],[0,10]]
-data = np.around(np.random.multivariate_normal((0,0),cov,1000),2)
-#对应分类随机取0或1
-label = np.random.choice([0,1],size=1000,replace=True)
-#按8:2的比例分为训练集和测试集
-n = len(data)//5
-train_data = data[0:4*n]
-train_label = label[0:4*n]
-test_data = data[4*n:]
-test_label = label[4*n:]
-#调用KNN类,k赋值5,将训练集输入模型
-model = KNN(5)
-model.fit(train_data, train_label)
-
-#绘制分类图
-#第一维和第二维分别作为x,y轴
-x_show = train_data[:,0]
-y_show = train_data[:,1]
-x_min,x_max=x_show.min(),x_show.max()
-y_min,y_max=y_show.min(),y_show.max()
-#将坐标系分为200×200的网格
-xx,yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(x_min,x_max,200),np.linspace(y_min,y_max,200))
-#将网格放入模型预测,预测每一个网格的分类
-z1 = np.c_[xx.ravel(),yy.ravel()]
-z = np.array(z1)
-pred = model.predict(z)
-pred = pred.reshape(xx.shape)
-#绘制网格分类图和训练集的散点图
-plt.pcolormesh(xx,yy,pred,cmap=plt.cm.Pastel1)
-plt.scatter(x_show,y_show,s=80,c=train_label,cmap=plt.cm.spring,edgecolors='k')
-plt.xlim(xx.min(),xx.max())
-plt.ylim(yy.min(),yy.max())
-plt.show()
-```
-
-
-
-结果如图所示。由于data是根据二元正态分布随机取值的,并且label也是在0-1之间随机选取的,所以data和label之间是完全无关的。所以分类图也是不规则的。
-
-(2)二维之间完全正相关
-
-```python
-#使两个维度相关系数为1
-cov = [[10,10],[10,10]]
-```
-
-
-
-结果如图所示。由于两维相关系数为1,所以所有点都在y=x的直线上。由于label的随机选取,所以0-1分类区域是在这条直线上的随机分布。
-
-(3)完全负相关
-
-```python
-#两个维度相关系数为-1
-cov = [[10,-10],[-10,10]]
-```
-
-
-
-结果如图所示。
-
-(4)一般情况下
-
-```python
-#使相关系数为0.2
-cov = [[10,2],[2,10]]
-```
-
-
-
-```python
-#使相关系数为0.8
-cov = [[10,8],[8,10]]
-```
-
-
-
-分别将相关系数设为0.2与0.8,可以看出0.2时分布还相对散乱,而0.8时已经可以看出明显的线性关系。同样,由于label的随机选取,在直线上0-1的分布仍然是随机的。
-
-### 2.二维随机正态分布的多分类实验
-
-```python
-#相关系数取0.8
-cov = [[10,8],[8,10]]
-#五分类任务
-label = np.random.choice([0,1,2,3,4],size=1000,replace=True)
-```
-
-
-
-```python
-#相关系数取0.2
-cov = [[10,2],[2,10]]
-#五分类任务
-label = np.random.choice([0,1,2,3,4],size=1000,replace=True)
-```
-
-
-
-结果如图所示。与简单分类结果类似,这是由于两维的相关系数是一样的,而仅仅是将label从0-1随机取值变为0-1-2-3-4随机取值,并没有本质变化,只是人为定义的分类数变多了。
-
-### 3. 实验发现
-
-#### (1)简单分类与多分类
-
-以相关系数为0.2的二维正态分布,k值取5为例。
-
-运行10次0-1的简单二分类实验,结果分别为:
-
-acc = 0.51,0.545,0.535,0.515 ,0.435, 0.465,0.56,0.53, 0.515,0.53
-
-平均acc=0.514
-
-运行10次三分类实验,结果如下:
-
-acc = 0.295,0.32,0.35,0.34,0.31,0.405 ,0.325 ,0.3,0.32,0.32
-
-平均acc = 0.329
-
-运行10次四分类实验,结果如下:
-
-acc = 0.25,0.22,0.255,0.19,0.215,0.335,0.3,0.25,0.28,0.225
-
-平均acc = 0.252
-
-运行10此五分类实验,结果如下:
-
-acc = 0.265,0.185,0.22,0.235,0.195,0.19,0.22, 0.23,0.2,0.215
-
-平均acc = 0.2155
-
-
-
-可以发现,当分类数越多时,预测的准确率越低。这应该是由于data和label本身之间没有相关性,acc近似等于(1/分类数),和瞎猜的准确率是近似的。
-
-#### (2)k值的选取
-
-以简单二分类为例。
-
-k值取5,运行10次的平均acc =0.512
-
-k值取4,运行10次的平均acc =0.507
-
-k值取6,运行10次的平均acc =0.485
-
-k值取3,运行10次的平均acc =0.495
-
-k值取7,运行10次的平均acc =0.508
-
-
-
-可知,k取5是恰当的。但同样由于data和label之间没有相关性,所以不同k值之间准确率的差异不大,都在0.5左右,近似于瞎猜。因为分类区域本身就是随机的,距离预测点越近的点并不代表属于该点类别的概率越大。
-
-所以,该次尝试的调参是没有意义的。如果选取本身有意义,并且属性与分类有关系的数据组进行测试,取不同的k值的准确率才会有显著差异,此时的调参才有意义。
-
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/.keep b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/.keep
deleted file mode 100644
index e69de29bb2d1d6434b8b29ae775ad8c2e48c5391..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/0.2.png b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/0.2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 5cc12d92a5e696a6181dc47fef6caf9de5a4d7c9..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/0.2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/0.8.png b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/0.8.png
deleted file mode 100644
index abe0d2e4626cc82b2e44961f668c4d732aa057cf..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/0.8.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\214\347\273\264\347\233\270\345\205\263.png" "b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\214\347\273\264\347\233\270\345\205\263.png"
deleted file mode 100644
index 4eb7d1805b16224826b6522b18680a6951f08085..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files "a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\214\347\273\264\347\233\270\345\205\263.png" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\214\347\273\264\347\273\223\346\236\234.png" "b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\214\347\273\264\347\273\223\346\236\234.png"
deleted file mode 100644
index cfb88bc7cf41bc6bb02cd3467b2f475c43a405a2..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files "a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\214\347\273\264\347\273\223\346\236\234.png" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\2240.2.png" "b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\2240.2.png"
deleted file mode 100644
index 5d151517b7b0da7e0ccf89ae43a44b848831e19c..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files "a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\2240.2.png" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\224\345\210\206\347\261\2730.8.png" "b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\224\345\210\206\347\261\2730.8.png"
deleted file mode 100644
index d5d72a9445ffdab5b80e24d02ee76a3789244d50..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files "a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\224\345\210\206\347\261\2730.8.png" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\350\264\237\344\272\214\347\273\264.png" "b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\350\264\237\344\272\214\347\273\264.png"
deleted file mode 100644
index 5f28d4a81b3deaa217a3d1a78602d6df915b3226..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files "a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\350\264\237\344\272\214\347\273\264.png" and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 4ae97853ca5174d7f23998d209a5603a4a7b7c58..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
-#算法代码
-import numpy as np
-from collections import Counter
-class KNN:
-
- def __init__(self,k):
- self._k = k
- self._train_data=None
- self._train_label = None
- self._test_data=None
-
- def fit(self,train_data,train_label):
- self._train_data=train_data
- self._train_label=train_label
-
-
- def predict(self,test_data):
- self._test_data=test_data
- predicts_ =[]
- #遍历测试集
- for i in self._test_data:
- #对测试集中的数据求距离每一个训练集中数据的欧氏距离
- distances_ = [np.sum((i-x)**2)**0.5 for x in self._train_data]
- distances = np.array(distances_)
- #用Counter函数求距离前k个
- sorted_distances = np.argsort(distances)
- topK = [self._train_label[j] for j in sorted_distances[0:self._k]]
- votes = Counter(topK)
- #预测结果
- predict = votes.most_common(1)[0][0]
- predicts_.append(predict)
- predicts = np.array(predicts_)
- return predicts
-
-
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/train&test.py b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/train&test.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 31f28e4c3580e54f001d4ac69fb1c3f9ddf533a9..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/train&test.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
-#实验代码
-import numpy as np
-from lknn import KNN
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-#每一维均值为0,方差为10,并且两维独立,创建1000个数据
-cov = [[10,0],[0,10]]
-data = np.around(np.random.multivariate_normal((0,0),cov,1000),2)
-#对应分类随机取0或1
-label = np.random.choice([0,1],size=1000,replace=True)
-#按8:2的比例分为训练集和测试集
-n = len(data)//5
-train_data = data[0:4*n]
-train_label = label[0:4*n]
-test_data = data[4*n:]
-test_label = label[4*n:]
-#调用KNN类,k赋值5,将训练集输入模型
-model = KNN(5)
-model.fit(train_data, train_label)
-#绘制分类图
-#第一维和第二维分别作为x,y轴
-x_show = train_data[:,0]
-y_show = train_data[:,1]
-x_min,x_max=x_show.min(),x_show.max()
-y_min,y_max=y_show.min(),y_show.max()
-xx,yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(x_min,x_max,200),np.linspace(y_min,y_max,200))
-#将网格放入模型预测,预测每一个网格的分类
-z1 = np.c_[xx.ravel(),yy.ravel()]
-z = np.array(z1)
-pred = model.predict(z)
-pred = pred.reshape(xx.shape)
-#绘制网格分类图和训练集的散点图
-plt.pcolormesh(xx,yy,pred,cmap=plt.cm.Pastel1)
-plt.scatter(x_show,y_show,s=80,c=train_label,cmap=plt.cm.spring,edgecolors='k')
-plt.xlim(xx.min(),xx.max())
-plt.ylim(yy.min(),yy.max())
-plt.show()
-#计算acc
-res = model.predict(test_data)
-print("acc =",np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label)))
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 8c6b9b94639e4ef0462ed57212e65dc05b741d32..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
-# 实验报告1
-
-
-
-### 1,KNN的实现
-
-```python
- def predict1(self,test_data,k):
- predict=[]
- for instance in test_data:
- distances=np.array([self.distance (x,instance) for x in self.X])
-
- kneighbors=np.argsort(np.array(distances))[:k]
- count = Counter(self.y[kneighbors])
- predict.append(count.most_common()[0][0])
- return predict
-```
-
-将测试点最近的k个点列出,并找出其中出现最多的标签,作为预测的结果。
-
-```python
- def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=self.train_test_split(train_data, train_label)
- self.X=np.array(X_train)
- self.y=np.array(y_train)
- max_accurate=0
- best_k=0
- for k in self.k_n:
- accurate=0
- train_predict=self.predict1(X_test,k)
- correct = np.count_nonzero((train_predict==y_test)==True)
-
- accurate=correct/len(X_test)
- if (accurate>max_accurate):
- max_accurate=accurate
- best_k=k
- self.k_select=best_k
-```
-
-k_n为[1,2,3,4,5],knn将输入的数据分为训练集和测试集,并从k_n中选择一个准确率最高的k值。
-
-### 2,实验部分
-
-```python
-def generate():
- X1 = np.random.multivariate_normal([1,50], [[1,0],[0,10]], 100)
- X2 = np.random.multivariate_normal([3,50], [[1,0],[0,10]], 100)
- X3 = np.random.multivariate_normal([5,50], [[1,0],[0,10]], 100)
- X = np.concatenate([X1,X2,X3])
- y = np.array([0]*100 + [1]*100 +[2]*100)
- idx = np.arange(300)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- data=X=X[idx]
- label=y=y[idx]
-
- X_train=X[:240]
- X_test=X[240:]
- y_train=y[:240]
- y_test=y[240:]
- return np.array(X_train),np.array(X_test),np.array(y_train),np.array(y_test)
-
-```
-
-生成数据,将它们分为训练集和测试集。将训练集输入KNN,之后利用KNN预测测试集的标签。
-
-这是训练集:
-
-
-
-这是测试集:
-
-
-
- 
-
-这是对测试集的预测:
-
-
-
-这个预测的准确度为0.75.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/img/predict.png b/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/img/predict.png
deleted file mode 100644
index a853678b11d98ccc9a012b637a588a37723b42ff..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/img/predict.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/img/test.png b/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/img/test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index d9d8b3f379704464fcf2c4bff575425ef3404c0f..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/img/test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/img/train.png b/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/img/train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 2d61295b21b4bf115c35c594ca716f564a79a00a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/img/train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 397fbc05ad396f8bac4e0fee34426e6ee57d7f8f..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,94 +0,0 @@
-import numpy as np
-from collections import Counter
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
-class KNN:
- k_n=[1,2,3,4,5]
- k_select=0
- X=[]
- y=[]
- def __init__(self):
- pass
-
- def train_test_split(self,X,y):
- offset=int(len(X)*0.8)
- X_train=X[:offset]
- X_test=X[offset:]
- y_train=y[:offset]
- y_test=y[offset:]
-
- return np.array(X_train),np.array(X_test),np.array(y_train),np.array(y_test)
-
- def distance(self,instance1,instance2):
- dist = np.sqrt(sum((instance1 - instance2)**2))
- return dist
-
- def predict1(self,test_data,k):
- predict=[]
- for instance in test_data:
- distances=np.array([self.distance (x,instance) for x in self.X])
-
- kneighbors=np.argsort(np.array(distances))[:k]
- count = Counter(self.y[kneighbors])
- predict.append(count.most_common()[0][0])
- return predict
-
- def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=self.train_test_split(train_data, train_label)
- self.X=np.array(X_train)
- self.y=np.array(y_train)
- max_accurate=0
- best_k=0
- for k in self.k_n:
- accurate=0
- train_predict=self.predict1(X_test,k)
- correct = np.count_nonzero((train_predict==y_test)==True)
-
- accurate=correct/len(X_test)
- if (accurate>max_accurate):
- max_accurate=accurate
- best_k=k
- self.k_select=best_k
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- return self.predict1(test_data,self.k_select)
-
-def generate():
- X1 = np.random.multivariate_normal([1,50], [[1,0],[0,10]], 100)
- X2 = np.random.multivariate_normal([3,50], [[1,0],[0,10]], 100)
- X3 = np.random.multivariate_normal([5,50], [[1,0],[0,10]], 100)
- X = np.concatenate([X1,X2,X3])
- y = np.array([0]*100 + [1]*100 +[2]*100)
- idx = np.arange(300)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
-
- data=X=X[idx]
- label=y=y[idx]
-
- X_train=X[:240]
- X_test=X[240:]
- y_train=y[:240]
- y_test=y[240:]
- return np.array(X_train),np.array(X_test),np.array(y_train),np.array(y_test)
-
-def display(data, label, name):
- datas =[[],[],[]]
- colors=['b','r','y']
- for i in range(len(data)):
- datas[label[i]].append(data[i])
- for i,each in enumerate(datas):
- each = np.array(each)
- plt.scatter(each[:, 0], each[:, 1],c=colors[i])
- plt.show()
-
-if __name__ == '__main__':
- X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=generate()
- model=KNN()
- model.fit(X_train,y_train)
- predict=model.predict(X_test)
- display(X_train,y_train,'train')
- display(X_test,y_test,'test')
- display(X_test,predict,'predict')
- correct = np.count_nonzero((predict==y_test))
- accurate=correct/len(X_test)
- print('accu=',accurate)
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 7e209eba20b4f93de8019d642a8fdc6979914d38..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,362 +0,0 @@
-# 课程报告
-
-## KNN类实现
-
-### fit()函数
-
-fit(X, y,cate = 'euclidean',metric='accuracy',preprocess =None)
-
-X: 训练集
-
-y:训练集标签
-
-cate:距离计算方式,如euclidean、manhattan距离
-
-metric:模型评估方式,如accuracy
-
-preprocess:预处理方式,包含min_max归一化、z_score标准化、不处理
-
-
-
-fit函数包含以下功能:
-
- 1、预处理;
-
- 2、随机打乱数据集顺序
-
- 3、以8:2的比例划分train_data,dev_data,训练选出评估结果最优的k值
-
-### predict()函数
-
-predict用于预测测试集样本
-
-### 辅助函数
-
-distance( d1, d2,cate ='eulidean')
-
-d1,d2表示计算距离的点,cate默认为euclidean距离,可以选择manhattan距离
-
-
-
-## 实验1
-
-### Group1:各个类别相差较大,成较为明显的线性位置
-
-$$
-\Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 52 & 0 \\
- 0 & 22
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 21.1 & 0 \\
- 0 & 32.1
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 10 & 0 \\
- 0 & 10
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
-$$
-
-$$
-\mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 2 &5
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 20 & -5
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- -5 & 22
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
-$$
-
-train_data
-
-
-
- 同样进行十次实验,结果如下:
- | 序号 | K | Acc |
- | :------- | :------- | ---------- |
- | 1 | 17 | 84.50% |
- | 2 | 19 | 82.50% |
- | 3 | 21 | 83.50% |
- | 4 | 19 | 84.63% |
- | 5 | 15 | 85.88% |
- | 6 | 7 | 81.13% |
- | 7 | 15 | 83.38% |
- | 8 | 13 | 82.63% |
- | 9 | 23 | 84.75% |
- | 10 | 29 | 83.50% |
- | **均值** | **17.8** | **83.64%** |
-
- 这十次实验的k取值变大,准确率降低,表明方差增大有可能降低KNN分类器的准确率。
-
-
-总而言之,数据集分布的离散程度会影响分类器的准确率,同一分布的数据越集中,分类准确率越高,反之越低。数据越分散,相当于不同的数据之间重合的可能性越高,因此更难进行准确地分类。
-### 3、数据的数量
-将每个标签下数据的数量降低为原来的1/10、扩大为原来的2倍,分别进行10次实验,实验结果如下:
-
-| 序号 | k(数量减少) | Acc(数量减少) | k(数量增大) | Acc(数量增大) |
-| -------- | ------------- | --------------- | ------------- | --------------- |
-| 1 | 15 | 95.00% | 5 | 94.69% |
-| 2 | 1 | 95.00% | 25 | 94.50% |
-| 3 | 5 | 92.50% | 13 | 93.88% |
-| 4 | 3 | 93.75% | 21 | 93.56% |
-| 5 | 27 | 98.75% | 15 | 94.88% |
-| 6 | 19 | 93.75% | 23 | 94.06% |
-| 7 | 3 | 96.25% | 29 | 94.50% |
-| 8 | 5 | 93.75% | 13 | 94.63% |
-| 9 | 3 | 90.00% | 17 | 93.63% |
-| 10 | 11 | 98.75% | 15 | 95.19% |
-| **均值** | **9.2** | **94.75%** | **17.6** | **94.35%** |
-
-可见,在一定范围内,数量的改变并不能影响模型的准确率,但是通过实验发现当样本数量增大时,KNN模型的速度会变慢。
-
-### 4、样本距离计算方式
-
-下面,笔者分别采用以下距离进行实验:
-
-曼哈顿距离(L1范数):
-
-$$
-L_ 1(x_ i,x_ j) = \sum^{n}_ {l=1} |x^{(l)}_ {i} - x^{(l)}_ {j}|
-\tag{1}
-$$
-
-欧氏距离(L2范数):
-
-$$
-L_2(x_i,x_j) =
-(\sum^{n}_ {l=1} |x^{(l)}_ i-x^{(l)}_ {j}|^2 )^{\frac{1}{2}}
-\tag{2}$$
-
-切比雪夫距离(L∞范数):
-$$
-L_{\infty}(x_i,x_j) = max_l|x^{(l)}_i-x^{(l)}_j|
-\tag{3}
-$$
-
-此外,笔者还引入了高斯核函数$K(x_i,x_j)$,将原始样本$x_i$映射入新的特征空间变为$\phi(x_i)$,在新的空间内进行距离计算。实际上,通过核函数,可以不用直接转换样本的坐标而隐式地计算样本在新特征空间内的距离,因为在新的特征空间中,两个样本点之间的距离$D(x_i,x_j)$可以通过核函数隐式地获得:
-$$
-\begin{align}
-D^2(x_i,x_j)&=||\phi(x_i)-\phi(x_j)||^2\\\\
-&=K(x_i, x_i) - 2K(x_i,x_j) + K(x_j,x_j)
-\end{align}
-$$
-这三种距离的控制主要通过`dis_function()`函数实现:
-
-```python
-def dis_function(x, y, mode='L2'):
- d = y.shape[1]
- x = x.reshape(1, -1)
- y = y.reshape(-1, d)
- if mode == 'L2':
- return np.linalg.norm(x - y, axis=1)
- elif mode == 'L1':
- return np.linalg.norm(x - y, axis=1, ord=1)
- elif mode == 'L_inf':
- return np.linalg.norm(x - y, axis=1, ord=np.inf)
- elif mode == 'Gaussian':
- gamma = 1e-3
- var = lambda x_i, x_j: np.exp(- gamma * np.square(np.linalg.norm(x_i - x_j, axis=1)))
- return np.sqrt(var(x, x) - 2 * var(x, y) + var(y, y))
-```
-
-为了使采用不同距离的分类器具有区别性,笔者将原数据集的参数$\Sigma$扩大为原来的两倍,实验结果如下:
-
-| 序号 | k_L1 | Acc_L1 | k_L2 | Acc_L2 | k_L∞ | Acc_L∞ | k_Gaussian | Acc_Gaussian |
-| -------- | -------- | ---------- | -------- | ---------- | -------- | ---------- | ---------- | ------------ |
-| 1 | 23 | 84.25% | 17 | 84.50% | 15 | 83.88% | 17 | 84.50% |
-| 2 | 19 | 82.63% | 19 | 82.50% | 15 | 82.38% | 19 | 82.50% |
-| 3 | 21 | 83.23% | 21 | 83.50% | 15 | 83.63% | 21 | 83.50% |
-| 4 | 19 | 85.25% | 19 | 84.63% | 21 | 85.00% | 19 | 84.63% |
-| 5 | 13 | 85.50% | 15 | 85.88% | 23 | 85.88% | 15 | 85.88% |
-| 6 | 21 | 82.75% | 7 | 81.13% | 13 | 83.13% | 7 | 81.13% |
-| 7 | 13 | 83.38% | 15 | 83.38% | 19 | 84.13% | 15 | 83.38% |
-| 8 | 11 | 82.87% | 13 | 82.63% | 17 | 82.26% | 13 | 82.63% |
-| 9 | 21 | 84.63% | 23 | 84.75% | 9 | 83.63% | 23 | 84.75% |
-| 10 | 27 | 84.00% | 29 | 83.50% | 23 | 83.38% | 29 | 83.50% |
-| **均值** | **18.8** | **83.89%** | **17.8** | **83.64%** | **17.0** | **83.72%** | **17.8** | **83.64%** |
-
-可以看出,在此数据分布下,不同的距离计算方式并没有产生较大的影响。此外,采用高斯核函数映射原数据所得到的结果并无不同,可见此情景下,高斯核函数也没有产生促进分类的作用。
-
-### 5、标准化
-
-下面是分别是在原数据集上进行的实验结果,区别是是否执行了标准化:
-
-| 序号 | k_without_normalization | Acc_without_normalization | k_with_normalization | Acc_with_normalization |
-| -------- | ----------------------- | ------------------------- | -------------------- | ---------------------- |
-| 1 | 5 | 93.50% | 5 | 93.63% |
-| 2 | 25 | 94.63% | 29 | 95.00% |
-| 3 | 27 | 94.50% | 25 | 94.13% |
-| 4 | 9 | 95.50% | 19 | 96.38% |
-| 5 | 25 | 94.50% | 23 | 94.63% |
-| 6 | 9 | 94.88% | 9 | 94.75% |
-| 7 | 9 | 93.13% | 9 | 93.50% |
-| 8 | 19 | 93.25% | 21 | 93.13% |
-| 9 | 5 | 95.50% | 9 | 94.75% |
-| 10 | 17 | 93.25% | 19 | 92.63% |
-| **均值** | **18.8** | **94.26%** | **16.8** | **94.23%** |
-
-从现有的实验结果来看,标准化并不能明显地提升KNN分类器的准确率,其是否有效还需要进一步的探究。
-
-## 五、代码使用方式
-
-```bash
-python source.py g # 生成数据集
-python source.py d # 展示数据集
-python source.py # 训练和测试
-```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test.png b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index d134664a436ac258eae767ab0245d0a6af0753fe..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_close.png b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_close.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 5dc3292a77d8176c8446cfab2fc11726dd1a8ee7..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_close.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_divide.png b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_divide.png
deleted file mode 100644
index d019e98a5c41530e60920e67a903277f088d6ee6..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_divide.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_far.png b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_far.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 1fed8f774e5b48753f86fa7336be29ad407fa70c..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_far.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_gather.png b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_gather.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 34733b975ead375a61abfbb15b59e16f1ea182b4..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/test_gather.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train.png b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index f083fb235fba9f5e34175a9708fe5ac6979b423d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_close.png b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_close.png
deleted file mode 100644
index efce494fc03a80b7d587ea1dae9f7c8dfb20f56a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_close.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_divide.png b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_divide.png
deleted file mode 100644
index bea982d45d81519fbaa9b1dbb10c89fb3949d224..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_divide.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_far.png b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_far.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 80e7c6dd3a3d62ae39533f32ea0b29b52833e96a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_far.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_gather.png b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_gather.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 6860b6113ea0c0ee832491ea37e9d5b136e7869a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/img/train_gather.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 712d25173c94b0c8107c7808267ed8482c464af1..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/16300110008/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,244 +0,0 @@
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import random
-import sys
-
-NUM_OF_LABELS = 4
-DIMENSION = 2
-# 用来控制数据集的样本个数
-NUM_BASIS = 200
-
-
-
-def set_random_seed(seed):
- np.random.seed(seed)
- random.seed(seed)
-
-
-def dis_function(x, y, mode='L2'):
- d = y.shape[1]
- x = x.reshape(1, -1)
- y = y.reshape(-1, d)
- if mode == 'L2':
- return np.linalg.norm(x - y, axis=1)
- elif mode == 'L1':
- return np.linalg.norm(x - y, axis=1, ord=1)
- elif mode == 'L_inf':
- return np.linalg.norm(x - y, axis=1, ord=np.inf)
- elif mode == 'Gaussian':
- gamma = 1e-3
- var = lambda x_i, x_j: np.exp(- gamma * np.square(np.linalg.norm(x_i - x_j, axis=1)))
- return np.sqrt(var(x, x) - 2 * var(x, y) + var(y, y))
-
-
-
-class KNN:
-
- def __init__(self):
- self.k = 1
- self.data = None
- self.label = None
- self.mean = 0
- self.std = 0
-
- def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- n, d = train_data.shape
- acc_best = 0
- k_best = self.k
- k_max = min(30, int(n * 0.8))
-
- # 归一化
- self.mean = np.mean(train_data, axis=0)
- self.std = np.std(train_data, axis=0)
- train_data = (train_data - self.mean) / self.std
-
- idx = np.arange(n)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
-
- train_data = train_data[idx]
- train_label = train_label[idx]
-
- acc_best = 0
- k_best = 0
-
- for j in range(5):
- val_start_point = int(n * j * .2)
- val_end_point = int(n * (j + 1) * .2)
-
- temp_val_data = train_data[
- val_start_point: val_end_point, :
- ]
- temp_val_label = train_label[
- val_start_point: val_end_point
- ]
-
- temp_train_data = np.vstack(
- [
- train_data[:val_start_point, :],
- train_data[val_end_point:, :]
- ]
- )
-
- temp_train_label = np.concatenate(
- [
- train_label[:val_start_point],
- train_label[val_end_point:]
- ]
- )
-
- # temp_train_data, temp_val_data = train_data[:int(
- # n * 0.8), :], train_data[int(n * 0.8):, :]
- # temp_train_label, temp_val_label = train_label[:int(
- # n * 0.8)], train_label[int(n * 0.8):]
- self.data = temp_train_data
- self.label = temp_train_label
-
- for i in range(1, k_max, 2):
- self.k = i
- res = self.predict(temp_val_data, normalization=False)
- acc = np.mean(np.equal(res, temp_val_label))
- # print(i, acc)
- if acc > acc_best:
- acc_best = acc
- k_best = i
- # print(acc_best, k_best)
- self.k = k_best
- # print(f'j={j}')
- self.data = train_data
- self.label = train_label
-
- def predict(self, test_data, normalization=True, mode='Gaussian'):
- n, d = test_data.shape
- if normalization:
- test_data = (test_data - self.mean) / self.std
- res = []
- for i in range(n):
- temp = test_data[i, :]
- # dis = np.linalg.norm(temp - self.data, axis=1) # 使用欧式距离
- # 使用核函数
- dis = dis_function(temp, self.data, mode=mode)
- idx = np.argpartition(dis, self.k)[:self.k]
- # print(self.data[idx], self.label[idx], np.argmax(np.bincount(self.label[idx])))
- res.append(np.argmax(np.bincount(self.label[idx])))
- return np.array(res)
-
-
-def generate_cov(dimension):
- # 用于生成随机的数据集
- A = np.abs(np.random.randn(dimension, dimension))
- B = np.dot(A, A.T)
- return B
-
-
-def generate():
- global NUM_OF_LABELS
- global DIMENSION
- # 通过控制系数调整mean和cov
- mean = [(13 * 1, 4 * 1), (1 * 1, 14 * 1), (-8 * 1, -3 * 1), (-15 * 1, 10 * 1)]
- # mean = [tuple(np.random.randn(DIMENSION,) * mean_factor)
- # for i in range(NUM_OF_LABELS)]
-
- cov = [
- np.array([[35, 0], [0, 23]]) * 1,
- np.array([[12, 1], [1, 35]]) * 1,
- np.array([[33, 5], [5, 9]]) * 1,
- np.array([[25, 6], [6, 18]]) * 1,
- ]
- # cov = [
- # generate_cov(DIMENSION) * cov_factor for i in range(NUM_OF_LABELS)
- # ]
- dataset = [None] * NUM_OF_LABELS
- data_num = []
- num_of_examples = 0
- for i in range(NUM_OF_LABELS):
- data_num.append((i + 1) * 2 * NUM_BASIS)
- num_of_examples += (i + 1) * 2 * NUM_BASIS
- dataset[i] = np.random.multivariate_normal(
- mean[i], cov[i], ((i + 1) * 2 * NUM_BASIS, ))
- # print(data_num)
- idx = np.arange(num_of_examples)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- data = np.concatenate([item for item in dataset])
- label = np.concatenate(
- # [
- # np.zeros((data_num[0],), dtype=int),
- # np.ones((data_num[1],), dtype=int),
- # np.ones((data_num[2],), dtype=int) * 2,
- # np.ones((data_num[3],), dtype=int) * 3
- # ]
- [np.ones((data_num[i],), dtype=int) * i for i in range(NUM_OF_LABELS)]
- )
-
- data = data[idx]
- label = label[idx]
-
- train_data, test_data = data[:int(
- num_of_examples * 0.8), :], data[int(num_of_examples * 0.8):, :]
- train_label, test_label = label[:int(
- num_of_examples * 0.8)], label[int(num_of_examples * 0.8):]
-
- np.save(
- 'data.npy',
- (
- (train_data, train_label),
- (test_data, test_label)
- )
- )
-
-
-def read():
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = np.load(
- 'data.npy', allow_pickle=True)
- return (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
-
-
-def display(data, label, name):
- global NUM_OF_LABELS
- datas = [[] for i in range(NUM_OF_LABELS)]
- for i in range(len(data)):
- datas[label[i]].append(data[i])
-
- for each in datas:
- each = np.array(each)
- plt.scatter(each[:, 0], each[:, 1])
- plt.savefig(f'img/{name}')
- plt.show()
-
-def experiment():
- generate()
- data = read()
- train_data, train_label = data[0][0], data[0][1]
- test_data, test_label = data[1][0], data[1][1]
- # display(train_data, train_label, 'train_divide')
- # display(test_data, test_label, 'test_divide')
- model = KNN()
- model.fit(train_data, train_label)
- res = model.predict(test_data, normalization=True)
- acc = np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label))
- print(model.k)
- print("acc =", acc)
- return model.k, acc, compute_index(res, test_label)
-
-def compute_index(res, label):
- res_bin = np.bincount(res)
- label_bin = np.bincount(label)
- return res_bin, label_bin
-
-
-if __name__ == '__main__':
-
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "g":
- generate()
- elif len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "d":
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
- display(train_data, train_label, 'train')
- display(test_data, test_label, 'test')
- else:
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
-
- model = KNN()
- model.fit(train_data, train_label)
- res = model.predict(test_data)
- print("acc =",np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label)))
-
-
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/.keep b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/.keep
deleted file mode 100644
index e69de29bb2d1d6434b8b29ae775ad8c2e48c5391..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 06a0098602e802319c84db26985360e4c9e99cfb..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,214 +0,0 @@
-# KNN实验探索
-
-## 一.KNN算法代码实现
-
-首先定义KNN类,KNN类中包括三个方法:
-
-```python
-import numpy as np
-from collections import Counter #用于计数
-def __init__(self,k):
- #输入超参k,并赋给内部变量self._k;定义另外内部三个重要变量
- #self._train_data,self._train_label,self._test_data
- self._k = k
- self._train_data=None
- self._train_label = None
- self._test_data=None
-```
-
-```python
-def fit(self,train_data,train_label):
- #输入train_data,train_label并赋给内部变量
- self._train_data=train_data
- self._train_label=train_label
-```
-
-```python
-def predict(self,test_data):
- #输入test_data并赋给内部变量
- self._test_data=test_data
- predicts_ =[]
- #遍历测试集
- for i in self._test_data:
- #对测试集中的数据求与每一个训练集中数据的欧氏距离
- distances_ = [np.sum((i-x)**2)**0.5 for x in self._train_data]
- distances = np.array(distances_)
- #用Counter函数求距离前k个中0-1的个数
- sorted_distances = np.argsort(distances)
- topK = [self._train_label[j] for j in sorted_distances[0:self._k]]
- votes = Counter(topK)
- #预测结果为距离前k个中0-1数量多的种类
- predict = votes.most_common(1)[0][0]
- predicts_.append(predict)
- predicts = np.array(predicts_)
- return predicts
-```
-
-
-
-## 二.试验探究
-
-### 1.二维随机正态分布的简单分类实验
-
-(1)两维之间完全不相关
-
-```python
-import numpy as np
-from source import KNN
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-#每一维均值为0,方差为10,并且两维独立,创建1000个数据
-cov = [[10,0],[0,10]]
-data = np.around(np.random.multivariate_normal((0,0),cov,1000),2)
-#对应分类随机取0或1
-label = np.random.choice([0,1],size=1000,replace=True)
-#按8:2的比例分为训练集和测试集
-n = len(data)//5
-train_data = data[0:4*n]
-train_label = label[0:4*n]
-test_data = data[4*n:]
-test_label = label[4*n:]
-#调用KNN类,k赋值5,将训练集输入模型
-model = KNN(5)
-model.fit(train_data, train_label)
-
-#绘制分类图
-#第一维和第二维分别作为x,y轴
-x_show = train_data[:,0]
-y_show = train_data[:,1]
-x_min,x_max=x_show.min(),x_show.max()
-y_min,y_max=y_show.min(),y_show.max()
-#将坐标系分为200×200的网格
-xx,yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(x_min,x_max,200),np.linspace(y_min,y_max,200))
-#将网格放入模型预测,预测每一个网格的分类
-z1 = np.c_[xx.ravel(),yy.ravel()]
-z = np.array(z1)
-pred = model.predict(z)
-pred = pred.reshape(xx.shape)
-#绘制网格分类图和训练集的散点图
-plt.pcolormesh(xx,yy,pred,cmap=plt.cm.Pastel1)
-plt.scatter(x_show,y_show,s=80,c=train_label,cmap=plt.cm.spring,edgecolors='k')
-plt.xlim(xx.min(),xx.max())
-plt.ylim(yy.min(),yy.max())
-plt.show()
-```
-
-
-
-结果如图所示。由于data是根据二元正态分布随机取值的,并且label也是在0-1之间随机选取的,所以data和label之间是完全无关的。所以分类图也是不规则的。
-
-(2)二维之间完全正相关
-
-```python
-#使两个维度相关系数为1
-cov = [[10,10],[10,10]]
-```
-
-
-
-结果如图所示。由于两维相关系数为1,所以所有点都在y=x的直线上。由于label的随机选取,所以0-1分类区域是在这条直线上的随机分布。
-
-(3)完全负相关
-
-```python
-#两个维度相关系数为-1
-cov = [[10,-10],[-10,10]]
-```
-
-
-
-结果如图所示。
-
-(4)一般情况下
-
-```python
-#使相关系数为0.2
-cov = [[10,2],[2,10]]
-```
-
-
-
-```python
-#使相关系数为0.8
-cov = [[10,8],[8,10]]
-```
-
-
-
-分别将相关系数设为0.2与0.8,可以看出0.2时分布还相对散乱,而0.8时已经可以看出明显的线性关系。同样,由于label的随机选取,在直线上0-1的分布仍然是随机的。
-
-### 2.二维随机正态分布的多分类实验
-
-```python
-#相关系数取0.8
-cov = [[10,8],[8,10]]
-#五分类任务
-label = np.random.choice([0,1,2,3,4],size=1000,replace=True)
-```
-
-
-
-```python
-#相关系数取0.2
-cov = [[10,2],[2,10]]
-#五分类任务
-label = np.random.choice([0,1,2,3,4],size=1000,replace=True)
-```
-
-
-
-结果如图所示。与简单分类结果类似,这是由于两维的相关系数是一样的,而仅仅是将label从0-1随机取值变为0-1-2-3-4随机取值,并没有本质变化,只是人为定义的分类数变多了。
-
-### 3. 实验发现
-
-#### (1)简单分类与多分类
-
-以相关系数为0.2的二维正态分布,k值取5为例。
-
-运行10次0-1的简单二分类实验,结果分别为:
-
-acc = 0.51,0.545,0.535,0.515 ,0.435, 0.465,0.56,0.53, 0.515,0.53
-
-平均acc=0.514
-
-运行10次三分类实验,结果如下:
-
-acc = 0.295,0.32,0.35,0.34,0.31,0.405 ,0.325 ,0.3,0.32,0.32
-
-平均acc = 0.329
-
-运行10次四分类实验,结果如下:
-
-acc = 0.25,0.22,0.255,0.19,0.215,0.335,0.3,0.25,0.28,0.225
-
-平均acc = 0.252
-
-运行10此五分类实验,结果如下:
-
-acc = 0.265,0.185,0.22,0.235,0.195,0.19,0.22, 0.23,0.2,0.215
-
-平均acc = 0.2155
-
-
-
-可以发现,当分类数越多时,预测的准确率越低。这应该是由于data和label本身之间没有相关性,acc近似等于(1/分类数),和瞎猜的准确率是近似的。
-
-#### (2)k值的选取
-
-以简单二分类为例。
-
-k值取5,运行10次的平均acc =0.512
-
-k值取4,运行10次的平均acc =0.507
-
-k值取6,运行10次的平均acc =0.485
-
-k值取3,运行10次的平均acc =0.495
-
-k值取7,运行10次的平均acc =0.508
-
-
-
-可知,k取5是恰当的。但同样由于data和label之间没有相关性,所以不同k值之间准确率的差异不大,都在0.5左右,近似于瞎猜。因为分类区域本身就是随机的,距离预测点越近的点并不代表属于该点类别的概率越大。
-
-所以,该次尝试的调参是没有意义的。如果选取本身有意义,并且属性与分类有关系的数据组进行测试,取不同的k值的准确率才会有显著差异,此时的调参才有意义。
-
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/.keep b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/.keep
deleted file mode 100644
index e69de29bb2d1d6434b8b29ae775ad8c2e48c5391..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/0.2.png b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/0.2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 5cc12d92a5e696a6181dc47fef6caf9de5a4d7c9..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/0.2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/0.8.png b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/0.8.png
deleted file mode 100644
index abe0d2e4626cc82b2e44961f668c4d732aa057cf..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/0.8.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\214\347\273\264\347\233\270\345\205\263.png" "b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\214\347\273\264\347\233\270\345\205\263.png"
deleted file mode 100644
index 4eb7d1805b16224826b6522b18680a6951f08085..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files "a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\214\347\273\264\347\233\270\345\205\263.png" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\214\347\273\264\347\273\223\346\236\234.png" "b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\214\347\273\264\347\273\223\346\236\234.png"
deleted file mode 100644
index cfb88bc7cf41bc6bb02cd3467b2f475c43a405a2..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files "a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\214\347\273\264\347\273\223\346\236\234.png" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\2240.2.png" "b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\2240.2.png"
deleted file mode 100644
index 5d151517b7b0da7e0ccf89ae43a44b848831e19c..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files "a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\2240.2.png" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\224\345\210\206\347\261\2730.8.png" "b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\224\345\210\206\347\261\2730.8.png"
deleted file mode 100644
index d5d72a9445ffdab5b80e24d02ee76a3789244d50..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files "a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\344\272\224\345\210\206\347\261\2730.8.png" and /dev/null differ
diff --git "a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\350\264\237\344\272\214\347\273\264.png" "b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\350\264\237\344\272\214\347\273\264.png"
deleted file mode 100644
index 5f28d4a81b3deaa217a3d1a78602d6df915b3226..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files "a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/img/\350\264\237\344\272\214\347\273\264.png" and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 4ae97853ca5174d7f23998d209a5603a4a7b7c58..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
-#算法代码
-import numpy as np
-from collections import Counter
-class KNN:
-
- def __init__(self,k):
- self._k = k
- self._train_data=None
- self._train_label = None
- self._test_data=None
-
- def fit(self,train_data,train_label):
- self._train_data=train_data
- self._train_label=train_label
-
-
- def predict(self,test_data):
- self._test_data=test_data
- predicts_ =[]
- #遍历测试集
- for i in self._test_data:
- #对测试集中的数据求距离每一个训练集中数据的欧氏距离
- distances_ = [np.sum((i-x)**2)**0.5 for x in self._train_data]
- distances = np.array(distances_)
- #用Counter函数求距离前k个
- sorted_distances = np.argsort(distances)
- topK = [self._train_label[j] for j in sorted_distances[0:self._k]]
- votes = Counter(topK)
- #预测结果
- predict = votes.most_common(1)[0][0]
- predicts_.append(predict)
- predicts = np.array(predicts_)
- return predicts
-
-
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/train&test.py b/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/train&test.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 31f28e4c3580e54f001d4ac69fb1c3f9ddf533a9..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/16307100065/train&test.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
-#实验代码
-import numpy as np
-from lknn import KNN
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-#每一维均值为0,方差为10,并且两维独立,创建1000个数据
-cov = [[10,0],[0,10]]
-data = np.around(np.random.multivariate_normal((0,0),cov,1000),2)
-#对应分类随机取0或1
-label = np.random.choice([0,1],size=1000,replace=True)
-#按8:2的比例分为训练集和测试集
-n = len(data)//5
-train_data = data[0:4*n]
-train_label = label[0:4*n]
-test_data = data[4*n:]
-test_label = label[4*n:]
-#调用KNN类,k赋值5,将训练集输入模型
-model = KNN(5)
-model.fit(train_data, train_label)
-#绘制分类图
-#第一维和第二维分别作为x,y轴
-x_show = train_data[:,0]
-y_show = train_data[:,1]
-x_min,x_max=x_show.min(),x_show.max()
-y_min,y_max=y_show.min(),y_show.max()
-xx,yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(x_min,x_max,200),np.linspace(y_min,y_max,200))
-#将网格放入模型预测,预测每一个网格的分类
-z1 = np.c_[xx.ravel(),yy.ravel()]
-z = np.array(z1)
-pred = model.predict(z)
-pred = pred.reshape(xx.shape)
-#绘制网格分类图和训练集的散点图
-plt.pcolormesh(xx,yy,pred,cmap=plt.cm.Pastel1)
-plt.scatter(x_show,y_show,s=80,c=train_label,cmap=plt.cm.spring,edgecolors='k')
-plt.xlim(xx.min(),xx.max())
-plt.ylim(yy.min(),yy.max())
-plt.show()
-#计算acc
-res = model.predict(test_data)
-print("acc =",np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label)))
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 8c6b9b94639e4ef0462ed57212e65dc05b741d32..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
-# 实验报告1
-
-
-
-### 1,KNN的实现
-
-```python
- def predict1(self,test_data,k):
- predict=[]
- for instance in test_data:
- distances=np.array([self.distance (x,instance) for x in self.X])
-
- kneighbors=np.argsort(np.array(distances))[:k]
- count = Counter(self.y[kneighbors])
- predict.append(count.most_common()[0][0])
- return predict
-```
-
-将测试点最近的k个点列出,并找出其中出现最多的标签,作为预测的结果。
-
-```python
- def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=self.train_test_split(train_data, train_label)
- self.X=np.array(X_train)
- self.y=np.array(y_train)
- max_accurate=0
- best_k=0
- for k in self.k_n:
- accurate=0
- train_predict=self.predict1(X_test,k)
- correct = np.count_nonzero((train_predict==y_test)==True)
-
- accurate=correct/len(X_test)
- if (accurate>max_accurate):
- max_accurate=accurate
- best_k=k
- self.k_select=best_k
-```
-
-k_n为[1,2,3,4,5],knn将输入的数据分为训练集和测试集,并从k_n中选择一个准确率最高的k值。
-
-### 2,实验部分
-
-```python
-def generate():
- X1 = np.random.multivariate_normal([1,50], [[1,0],[0,10]], 100)
- X2 = np.random.multivariate_normal([3,50], [[1,0],[0,10]], 100)
- X3 = np.random.multivariate_normal([5,50], [[1,0],[0,10]], 100)
- X = np.concatenate([X1,X2,X3])
- y = np.array([0]*100 + [1]*100 +[2]*100)
- idx = np.arange(300)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- data=X=X[idx]
- label=y=y[idx]
-
- X_train=X[:240]
- X_test=X[240:]
- y_train=y[:240]
- y_test=y[240:]
- return np.array(X_train),np.array(X_test),np.array(y_train),np.array(y_test)
-
-```
-
-生成数据,将它们分为训练集和测试集。将训练集输入KNN,之后利用KNN预测测试集的标签。
-
-这是训练集:
-
-
-
-这是测试集:
-
-
-
- 
-
-这是对测试集的预测:
-
-
-
-这个预测的准确度为0.75.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/img/predict.png b/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/img/predict.png
deleted file mode 100644
index a853678b11d98ccc9a012b637a588a37723b42ff..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/img/predict.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/img/test.png b/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/img/test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index d9d8b3f379704464fcf2c4bff575425ef3404c0f..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/img/test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/img/train.png b/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/img/train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 2d61295b21b4bf115c35c594ca716f564a79a00a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/img/train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 397fbc05ad396f8bac4e0fee34426e6ee57d7f8f..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/16307130040/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,94 +0,0 @@
-import numpy as np
-from collections import Counter
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
-class KNN:
- k_n=[1,2,3,4,5]
- k_select=0
- X=[]
- y=[]
- def __init__(self):
- pass
-
- def train_test_split(self,X,y):
- offset=int(len(X)*0.8)
- X_train=X[:offset]
- X_test=X[offset:]
- y_train=y[:offset]
- y_test=y[offset:]
-
- return np.array(X_train),np.array(X_test),np.array(y_train),np.array(y_test)
-
- def distance(self,instance1,instance2):
- dist = np.sqrt(sum((instance1 - instance2)**2))
- return dist
-
- def predict1(self,test_data,k):
- predict=[]
- for instance in test_data:
- distances=np.array([self.distance (x,instance) for x in self.X])
-
- kneighbors=np.argsort(np.array(distances))[:k]
- count = Counter(self.y[kneighbors])
- predict.append(count.most_common()[0][0])
- return predict
-
- def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=self.train_test_split(train_data, train_label)
- self.X=np.array(X_train)
- self.y=np.array(y_train)
- max_accurate=0
- best_k=0
- for k in self.k_n:
- accurate=0
- train_predict=self.predict1(X_test,k)
- correct = np.count_nonzero((train_predict==y_test)==True)
-
- accurate=correct/len(X_test)
- if (accurate>max_accurate):
- max_accurate=accurate
- best_k=k
- self.k_select=best_k
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- return self.predict1(test_data,self.k_select)
-
-def generate():
- X1 = np.random.multivariate_normal([1,50], [[1,0],[0,10]], 100)
- X2 = np.random.multivariate_normal([3,50], [[1,0],[0,10]], 100)
- X3 = np.random.multivariate_normal([5,50], [[1,0],[0,10]], 100)
- X = np.concatenate([X1,X2,X3])
- y = np.array([0]*100 + [1]*100 +[2]*100)
- idx = np.arange(300)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
-
- data=X=X[idx]
- label=y=y[idx]
-
- X_train=X[:240]
- X_test=X[240:]
- y_train=y[:240]
- y_test=y[240:]
- return np.array(X_train),np.array(X_test),np.array(y_train),np.array(y_test)
-
-def display(data, label, name):
- datas =[[],[],[]]
- colors=['b','r','y']
- for i in range(len(data)):
- datas[label[i]].append(data[i])
- for i,each in enumerate(datas):
- each = np.array(each)
- plt.scatter(each[:, 0], each[:, 1],c=colors[i])
- plt.show()
-
-if __name__ == '__main__':
- X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=generate()
- model=KNN()
- model.fit(X_train,y_train)
- predict=model.predict(X_test)
- display(X_train,y_train,'train')
- display(X_test,y_test,'test')
- display(X_test,predict,'predict')
- correct = np.count_nonzero((predict==y_test))
- accurate=correct/len(X_test)
- print('accu=',accurate)
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 7e209eba20b4f93de8019d642a8fdc6979914d38..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,362 +0,0 @@
-# 课程报告
-
-## KNN类实现
-
-### fit()函数
-
-fit(X, y,cate = 'euclidean',metric='accuracy',preprocess =None)
-
-X: 训练集
-
-y:训练集标签
-
-cate:距离计算方式,如euclidean、manhattan距离
-
-metric:模型评估方式,如accuracy
-
-preprocess:预处理方式,包含min_max归一化、z_score标准化、不处理
-
-
-
-fit函数包含以下功能:
-
- 1、预处理;
-
- 2、随机打乱数据集顺序
-
- 3、以8:2的比例划分train_data,dev_data,训练选出评估结果最优的k值
-
-### predict()函数
-
-predict用于预测测试集样本
-
-### 辅助函数
-
-distance( d1, d2,cate ='eulidean')
-
-d1,d2表示计算距离的点,cate默认为euclidean距离,可以选择manhattan距离
-
-
-
-## 实验1
-
-### Group1:各个类别相差较大,成较为明显的线性位置
-
-$$
-\Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 52 & 0 \\
- 0 & 22
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 21.1 & 0 \\
- 0 & 32.1
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 10 & 0 \\
- 0 & 10
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
-$$
-
-$$
-\mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 2 &5
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 20 & -5
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- -5 & 22
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
-$$
-
-train_data
-
- -
-测试集
-
-
-
-测试集
-
- -
-测试在两种距离下的准确率如下:
-
-| k | distance | acc |
-| ---- | --------- | ------- |
-| 8 | euclidean | 96.250% |
-| 9 | euclidean | 95.625% |
-| 3 | euclidean | 95.833% |
-| 13 | euclidean | 96.458% |
-| 3 | manhattan | 95.417% |
-| 13 | manhattan | 96.250% |
-| 5 | manhattan | 95.625% |
-| 5 | manhattan | 95.625% |
-
-### Group2:各个类别之间相差较大,成较为明显的分散位置
-
-$$
-\Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 52 & 0 \\
- 0 & 22
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 21.1 & 0 \\
- 0 & 32.1
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 10 & 0 \\
- 0 & 10
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
-$$
-
-$$
-\mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 2 &5
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 20 & 16
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- -5 & 22
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
-$$
-
-train_data:
-
-
-
-测试在两种距离下的准确率如下:
-
-| k | distance | acc |
-| ---- | --------- | ------- |
-| 8 | euclidean | 96.250% |
-| 9 | euclidean | 95.625% |
-| 3 | euclidean | 95.833% |
-| 13 | euclidean | 96.458% |
-| 3 | manhattan | 95.417% |
-| 13 | manhattan | 96.250% |
-| 5 | manhattan | 95.625% |
-| 5 | manhattan | 95.625% |
-
-### Group2:各个类别之间相差较大,成较为明显的分散位置
-
-$$
-\Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 52 & 0 \\
- 0 & 22
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 21.1 & 0 \\
- 0 & 32.1
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 10 & 0 \\
- 0 & 10
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
-$$
-
-$$
-\mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 2 &5
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 20 & 16
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- -5 & 22
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
-$$
-
-train_data:
-
- -
-test_data:
-
-
-
-test_data:
-
- -
-测试在两种距离下的准确率如下:
-
-| k | distance | acc |
-| ---- | --------- | ------- |
-| 7 | euclidean | 96.875% |
-| 7 | euclidean | 96.875% |
-| 9 | euclidean | 97.083% |
-| 8 | euclidean | 97.083% |
-| 12 | manhattan | 97.708% |
-| 14 | manhattan | 97.500% |
-| 5 | manhattan | 97.083% |
-| 12 | manhattan | 97.708% |
-
-*可见不同群之间的几何分布类型对knn的效果影响不明显*
-
-## 实验2
-
-控制均值不变,倍数扩大协方差的各个数值至2倍
-$$
-\Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 52 & 0 \\
- 0 & 22
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 21.1 & 0 \\
- 0 & 32.1
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 10 & 0 \\
- 0 & 10
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
-$$
-
-$$
-\left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 2 &5
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 20 & 16
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- -5 & 22
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
-$$
-
-得到准确率改变如下图:
-
-
-
-测试在两种距离下的准确率如下:
-
-| k | distance | acc |
-| ---- | --------- | ------- |
-| 7 | euclidean | 96.875% |
-| 7 | euclidean | 96.875% |
-| 9 | euclidean | 97.083% |
-| 8 | euclidean | 97.083% |
-| 12 | manhattan | 97.708% |
-| 14 | manhattan | 97.500% |
-| 5 | manhattan | 97.083% |
-| 12 | manhattan | 97.708% |
-
-*可见不同群之间的几何分布类型对knn的效果影响不明显*
-
-## 实验2
-
-控制均值不变,倍数扩大协方差的各个数值至2倍
-$$
-\Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 52 & 0 \\
- 0 & 22
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 21.1 & 0 \\
- 0 & 32.1
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 10 & 0 \\
- 0 & 10
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
-$$
-
-$$
-\left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 2 &5
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 20 & 16
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- -5 & 22
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
-$$
-
-得到准确率改变如下图:
-
- -
-*方差对于KNN的准确率影响显著,随着方差增大,模型准确率下降*
-
-## 实验3
-
-对比采用归一化、标准化前后
-$$
-\Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 20 & 0 \\
- 0 & 1250
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 25 & 0 \\
- 0 & 2500
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 10 & 0 \\
- 0 & 950
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
-$$
-
-$$
-\mu=
-\left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 2 &5
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 10 & -60
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- -5 & 72
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
-$$
-
-无预处理:
-
-
-
-*方差对于KNN的准确率影响显著,随着方差增大,模型准确率下降*
-
-## 实验3
-
-对比采用归一化、标准化前后
-$$
-\Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 20 & 0 \\
- 0 & 1250
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 25 & 0 \\
- 0 & 2500
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 10 & 0 \\
- 0 & 950
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
-$$
-
-$$
-\mu=
-\left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 2 &5
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 10 & -60
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- -5 & 72
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
-$$
-
-无预处理:
-
- -
-min_max 归一化:
-
-
-
-min_max 归一化:
-
- -
-Z_score标准化:
-
-
-
-Z_score标准化:
-
- -
-得到对应的准确率如下:
-
-| preprocessing | accuracy |
-| ------------- | -------- |
-| None | 82.917% |
-| min_max | 83.542% |
-| z_score | 84.17% |
-
-通过变小均值和方差的差距,重新实验得到如下结果:
-$$
-\Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 20 & 0 \\
- 0 & 750
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 25 & 0 \\
- 0 & 1200
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 10 & 0 \\
- 0 & 650
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
-$$
-
-$$
-\mu=
-\left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 2 &5
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 10 & -50
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- -5 & 55
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
-$$
-
-| preprocessing | accuracy |
-| ------------- | -------- |
-| None | 90.417% |
-| min_max | 90.625# |
-| z_score | 90.833% |
-
-*标准化、归一化对于KNN模型的准确率有一定提升,数据集各个feature的数量级差别越大,效果越明显*
-
-## 总结
-
-1、KNN模型中不同类别点的几何分布类型对模型预测准确率影响不明显
-
-2、方差对于KNN的准确率影响显著,随着方差增大,模型准确率下降
-
-3、标准化、归一化对于KNN模型的准确率有一定提升,数据集各个feature的数量级差别越大,效果越明显;在数量级相差不大的情况下,性能提升不明显
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/change_cov.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/change_cov.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 90c6e3d31b490ac4e6f2e9a05f21f24bc71627ea..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/change_cov.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/data_minmax.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/data_minmax.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 2bf4c70c5448506cd1bb4c074e8a1a9e569c7716..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/data_minmax.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/data_original.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/data_original.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 76b9b4aa00c3807e7eb0c973d717e15b8f6ebdc4..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/data_original.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/data_zscore.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/data_zscore.png
deleted file mode 100644
index c79fe49fa23ed2cf8aec87519e4770fd9b3930aa..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/data_zscore.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/test_g1.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/test_g1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 6ba84cf0de903969371c4bb50b7dd8da40b2f1e4..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/test_g1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/test_g2.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/test_g2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 2155370c1ac0fa5544e7e9e4c9baee3b53fb834e..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/test_g2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/train_g1.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/train_g1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 1b1c264c47eadb1f85822cf8ab1364ced2405f8d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/train_g1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/train_g2.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/train_g2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 5530bce8dde2a7a3787fa58ee3e9a37b45726b02..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/train_g2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index be07e0492b7b13cde2148ce694ddd252ad0426dc..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,227 +0,0 @@
-import sys
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
-class KNN:
- def __init__(self):
- self.X = None
- self.y = None
- self.k = None
- self.cate = None # 距离计算公式
- self.metric = None # 评分方式,如accuracy
- self.preprocess = None
- self.min = None
- self.max =None
- self.mean = None
- self.std = None
-
- def distance(self, d1, d2):
- '''计算距离,如欧式距离、曼哈顿距离等'''
- if self.cate == 'euclidean':
- dist = np.sum(np.square(d1 - d2))
- elif self.cate == 'manhattan':
- dist = np.sum(np.abs(d1-d2))
- return dist
-
- def score(self, y_pred, test_label):
- '''分数评估如accuracy、macro_f1、micro_f1等'''
- if self.metric == 'accuracy':
- cnt = 0
- for i in range(len(y_pred)):
- if y_pred[i] == test_label[i]:
- cnt += 1
- score = cnt / len(y_pred)
- return score
-
- def fit(self, X, y,cate = 'euclidean',metric='accuracy',preprocess =None):
- '''包含K值的选择、建立模型'''
- self.cate = cate
- self.metric = metric
- self.preprocess = preprocess
-
- # 1、preprocessing
- if preprocess == 'Min_Max': #标准化
- self.min = X.min(axis = 0)
- self.max = X.max(axis = 0)
- X = (X -self.min)/(self.max - self.min)
- elif preprocess == 'Z_score': # 归一化
- self.mean = X.mean(axis=0)
- self.std = X.std(axis=0)
- X = (X - self.mean) / self.std
- else:
- X = X
-
- # 2、打乱顺序
- random_index = np.random.permutation(len(X))
- X = X[random_index]
- y= y[random_index]
-
- # 3、分为train_data,dev_data
- N = X.shape[0]
- cut = int(N * 0.8) # 防止非整数情况
- train_data, dev_data = X[:cut, ], X[cut:, ]
- train_label, dev_label = y[:cut, ], y[cut:, ]
-
- # 4、训练K值
- max_score = 0
- max_score_K = 0
- for k in range(2, 15):
- '''计算每个k下的accuracy:
- 1、对每个dev_data,计算其与train_data的距离
- 2、排序得到距离最近的k个index
- 3、获取该dev_data的y_pred
- 4、计算accuracy
- '''
- y_pred = []
- for i in range(len(dev_data)):
- dist_arr = [self.distance(dev_data[i], train_data[j]) for j in range(len(train_data))] # 每个测试点距离训练集各个点的距离列表
- sorted_index = np.argsort(dist_arr) # arg 排序各个距离的大小,得到index
- first_k_index = sorted_index[:k] # 最小的k个index
- first_k_label = train_label[first_k_index]
- y_pred.append(np.argmax(np.bincount(first_k_label))) # 取众数为预测值
- y_pred = np.array(y_pred)
- score = self.score(y_pred, dev_label)
-
- if score > max_score:
- max_score, max_score_K = score, k
-
- # 5、确立参数
- self.X = X
- self.y = y
- self.k = max_score_K
- # print('k:%d' % self.k)
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- # preprocessing
- if self.preprocess == 'Min_Max': #标准化
- test_data = (test_data -self.min)/(self.max - self.min)
- elif self.preprocess == 'Z_score': # 归一化
- test_data = (test_data - self.mean) / self.std
- else:
- test_data = test_data
-
- y_pred = []
- for i in range(len(test_data)):
- dist_arr = [self.distance(test_data[i], self.X[j]) for j in range(len(self.X))]
- first_k_index = np.argsort(dist_arr)[:self.k]
- first_k_label = self.y[first_k_index]
- y_pred.append(np.argmax(np.bincount(first_k_label)))
- return np.array(y_pred)
-
-
-def generate():
- mean = (2, 5)
- cov = np.array([[20, 0], [0, 750]])
- x = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (800,))
-
- mean = (10, -60)
- cov = np.array([[25, 0], [0, 2500]])
- y = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (600,))
-
- mean = (-5, 72)
- cov = np.array([[10, 0], [0, 650]])
- z = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (1000,))
-
- idx = np.arange(2400)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- data = np.concatenate([x, y, z])
- label = np.concatenate([
- np.zeros((800,), dtype=int),
- np.ones((600,), dtype=int),
- np.ones((1000,), dtype=int) * 2
- ])
- data = data[idx]
- label = label[idx]
-
- train_data, test_data = data[:1920, ], data[1920:, ]
- train_label, test_label = label[:1920, ], label[1920:, ]
- np.save("data.npy", (
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
- ))
-
-
-def read():
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = np.load("data.npy", allow_pickle=True)
- return (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
-
-
-def display(data, label, name):
- datas = [[], [], []]
- for i in range(len(data)):
- datas[label[i]].append(data[i])
-
- for each in datas:
- each = np.array(each)
- plt.scatter(each[:, 0], each[:, 1])
- plt.savefig(f'img/{name}')
- plt.show()
-
-
-'''测试改变方差对结果的影响'''
-def generate_ball(r=1):
- mean = (2, 5)
- cov = np.array([[40, 0], [0, 30]])
- x = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov*r, (800,))
-
- mean = (20, 16)
- cov = np.array([[25, 0], [0, 35.1]])
- y = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov*r, (600,))
-
- mean = (-5, 22)
- cov = np.array([[30, 0], [0, 25]])
- z = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov*r, (1000,))
-
- idx = np.arange(2400)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- data = np.concatenate([x, y, z])
- label = np.concatenate([
- np.zeros((800,), dtype=int),
- np.ones((600,), dtype=int),
- np.ones((1000,), dtype=int) * 2
- ])
- data = data[idx]
- label = label[idx]
-
- train_data, test_data = data[:1920, ], data[1920:, ]
- train_label, test_label = label[:1920, ], label[1920:, ]
- return train_data, train_label, test_data, test_label
-
-def change_cov():
- acc_1 = []
- acc_2 = []
- for each in np.arange(1, 2.1, 0.1):
- train_data, train_label, test_data, test_label = generate_ball(r=each)
- # euclidean
- model = KNN()
- model.fit(train_data, train_label, cate='euclidean', metric='accuracy')
- res = model.predict(test_data)
- acc1 = np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label))
- acc_1.append(acc1)
- # manhattan
- model = KNN()
- model.fit(train_data, train_label, cate='manhattan', metric='accuracy')
- res = model.predict(test_data)
- acc2 = np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label))
- acc_2.append(acc2)
- plt.plot(np.arange(1,2.1,0.1), acc_1,color = 'r')
- plt.plot(np.arange(1,2.1,0.1), acc_2,color = 'b')
- plt.title('accuracy at different cov')
- plt.legend(['euclidean','manhattan'])
- plt.savefig('change_cov.png')
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "g":
- generate()
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "d":
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
- display(train_data, train_label, 'train')
- display(test_data, test_label, 'test')
- else:
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
-
- model = KNN()
- # 选择距离计算公式、评估公式
- model.fit(train_data, train_label, cate='manhattan',metric='accuracy')
- res = model.predict(test_data)
- print("acc =", np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label)))
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index f34b168681d1fdb43378914439a666a038baab1d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,163 +0,0 @@
-# 课程报告
- 我的KNN模型**只用到了numpy包**,所以我的代码应该可以通过限定依赖包的自动测试。
- ## 一、数据集的生成和划分
- 首先我以如下参数生成了3个符合二维高斯分布的集合的数据集。
-
- 第一类数据800个,标注为0:
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-73 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 22
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-1 & 2
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-
- 第二类数据200个,标注为1:
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-21.2 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 32.1
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-16 & -5
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
- 第三类数据1000个,标注为2:
-
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-10 & 5 \\\\
-5 & 10
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-10 & 22
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
- 将这些图片和对应的标注混合并打乱次序,就能够得到我们数据集。从其中取出80%(1600对)作为我们的训练集。
- 这是我生成的训练集
-
-
-
-取出其中另外的20%(400对)作为我们的测试集。
-这是我生成的测试集
-
-
- ## 二、KNN模型的建立
- 我的KNN模型主要分为两部分。第一部分的fit函数将训练集分为训练集和验证集,根据KNN模型在验证集上的最优结果自动地选择最优的K值。第二部分的predict函数用已选择出的K值代入KNN模型中,预测测试集的标签。
- ### 2.1 fit函数的编写
- fit函数主要包含以下几个步骤:
- (1)将已有的训练集的次序打乱,分出其中的20%作为验证集,80%作为测试集。
-
- (2)遍历待选的K值,在暂时确定K值的情况下在验证集上测试模型的结果。若训练集数量小于20,则待选K值的范围是range(1,训练集数量,2);若训练集数量大于20,则待选K值的范围是range(1,20,2)。
-
- (3)找到验证集预测准确率最高的模型所对应的K值。将该值作为后续在predict函数中运用的K值。
-
- ### 2.2 predict函数的编写
- predict函数主要包含以下几个步骤:
- (1)遍历测试集中的每一个点。当取出测试集中的某一点时,计算该点与训练集中的每个点的距离。
-
- (2)对计算好的距离进行从小到大排序,取出前K个点
-
- (3)统计前K个值中各个类别的数量
-
- (4)数量最多的类别便是预测结果。
-
-
- ## 三、实验结果与分析
- 在命令行运行 python source.py g即可生成数据集并查看准确率结果。由于每次随机生成的数据集略有差异,每次的K值和准确率也略有差异。重复实验10次,结果如下表:
-
-
-实验次数 |K值 |准确率
----|---|---
-1| 11| 0.96
-2 | 9|0.9675
-3| 15| 0.955
-4 | 11|0.9475
-5| 5| 0.94
-6 | 5|0.94
-7| 11| 0.96
-8 | 7|0.945
-9| 7| 0.95
-10 | 19|0.955
-
-取这10次实验准确率的均值,得到模型的最终准确率为0.952。
-最终的模型准确率较高。准确率不为1的原因是测试集中蓝色与橙色的点有着一定的交集,对于处于交集中的数据我们也很难分清楚数据点到底属于哪一个类别。这部分的失误对于KNN来说似乎是无法避免的。
-
-
-## 三、修改数据集进行实验探究
-### 3.1 修改高斯分布的距离
-我们的预期是:在其它条件不变的情况下,高斯分布的距离越大,数据分的越开,KNN越容易预测准确。高斯分布的距离越小,数据离得越近,KNN的准确率越低。
-#### (1)设置参数使得三个类别分的更开。
-
- 修改第二类数据的均值,使得它与另外两类数据分的更开:
-$$
-\mu_2 = [\begin{matrix}30 & -20\end{matrix}]
-$$
-
- 此时测试集的数据分布如下图:
- 
- 多次实验得到模型的准确率为0.99。符合我们的预期。
-
-#### (2)设置参数使得三个类别离得更近。
-
- 修改每一类数据的均值,使得它们离得更近:
-
-$$
-\mu_1 = [\begin{matrix}1 & 2\end{matrix}]
-$$
-
-$$
-\mu_2 = [\begin{matrix}15 & 0\end{matrix}]
-$$
-$$
-\mu_3 = [\begin{matrix}10 & 10\end{matrix}]
-$$
-
- 此时测试集的数据分布如下图:
-
- 
- 此时模型的准确率均值只有0.84。符合我们的预期。
-
- ### 3.2 修改高斯分布的方差
- 我们的预期是:在其它条件不变的情况下,高斯分布的方差越大,数据越容易混淆,因此KNN的结果越差。高斯分布的方差越小,数据越集中,KNN的结果越好。
-#### 设置参数使得第二和第三类数据的协方差更大。
- 修改第二,三类数据的方差如下:
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-73 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 22
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
- 此时测试集的数据分布如下图:
-
- 
-
- 此时模型的准确率均值只有0.74,符合我们的预期。显然KNN的结果在这种情况下并不理想。
-
- ### 3.3 修改数据的数量
- #### (1)使各类数据翻倍。
- 对第一,第二,第三类的训练和测试数据翻倍。
- 此时测试集的数据分布如下图:
- 
-
- 对模型运行多次求均值,得到模型的准确率约为0.956。准确率相比于原先提升了一点点。这点提升微乎其微,背后的原因可能是数据翻倍时同样也使得数据间的交叠翻倍,对于这部分的交叠数据,模型很难判别正确。因此准确率没有什么改变。
-
- #### (2)使第一类数据翻倍
- 只对第一类的训练和测试数据翻倍。
- 此时测试集的数据分布如下图:
- 
- 对模型运行多次求均值,得到模型的准确率约为0.96。可见准确率提升了一些。这是由于第一类的数据翻倍,导致在数据交叠区域数据点更倾向于被判别为第一类数据,因此准确率必定会有一定的提升
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/.keep b/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/.keep
deleted file mode 100644
index e69de29bb2d1d6434b8b29ae775ad8c2e48c5391..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_1.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index eec47aac6c3a4a91fbb79b4e46c19b4dcaf56ad7..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_2.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index b7273b4820997fc7ccf6f1238e0f6d5dc53776f1..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_3.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 1389dfe352cc414a710dab394b0a5cbd5173c5e9..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_4.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_4.png
deleted file mode 100644
index c33f255f7f5c059f8b3fa50fd5f02ebdf81a8204..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_4.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_5.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_5.png
deleted file mode 100644
index f15a0935c5fc56cadf8f259b40b0b960831d256f..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_5.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_6.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_6.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 528bd1180529c99a903a7affc9c08cbb6f0af35b..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_6.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/train_1.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/train_1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 580335fd8c4753ea64df8189940b63039eb02168..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/train_1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index bc70f0c0f1ea938f09f35eee810449c19758ef39..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,172 +0,0 @@
-import sys
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
-class KNN:
-
- def __init__(self):
- self.train_data = None
- self.train_label = None
- self.k = None
-
- def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- self.train_data = train_data
- self.train_label = train_label
- # 将训练集打乱
- data_size = self.train_data.shape[0]
- shuffled_indices = np.random.permutation(data_size)
- shuffled_data = train_data[shuffled_indices]
- shuffled_label = train_label[shuffled_indices]
- # test_ratio为测试集所占的百分比,划分训练集和验证集
- test_ratio = 0.2
- test_set_size = int(data_size * test_ratio)
- valid_data = shuffled_data[:test_set_size]
- valid_label = shuffled_label[:test_set_size]
- training_data = shuffled_data[test_set_size:]
- training_label = shuffled_label[test_set_size:]
- # 在验证集上对不同的K值进行测试
- record ={}
- if training_data.shape[0] < 20:
- k_number = training_data.shape[0]
- else:
- k_number = 20
- for k in range(1,k_number,2):
- data_size = training_data.shape[0]
- predict_result = np.array([])
- for i in range(valid_data.shape[0]):
- diff = np.tile(valid_data[i], (data_size, 1)) - training_data
- sqdiff = diff ** 2
- squareDist = np.sum(sqdiff, axis=1)
- dist = squareDist ** 0.5
- # test_data到其它点的距离
- sorteddiffdist = np.argsort(dist)
- # 对这些距离从小到大排序
- classCount = {}
- for j in range(k):
- Label = training_label[sorteddiffdist[j]]
- classCount[Label] = classCount.get(Label, 0) + 1
- # 统计距离中前K个值中各个类别的数量
- maxCount = 0
- for key, value in classCount.items():
- if value > maxCount:
- maxCount = value
- result = key
- predict_result = np.append(predict_result, result)
- acc = np.mean(np.equal(predict_result, valid_label))
- record[k] = acc
- # 取验证准确率最高的K值作为K值
- maxCount = 0
- for key, value in record.items():
- if value > maxCount:
- maxCount = value
- k_result = key
- print("k=",k_result)
- self.k = k_result
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- data_size = self.train_data.shape[0]
- predict_result = np.array([])
- for i in range(test_data.shape[0]):
- diff = np.tile(test_data[i],(data_size,1)) - self.train_data
- sqdiff = diff **2
- squareDist = np.sum(sqdiff, axis =1)
- dist = squareDist **0.5
- # test_data到其它点的距离
- sorteddiffdist = np.argsort(dist)
- # 对这些距离从小到大排序
- classCount ={}
- for j in range(self.k):
- Label = self.train_label[sorteddiffdist[j]]
- classCount[Label] = classCount.get(Label,0) + 1
- # 统计距离中前K个值中各个类别的数量
- maxCount = 0
- for key, value in classCount.items():
- if value > maxCount:
- maxCount = value
- result = key
- predict_result = np.append(predict_result,result)
- # 数量最多的就是预测的结果
- return predict_result
-
-
-def generate():
- mean = (1, 2)
- cov = np.array([[73, 0], [0, 22]])
- x = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (800,))
- #x = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (1600,))
-
- mean = (16, -5)
- #mean = (30, -20)
- #mean = (15, 0)
- cov = np.array([[21.2, 0], [0, 32.1]])
- #cov = np.array([[73, 0], [0, 22]])
- y = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (200,))
- #y = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (400,))
-
- mean = (10, 22)
- #mean = (10,10)
- cov = np.array([[10, 5], [5, 10]])
- #cov = np.array([[73, 0], [0, 22]])
- z = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (1000,))
- #z = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (2000,))
-
- idx = np.arange(2000)
- #idx = np.arange(2800)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- data = np.concatenate([x, y, z])
- label = np.concatenate([
- np.zeros((800,), dtype=int),
- np.ones((200,), dtype=int),
- np.ones((1000,), dtype=int) * 2
- ])
- # label = np.concatenate([
- # np.zeros((1600,), dtype=int),
- # np.ones((200,), dtype=int),
- # np.ones((1000,), dtype=int) * 2
- # ])
- # data = data[idx]
- # label = label[idx]
-
- train_data, test_data = data[:1600, ], data[1600:, ]
- train_label, test_label = label[:1600, ], label[1600:, ]
- # train_data, test_data = data[:2240, ], data[2240:, ]
- # train_label, test_label = label[:2240, ], label[2240:, ]
- np.save("data.npy", (
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
- ))
-
-
-def read():
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = np.load("data.npy", allow_pickle=True)
- return (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
-
-
-def display(data, label, name):
- datas = [[], [], []]
- for i in range(len(data)):
- datas[label[i]].append(data[i])
-
- for each in datas:
- each = np.array(each)
- plt.scatter(each[:, 0], each[:, 1])
- plt.savefig(f'./{name}')
- plt.show()
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "g":
- generate()
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "d":
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
- display(train_data, train_label, 'train')
- display(test_data, test_label, 'test')
- else:
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
-
- model = KNN()
- model.fit(train_data, train_label)
- res = model.predict(test_data)
- print("acc =", np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label)))
-
-
-
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index b4ef5ec932b48a64641332fa51b023e214123724..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,129 +0,0 @@
-# 课程报告
-
-## KNN实现
-
-### 距离的计算
-
-$$
-\begin{array}\\\\
-assume\ test\ matrix\ P: M\times D,\ train\ matrix\ C:N\times D. D\ is\ the\ dimension\ of\ data.\\\\
-let\ P_i\ is\ ith\ row\ in\ P,\ C_j\ is\ jth\ row\ in\ C.\\\\
-distance\ between\ P_i\ and\ C_j:\\\\
-d(P_i,C_j) = \sqrt{\sum_{k=1}^{D}(P_{ik}-C_{jk})^2}\\\\
-=\sqrt{\sum_{k=1}^DP_{ik}^2+\sum_{k=1}^DC_{jk}^2-2\sum_{k=1}^D(P_{ik}C_{jk})}\\\\
-=\sqrt{||P_i||^2+||C_j||^2-2P_iC_j^T}\\\\
-then\ we\ can\ calculate\ the\ whole\ distance\ matrix\ only\ with\ matrix\ operations.
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-### 数据预处理:归一化
-
-将数据归一化到[0, 1],在服从正态分布的数据集上测试时表现不佳(详见实验部分)。最终代码中有实现归一化(normalize中),但是并未应用。
-
-### k的取值
-
-fit函数中,k在[2, 6]中取最优值。fit函数先把train_data划分为train_data和dev_data,比例为1:4;然后计算出距离矩阵;最后k遍历[2, 6],找到在dev_data上测试所得到最高正确率的k值,应用于最后的预测。
-
-## 实验
-
-### 实验一 正则化
-
-此实验目的是探究KNN中数据正则化的影响。
-
-实验了多组数据,只有在测试数据参数为
-
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-&\Sigma_1&=&\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-3 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 70
-\end{array}\right] \qquad
-&\Sigma_2&=&\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-4 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 65
-\end{array}\right] \qquad
-&\Sigma_3&=&\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-2 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 75
-\end{array}\right]\\\\
-&\mu_1&=&\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-4 & -20
-\end{array}\right]
-&\mu_2&=&\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-5 & 0
-\end{array}\right]
-&\mu_3&=&\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-6 & 20
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-时,使用正则化取得更好的结果。
-
-训练集:
-
-
-
-得到对应的准确率如下:
-
-| preprocessing | accuracy |
-| ------------- | -------- |
-| None | 82.917% |
-| min_max | 83.542% |
-| z_score | 84.17% |
-
-通过变小均值和方差的差距,重新实验得到如下结果:
-$$
-\Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 20 & 0 \\
- 0 & 750
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 25 & 0 \\
- 0 & 1200
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \Sigma =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 10 & 0 \\
- 0 & 650
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
-$$
-
-$$
-\mu=
-\left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 2 &5
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- 10 & -50
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
- \mu =
- \left[
- \begin{matrix}
- -5 & 55
- \end{matrix}
- \right]
-$$
-
-| preprocessing | accuracy |
-| ------------- | -------- |
-| None | 90.417% |
-| min_max | 90.625# |
-| z_score | 90.833% |
-
-*标准化、归一化对于KNN模型的准确率有一定提升,数据集各个feature的数量级差别越大,效果越明显*
-
-## 总结
-
-1、KNN模型中不同类别点的几何分布类型对模型预测准确率影响不明显
-
-2、方差对于KNN的准确率影响显著,随着方差增大,模型准确率下降
-
-3、标准化、归一化对于KNN模型的准确率有一定提升,数据集各个feature的数量级差别越大,效果越明显;在数量级相差不大的情况下,性能提升不明显
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/change_cov.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/change_cov.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 90c6e3d31b490ac4e6f2e9a05f21f24bc71627ea..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/change_cov.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/data_minmax.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/data_minmax.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 2bf4c70c5448506cd1bb4c074e8a1a9e569c7716..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/data_minmax.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/data_original.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/data_original.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 76b9b4aa00c3807e7eb0c973d717e15b8f6ebdc4..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/data_original.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/data_zscore.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/data_zscore.png
deleted file mode 100644
index c79fe49fa23ed2cf8aec87519e4770fd9b3930aa..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/data_zscore.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/test_g1.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/test_g1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 6ba84cf0de903969371c4bb50b7dd8da40b2f1e4..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/test_g1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/test_g2.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/test_g2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 2155370c1ac0fa5544e7e9e4c9baee3b53fb834e..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/test_g2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/train_g1.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/train_g1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 1b1c264c47eadb1f85822cf8ab1364ced2405f8d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/train_g1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/train_g2.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/train_g2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 5530bce8dde2a7a3787fa58ee3e9a37b45726b02..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/img/train_g2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index be07e0492b7b13cde2148ce694ddd252ad0426dc..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/17307100038/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,227 +0,0 @@
-import sys
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
-class KNN:
- def __init__(self):
- self.X = None
- self.y = None
- self.k = None
- self.cate = None # 距离计算公式
- self.metric = None # 评分方式,如accuracy
- self.preprocess = None
- self.min = None
- self.max =None
- self.mean = None
- self.std = None
-
- def distance(self, d1, d2):
- '''计算距离,如欧式距离、曼哈顿距离等'''
- if self.cate == 'euclidean':
- dist = np.sum(np.square(d1 - d2))
- elif self.cate == 'manhattan':
- dist = np.sum(np.abs(d1-d2))
- return dist
-
- def score(self, y_pred, test_label):
- '''分数评估如accuracy、macro_f1、micro_f1等'''
- if self.metric == 'accuracy':
- cnt = 0
- for i in range(len(y_pred)):
- if y_pred[i] == test_label[i]:
- cnt += 1
- score = cnt / len(y_pred)
- return score
-
- def fit(self, X, y,cate = 'euclidean',metric='accuracy',preprocess =None):
- '''包含K值的选择、建立模型'''
- self.cate = cate
- self.metric = metric
- self.preprocess = preprocess
-
- # 1、preprocessing
- if preprocess == 'Min_Max': #标准化
- self.min = X.min(axis = 0)
- self.max = X.max(axis = 0)
- X = (X -self.min)/(self.max - self.min)
- elif preprocess == 'Z_score': # 归一化
- self.mean = X.mean(axis=0)
- self.std = X.std(axis=0)
- X = (X - self.mean) / self.std
- else:
- X = X
-
- # 2、打乱顺序
- random_index = np.random.permutation(len(X))
- X = X[random_index]
- y= y[random_index]
-
- # 3、分为train_data,dev_data
- N = X.shape[0]
- cut = int(N * 0.8) # 防止非整数情况
- train_data, dev_data = X[:cut, ], X[cut:, ]
- train_label, dev_label = y[:cut, ], y[cut:, ]
-
- # 4、训练K值
- max_score = 0
- max_score_K = 0
- for k in range(2, 15):
- '''计算每个k下的accuracy:
- 1、对每个dev_data,计算其与train_data的距离
- 2、排序得到距离最近的k个index
- 3、获取该dev_data的y_pred
- 4、计算accuracy
- '''
- y_pred = []
- for i in range(len(dev_data)):
- dist_arr = [self.distance(dev_data[i], train_data[j]) for j in range(len(train_data))] # 每个测试点距离训练集各个点的距离列表
- sorted_index = np.argsort(dist_arr) # arg 排序各个距离的大小,得到index
- first_k_index = sorted_index[:k] # 最小的k个index
- first_k_label = train_label[first_k_index]
- y_pred.append(np.argmax(np.bincount(first_k_label))) # 取众数为预测值
- y_pred = np.array(y_pred)
- score = self.score(y_pred, dev_label)
-
- if score > max_score:
- max_score, max_score_K = score, k
-
- # 5、确立参数
- self.X = X
- self.y = y
- self.k = max_score_K
- # print('k:%d' % self.k)
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- # preprocessing
- if self.preprocess == 'Min_Max': #标准化
- test_data = (test_data -self.min)/(self.max - self.min)
- elif self.preprocess == 'Z_score': # 归一化
- test_data = (test_data - self.mean) / self.std
- else:
- test_data = test_data
-
- y_pred = []
- for i in range(len(test_data)):
- dist_arr = [self.distance(test_data[i], self.X[j]) for j in range(len(self.X))]
- first_k_index = np.argsort(dist_arr)[:self.k]
- first_k_label = self.y[first_k_index]
- y_pred.append(np.argmax(np.bincount(first_k_label)))
- return np.array(y_pred)
-
-
-def generate():
- mean = (2, 5)
- cov = np.array([[20, 0], [0, 750]])
- x = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (800,))
-
- mean = (10, -60)
- cov = np.array([[25, 0], [0, 2500]])
- y = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (600,))
-
- mean = (-5, 72)
- cov = np.array([[10, 0], [0, 650]])
- z = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (1000,))
-
- idx = np.arange(2400)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- data = np.concatenate([x, y, z])
- label = np.concatenate([
- np.zeros((800,), dtype=int),
- np.ones((600,), dtype=int),
- np.ones((1000,), dtype=int) * 2
- ])
- data = data[idx]
- label = label[idx]
-
- train_data, test_data = data[:1920, ], data[1920:, ]
- train_label, test_label = label[:1920, ], label[1920:, ]
- np.save("data.npy", (
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
- ))
-
-
-def read():
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = np.load("data.npy", allow_pickle=True)
- return (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
-
-
-def display(data, label, name):
- datas = [[], [], []]
- for i in range(len(data)):
- datas[label[i]].append(data[i])
-
- for each in datas:
- each = np.array(each)
- plt.scatter(each[:, 0], each[:, 1])
- plt.savefig(f'img/{name}')
- plt.show()
-
-
-'''测试改变方差对结果的影响'''
-def generate_ball(r=1):
- mean = (2, 5)
- cov = np.array([[40, 0], [0, 30]])
- x = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov*r, (800,))
-
- mean = (20, 16)
- cov = np.array([[25, 0], [0, 35.1]])
- y = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov*r, (600,))
-
- mean = (-5, 22)
- cov = np.array([[30, 0], [0, 25]])
- z = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov*r, (1000,))
-
- idx = np.arange(2400)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- data = np.concatenate([x, y, z])
- label = np.concatenate([
- np.zeros((800,), dtype=int),
- np.ones((600,), dtype=int),
- np.ones((1000,), dtype=int) * 2
- ])
- data = data[idx]
- label = label[idx]
-
- train_data, test_data = data[:1920, ], data[1920:, ]
- train_label, test_label = label[:1920, ], label[1920:, ]
- return train_data, train_label, test_data, test_label
-
-def change_cov():
- acc_1 = []
- acc_2 = []
- for each in np.arange(1, 2.1, 0.1):
- train_data, train_label, test_data, test_label = generate_ball(r=each)
- # euclidean
- model = KNN()
- model.fit(train_data, train_label, cate='euclidean', metric='accuracy')
- res = model.predict(test_data)
- acc1 = np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label))
- acc_1.append(acc1)
- # manhattan
- model = KNN()
- model.fit(train_data, train_label, cate='manhattan', metric='accuracy')
- res = model.predict(test_data)
- acc2 = np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label))
- acc_2.append(acc2)
- plt.plot(np.arange(1,2.1,0.1), acc_1,color = 'r')
- plt.plot(np.arange(1,2.1,0.1), acc_2,color = 'b')
- plt.title('accuracy at different cov')
- plt.legend(['euclidean','manhattan'])
- plt.savefig('change_cov.png')
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "g":
- generate()
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "d":
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
- display(train_data, train_label, 'train')
- display(test_data, test_label, 'test')
- else:
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
-
- model = KNN()
- # 选择距离计算公式、评估公式
- model.fit(train_data, train_label, cate='manhattan',metric='accuracy')
- res = model.predict(test_data)
- print("acc =", np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label)))
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index f34b168681d1fdb43378914439a666a038baab1d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,163 +0,0 @@
-# 课程报告
- 我的KNN模型**只用到了numpy包**,所以我的代码应该可以通过限定依赖包的自动测试。
- ## 一、数据集的生成和划分
- 首先我以如下参数生成了3个符合二维高斯分布的集合的数据集。
-
- 第一类数据800个,标注为0:
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-73 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 22
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-1 & 2
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-
- 第二类数据200个,标注为1:
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-21.2 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 32.1
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-16 & -5
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
- 第三类数据1000个,标注为2:
-
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-10 & 5 \\\\
-5 & 10
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-10 & 22
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
- 将这些图片和对应的标注混合并打乱次序,就能够得到我们数据集。从其中取出80%(1600对)作为我们的训练集。
- 这是我生成的训练集
-
-
-
-取出其中另外的20%(400对)作为我们的测试集。
-这是我生成的测试集
-
-
- ## 二、KNN模型的建立
- 我的KNN模型主要分为两部分。第一部分的fit函数将训练集分为训练集和验证集,根据KNN模型在验证集上的最优结果自动地选择最优的K值。第二部分的predict函数用已选择出的K值代入KNN模型中,预测测试集的标签。
- ### 2.1 fit函数的编写
- fit函数主要包含以下几个步骤:
- (1)将已有的训练集的次序打乱,分出其中的20%作为验证集,80%作为测试集。
-
- (2)遍历待选的K值,在暂时确定K值的情况下在验证集上测试模型的结果。若训练集数量小于20,则待选K值的范围是range(1,训练集数量,2);若训练集数量大于20,则待选K值的范围是range(1,20,2)。
-
- (3)找到验证集预测准确率最高的模型所对应的K值。将该值作为后续在predict函数中运用的K值。
-
- ### 2.2 predict函数的编写
- predict函数主要包含以下几个步骤:
- (1)遍历测试集中的每一个点。当取出测试集中的某一点时,计算该点与训练集中的每个点的距离。
-
- (2)对计算好的距离进行从小到大排序,取出前K个点
-
- (3)统计前K个值中各个类别的数量
-
- (4)数量最多的类别便是预测结果。
-
-
- ## 三、实验结果与分析
- 在命令行运行 python source.py g即可生成数据集并查看准确率结果。由于每次随机生成的数据集略有差异,每次的K值和准确率也略有差异。重复实验10次,结果如下表:
-
-
-实验次数 |K值 |准确率
----|---|---
-1| 11| 0.96
-2 | 9|0.9675
-3| 15| 0.955
-4 | 11|0.9475
-5| 5| 0.94
-6 | 5|0.94
-7| 11| 0.96
-8 | 7|0.945
-9| 7| 0.95
-10 | 19|0.955
-
-取这10次实验准确率的均值,得到模型的最终准确率为0.952。
-最终的模型准确率较高。准确率不为1的原因是测试集中蓝色与橙色的点有着一定的交集,对于处于交集中的数据我们也很难分清楚数据点到底属于哪一个类别。这部分的失误对于KNN来说似乎是无法避免的。
-
-
-## 三、修改数据集进行实验探究
-### 3.1 修改高斯分布的距离
-我们的预期是:在其它条件不变的情况下,高斯分布的距离越大,数据分的越开,KNN越容易预测准确。高斯分布的距离越小,数据离得越近,KNN的准确率越低。
-#### (1)设置参数使得三个类别分的更开。
-
- 修改第二类数据的均值,使得它与另外两类数据分的更开:
-$$
-\mu_2 = [\begin{matrix}30 & -20\end{matrix}]
-$$
-
- 此时测试集的数据分布如下图:
- 
- 多次实验得到模型的准确率为0.99。符合我们的预期。
-
-#### (2)设置参数使得三个类别离得更近。
-
- 修改每一类数据的均值,使得它们离得更近:
-
-$$
-\mu_1 = [\begin{matrix}1 & 2\end{matrix}]
-$$
-
-$$
-\mu_2 = [\begin{matrix}15 & 0\end{matrix}]
-$$
-$$
-\mu_3 = [\begin{matrix}10 & 10\end{matrix}]
-$$
-
- 此时测试集的数据分布如下图:
-
- 
- 此时模型的准确率均值只有0.84。符合我们的预期。
-
- ### 3.2 修改高斯分布的方差
- 我们的预期是:在其它条件不变的情况下,高斯分布的方差越大,数据越容易混淆,因此KNN的结果越差。高斯分布的方差越小,数据越集中,KNN的结果越好。
-#### 设置参数使得第二和第三类数据的协方差更大。
- 修改第二,三类数据的方差如下:
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-73 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 22
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
- 此时测试集的数据分布如下图:
-
- 
-
- 此时模型的准确率均值只有0.74,符合我们的预期。显然KNN的结果在这种情况下并不理想。
-
- ### 3.3 修改数据的数量
- #### (1)使各类数据翻倍。
- 对第一,第二,第三类的训练和测试数据翻倍。
- 此时测试集的数据分布如下图:
- 
-
- 对模型运行多次求均值,得到模型的准确率约为0.956。准确率相比于原先提升了一点点。这点提升微乎其微,背后的原因可能是数据翻倍时同样也使得数据间的交叠翻倍,对于这部分的交叠数据,模型很难判别正确。因此准确率没有什么改变。
-
- #### (2)使第一类数据翻倍
- 只对第一类的训练和测试数据翻倍。
- 此时测试集的数据分布如下图:
- 
- 对模型运行多次求均值,得到模型的准确率约为0.96。可见准确率提升了一些。这是由于第一类的数据翻倍,导致在数据交叠区域数据点更倾向于被判别为第一类数据,因此准确率必定会有一定的提升
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/.keep b/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/.keep
deleted file mode 100644
index e69de29bb2d1d6434b8b29ae775ad8c2e48c5391..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_1.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index eec47aac6c3a4a91fbb79b4e46c19b4dcaf56ad7..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_2.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index b7273b4820997fc7ccf6f1238e0f6d5dc53776f1..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_3.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 1389dfe352cc414a710dab394b0a5cbd5173c5e9..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_4.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_4.png
deleted file mode 100644
index c33f255f7f5c059f8b3fa50fd5f02ebdf81a8204..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_4.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_5.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_5.png
deleted file mode 100644
index f15a0935c5fc56cadf8f259b40b0b960831d256f..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_5.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_6.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_6.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 528bd1180529c99a903a7affc9c08cbb6f0af35b..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/test_6.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/train_1.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/train_1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 580335fd8c4753ea64df8189940b63039eb02168..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/img/train_1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index bc70f0c0f1ea938f09f35eee810449c19758ef39..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/17307110367/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,172 +0,0 @@
-import sys
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
-class KNN:
-
- def __init__(self):
- self.train_data = None
- self.train_label = None
- self.k = None
-
- def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- self.train_data = train_data
- self.train_label = train_label
- # 将训练集打乱
- data_size = self.train_data.shape[0]
- shuffled_indices = np.random.permutation(data_size)
- shuffled_data = train_data[shuffled_indices]
- shuffled_label = train_label[shuffled_indices]
- # test_ratio为测试集所占的百分比,划分训练集和验证集
- test_ratio = 0.2
- test_set_size = int(data_size * test_ratio)
- valid_data = shuffled_data[:test_set_size]
- valid_label = shuffled_label[:test_set_size]
- training_data = shuffled_data[test_set_size:]
- training_label = shuffled_label[test_set_size:]
- # 在验证集上对不同的K值进行测试
- record ={}
- if training_data.shape[0] < 20:
- k_number = training_data.shape[0]
- else:
- k_number = 20
- for k in range(1,k_number,2):
- data_size = training_data.shape[0]
- predict_result = np.array([])
- for i in range(valid_data.shape[0]):
- diff = np.tile(valid_data[i], (data_size, 1)) - training_data
- sqdiff = diff ** 2
- squareDist = np.sum(sqdiff, axis=1)
- dist = squareDist ** 0.5
- # test_data到其它点的距离
- sorteddiffdist = np.argsort(dist)
- # 对这些距离从小到大排序
- classCount = {}
- for j in range(k):
- Label = training_label[sorteddiffdist[j]]
- classCount[Label] = classCount.get(Label, 0) + 1
- # 统计距离中前K个值中各个类别的数量
- maxCount = 0
- for key, value in classCount.items():
- if value > maxCount:
- maxCount = value
- result = key
- predict_result = np.append(predict_result, result)
- acc = np.mean(np.equal(predict_result, valid_label))
- record[k] = acc
- # 取验证准确率最高的K值作为K值
- maxCount = 0
- for key, value in record.items():
- if value > maxCount:
- maxCount = value
- k_result = key
- print("k=",k_result)
- self.k = k_result
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- data_size = self.train_data.shape[0]
- predict_result = np.array([])
- for i in range(test_data.shape[0]):
- diff = np.tile(test_data[i],(data_size,1)) - self.train_data
- sqdiff = diff **2
- squareDist = np.sum(sqdiff, axis =1)
- dist = squareDist **0.5
- # test_data到其它点的距离
- sorteddiffdist = np.argsort(dist)
- # 对这些距离从小到大排序
- classCount ={}
- for j in range(self.k):
- Label = self.train_label[sorteddiffdist[j]]
- classCount[Label] = classCount.get(Label,0) + 1
- # 统计距离中前K个值中各个类别的数量
- maxCount = 0
- for key, value in classCount.items():
- if value > maxCount:
- maxCount = value
- result = key
- predict_result = np.append(predict_result,result)
- # 数量最多的就是预测的结果
- return predict_result
-
-
-def generate():
- mean = (1, 2)
- cov = np.array([[73, 0], [0, 22]])
- x = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (800,))
- #x = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (1600,))
-
- mean = (16, -5)
- #mean = (30, -20)
- #mean = (15, 0)
- cov = np.array([[21.2, 0], [0, 32.1]])
- #cov = np.array([[73, 0], [0, 22]])
- y = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (200,))
- #y = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (400,))
-
- mean = (10, 22)
- #mean = (10,10)
- cov = np.array([[10, 5], [5, 10]])
- #cov = np.array([[73, 0], [0, 22]])
- z = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (1000,))
- #z = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (2000,))
-
- idx = np.arange(2000)
- #idx = np.arange(2800)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- data = np.concatenate([x, y, z])
- label = np.concatenate([
- np.zeros((800,), dtype=int),
- np.ones((200,), dtype=int),
- np.ones((1000,), dtype=int) * 2
- ])
- # label = np.concatenate([
- # np.zeros((1600,), dtype=int),
- # np.ones((200,), dtype=int),
- # np.ones((1000,), dtype=int) * 2
- # ])
- # data = data[idx]
- # label = label[idx]
-
- train_data, test_data = data[:1600, ], data[1600:, ]
- train_label, test_label = label[:1600, ], label[1600:, ]
- # train_data, test_data = data[:2240, ], data[2240:, ]
- # train_label, test_label = label[:2240, ], label[2240:, ]
- np.save("data.npy", (
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
- ))
-
-
-def read():
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = np.load("data.npy", allow_pickle=True)
- return (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
-
-
-def display(data, label, name):
- datas = [[], [], []]
- for i in range(len(data)):
- datas[label[i]].append(data[i])
-
- for each in datas:
- each = np.array(each)
- plt.scatter(each[:, 0], each[:, 1])
- plt.savefig(f'./{name}')
- plt.show()
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "g":
- generate()
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "d":
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
- display(train_data, train_label, 'train')
- display(test_data, test_label, 'test')
- else:
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
-
- model = KNN()
- model.fit(train_data, train_label)
- res = model.predict(test_data)
- print("acc =", np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label)))
-
-
-
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index b4ef5ec932b48a64641332fa51b023e214123724..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,129 +0,0 @@
-# 课程报告
-
-## KNN实现
-
-### 距离的计算
-
-$$
-\begin{array}\\\\
-assume\ test\ matrix\ P: M\times D,\ train\ matrix\ C:N\times D. D\ is\ the\ dimension\ of\ data.\\\\
-let\ P_i\ is\ ith\ row\ in\ P,\ C_j\ is\ jth\ row\ in\ C.\\\\
-distance\ between\ P_i\ and\ C_j:\\\\
-d(P_i,C_j) = \sqrt{\sum_{k=1}^{D}(P_{ik}-C_{jk})^2}\\\\
-=\sqrt{\sum_{k=1}^DP_{ik}^2+\sum_{k=1}^DC_{jk}^2-2\sum_{k=1}^D(P_{ik}C_{jk})}\\\\
-=\sqrt{||P_i||^2+||C_j||^2-2P_iC_j^T}\\\\
-then\ we\ can\ calculate\ the\ whole\ distance\ matrix\ only\ with\ matrix\ operations.
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-### 数据预处理:归一化
-
-将数据归一化到[0, 1],在服从正态分布的数据集上测试时表现不佳(详见实验部分)。最终代码中有实现归一化(normalize中),但是并未应用。
-
-### k的取值
-
-fit函数中,k在[2, 6]中取最优值。fit函数先把train_data划分为train_data和dev_data,比例为1:4;然后计算出距离矩阵;最后k遍历[2, 6],找到在dev_data上测试所得到最高正确率的k值,应用于最后的预测。
-
-## 实验
-
-### 实验一 正则化
-
-此实验目的是探究KNN中数据正则化的影响。
-
-实验了多组数据,只有在测试数据参数为
-
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-&\Sigma_1&=&\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-3 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 70
-\end{array}\right] \qquad
-&\Sigma_2&=&\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-4 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 65
-\end{array}\right] \qquad
-&\Sigma_3&=&\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-2 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 75
-\end{array}\right]\\\\
-&\mu_1&=&\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-4 & -20
-\end{array}\right]
-&\mu_2&=&\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-5 & 0
-\end{array}\right]
-&\mu_3&=&\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-6 & 20
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-时,使用正则化取得更好的结果。
-
-训练集:
-
- -
-测试集:
-
-
-
-测试集:
-
- -
-| k | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
-| ---------------- | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ |
-| acc_dev 无归一化 | 87.81% | 91.88% | 91.25% | 91.25% | 91.25% |
-| acc_dev 有归一化 | 87.81% | 91.88% | 91.25% | 91.25% | 91.25% |
-
-最佳k值都为3,无归一化时,在test上为准确率:88.25%;有归一化时,在test上准确率为89.25%。
-
-在其他使用正态分布生成的数据中,都是不使用归一化准确率更高。在上例中,使用归一化正确率提升仅1%,而在其他数据上,不使用归一化正确率提高会高得多。所以在最终的代码中并未对数据进行归一化处理。在本系列实验中,归一化与否并不影响k的最佳取值。
-
-实验结论:首先,归一化并不适合在正态分布上的KNN分类。其次,归一化不影响最佳k值。
-
-### 实验二 改变分布之间的距离
-
-使用两个正态分布探究不同高斯分布之间距离的影响。先保持高斯分布的协方差矩阵不变,改变均值之间的距离。
-
-训练集:
-
-
-
-测试集:
-
-
-
-| 序号 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
-| ------- | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ |
-| 准确率 | 97.75% | 98.25% | 98.50% | 92.25% | 87.75% | 85.00% |
-| 最佳k值 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
-
-可以看出,两个分布的数据点范围开始重叠时,准确率开始下降,重叠范围越大,准确率越低,k值也在相应增大。
-
-接下来,保持两个分布均值距离不变,仅改变高斯分布的协方差矩阵。
-
-训练集:
-
-
-
-| k | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
-| ---------------- | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ |
-| acc_dev 无归一化 | 87.81% | 91.88% | 91.25% | 91.25% | 91.25% |
-| acc_dev 有归一化 | 87.81% | 91.88% | 91.25% | 91.25% | 91.25% |
-
-最佳k值都为3,无归一化时,在test上为准确率:88.25%;有归一化时,在test上准确率为89.25%。
-
-在其他使用正态分布生成的数据中,都是不使用归一化准确率更高。在上例中,使用归一化正确率提升仅1%,而在其他数据上,不使用归一化正确率提高会高得多。所以在最终的代码中并未对数据进行归一化处理。在本系列实验中,归一化与否并不影响k的最佳取值。
-
-实验结论:首先,归一化并不适合在正态分布上的KNN分类。其次,归一化不影响最佳k值。
-
-### 实验二 改变分布之间的距离
-
-使用两个正态分布探究不同高斯分布之间距离的影响。先保持高斯分布的协方差矩阵不变,改变均值之间的距离。
-
-训练集:
-
-
-
-测试集:
-
-
-
-| 序号 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
-| ------- | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ |
-| 准确率 | 97.75% | 98.25% | 98.50% | 92.25% | 87.75% | 85.00% |
-| 最佳k值 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
-
-可以看出,两个分布的数据点范围开始重叠时,准确率开始下降,重叠范围越大,准确率越低,k值也在相应增大。
-
-接下来,保持两个分布均值距离不变,仅改变高斯分布的协方差矩阵。
-
-训练集:
-
- -
-测试集:
-
-
-
-测试集:
-
- -
-| 序号 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
-| ------- | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ |
-| 准确率 | 96.75% | 96.25% | 95.00% | 92.50% |
-| 最佳k值 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 3 |
-
-类似地,准确率随着分布的重叠而降低。
-
-## 代码使用方法
-
-```bash
-python source.py g # 生成数据集
-python source.py d # 展示数据集
-python source.py # 训练和测试
-```
-
-# 参考
-
-距离的计算:https://blog.csdn.net/IT_forlearn/article/details/100022244?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromMachineLearnPai2-1.control&dist_request_id=&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromMachineLearnPai2-1.control
-
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/test_1.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/test_1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 1b3ef8c56c035e5122cdfacd83b9c436051d4b02..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/test_1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/test_2.jpg b/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/test_2.jpg
deleted file mode 100644
index 3ceff6d6091c5d283fcba0023e053e079e4720d0..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/test_2.jpg and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/test_3.jpg b/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/test_3.jpg
deleted file mode 100644
index 784506a6a23f0fcfaac61f422d03f0de9a4aab95..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/test_3.jpg and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/train_1.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/train_1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index fab155cdf1d85d91e888e28a678ee2dc11d63d68..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/train_1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/train_2.jpg b/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/train_2.jpg
deleted file mode 100644
index b723ef988fb70cc8f5efe0dd7e502798135578e0..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/train_2.jpg and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/train_3.jpg b/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/train_3.jpg
deleted file mode 100644
index 5ba83b8810ff506b4eae19ce531494986142458d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/train_3.jpg and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index dc9938a32ac6c410feff6fb95204e0861363809d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,132 +0,0 @@
-import sys
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
-class KNN:
-
- def __init__(self):
- self.train_data = None
- self.train_label = None
- self.k = 2
-
- def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- # train_data = self.normalize(train_data)
- self.train_data = train_data
- self.train_label = train_label
-
- N = train_data.shape[0]
- cut = N // 5 * 4
- train_data, dev_data = train_data[:cut,], train_data[cut:,]
- train_label, dev_label = train_label[:cut,], train_label[cut:,]
-
- dists = self.compute_distances(train_data, dev_data)
-
- max_acc = 0
- max_acc_k = 2
- for k in range(2,7):
- res = self.get_label(dists, train_label, k)
- acc = np.mean(np.equal(res, dev_label))
- print("k = %d, acc = %f" % (k, acc))
- if acc > max_acc:
- max_acc = acc
- max_acc_k = k
- print("best k = %d" % max_acc_k)
- self.k = max_acc_k
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- # test_data = self.normalize(test_data)
- dists = self.compute_distances(self.train_data, test_data)
- return self.get_label(dists, self.train_label, self.k)
-
- def compute_distances(self, train_data, test_data):
- num_train = train_data.shape[0]
- num_test = test_data.shape[0]
- dists = np.zeros((num_test, num_train))
-
- train_square = np.sum(np.square(train_data), axis=1).reshape(1, num_train)
- test_square = np.sum(np.square(test_data), axis=1).reshape(num_test, 1)
- dists = np.sqrt(train_square + test_square - 2 * np.dot(test_data, train_data.T))
-
- return dists
-
- def get_label(self, dists, train_label, k):
- num_test = dists.shape[0]
- y_predict = np.zeros(num_test, dtype=train_label.dtype)
- for i in range(num_test):
- closest_y = list(train_label[np.argsort(dists[i,:])[:k]])
- y_predict[i] = max(closest_y, key = closest_y.count)
- return y_predict
-
- def normalize(self, data):
- if len(data) == 0:
- return data
- return (data - np.min(data)) / (np.max(data) - np.min(data))
-
-
-def generate():
- # mean = (1, 2)
- # cov = np.array([[73, 0], [0, 22]])
- mean = (-17, 2)
- cov = np.array([[103, 0],[0, 22]])
- x = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (1200,))
-
- # mean = (16, -5)
- # cov = np.array([[21.2, 0], [0, 32.1]])
- mean = (10, -5)
- cov = np.array([[101.2, 0],[0, 32.1]])
- y = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (800,))
-
- # mean = (10, 22)
- # cov = np.array([[10,5],[5,10]])
- # z = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (1000,))
-
- idx = np.arange(2000)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- # data = np.concatenate([x,y,z])
- data = np.concatenate([x,y])
- label = np.concatenate([
- # np.zeros((800,),dtype=int),
- # np.ones((200,),dtype=int),
- # np.ones((1000,),dtype=int)*2
- np.zeros((1200,),dtype=int),
- np.ones((800,),dtype=int),
- ])
- data = data[idx]
- label = label[idx]
-
- train_data, test_data = data[:1600,], data[1600:,]
- train_label, test_label = label[:1600,], label[1600:,]
- np.save("data.npy",(
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
- ))
-
-def read():
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = np.load("data.npy", allow_pickle=True)
- return (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
-
-def display(data, label, name):
- # datas = [[], [], []]
- datas = [[], []]
- for i in range(len(data)):
- datas[label[i]].append(data[i])
-
- for each in datas:
- each = np.array(each)
- plt.scatter(each[:, 0], each[:, 1])
- plt.savefig(f'img/{name}')
- plt.show()
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "g":
- generate()
- elif len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "d":
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
- display(train_data, train_label, 'train')
- display(test_data, test_label, 'test')
- else:
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
-
- model = KNN()
- model.fit(train_data, train_label)
- res = model.predict(test_data)
- print("acc =",np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label)))
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/1test.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/1test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 3d3172d1f183248a2d7c4443ea469d574a48e337..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/1test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/1train.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/1train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index cde346b5c7c06d576910a6df2a66029b0670b6e3..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/1train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/2test.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/2test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 6deaec8880ed4997651cf23c37e9e7abece9516c..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/2test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/2train.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/2train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 643e46c2343e7743d6cd6bb2a94ac58eda4fd3fe..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/2train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/3test.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/3test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 5e75e15ce5ea8f09568b3138dac23866c2423701..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/3test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/3train.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/3train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 34be5d5a681d0fa8a5ff9186e9a8a08034d21f21..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/3train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/4test.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/4test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index e3a4f0b2caf50db06112042356688b28465efab6..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/4test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/4train.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/4train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index b58b79676726ad8b34e82a2b4e2f918d5fce2975..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/4train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/5test.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/5test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 365c0cef40fa9d80536197fbde693acb25cd552b..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/5test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/5train.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/5train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 266f3fa6ea5f349d8705e4a8f22f92e6f5c2600c..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/5train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/readme.md b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/readme.md
deleted file mode 100644
index d830733fb3c4e45ed7398fedde30c850d6366d10..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/readme.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,259 +0,0 @@
-# KNN Classifier
-
-[TOC]
-
-
-
-## 1. Code Introduction
-
-所有代码都在**source.py**中展示
-
-引用库包括**numpy**&**matplotlib**
-
-```
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as mp
-```
-
-**KNN**类包括如下几个函数**partition**, **distance**, **predict_label**, **fit**, **predict**
-
-首先需要初始化KNN类中的成员变量
-
-```
-def __init__(self):
-
- self.train_data_num = 0
- self.valid_data_num = 0
- self.train_data_dimension = 0
-
- self.train_data = None
- self.valid_data = None
- self.train_label = None
- self.valid_label = None
-
- self.K = 20
-```
-
-其中train_data_num表示训练集数量,valid_data_num表示验证集数量,train_data_dimension表示数据维度(在本次实验中我们默认你使用二维数据),(train_data,valid_data,train_label,valid_label)分别表示(训练集数据,验证集数据,训练集标签,验证集标签),K表示通过训练所得出来的最优K值
-
-**partition**函数输入的**参数**包括:数据集和标签集,**作用**是:将输入的数据和标签随机取80%作为训练集的数据和标签,其余20%作为验证集的数据和标签。
-
-**distance**函数输入的**参数**包括:点1,点2,计算距离的方式(默认为Euclid即欧几里得距离),**作用**是:以给定的方式计算两个点之间的距离
-
-**predict_label**函数输入的**参数**包括:k值,数据集1,标签集1,数据集2,计算距离的方式, **作用**是:给定k值,以数据集1和标签集1作为已知的点集,通过k近邻算法计算并返回数据集2所对应的标签集
-
-**fit**函数输入的**参数**包括:数据集和标签集,**作用**是:首先利用**partition**函数将数据集和标签集按照8:2的比例分为训练集和验证集,然后枚举k的值,并通过**predict_label**函数预测训练集的标签集,并对比该结果和给定的训练集标签,得到准确率。选取准确率最高的k值作为模型的k值。
-
-**predict**函数输入的**参数**包括:数据集,**作用**是:将该数据集作为测试集,利用已经训练好的KNN模型返回测试集的标签,一般配合**fit**函数使用。
-
-**一些其他的函数**:
-
-1. **data_maker**函数输入的**参数**包括:id,平均值,协方差矩阵,数量,**作用**是:通过np.random.multivariate_normal函数以及给定的参数生成数据,并将数据分为训练集和测试集,通过np.save储存
-
-2. **data_reader**函数输入的**参数**包括:id,**作用**是:通过np.read读取**data_maker**生成的数据
-
-3. **data_painter**函数输入的**参数**包括:id,数据集,标签集,name,**作用**是:通过matplotlib.pyplot.scatter来画出数据的散点图,便于直观观察数据的分布
-
-## 2. Experiment
-
-### 1. Initial Data
-
-数据集参数
-$$
-\mu_x=[10,10] ,\Sigma_x=\begin{bmatrix}30&5 \\\\ 5&10\end{bmatrix},|x|=400\\\\
-\mu_y=[5,15],\Sigma_y=\begin{bmatrix}20&4 \\\\ 4&10\end{bmatrix},|y|=400\\\\
-\mu_z=[15,5],\Sigma_z=\begin{bmatrix}20&3 \\\\ 3&4\end{bmatrix},|z|=400
-$$
-训练集和测试集散点图
-
-
-
-| 序号 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
-| ------- | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ |
-| 准确率 | 96.75% | 96.25% | 95.00% | 92.50% |
-| 最佳k值 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 3 |
-
-类似地,准确率随着分布的重叠而降低。
-
-## 代码使用方法
-
-```bash
-python source.py g # 生成数据集
-python source.py d # 展示数据集
-python source.py # 训练和测试
-```
-
-# 参考
-
-距离的计算:https://blog.csdn.net/IT_forlearn/article/details/100022244?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromMachineLearnPai2-1.control&dist_request_id=&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromMachineLearnPai2-1.control
-
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/test_1.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/test_1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 1b3ef8c56c035e5122cdfacd83b9c436051d4b02..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/test_1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/test_2.jpg b/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/test_2.jpg
deleted file mode 100644
index 3ceff6d6091c5d283fcba0023e053e079e4720d0..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/test_2.jpg and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/test_3.jpg b/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/test_3.jpg
deleted file mode 100644
index 784506a6a23f0fcfaac61f422d03f0de9a4aab95..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/test_3.jpg and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/train_1.png b/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/train_1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index fab155cdf1d85d91e888e28a678ee2dc11d63d68..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/train_1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/train_2.jpg b/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/train_2.jpg
deleted file mode 100644
index b723ef988fb70cc8f5efe0dd7e502798135578e0..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/train_2.jpg and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/train_3.jpg b/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/train_3.jpg
deleted file mode 100644
index 5ba83b8810ff506b4eae19ce531494986142458d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/img/train_3.jpg and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index dc9938a32ac6c410feff6fb95204e0861363809d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/17307130133/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,132 +0,0 @@
-import sys
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
-class KNN:
-
- def __init__(self):
- self.train_data = None
- self.train_label = None
- self.k = 2
-
- def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- # train_data = self.normalize(train_data)
- self.train_data = train_data
- self.train_label = train_label
-
- N = train_data.shape[0]
- cut = N // 5 * 4
- train_data, dev_data = train_data[:cut,], train_data[cut:,]
- train_label, dev_label = train_label[:cut,], train_label[cut:,]
-
- dists = self.compute_distances(train_data, dev_data)
-
- max_acc = 0
- max_acc_k = 2
- for k in range(2,7):
- res = self.get_label(dists, train_label, k)
- acc = np.mean(np.equal(res, dev_label))
- print("k = %d, acc = %f" % (k, acc))
- if acc > max_acc:
- max_acc = acc
- max_acc_k = k
- print("best k = %d" % max_acc_k)
- self.k = max_acc_k
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- # test_data = self.normalize(test_data)
- dists = self.compute_distances(self.train_data, test_data)
- return self.get_label(dists, self.train_label, self.k)
-
- def compute_distances(self, train_data, test_data):
- num_train = train_data.shape[0]
- num_test = test_data.shape[0]
- dists = np.zeros((num_test, num_train))
-
- train_square = np.sum(np.square(train_data), axis=1).reshape(1, num_train)
- test_square = np.sum(np.square(test_data), axis=1).reshape(num_test, 1)
- dists = np.sqrt(train_square + test_square - 2 * np.dot(test_data, train_data.T))
-
- return dists
-
- def get_label(self, dists, train_label, k):
- num_test = dists.shape[0]
- y_predict = np.zeros(num_test, dtype=train_label.dtype)
- for i in range(num_test):
- closest_y = list(train_label[np.argsort(dists[i,:])[:k]])
- y_predict[i] = max(closest_y, key = closest_y.count)
- return y_predict
-
- def normalize(self, data):
- if len(data) == 0:
- return data
- return (data - np.min(data)) / (np.max(data) - np.min(data))
-
-
-def generate():
- # mean = (1, 2)
- # cov = np.array([[73, 0], [0, 22]])
- mean = (-17, 2)
- cov = np.array([[103, 0],[0, 22]])
- x = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (1200,))
-
- # mean = (16, -5)
- # cov = np.array([[21.2, 0], [0, 32.1]])
- mean = (10, -5)
- cov = np.array([[101.2, 0],[0, 32.1]])
- y = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (800,))
-
- # mean = (10, 22)
- # cov = np.array([[10,5],[5,10]])
- # z = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (1000,))
-
- idx = np.arange(2000)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- # data = np.concatenate([x,y,z])
- data = np.concatenate([x,y])
- label = np.concatenate([
- # np.zeros((800,),dtype=int),
- # np.ones((200,),dtype=int),
- # np.ones((1000,),dtype=int)*2
- np.zeros((1200,),dtype=int),
- np.ones((800,),dtype=int),
- ])
- data = data[idx]
- label = label[idx]
-
- train_data, test_data = data[:1600,], data[1600:,]
- train_label, test_label = label[:1600,], label[1600:,]
- np.save("data.npy",(
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
- ))
-
-def read():
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = np.load("data.npy", allow_pickle=True)
- return (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
-
-def display(data, label, name):
- # datas = [[], [], []]
- datas = [[], []]
- for i in range(len(data)):
- datas[label[i]].append(data[i])
-
- for each in datas:
- each = np.array(each)
- plt.scatter(each[:, 0], each[:, 1])
- plt.savefig(f'img/{name}')
- plt.show()
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "g":
- generate()
- elif len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "d":
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
- display(train_data, train_label, 'train')
- display(test_data, test_label, 'test')
- else:
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
-
- model = KNN()
- model.fit(train_data, train_label)
- res = model.predict(test_data)
- print("acc =",np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label)))
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/1test.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/1test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 3d3172d1f183248a2d7c4443ea469d574a48e337..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/1test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/1train.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/1train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index cde346b5c7c06d576910a6df2a66029b0670b6e3..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/1train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/2test.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/2test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 6deaec8880ed4997651cf23c37e9e7abece9516c..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/2test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/2train.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/2train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 643e46c2343e7743d6cd6bb2a94ac58eda4fd3fe..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/2train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/3test.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/3test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 5e75e15ce5ea8f09568b3138dac23866c2423701..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/3test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/3train.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/3train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 34be5d5a681d0fa8a5ff9186e9a8a08034d21f21..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/3train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/4test.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/4test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index e3a4f0b2caf50db06112042356688b28465efab6..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/4test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/4train.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/4train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index b58b79676726ad8b34e82a2b4e2f918d5fce2975..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/4train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/5test.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/5test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 365c0cef40fa9d80536197fbde693acb25cd552b..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/5test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/5train.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/5train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 266f3fa6ea5f349d8705e4a8f22f92e6f5c2600c..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/img/5train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/readme.md b/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/readme.md
deleted file mode 100644
index d830733fb3c4e45ed7398fedde30c850d6366d10..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/18307130074/readme.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,259 +0,0 @@
-# KNN Classifier
-
-[TOC]
-
-
-
-## 1. Code Introduction
-
-所有代码都在**source.py**中展示
-
-引用库包括**numpy**&**matplotlib**
-
-```
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as mp
-```
-
-**KNN**类包括如下几个函数**partition**, **distance**, **predict_label**, **fit**, **predict**
-
-首先需要初始化KNN类中的成员变量
-
-```
-def __init__(self):
-
- self.train_data_num = 0
- self.valid_data_num = 0
- self.train_data_dimension = 0
-
- self.train_data = None
- self.valid_data = None
- self.train_label = None
- self.valid_label = None
-
- self.K = 20
-```
-
-其中train_data_num表示训练集数量,valid_data_num表示验证集数量,train_data_dimension表示数据维度(在本次实验中我们默认你使用二维数据),(train_data,valid_data,train_label,valid_label)分别表示(训练集数据,验证集数据,训练集标签,验证集标签),K表示通过训练所得出来的最优K值
-
-**partition**函数输入的**参数**包括:数据集和标签集,**作用**是:将输入的数据和标签随机取80%作为训练集的数据和标签,其余20%作为验证集的数据和标签。
-
-**distance**函数输入的**参数**包括:点1,点2,计算距离的方式(默认为Euclid即欧几里得距离),**作用**是:以给定的方式计算两个点之间的距离
-
-**predict_label**函数输入的**参数**包括:k值,数据集1,标签集1,数据集2,计算距离的方式, **作用**是:给定k值,以数据集1和标签集1作为已知的点集,通过k近邻算法计算并返回数据集2所对应的标签集
-
-**fit**函数输入的**参数**包括:数据集和标签集,**作用**是:首先利用**partition**函数将数据集和标签集按照8:2的比例分为训练集和验证集,然后枚举k的值,并通过**predict_label**函数预测训练集的标签集,并对比该结果和给定的训练集标签,得到准确率。选取准确率最高的k值作为模型的k值。
-
-**predict**函数输入的**参数**包括:数据集,**作用**是:将该数据集作为测试集,利用已经训练好的KNN模型返回测试集的标签,一般配合**fit**函数使用。
-
-**一些其他的函数**:
-
-1. **data_maker**函数输入的**参数**包括:id,平均值,协方差矩阵,数量,**作用**是:通过np.random.multivariate_normal函数以及给定的参数生成数据,并将数据分为训练集和测试集,通过np.save储存
-
-2. **data_reader**函数输入的**参数**包括:id,**作用**是:通过np.read读取**data_maker**生成的数据
-
-3. **data_painter**函数输入的**参数**包括:id,数据集,标签集,name,**作用**是:通过matplotlib.pyplot.scatter来画出数据的散点图,便于直观观察数据的分布
-
-## 2. Experiment
-
-### 1. Initial Data
-
-数据集参数
-$$
-\mu_x=[10,10] ,\Sigma_x=\begin{bmatrix}30&5 \\\\ 5&10\end{bmatrix},|x|=400\\\\
-\mu_y=[5,15],\Sigma_y=\begin{bmatrix}20&4 \\\\ 4&10\end{bmatrix},|y|=400\\\\
-\mu_z=[15,5],\Sigma_z=\begin{bmatrix}20&3 \\\\ 3&4\end{bmatrix},|z|=400
-$$
-训练集和测试集散点图
-
- -
-  -
- -
-  -
- -
-  -
- -
-  -
- -
-  -
- -
-  -
- -
-  -
- -
-  -
- -
-由图可知,数据集容量的大小对于模型性能没有明显的影响。
-
-推测:出现这种现象的原因可能是K近邻模型过于简单,样本容量较小时也能得到较好的性能。
-
-#### 数据集距离
-
-固定上述数据集的协方差和容量,改变均值为原先的$k$倍$(k\in[0.1,2])$,作出$k$关于`acc`的图如下:
-
-
-
-由图可知,数据集容量的大小对于模型性能没有明显的影响。
-
-推测:出现这种现象的原因可能是K近邻模型过于简单,样本容量较小时也能得到较好的性能。
-
-#### 数据集距离
-
-固定上述数据集的协方差和容量,改变均值为原先的$k$倍$(k\in[0.1,2])$,作出$k$关于`acc`的图如下:
-
- -
-由图可知,数据集的均值越大(即不同数据集的距离越大),模型效果越好。
-
-推测:出现这种现象的原因可能是不同数据集之间距离越远,测试点周围属于自己的类的训练点比例越高,因此性能越好。
-
-#### 数据集方差
-
-固定上述数据集的均值和容量,改变协方差为原先的$k$倍$(k\in[0.1,2])$,作出$k$关于`acc`的图如下:
-
-
-
-由图可知,数据集的均值越大(即不同数据集的距离越大),模型效果越好。
-
-推测:出现这种现象的原因可能是不同数据集之间距离越远,测试点周围属于自己的类的训练点比例越高,因此性能越好。
-
-#### 数据集方差
-
-固定上述数据集的均值和容量,改变协方差为原先的$k$倍$(k\in[0.1,2])$,作出$k$关于`acc`的图如下:
-
- -
-由图可知,数据集的协方差越大,模型效果越好。
-
-推测:出现这种现象的原因和数据集距离的原因类似。数据集协方差增大时,不同数据集越倾向于“混合”在一起,使得测试点周围属于自己的类的点比例不断减小,性能随之降低。
-
-#### 总结
-
-综上,数据集的容量对K近邻模型的影响较小,而不同数据集的距离和协方差分别对K近邻模型性能产生了正面和负面的影响。
-
-## 性能优化
-
-### 问题归纳
-
-注意到K近邻算法的核心操作是:给定$n$个点$x_1,x_2,\cdots,x_n$和一个查询点$y$,要求返回距离$y$最近的$k$个点。常见的算法为计算出$x_i(i=1,2,\cdots,n)$与$y$的距离后按照距离进行排序,取出前$k$个点。这样做的时间复杂度为$O(n\log n)$。
-
-### 优化1
-
-考虑到$k$一般很小(具体实现中$k\le25$),因此尝试使用堆进行优化。算法步骤为:
-
-1. 计算出$x_1,\cdots,x_k$与$y$的距离,插入大根堆中;
-2. 计算出$x_i(i=k+1,k+2,\cdots,n)$与$y$的距离,与堆顶元素比较。如果$dist(x_i,y)$比堆顶元素小,则弹出堆顶元素,将$dist(x_i,y)$插入堆中。
-
-算法结束时堆中的元素即为$x_i$与$y$的距离中最近的$k$个。时间复杂度$O(n\log k)$。由于$k\le25$,因此算法近似为$O(n)$。
-
-然而在具体实现中发现优化后速度反而慢于优化前。可能原因是暴力排序调用的是`numpy.argsort`,其底层调用了C的库,常数较小;而堆优化调用的是`heapq`库,完全由Python实现,常数较大,因此性能反而不如优化前。
-
-### 优化2
-
-后来发现`numpy`库提供了一个名为`numpy.argpartition`的方法。该方法与快速排序的`partition`操作类似,接收一个`ndarray`参数和一个`int`参数并返回一个数组,其中前$k$个为前$k$小的元素参数。由主定理可知,该方法的时间复杂度为$O(n)$。因此改用`numpy.argpartition`计算距离$y$最近的$k$个点,提高了运算速度。
-
-`fit`方法分别在使用`numpy.argsort`和`numpy.argpartition`的情况下的运行时间比较图:
-
-
-
-由图可知,数据集的协方差越大,模型效果越好。
-
-推测:出现这种现象的原因和数据集距离的原因类似。数据集协方差增大时,不同数据集越倾向于“混合”在一起,使得测试点周围属于自己的类的点比例不断减小,性能随之降低。
-
-#### 总结
-
-综上,数据集的容量对K近邻模型的影响较小,而不同数据集的距离和协方差分别对K近邻模型性能产生了正面和负面的影响。
-
-## 性能优化
-
-### 问题归纳
-
-注意到K近邻算法的核心操作是:给定$n$个点$x_1,x_2,\cdots,x_n$和一个查询点$y$,要求返回距离$y$最近的$k$个点。常见的算法为计算出$x_i(i=1,2,\cdots,n)$与$y$的距离后按照距离进行排序,取出前$k$个点。这样做的时间复杂度为$O(n\log n)$。
-
-### 优化1
-
-考虑到$k$一般很小(具体实现中$k\le25$),因此尝试使用堆进行优化。算法步骤为:
-
-1. 计算出$x_1,\cdots,x_k$与$y$的距离,插入大根堆中;
-2. 计算出$x_i(i=k+1,k+2,\cdots,n)$与$y$的距离,与堆顶元素比较。如果$dist(x_i,y)$比堆顶元素小,则弹出堆顶元素,将$dist(x_i,y)$插入堆中。
-
-算法结束时堆中的元素即为$x_i$与$y$的距离中最近的$k$个。时间复杂度$O(n\log k)$。由于$k\le25$,因此算法近似为$O(n)$。
-
-然而在具体实现中发现优化后速度反而慢于优化前。可能原因是暴力排序调用的是`numpy.argsort`,其底层调用了C的库,常数较小;而堆优化调用的是`heapq`库,完全由Python实现,常数较大,因此性能反而不如优化前。
-
-### 优化2
-
-后来发现`numpy`库提供了一个名为`numpy.argpartition`的方法。该方法与快速排序的`partition`操作类似,接收一个`ndarray`参数和一个`int`参数并返回一个数组,其中前$k$个为前$k$小的元素参数。由主定理可知,该方法的时间复杂度为$O(n)$。因此改用`numpy.argpartition`计算距离$y$最近的$k$个点,提高了运算速度。
-
-`fit`方法分别在使用`numpy.argsort`和`numpy.argpartition`的情况下的运行时间比较图:
-
- \ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/acc_cov.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/acc_cov.png
deleted file mode 100644
index e187ecebdb9c294dfcbad886487b4b0f7fceb4f2..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/acc_cov.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/acc_mean.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/acc_mean.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 8419fdf833238cfada421178870aa5e86d62923b..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/acc_mean.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/acc_nums.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/acc_nums.png
deleted file mode 100644
index d84bc984a7c161e0f9b764b4a267ee990d44785a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/acc_nums.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/test.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 893580fcb95deac02a084e15583e5cf2e95ad5d8..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/time.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/time.png
deleted file mode 100644
index f76d49f9fabe732cb07eb2a271db4a22b3ed83d0..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/time.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/train.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index b0b19b6f518c4d8a79848be7aa76dbff4050f88e..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/test.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index bb50d7cd57a3ccd2d5e87dfd3abb59cbea12d934..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/train.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 2f2105f7befcf80573111eb2b64f77dda866c295..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 766de86932d9baf64d44cfc385daed350b70935e..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,160 +0,0 @@
-import random
-import sys
-import time
-
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import numpy as np
-
-
-class KNN:
-
- def __init__(self):
- self.train_data = None
- self.train_labels = None
- self.k = None
-
- # func=bf表示使用O(nlogn)的算法 func=opt表示使用O(n)的算法
- def get_predict_labels(self, k, train_data, train_labels, valid_data, func='bf'):
-
- # 确保func字段只能取bf或者opt
- assert func in {'bf', 'opt'}
-
- predict_labels = np.array([])
- for valid_dot in valid_data:
-
- # 计算每个train_dot与valid_dot之间的距离
- dist = np.linalg.norm(train_data - valid_dot, axis=1)
-
- # 计算距离最小的k个train_dot的下标
- dist_index = np.argsort(dist)[:k] if func == 'bf' else np.argpartition(dist, k)[:k]
-
- # 计算数量最多的标签
- count_dict = {}
- max_count = 0
- for index in dist_index:
- index = int(index)
- train_label = train_labels[index]
- count_dict[train_label] = count_dict.get(train_label, 0) + 1
- max_count = max(max_count, count_dict[train_label])
- predict_label = np.array([])
- for train_label, count in count_dict.items():
- if max_count != count: continue
- predict_label = np.append(predict_label, train_label)
- predict_labels = np.append(predict_labels, np.random.choice(predict_label))
-
- return predict_labels
-
- def fit(self, input_data, input_labels):
- self.train_data = input_data
- self.train_labels = input_labels
-
- # 将数据打乱
- shuffled_data, shuffled_labels = shuffle(input_data, input_labels)
-
- # 划分为训练集和验证集
- ratio, data_size = 0.2, shuffled_data.shape[0]
- valid_size = int(data_size * ratio)
- train_size = data_size - valid_size
- valid_data, valid_labels = shuffled_data[:valid_size], shuffled_labels[:valid_size]
- train_data, train_labels = shuffled_data[valid_size:], shuffled_labels[valid_size:]
-
- # 枚举k,求出最佳参数
- k_size = min(25, train_size)
- max_acc, best_k = -1, 0
- for k in range(1, k_size):
- predict_labels = self.get_predict_labels(k, train_data, train_labels, valid_data, func='opt')
- acc = np.mean(np.equal(predict_labels, valid_labels))
- # print(f'k={k} acc={acc}')
- if acc > max_acc:
- max_acc = acc
- best_k = k
- print(f'k={best_k} train_acc={max_acc}')
- self.k = best_k
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- return self.get_predict_labels(self.k, self.train_data, self.train_labels, test_data, func='opt')
-
-
-def generate_data(mean, cov, nums):
- n = len(mean)
- assert n == len(cov) and n == len(nums)
- data = np.concatenate([np.random.multivariate_normal(mean[i], cov[i], int(nums[i])) for i in range(n)])
- labels = np.concatenate([np.ones(int(nums[i]), dtype=int) * i for i in range(n)])
-
- data, labels = shuffle(data, labels)
-
- ratio, data_size = 0.2, len(data)
- test_size = int(ratio * data_size)
- test_data, test_label = data[:test_size], labels[:test_size]
- train_data, train_label = data[test_size:], labels[test_size:]
- np.save('data.npy', (train_data, train_label, test_data, test_label))
-
-
-def shuffle(data, labels):
- data_size = len(data)
- assert data_size == len(labels)
-
- indices = np.random.permutation(data_size)
- return data[indices], labels[indices]
-
-
-def save_plot(data, labels, name):
- data_size = len(data)
- assert data_size == len(labels)
- total = {}
- for i in range(data_size):
- label = labels[i]
- if label not in total:
- total[label] = []
- else:
- total[label].append(data[i])
- for category in total.values():
- if category == []: continue
- category = np.array(category)
- plt.scatter(category[:, 0], category[:, 1])
- plt.title(name)
- plt.savefig(f'./img/{name}')
- plt.close()
-
-
-def read():
- return np.load('data.npy', allow_pickle=True)
-
-
-def generate_control(nums, length):
- n = len(nums)
- labels = [i for i in range(n)]
- return random.choices(labels, nums, k=length)
-
-
-def train(mean, cov, nums, generate, ratio=(1, 1, 1)):
- if generate:
- generate_data(mean * ratio[0], cov * ratio[1], nums * ratio[2])
- train_data, train_label, test_data, test_label = read()
- save_plot(train_data, train_label, 'train')
- save_plot(test_data, test_label, 'test')
- knn = KNN()
- start_time = time.time()
- knn.fit(train_data, train_label)
- end_time = time.time()
- training_time = end_time - start_time
- # print(f'training stime={training_time} s')
- ans = knn.predict(test_data)
- control_group = generate_control(nums, len(test_label))
- test_acc = np.mean(np.equal(ans, test_label))
- control = np.mean(np.equal(control_group, test_label))
- return test_acc, control
-
-
-if __name__ == '__main__':
- nums = np.array([1600, 400, 2000], dtype=int)
- mean = np.array([[5, 5], [10, 15], [20, 5]])
- cov = np.array([
- [[34, 5], [5, 10]],
- [[20, 5], [5, 24]],
- [[30, 5], [5, 10]]
- ])
- generate = True if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == 'g' else False
- acc, control = train(mean, cov, nums, generate)
- print(f'acc={acc} control={control}')
- pass
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 547377052cdbe1f8ecf6c88d8f20086418b3842e..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,195 +0,0 @@
-
-
-18307130104
-
-# 课程报告
-
-这是 prml 的 assignment-1 课程报告,我的代码在 [source.py](./source.py) 中。
-
-在 assignment-1 中,用 python 实现了一个 KNN 类,调用该类下 fit() 函数可以对数据进行训练,调用 predict() 可以对多组目标数据进行预测,返回一个 list 对应每组数据的结果。
-
-## KNN 类实现
-
-### fit() 函数
-
-fit() 函数的任务有两个:将用于训练的点按照类别分别进行储存;选择合适的 K,也就是用于预测的最近点个数。
-
-接下来说明 K 数值的选择方法。对于输入的数据,选择前 $\frac 3 4$ 的数据作为训练集,后 $\frac 1 4$ 的数据作为验证集。逐一尝试 1~14 作为 K 值时模型在验证集上的正确率,选取其中正确率最高的 K 作为模型的 K 值保存下来。
-
-选择 1~14 是因为训练数据的规模为 2000,如果训练数据的规模进行了修改,这一个范围也可以进行修改,不过这一范围对大部分数据规模都比较适用。
-
-### predict() 函数
-
-predict() 函数会根据模型中存储的数据和选定的 K 对给定数据进行预测。
-
-采用欧拉距离作为两个点的距离数值,选择距离最近的 K 个点进行投票,获票最多的类别就是预测结果。对于获票相同的情况选择编号比较小的类别。
-
-## 测试与展示
-
-```shell
-python source.py g // 生成数据
-python source.py // 进行测试
-python source.py d // 生成展示图片
-```
-
-generate() 和 display() 函数均从示例代码中获得。其中 display() 函数中增加了对某种类别预测结果为空的判断防止报错。
-
-> 需要保证运行环境中有 img 文件夹,否则程序无法正确运行。(由于不能用 os 包所以不知道怎么判断是否存在文件夹)
->
-> 另外,如果使用 wsl 等环境会导致输出图像有重叠。
-
-## 探究性实验
-
-## 实验1
-
-采用以下参数生成 3 组数据。
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-73 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 22
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-1 & 2
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-21.2 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 32.1
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-16 & -5
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-10 & 5 \\\\
-5 & 10
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-10 & 22
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-训练数据,测试数据,测试结果如下三图
-
-
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/acc_cov.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/acc_cov.png
deleted file mode 100644
index e187ecebdb9c294dfcbad886487b4b0f7fceb4f2..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/acc_cov.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/acc_mean.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/acc_mean.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 8419fdf833238cfada421178870aa5e86d62923b..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/acc_mean.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/acc_nums.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/acc_nums.png
deleted file mode 100644
index d84bc984a7c161e0f9b764b4a267ee990d44785a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/acc_nums.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/test.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 893580fcb95deac02a084e15583e5cf2e95ad5d8..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/time.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/time.png
deleted file mode 100644
index f76d49f9fabe732cb07eb2a271db4a22b3ed83d0..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/time.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/train.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index b0b19b6f518c4d8a79848be7aa76dbff4050f88e..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/readme/train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/test.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index bb50d7cd57a3ccd2d5e87dfd3abb59cbea12d934..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/train.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 2f2105f7befcf80573111eb2b64f77dda866c295..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/img/train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 766de86932d9baf64d44cfc385daed350b70935e..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/18307130090/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,160 +0,0 @@
-import random
-import sys
-import time
-
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import numpy as np
-
-
-class KNN:
-
- def __init__(self):
- self.train_data = None
- self.train_labels = None
- self.k = None
-
- # func=bf表示使用O(nlogn)的算法 func=opt表示使用O(n)的算法
- def get_predict_labels(self, k, train_data, train_labels, valid_data, func='bf'):
-
- # 确保func字段只能取bf或者opt
- assert func in {'bf', 'opt'}
-
- predict_labels = np.array([])
- for valid_dot in valid_data:
-
- # 计算每个train_dot与valid_dot之间的距离
- dist = np.linalg.norm(train_data - valid_dot, axis=1)
-
- # 计算距离最小的k个train_dot的下标
- dist_index = np.argsort(dist)[:k] if func == 'bf' else np.argpartition(dist, k)[:k]
-
- # 计算数量最多的标签
- count_dict = {}
- max_count = 0
- for index in dist_index:
- index = int(index)
- train_label = train_labels[index]
- count_dict[train_label] = count_dict.get(train_label, 0) + 1
- max_count = max(max_count, count_dict[train_label])
- predict_label = np.array([])
- for train_label, count in count_dict.items():
- if max_count != count: continue
- predict_label = np.append(predict_label, train_label)
- predict_labels = np.append(predict_labels, np.random.choice(predict_label))
-
- return predict_labels
-
- def fit(self, input_data, input_labels):
- self.train_data = input_data
- self.train_labels = input_labels
-
- # 将数据打乱
- shuffled_data, shuffled_labels = shuffle(input_data, input_labels)
-
- # 划分为训练集和验证集
- ratio, data_size = 0.2, shuffled_data.shape[0]
- valid_size = int(data_size * ratio)
- train_size = data_size - valid_size
- valid_data, valid_labels = shuffled_data[:valid_size], shuffled_labels[:valid_size]
- train_data, train_labels = shuffled_data[valid_size:], shuffled_labels[valid_size:]
-
- # 枚举k,求出最佳参数
- k_size = min(25, train_size)
- max_acc, best_k = -1, 0
- for k in range(1, k_size):
- predict_labels = self.get_predict_labels(k, train_data, train_labels, valid_data, func='opt')
- acc = np.mean(np.equal(predict_labels, valid_labels))
- # print(f'k={k} acc={acc}')
- if acc > max_acc:
- max_acc = acc
- best_k = k
- print(f'k={best_k} train_acc={max_acc}')
- self.k = best_k
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- return self.get_predict_labels(self.k, self.train_data, self.train_labels, test_data, func='opt')
-
-
-def generate_data(mean, cov, nums):
- n = len(mean)
- assert n == len(cov) and n == len(nums)
- data = np.concatenate([np.random.multivariate_normal(mean[i], cov[i], int(nums[i])) for i in range(n)])
- labels = np.concatenate([np.ones(int(nums[i]), dtype=int) * i for i in range(n)])
-
- data, labels = shuffle(data, labels)
-
- ratio, data_size = 0.2, len(data)
- test_size = int(ratio * data_size)
- test_data, test_label = data[:test_size], labels[:test_size]
- train_data, train_label = data[test_size:], labels[test_size:]
- np.save('data.npy', (train_data, train_label, test_data, test_label))
-
-
-def shuffle(data, labels):
- data_size = len(data)
- assert data_size == len(labels)
-
- indices = np.random.permutation(data_size)
- return data[indices], labels[indices]
-
-
-def save_plot(data, labels, name):
- data_size = len(data)
- assert data_size == len(labels)
- total = {}
- for i in range(data_size):
- label = labels[i]
- if label not in total:
- total[label] = []
- else:
- total[label].append(data[i])
- for category in total.values():
- if category == []: continue
- category = np.array(category)
- plt.scatter(category[:, 0], category[:, 1])
- plt.title(name)
- plt.savefig(f'./img/{name}')
- plt.close()
-
-
-def read():
- return np.load('data.npy', allow_pickle=True)
-
-
-def generate_control(nums, length):
- n = len(nums)
- labels = [i for i in range(n)]
- return random.choices(labels, nums, k=length)
-
-
-def train(mean, cov, nums, generate, ratio=(1, 1, 1)):
- if generate:
- generate_data(mean * ratio[0], cov * ratio[1], nums * ratio[2])
- train_data, train_label, test_data, test_label = read()
- save_plot(train_data, train_label, 'train')
- save_plot(test_data, test_label, 'test')
- knn = KNN()
- start_time = time.time()
- knn.fit(train_data, train_label)
- end_time = time.time()
- training_time = end_time - start_time
- # print(f'training stime={training_time} s')
- ans = knn.predict(test_data)
- control_group = generate_control(nums, len(test_label))
- test_acc = np.mean(np.equal(ans, test_label))
- control = np.mean(np.equal(control_group, test_label))
- return test_acc, control
-
-
-if __name__ == '__main__':
- nums = np.array([1600, 400, 2000], dtype=int)
- mean = np.array([[5, 5], [10, 15], [20, 5]])
- cov = np.array([
- [[34, 5], [5, 10]],
- [[20, 5], [5, 24]],
- [[30, 5], [5, 10]]
- ])
- generate = True if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == 'g' else False
- acc, control = train(mean, cov, nums, generate)
- print(f'acc={acc} control={control}')
- pass
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 547377052cdbe1f8ecf6c88d8f20086418b3842e..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,195 +0,0 @@
-
-
-18307130104
-
-# 课程报告
-
-这是 prml 的 assignment-1 课程报告,我的代码在 [source.py](./source.py) 中。
-
-在 assignment-1 中,用 python 实现了一个 KNN 类,调用该类下 fit() 函数可以对数据进行训练,调用 predict() 可以对多组目标数据进行预测,返回一个 list 对应每组数据的结果。
-
-## KNN 类实现
-
-### fit() 函数
-
-fit() 函数的任务有两个:将用于训练的点按照类别分别进行储存;选择合适的 K,也就是用于预测的最近点个数。
-
-接下来说明 K 数值的选择方法。对于输入的数据,选择前 $\frac 3 4$ 的数据作为训练集,后 $\frac 1 4$ 的数据作为验证集。逐一尝试 1~14 作为 K 值时模型在验证集上的正确率,选取其中正确率最高的 K 作为模型的 K 值保存下来。
-
-选择 1~14 是因为训练数据的规模为 2000,如果训练数据的规模进行了修改,这一个范围也可以进行修改,不过这一范围对大部分数据规模都比较适用。
-
-### predict() 函数
-
-predict() 函数会根据模型中存储的数据和选定的 K 对给定数据进行预测。
-
-采用欧拉距离作为两个点的距离数值,选择距离最近的 K 个点进行投票,获票最多的类别就是预测结果。对于获票相同的情况选择编号比较小的类别。
-
-## 测试与展示
-
-```shell
-python source.py g // 生成数据
-python source.py // 进行测试
-python source.py d // 生成展示图片
-```
-
-generate() 和 display() 函数均从示例代码中获得。其中 display() 函数中增加了对某种类别预测结果为空的判断防止报错。
-
-> 需要保证运行环境中有 img 文件夹,否则程序无法正确运行。(由于不能用 os 包所以不知道怎么判断是否存在文件夹)
->
-> 另外,如果使用 wsl 等环境会导致输出图像有重叠。
-
-## 探究性实验
-
-## 实验1
-
-采用以下参数生成 3 组数据。
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-73 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 22
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-1 & 2
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-21.2 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 32.1
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-16 & -5
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-10 & 5 \\\\
-5 & 10
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-10 & 22
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-训练数据,测试数据,测试结果如下三图
-
-

 -
-程序输出如下(之后的实验输出均采用如下的输出格式)
-
-| K | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
-| ------ | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
-| 正确率 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 |
-
-| 选取 K | 正确率 |
-| -- | -- |
-| 14 | 0.96 |
-
-将实验1作为基准,对不同数据集上的模型效果进行对比。这组数据的特点在于虽然不同种类之间的点有交集,但是区分仍然非常明显,比较符合实际中的分类问题的特征。
-
-## 实验2
-
-采用以下参数生成 3 组数据。
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-6 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 4
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-1 & 2
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-5 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 7
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-16 & -5
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-9 & 5 \\\\
-0 & 5
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-10 & 22
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-训练数据,测试数据,测试结果如下三图
-
-
-
-程序输出如下(之后的实验输出均采用如下的输出格式)
-
-| K | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
-| ------ | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
-| 正确率 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 |
-
-| 选取 K | 正确率 |
-| -- | -- |
-| 14 | 0.96 |
-
-将实验1作为基准,对不同数据集上的模型效果进行对比。这组数据的特点在于虽然不同种类之间的点有交集,但是区分仍然非常明显,比较符合实际中的分类问题的特征。
-
-## 实验2
-
-采用以下参数生成 3 组数据。
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-6 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 4
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-1 & 2
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-5 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 7
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-16 & -5
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-9 & 5 \\\\
-0 & 5
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-10 & 22
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-训练数据,测试数据,测试结果如下三图
-
-

 -
-程序输出如下
-
-| K | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
-| ------ | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
-| 正确率 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
-
-
-| 选取 K | 正确率 |
-| -- | -- |
-|1|acc = 1.0|
-
-实验2的数据集中数据的协方差比较小,对应的,数据比较集中,数据集中区域的交叉比较小,所以对应的,模型的准确度非常高,这种情况的分类非常简单,因此模型表现优秀也在预期之中。
-
-## 实验3
-
-采用以下参数生成 3 组数据。
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-73 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 22
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-13 & -2
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-21.2 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 32.1
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-16 & -5
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-10 & 5 \\\\
-5 & 10
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-18 & -7
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-训练数据,测试数据,测试结果如下三图
-
-
-
-程序输出如下
-
-| K | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
-| ------ | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
-| 正确率 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
-
-
-| 选取 K | 正确率 |
-| -- | -- |
-|1|acc = 1.0|
-
-实验2的数据集中数据的协方差比较小,对应的,数据比较集中,数据集中区域的交叉比较小,所以对应的,模型的准确度非常高,这种情况的分类非常简单,因此模型表现优秀也在预期之中。
-
-## 实验3
-
-采用以下参数生成 3 组数据。
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-73 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 22
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-13 & -2
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-21.2 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 32.1
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-16 & -5
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-10 & 5 \\\\
-5 & 10
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-18 & -7
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-训练数据,测试数据,测试结果如下三图
-
-

 -
-程序输出如下
-
-| K | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
-| ------ | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
-| 正确率 | 0.67 | 0.76 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.73 | 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.74 | 0.75 | 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.74 |
-
-| 选取 K | 正确率 |
-| -- | -- |
-|2|acc = 0.71|
-
-相比于实验1,虽然数据的协方差没有变化,但是数据的中心点比较靠近,具体表现出来,数据集中区域的重合部分非常大,非常难以区别。可以看到正确率也有非常大幅度的下滑。
-
-如果再加大协方差,测试准确率也会进一步下降。
-
-## 结论
-
-可以看到对于数据集中不同类别区分度比较大的情况,KNN 有着非常优秀的表现。对于数据重叠情况比较大的情况,KNN 的效果也并不理想。
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test-1.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test-1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index dee425303e2612d99294b8b67d9d3caa62c45d19..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test-1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test-2.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test-2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index af4d06ba839eb16dc7864f7f9ccbbb0fc6288353..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test-2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test-3.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test-3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index df464c743c65e3df01aab75decd3d46b5040f981..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test-3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index d4880f0b716a928bb8c98e57db1450c4005e4de0..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res-1.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res-1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index b59def122bd96d11caef1846cbed617f2ff1e77a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res-1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res-2.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res-2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index af4d06ba839eb16dc7864f7f9ccbbb0fc6288353..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res-2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res-3.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res-3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 4e2e9e4b84105a214163ef8001950c84551cc868..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res-3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 3398f85d9e2c12e1aed1d46aef32b0ebfe40a736..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train-1.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train-1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 8ac4cafb374d598c4c81167a7a3e249856803f82..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train-1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train-2.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train-2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 5574b29d7ef53b5e38af79f85a1ae4ebcbb8f137..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train-2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train-3.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train-3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 4e5eb59db4f0293e1e59fa4747e61112138f3153..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train-3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 1906f232e9f385005824fea153d1c8c649000cdb..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 060fd3ca6cbd1b0c81fe22fb1c051eb7e275651d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,147 +0,0 @@
-import sys
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
-class KNN:
-
- def __init__(self):
- self.ldata = {}
- self.K = 10
- self.cnt = 0
-
- def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- totsz = len(train_data)
- pretrainsz = totsz * 3 // 4
- for i in range(0, pretrainsz):
- if train_label[i] in self.ldata:
- self.ldata[train_label[i]].append(train_data[i])
- else:
- self.ldata[train_label[i]] = [train_data[i]]
- pretraindata = train_data[pretrainsz : totsz]
- pretrainlabel = train_label[pretrainsz : totsz]
- maxAcc = 0
- takeK = 3
- for preK in range(1, 15):
- pretrainres = []
- self.K = preK
- for d in pretraindata:
- pretrainres.append(self.predict_one(d))
- acc = np.mean(np.equal(pretrainres, pretrainlabel))
- print(acc)
- if acc > maxAcc:
- maxAcc = acc
- takeK = preK
- self.K = takeK
- print("take K", takeK)
- self.ldata.clear()
- for (d, l) in zip(train_data, train_label):
- if(l in self.ldata):
- self.ldata[l].append(d)
- else:
- self.ldata[l] = [d]
-
- def dist(self, s1, s2):
- sum = 0
- for (k1, k2) in zip(s1, s2):
- sum += (k1 - k2) ** 2
- return sum
- def takeFirst(self, elem):
- return elem[0]
- def predict_one(self, data):
- result = None
- tmpl = []
- for l in self.ldata:
- for s in self.ldata[l]:
- tmpl.append([self.dist(s, data), l])
- tmpl.sort(key=self.takeFirst)
- num = {}
- for i in self.ldata:
- num[i] = 0
- cnt = 0
- # for l in tmpl:
- # print(l)
- # print(' ')
- for l in tmpl:
- num[l[1]] += 1
- cnt += 1
- if(cnt >= self.K):
- break
- maxi = -1
- for i in self.ldata:
- # print(i)
- if num[i] > maxi:
- maxi = num[i]
- result = i
- # print(result)
- return result
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- result = []
- for x in test_data:
- result.append(self.predict_one(x))
- return result
-
-def generate():
- mean = (1, 2)
- cov = np.array([[73, 0], [0, 22]])
- x = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (800,))
-
- mean = (16, -5)
- cov = np.array([[21.2, 0], [0, 32.1]])
- y = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (200,))
-
- mean = (10, 22)
- cov = np.array([[10,5],[5,10]])
- z = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (1000,))
-
- idx = np.arange(2000)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- data = np.concatenate([x,y,z])
- label = np.concatenate([
- np.zeros((800,),dtype=int),
- np.ones((200,),dtype=int),
- np.ones((1000,),dtype=int)*2
- ])
- data = data[idx]
- label = label[idx]
-
- train_data, test_data = data[:1600,], data[1600:,]
- train_label, test_label = label[:1600,], label[1600:,]
- np.save("data.npy",(
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
- ))
-
-def display(data, label, name):
- datas =[[],[],[]]
- for i in range(len(data)):
- datas[label[i]].append(data[i])
-
- for each in datas:
- each = np.array(each)
- if(each.size > 0):
- plt.scatter(each[:, 0], each[:, 1])
- plt.savefig(f'img/{name}')
- plt.show()
-
-def read():
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = np.load("data.npy",allow_pickle=True)
- return (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "g":
- print("generate")
- generate()
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "d":
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
- # for l in test_label:
- # print(l)
- display(train_data, train_label, 'train')
- display(test_data, test_label, 'test')
- else:
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
-
- model = KNN()
- model.fit(train_data, train_label)
- res = model.predict(test_data)
- display(test_data, res, 'test_res')
- print("acc =",np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label)))
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 142f441ff2c2994c3d62c3cbb861fd7c637837f8..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,235 +0,0 @@
-# KNN分类器
-
-[toc]
-
-## 依赖包
-
-`numpy`
-
-`matplotlib`
-
-## 函数功能介绍
-
-### KNN
-
-**`fit(self, train_data, train_label)`**
-
-`train_data`训练点集
-
-`train_label`训练标签
-
-**功能简介:**`fit`函数将会取出训练集中的10%用于寻找让准确率最大的K,如果训练集少于10个点,则会默认`K = 1`,否则将会选择1到10中使得准确率最大的K,作为预测时使用的K
-
----
-
-`predict(self, test_data)`
-
-**功能简介:**根据前一步学习到的K预测对应的类别
-
-### 实验函数与辅助函数
-
-**`distance(point1, point2, method="Euclid")`**
-
-`point1`和`point2`为需要计算距离的两个点
-
-`method`给出了计算距离的指标,默认为欧氏距离,`Manhattan`可按照曼哈顿距离计算
-
-**功能简介:**函数开始会将输入标准化为[m, 1]的向量,并按照相应的方式计算两个点之间的距离
-
--------
-
-**`dis(dis_label)`**
-
-**功能简介:**`sort`的`key`函数,取出二元组(distance, label)中的distance
-
----
-
-**`nearest_k_label_max(point, point_arr, label_arr, k)`**
-
-`point`需寻找k个临近点的目标点
-
-`point_arr`已有的点集
-
-`label_arr`已有点集对应的标签集合
-
-`k`考虑的最近的点的数量
-
-**功能简介:**函数将计算目标点和点集中所有点的距离,找到K个距离最近点,并返回出现最多次数的`label`
-
----
-
-**`data_generate_and_save(class_num, mean_list, cov_list, num_list, save_path = "")`**
-
-`class_num` 共包含的类的数量
-
-`mean_list` 各个类的高斯分布对应的均值矩阵
-
-`cov_list` 各个类的协方差矩阵
-
-`num_list` num_list[i]对应于第i个类的点数
-
-`save_path` 生成的点集的存储路径,默认为当前目录下的`data.npy`,路径需以下划线结尾
-
-**功能简介:**该函数通过调用`numpy.random.multivariate_normal`,生成指定数目的点,随机打乱后,划分其中的80%为训练数据,20%为测试数据,以元组`((train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label))`的形式保存
-
----
-
-**`data_load(path = "")`**
-
-`path` 加载点集的存储路径,默认为当前目录下的`data.npy`,路径需以下划线结尾
-
-**功能简介:**点集需以元组`((train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label))`的形式保存
-
----
-
-**`visualize(data, label, class_num = 1, test_data=[])`**
-
-*可视化目前只支持二维,如果是高维点集,将只可视化前两维*
-
-`data` 训练点集坐标
-
-`label`训练点集对应的标签
-
-`class_num`类别总数,默认值为1
-
-`test_data`测试点集坐标
-
-**功能简介:**绘制点集散点图,不同类别自适应的用不同颜色表征,测试点集将通过"+"表征
-
-## 实验
-
-首先,我们生成了三类坐标点,每类数量100
-
-其对应的数量和协方差矩阵如下表所示
-
-| | 均值 | 协方差矩阵 |
-| ------- | ------- | ----------------- |
-| class 1 | (1, 2) | [[10, 0], [0, 2]] |
-| class 2 | (4, 5) | [[7, 3], [15, 1]] |
-| class 3 | (-2, 6) | [[0, 1], [1, 2]] |
-
-测试了1-10对应的准确率,如下图所示
-
-
-
-程序输出如下
-
-| K | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
-| ------ | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
-| 正确率 | 0.67 | 0.76 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.73 | 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.74 | 0.75 | 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.74 |
-
-| 选取 K | 正确率 |
-| -- | -- |
-|2|acc = 0.71|
-
-相比于实验1,虽然数据的协方差没有变化,但是数据的中心点比较靠近,具体表现出来,数据集中区域的重合部分非常大,非常难以区别。可以看到正确率也有非常大幅度的下滑。
-
-如果再加大协方差,测试准确率也会进一步下降。
-
-## 结论
-
-可以看到对于数据集中不同类别区分度比较大的情况,KNN 有着非常优秀的表现。对于数据重叠情况比较大的情况,KNN 的效果也并不理想。
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test-1.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test-1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index dee425303e2612d99294b8b67d9d3caa62c45d19..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test-1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test-2.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test-2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index af4d06ba839eb16dc7864f7f9ccbbb0fc6288353..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test-2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test-3.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test-3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index df464c743c65e3df01aab75decd3d46b5040f981..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test-3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test.png
deleted file mode 100644
index d4880f0b716a928bb8c98e57db1450c4005e4de0..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res-1.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res-1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index b59def122bd96d11caef1846cbed617f2ff1e77a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res-1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res-2.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res-2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index af4d06ba839eb16dc7864f7f9ccbbb0fc6288353..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res-2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res-3.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res-3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 4e2e9e4b84105a214163ef8001950c84551cc868..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res-3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 3398f85d9e2c12e1aed1d46aef32b0ebfe40a736..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/test_res.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train-1.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train-1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 8ac4cafb374d598c4c81167a7a3e249856803f82..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train-1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train-2.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train-2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 5574b29d7ef53b5e38af79f85a1ae4ebcbb8f137..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train-2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train-3.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train-3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 4e5eb59db4f0293e1e59fa4747e61112138f3153..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train-3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 1906f232e9f385005824fea153d1c8c649000cdb..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/img/train.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 060fd3ca6cbd1b0c81fe22fb1c051eb7e275651d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/18307130104/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,147 +0,0 @@
-import sys
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
-class KNN:
-
- def __init__(self):
- self.ldata = {}
- self.K = 10
- self.cnt = 0
-
- def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- totsz = len(train_data)
- pretrainsz = totsz * 3 // 4
- for i in range(0, pretrainsz):
- if train_label[i] in self.ldata:
- self.ldata[train_label[i]].append(train_data[i])
- else:
- self.ldata[train_label[i]] = [train_data[i]]
- pretraindata = train_data[pretrainsz : totsz]
- pretrainlabel = train_label[pretrainsz : totsz]
- maxAcc = 0
- takeK = 3
- for preK in range(1, 15):
- pretrainres = []
- self.K = preK
- for d in pretraindata:
- pretrainres.append(self.predict_one(d))
- acc = np.mean(np.equal(pretrainres, pretrainlabel))
- print(acc)
- if acc > maxAcc:
- maxAcc = acc
- takeK = preK
- self.K = takeK
- print("take K", takeK)
- self.ldata.clear()
- for (d, l) in zip(train_data, train_label):
- if(l in self.ldata):
- self.ldata[l].append(d)
- else:
- self.ldata[l] = [d]
-
- def dist(self, s1, s2):
- sum = 0
- for (k1, k2) in zip(s1, s2):
- sum += (k1 - k2) ** 2
- return sum
- def takeFirst(self, elem):
- return elem[0]
- def predict_one(self, data):
- result = None
- tmpl = []
- for l in self.ldata:
- for s in self.ldata[l]:
- tmpl.append([self.dist(s, data), l])
- tmpl.sort(key=self.takeFirst)
- num = {}
- for i in self.ldata:
- num[i] = 0
- cnt = 0
- # for l in tmpl:
- # print(l)
- # print(' ')
- for l in tmpl:
- num[l[1]] += 1
- cnt += 1
- if(cnt >= self.K):
- break
- maxi = -1
- for i in self.ldata:
- # print(i)
- if num[i] > maxi:
- maxi = num[i]
- result = i
- # print(result)
- return result
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- result = []
- for x in test_data:
- result.append(self.predict_one(x))
- return result
-
-def generate():
- mean = (1, 2)
- cov = np.array([[73, 0], [0, 22]])
- x = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (800,))
-
- mean = (16, -5)
- cov = np.array([[21.2, 0], [0, 32.1]])
- y = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (200,))
-
- mean = (10, 22)
- cov = np.array([[10,5],[5,10]])
- z = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (1000,))
-
- idx = np.arange(2000)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- data = np.concatenate([x,y,z])
- label = np.concatenate([
- np.zeros((800,),dtype=int),
- np.ones((200,),dtype=int),
- np.ones((1000,),dtype=int)*2
- ])
- data = data[idx]
- label = label[idx]
-
- train_data, test_data = data[:1600,], data[1600:,]
- train_label, test_label = label[:1600,], label[1600:,]
- np.save("data.npy",(
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
- ))
-
-def display(data, label, name):
- datas =[[],[],[]]
- for i in range(len(data)):
- datas[label[i]].append(data[i])
-
- for each in datas:
- each = np.array(each)
- if(each.size > 0):
- plt.scatter(each[:, 0], each[:, 1])
- plt.savefig(f'img/{name}')
- plt.show()
-
-def read():
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = np.load("data.npy",allow_pickle=True)
- return (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "g":
- print("generate")
- generate()
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "d":
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
- # for l in test_label:
- # print(l)
- display(train_data, train_label, 'train')
- display(test_data, test_label, 'test')
- else:
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
-
- model = KNN()
- model.fit(train_data, train_label)
- res = model.predict(test_data)
- display(test_data, res, 'test_res')
- print("acc =",np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label)))
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 142f441ff2c2994c3d62c3cbb861fd7c637837f8..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,235 +0,0 @@
-# KNN分类器
-
-[toc]
-
-## 依赖包
-
-`numpy`
-
-`matplotlib`
-
-## 函数功能介绍
-
-### KNN
-
-**`fit(self, train_data, train_label)`**
-
-`train_data`训练点集
-
-`train_label`训练标签
-
-**功能简介:**`fit`函数将会取出训练集中的10%用于寻找让准确率最大的K,如果训练集少于10个点,则会默认`K = 1`,否则将会选择1到10中使得准确率最大的K,作为预测时使用的K
-
----
-
-`predict(self, test_data)`
-
-**功能简介:**根据前一步学习到的K预测对应的类别
-
-### 实验函数与辅助函数
-
-**`distance(point1, point2, method="Euclid")`**
-
-`point1`和`point2`为需要计算距离的两个点
-
-`method`给出了计算距离的指标,默认为欧氏距离,`Manhattan`可按照曼哈顿距离计算
-
-**功能简介:**函数开始会将输入标准化为[m, 1]的向量,并按照相应的方式计算两个点之间的距离
-
--------
-
-**`dis(dis_label)`**
-
-**功能简介:**`sort`的`key`函数,取出二元组(distance, label)中的distance
-
----
-
-**`nearest_k_label_max(point, point_arr, label_arr, k)`**
-
-`point`需寻找k个临近点的目标点
-
-`point_arr`已有的点集
-
-`label_arr`已有点集对应的标签集合
-
-`k`考虑的最近的点的数量
-
-**功能简介:**函数将计算目标点和点集中所有点的距离,找到K个距离最近点,并返回出现最多次数的`label`
-
----
-
-**`data_generate_and_save(class_num, mean_list, cov_list, num_list, save_path = "")`**
-
-`class_num` 共包含的类的数量
-
-`mean_list` 各个类的高斯分布对应的均值矩阵
-
-`cov_list` 各个类的协方差矩阵
-
-`num_list` num_list[i]对应于第i个类的点数
-
-`save_path` 生成的点集的存储路径,默认为当前目录下的`data.npy`,路径需以下划线结尾
-
-**功能简介:**该函数通过调用`numpy.random.multivariate_normal`,生成指定数目的点,随机打乱后,划分其中的80%为训练数据,20%为测试数据,以元组`((train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label))`的形式保存
-
----
-
-**`data_load(path = "")`**
-
-`path` 加载点集的存储路径,默认为当前目录下的`data.npy`,路径需以下划线结尾
-
-**功能简介:**点集需以元组`((train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label))`的形式保存
-
----
-
-**`visualize(data, label, class_num = 1, test_data=[])`**
-
-*可视化目前只支持二维,如果是高维点集,将只可视化前两维*
-
-`data` 训练点集坐标
-
-`label`训练点集对应的标签
-
-`class_num`类别总数,默认值为1
-
-`test_data`测试点集坐标
-
-**功能简介:**绘制点集散点图,不同类别自适应的用不同颜色表征,测试点集将通过"+"表征
-
-## 实验
-
-首先,我们生成了三类坐标点,每类数量100
-
-其对应的数量和协方差矩阵如下表所示
-
-| | 均值 | 协方差矩阵 |
-| ------- | ------- | ----------------- |
-| class 1 | (1, 2) | [[10, 0], [0, 2]] |
-| class 2 | (4, 5) | [[7, 3], [15, 1]] |
-| class 3 | (-2, 6) | [[0, 1], [1, 2]] |
-
-测试了1-10对应的准确率,如下图所示
-
- -
-在保证准确率不变的条件下,选择较小的数值k=5,预测的准确率达83.3%,对应数据可视化如下图
-
-
-
-在保证准确率不变的条件下,选择较小的数值k=5,预测的准确率达83.3%,对应数据可视化如下图
-
- -
-### 对比实验1:减少点集重叠
-
-上图能较为清晰的看到,三种颜色的点集分布基本分离开,但是仍存在一部分重叠,推测重叠部分会使得KNN效果变差,下面通过改变均值和协方差验证这一结论
-
-首先将协方差对应更改成为
-
-| | 均值 | 协方差矩阵 |
-| ------- | ------- | --------------- |
-| class 1 | (1, 2) | [[1,0], [0, 1]] |
-| class 2 | (4, 5) | [[1,0], [0, 1]] |
-| class 3 | (-2, 6) | [[1,0], [0, 1]] |
-
-对应K的曲线和点集分布图如下
-
-
-
-### 对比实验1:减少点集重叠
-
-上图能较为清晰的看到,三种颜色的点集分布基本分离开,但是仍存在一部分重叠,推测重叠部分会使得KNN效果变差,下面通过改变均值和协方差验证这一结论
-
-首先将协方差对应更改成为
-
-| | 均值 | 协方差矩阵 |
-| ------- | ------- | --------------- |
-| class 1 | (1, 2) | [[1,0], [0, 1]] |
-| class 2 | (4, 5) | [[1,0], [0, 1]] |
-| class 3 | (-2, 6) | [[1,0], [0, 1]] |
-
-对应K的曲线和点集分布图如下
-
-
 -
-此时选择K = 3,对应的KNN准确率已经提高到了96.7%符合预期
-
-同样的,我们更改对应的均值大小,使得高斯分布尽可能分开
-
-| | 均值 | 协方差矩阵 |
-| ------- | --------- | ----------------- |
-| class 1 | (-10, 2) | [[10, 0], [0, 2]] |
-| class 2 | (4, 5) | [[7, 3], [15, 1]] |
-| class 3 | (-2, -16) | [[0, 1], [1, 2]] |
-
-对应曲线如下,准确率达到1.0,此时K=1已经达到了最大值
-
-
-
-此时选择K = 3,对应的KNN准确率已经提高到了96.7%符合预期
-
-同样的,我们更改对应的均值大小,使得高斯分布尽可能分开
-
-| | 均值 | 协方差矩阵 |
-| ------- | --------- | ----------------- |
-| class 1 | (-10, 2) | [[10, 0], [0, 2]] |
-| class 2 | (4, 5) | [[7, 3], [15, 1]] |
-| class 3 | (-2, -16) | [[0, 1], [1, 2]] |
-
-对应曲线如下,准确率达到1.0,此时K=1已经达到了最大值
-
-
 -
-#### 结论
-
-从该对比实验中,我们能够较为清晰的看到点集分布对于KNN准确率的影响,当类之间重合度较低时,KNN的准确率显著提升
-
-### 对比实验2:距离选择
-
-在上述实验中,我们采用的距离为欧式距离,下面将更改距离计算方式为曼哈顿距离,考察对应的影响
-
-当点集区分较开时,曼哈顿距离与欧式距离在准确率上差别不大,这里不做展示,当点集重叠程度较高时,对以下分布生成了多组数据
-
-| | 均值 | 协方差矩阵 |
-| ------- | ------ | ----------------- |
-| class 1 | (1, 4) | [[10, 0], [0, 2]] |
-| class 2 | (2, 5) | [[7, 3], [15, 1]] |
-| class 3 | (2, 6) | [[0, 1], [1, 2]] |
-
-对应的k值选取和准确率(acc)如下表所示
-
-| 欧氏距离 | 曼哈顿距离 |
-| ----------------- | ------------------ |
-| k = 3, acc = 0.7 | k=3, acc= 0.683 |
-| k = 1, acc = 0.53 | k = 1, acc = 0.483 |
-| k = 7, acc = 0.63 | k = 8, acc = 0.567 |
-
-综合来看点集分布重叠程度较高时,欧氏距离优于曼哈顿距离,推测以高斯分布生成的点,欧式距离对某一维度上较大差距的惩罚大于曼哈顿距离,较符合高斯分布点生成方式,较好拟合当前位置的概率密度,从而准确率更高
-
-#### 结论
-
-当点集区分较开时,曼哈顿距离和欧式距离差别不大,点集重合较大时,欧式距离由于曼哈顿距离
-
-### 对比实验3:点集数量
-
-对于如下分布
-
-| | 均值 | 协方差矩阵 |
-| ------- | ------- | ----------------- |
-| class 1 | (1, 4) | [[10, 0], [0, 2]] |
-| class 2 | (2, -3) | [[7, 3], [15, 1]] |
-| class 3 | (2, 5) | [[0, 1], [1, 2]] |
-
-分别生成了[100, 100, 100], [100, 10, 100], [100, 50, 200],[200, 200, 200]四组,每组多次避免偶然误差
-
-结果如下表格所示
-
-| | [100, 100, 100] | [100, 10, 100] | [100, 50, 200] | [200, 200, 200] |
-| ---- | --------------- | -------------- | -------------- | --------------- |
-| 1 | 0.867 | 0.809 | 0.886 | 0.875 |
-| 2 | 0.800 | 0.809 | 0.843 | 0.825 |
-| 3 | 0.867 | 0.809 | 0.857 | 0.9 |
-| 4 | 0.917 | 0.761 | 0.886 | 0.792 |
-| 平均 | 0.862 | 0.797 | 0.868 | 0.848 |
-
-#### 结论
-
-当点集数量上升时,增大重叠面积,准确率相应下降,当某组点数量显著小于其他点集时,将会较大影响到准确率,当差距过大时,将会一定程度上退化成N-1分类问题,反而导致准确率提升
-
-### 对比实验4:各维度尺度
-
-当各个维度的尺度并不匹配时,例如(年龄,财产)二元组,基于空间上欧式距离相当于退化成为闵式距离,为进一步对比其影响,生成了如下数据
-
-| | 均值 | 协方差矩阵 |
-| ------- | -------- | --------------------- |
-| class 1 | (1, 400) | [[10, 0], [0, 20000]] |
-| class 2 | (2, 300) | [[7, 0], [0, 10000]] |
-| class 3 | (2, 300) | [[1, 0], [0, 10000]] |
-
-其中一组对应k和点集分布如下图所示,多次测量的平均准确率为0.399
-
-
-
-#### 结论
-
-从该对比实验中,我们能够较为清晰的看到点集分布对于KNN准确率的影响,当类之间重合度较低时,KNN的准确率显著提升
-
-### 对比实验2:距离选择
-
-在上述实验中,我们采用的距离为欧式距离,下面将更改距离计算方式为曼哈顿距离,考察对应的影响
-
-当点集区分较开时,曼哈顿距离与欧式距离在准确率上差别不大,这里不做展示,当点集重叠程度较高时,对以下分布生成了多组数据
-
-| | 均值 | 协方差矩阵 |
-| ------- | ------ | ----------------- |
-| class 1 | (1, 4) | [[10, 0], [0, 2]] |
-| class 2 | (2, 5) | [[7, 3], [15, 1]] |
-| class 3 | (2, 6) | [[0, 1], [1, 2]] |
-
-对应的k值选取和准确率(acc)如下表所示
-
-| 欧氏距离 | 曼哈顿距离 |
-| ----------------- | ------------------ |
-| k = 3, acc = 0.7 | k=3, acc= 0.683 |
-| k = 1, acc = 0.53 | k = 1, acc = 0.483 |
-| k = 7, acc = 0.63 | k = 8, acc = 0.567 |
-
-综合来看点集分布重叠程度较高时,欧氏距离优于曼哈顿距离,推测以高斯分布生成的点,欧式距离对某一维度上较大差距的惩罚大于曼哈顿距离,较符合高斯分布点生成方式,较好拟合当前位置的概率密度,从而准确率更高
-
-#### 结论
-
-当点集区分较开时,曼哈顿距离和欧式距离差别不大,点集重合较大时,欧式距离由于曼哈顿距离
-
-### 对比实验3:点集数量
-
-对于如下分布
-
-| | 均值 | 协方差矩阵 |
-| ------- | ------- | ----------------- |
-| class 1 | (1, 4) | [[10, 0], [0, 2]] |
-| class 2 | (2, -3) | [[7, 3], [15, 1]] |
-| class 3 | (2, 5) | [[0, 1], [1, 2]] |
-
-分别生成了[100, 100, 100], [100, 10, 100], [100, 50, 200],[200, 200, 200]四组,每组多次避免偶然误差
-
-结果如下表格所示
-
-| | [100, 100, 100] | [100, 10, 100] | [100, 50, 200] | [200, 200, 200] |
-| ---- | --------------- | -------------- | -------------- | --------------- |
-| 1 | 0.867 | 0.809 | 0.886 | 0.875 |
-| 2 | 0.800 | 0.809 | 0.843 | 0.825 |
-| 3 | 0.867 | 0.809 | 0.857 | 0.9 |
-| 4 | 0.917 | 0.761 | 0.886 | 0.792 |
-| 平均 | 0.862 | 0.797 | 0.868 | 0.848 |
-
-#### 结论
-
-当点集数量上升时,增大重叠面积,准确率相应下降,当某组点数量显著小于其他点集时,将会较大影响到准确率,当差距过大时,将会一定程度上退化成N-1分类问题,反而导致准确率提升
-
-### 对比实验4:各维度尺度
-
-当各个维度的尺度并不匹配时,例如(年龄,财产)二元组,基于空间上欧式距离相当于退化成为闵式距离,为进一步对比其影响,生成了如下数据
-
-| | 均值 | 协方差矩阵 |
-| ------- | -------- | --------------------- |
-| class 1 | (1, 400) | [[10, 0], [0, 20000]] |
-| class 2 | (2, 300) | [[7, 0], [0, 10000]] |
-| class 3 | (2, 300) | [[1, 0], [0, 10000]] |
-
-其中一组对应k和点集分布如下图所示,多次测量的平均准确率为0.399
-
-
 -
-为了对比其影响,我们等比例放缩对应的维度100倍,
-
-| | 均值 | 协方差矩阵 |
-| ------- | ------ | ----------------- |
-| class 1 | (1, 4) | [[10, 0], [0, 2]] |
-| class 2 | (2, 3) | [[7, 0], [15, 1]] |
-| class 3 | (2, 3) | [[1, 0], [0, 1]] |
-
-对应的k和点集可视化如下图
-
-
-
-为了对比其影响,我们等比例放缩对应的维度100倍,
-
-| | 均值 | 协方差矩阵 |
-| ------- | ------ | ----------------- |
-| class 1 | (1, 4) | [[10, 0], [0, 2]] |
-| class 2 | (2, 3) | [[7, 0], [15, 1]] |
-| class 3 | (2, 3) | [[1, 0], [0, 1]] |
-
-对应的k和点集可视化如下图
-
-
 -
-多次测量的平均准确率为0.539
-
-#### 结论
-
-尺度归一化较大程度的影响了准确率的大小,通过等比例尺度放缩,准确率有了较大提升,但是,结合前面点集分布的表现,推测当点集自身区分较开时,归一化的影响不大
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_1.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index b840aa5b2862be15a71968435433efc147086318..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_1.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 5e2b73e556a36aa5db294e9c2c42fc039728279d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_2.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 3c6ec2fa9693474116ae15a76359f69b442d99b1..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_3.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index a893f35d277af8c818a69f49cee5e2bbe06c2367..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_4.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_4.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 34e3cb5e2c15ae4104a1f12fbd9ef62af24cb03e..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_4.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_5_1.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_5_1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 09921dca1bbeebae81d5b0f71eafe9ab0f0ce75a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_5_1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_5_2.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_5_2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 18ed90b7cd1ec5f2c91a863393b21b655b040eb6..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_5_2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_6_1.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_6_1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 6fdc07c00f7cfdcead4f8cf98880ce1cd76f9526..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_6_1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_6_2.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_6_2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 72685efbfd9bc42f675811e5f92bf88c6bbc3851..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_6_2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/k1.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/k1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 8a81a8e624428a86d14851ca1a9848cf11c61be0..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/k1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 4daa13c95a45ed7371bb33f20bdd2f4d821894ae..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,154 +0,0 @@
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import matplotlib.cm as cm
-
-def distance(point1, point2, method="Euclid"):
- """
- suppose dimention of points is m * 1
- """
- if point1.ndim == 1:
- point1 = np.expand_dims(point1, axis=1)
- if point2.ndim == 1:
- point2 = np.expand_dims(point2, axis=1)
- if point1.shape[0] == 1:
- point1 = point1.reshape(-1, 1)
- if point2.shape[0] == 1:
- point2 = point2.reshape(-1, 1)
- dimention_num = point1.shape[0]
- result = 0
- if(method == "Euclid"):
- if dimention_num != point1.size:
- print("error")
- return -1
- for iter in range(dimention_num):
- result += (point1[iter, 0]-point2[iter, 0])**2
- return pow(result, 0.5)
- if(method == "Manhattan"):
- if dimention_num != point1.size:
- print("error")
- return -1
- for iter in range(dimention_num):
- result += abs(point1[iter, 0]-point2[iter, 0])
- return result
-
-def dis(dis_label):
- return dis_label[0]
-
-def nearest_k_label_max(point, point_arr, label_arr, k):
- distance_arr = []
- for iter in range(len(point_arr)):
- distance_arr.append((distance(point, point_arr[iter]), label_arr[iter]))
- distance_arr.sort(key=dis)
- result = []
- for iter in range(k):
- result.append(distance_arr[iter][1])
- return max(result, key=result.count)
-
-class KNN:
-
- def __init__(self):
- pass
-
- def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- num = train_data.shape[0]
- dimention_num = train_data.shape[1]
- self.train_data = train_data
- self.train_label = train_label
- dev_num = int(num * 0.1)
- dev_data = train_data[:dev_num]
- dev_label = train_label[:dev_num]
- train_data = train_data[dev_num:]
- train_label = train_label[dev_num:]
- correct_cout_max = 0
- k_max = 0
- accu = []
- if dev_num == 0:
- print("points number too few, so we choose k = 1")
- self.k = 1
- return
-
- for iter in range(1, min(num-dev_num, 10)):#find the best k
- correct_count = 0
- for j in range(len(dev_data)):
- predict_label = nearest_k_label_max(dev_data[j], train_data, train_label, iter)
- if(predict_label == dev_label[j]):
- correct_count += 1
- if correct_count > correct_cout_max:
- correct_cout_max = correct_count
- k_max = iter
- accu.append(correct_count/dev_num)
- x = range(1, min(num-dev_num, 10))
- #this part is only for experiment, so I commented it for auto test
- # plt.plot(x,accu)
- # plt.show()
- self.k = k_max
- print("choose k=", k_max)
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- result = []
- for iter in range(len(test_data)):
- result.append(nearest_k_label_max(test_data[iter,:], self.train_data, self.train_label, self.k))
- return np.array(result)
-
-#here we need some utils
-def data_generate_and_save(class_num, mean_list, cov_list, num_list, save_path = ""):
- """
- class_num: the number of class
- mean_list: mean_list[i] stand for the mean of class[i]
- cov_list: similar to mean_list, stand for the covariance
- num_list: similar to mean_list, stand for the number of points in class[i]
- save_path: the data storage path, end with slash.
- """
- data = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean_list[0], cov_list[0], (num_list[0],))
- label = np.zeros((num_list[0],),dtype=int)
- total = num_list[0]
-
- for iter in range(1, class_num):
- temp = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean_list[iter], cov_list[iter], (num_list[iter],))
- label_temp = np.ones((num_list[iter],),dtype=int)*iter
- data = np.concatenate([data, temp])
- label = np.concatenate([label, label_temp])
- total += num_list[iter]
-
- idx = np.arange(total)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- data = data[idx]
- label = label[idx]
- train_num = int(total * 0.8)
- train_data = data[:train_num, ]
- test_data = data[train_num:, ]
- train_label = label[:train_num, ]
- test_label = label[train_num:, ]
- # print(test_label.size)
- np.save(save_path+"data.npy", ((train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)))
-
-def data_load(path = ""):
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = np.load(path+"data.npy",allow_pickle=True)
- return (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
-
-def visualize(data, label, class_num = 1, test_data=[]):
- data_x = {}
- data_y = {}
- for iter in range(class_num):
- data_x[iter] = []
- data_y[iter] = []
- for iter in range(len(label)):
- data_x[label[iter]].append(data[iter, 0])
- data_y[label[iter]].append(data[iter, 1])
- colors = cm.rainbow(np.linspace(0, 1, class_num))
-
- for class_idx, c in zip(range(class_num), colors):
- plt.scatter(data_x[class_idx], data_y[class_idx], color=c)
- if(len(test_data) != 0):
- plt.scatter(test_data[:, 0], test_data[:, 1], marker='+')
- plt.show()
-
-#experiment begin
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- mean_list = [(1, 4), (2, 3), (2, 3)]
- cov_list = [np.array([[10, 0], [0, 2]]), np.array([[7, 0], [0, 1]]), np.array([[1, 0], [0, 1]])]
- num_list = [200, 200, 200]
- save_path = ""
- data_generate_and_save(3, mean_list, cov_list, num_list, save_path)
- # (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = data_load()
- # visualize(train_data, train_label, 3)
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130130/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/18307130130/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index d7c90382fa97a6f1912273d2058f10f7485f9dec..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/18307130130/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,239 +0,0 @@
-# Assignment-1 Report
-
-
-
-多次测量的平均准确率为0.539
-
-#### 结论
-
-尺度归一化较大程度的影响了准确率的大小,通过等比例尺度放缩,准确率有了较大提升,但是,结合前面点集分布的表现,推测当点集自身区分较开时,归一化的影响不大
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_1.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index b840aa5b2862be15a71968435433efc147086318..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_1.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 5e2b73e556a36aa5db294e9c2c42fc039728279d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_2.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 3c6ec2fa9693474116ae15a76359f69b442d99b1..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_3.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index a893f35d277af8c818a69f49cee5e2bbe06c2367..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_4.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_4.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 34e3cb5e2c15ae4104a1f12fbd9ef62af24cb03e..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2_4.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_5_1.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_5_1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 09921dca1bbeebae81d5b0f71eafe9ab0f0ce75a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_5_1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_5_2.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_5_2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 18ed90b7cd1ec5f2c91a863393b21b655b040eb6..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_5_2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_6_1.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_6_1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 6fdc07c00f7cfdcead4f8cf98880ce1cd76f9526..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_6_1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_6_2.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_6_2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 72685efbfd9bc42f675811e5f92bf88c6bbc3851..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_6_2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/k1.png b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/k1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 8a81a8e624428a86d14851ca1a9848cf11c61be0..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/img/k1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 4daa13c95a45ed7371bb33f20bdd2f4d821894ae..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/18307130116/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,154 +0,0 @@
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import matplotlib.cm as cm
-
-def distance(point1, point2, method="Euclid"):
- """
- suppose dimention of points is m * 1
- """
- if point1.ndim == 1:
- point1 = np.expand_dims(point1, axis=1)
- if point2.ndim == 1:
- point2 = np.expand_dims(point2, axis=1)
- if point1.shape[0] == 1:
- point1 = point1.reshape(-1, 1)
- if point2.shape[0] == 1:
- point2 = point2.reshape(-1, 1)
- dimention_num = point1.shape[0]
- result = 0
- if(method == "Euclid"):
- if dimention_num != point1.size:
- print("error")
- return -1
- for iter in range(dimention_num):
- result += (point1[iter, 0]-point2[iter, 0])**2
- return pow(result, 0.5)
- if(method == "Manhattan"):
- if dimention_num != point1.size:
- print("error")
- return -1
- for iter in range(dimention_num):
- result += abs(point1[iter, 0]-point2[iter, 0])
- return result
-
-def dis(dis_label):
- return dis_label[0]
-
-def nearest_k_label_max(point, point_arr, label_arr, k):
- distance_arr = []
- for iter in range(len(point_arr)):
- distance_arr.append((distance(point, point_arr[iter]), label_arr[iter]))
- distance_arr.sort(key=dis)
- result = []
- for iter in range(k):
- result.append(distance_arr[iter][1])
- return max(result, key=result.count)
-
-class KNN:
-
- def __init__(self):
- pass
-
- def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- num = train_data.shape[0]
- dimention_num = train_data.shape[1]
- self.train_data = train_data
- self.train_label = train_label
- dev_num = int(num * 0.1)
- dev_data = train_data[:dev_num]
- dev_label = train_label[:dev_num]
- train_data = train_data[dev_num:]
- train_label = train_label[dev_num:]
- correct_cout_max = 0
- k_max = 0
- accu = []
- if dev_num == 0:
- print("points number too few, so we choose k = 1")
- self.k = 1
- return
-
- for iter in range(1, min(num-dev_num, 10)):#find the best k
- correct_count = 0
- for j in range(len(dev_data)):
- predict_label = nearest_k_label_max(dev_data[j], train_data, train_label, iter)
- if(predict_label == dev_label[j]):
- correct_count += 1
- if correct_count > correct_cout_max:
- correct_cout_max = correct_count
- k_max = iter
- accu.append(correct_count/dev_num)
- x = range(1, min(num-dev_num, 10))
- #this part is only for experiment, so I commented it for auto test
- # plt.plot(x,accu)
- # plt.show()
- self.k = k_max
- print("choose k=", k_max)
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- result = []
- for iter in range(len(test_data)):
- result.append(nearest_k_label_max(test_data[iter,:], self.train_data, self.train_label, self.k))
- return np.array(result)
-
-#here we need some utils
-def data_generate_and_save(class_num, mean_list, cov_list, num_list, save_path = ""):
- """
- class_num: the number of class
- mean_list: mean_list[i] stand for the mean of class[i]
- cov_list: similar to mean_list, stand for the covariance
- num_list: similar to mean_list, stand for the number of points in class[i]
- save_path: the data storage path, end with slash.
- """
- data = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean_list[0], cov_list[0], (num_list[0],))
- label = np.zeros((num_list[0],),dtype=int)
- total = num_list[0]
-
- for iter in range(1, class_num):
- temp = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean_list[iter], cov_list[iter], (num_list[iter],))
- label_temp = np.ones((num_list[iter],),dtype=int)*iter
- data = np.concatenate([data, temp])
- label = np.concatenate([label, label_temp])
- total += num_list[iter]
-
- idx = np.arange(total)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- data = data[idx]
- label = label[idx]
- train_num = int(total * 0.8)
- train_data = data[:train_num, ]
- test_data = data[train_num:, ]
- train_label = label[:train_num, ]
- test_label = label[train_num:, ]
- # print(test_label.size)
- np.save(save_path+"data.npy", ((train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)))
-
-def data_load(path = ""):
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = np.load(path+"data.npy",allow_pickle=True)
- return (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
-
-def visualize(data, label, class_num = 1, test_data=[]):
- data_x = {}
- data_y = {}
- for iter in range(class_num):
- data_x[iter] = []
- data_y[iter] = []
- for iter in range(len(label)):
- data_x[label[iter]].append(data[iter, 0])
- data_y[label[iter]].append(data[iter, 1])
- colors = cm.rainbow(np.linspace(0, 1, class_num))
-
- for class_idx, c in zip(range(class_num), colors):
- plt.scatter(data_x[class_idx], data_y[class_idx], color=c)
- if(len(test_data) != 0):
- plt.scatter(test_data[:, 0], test_data[:, 1], marker='+')
- plt.show()
-
-#experiment begin
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- mean_list = [(1, 4), (2, 3), (2, 3)]
- cov_list = [np.array([[10, 0], [0, 2]]), np.array([[7, 0], [0, 1]]), np.array([[1, 0], [0, 1]])]
- num_list = [200, 200, 200]
- save_path = ""
- data_generate_and_save(3, mean_list, cov_list, num_list, save_path)
- # (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = data_load()
- # visualize(train_data, train_label, 3)
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18307130130/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/18307130130/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index d7c90382fa97a6f1912273d2058f10f7485f9dec..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/18307130130/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,239 +0,0 @@
-# Assignment-1 Report
-
-------李睿琛 18307130130
-## 一、数据集的生成与分割 - -### **数据集生成** - -`GenerateData`封装数据生成逻辑函数,修改参数数组,即可自定义分布特点。 - -> N:定义点的维度 -> -> means:定义分布均值 -> -> covs:定义分布协方差矩阵 -> -> nums:定义分布包含的点的数目 - -```python -# define two-dimension Gaussian distribution -N = 2 -means = [(1, 2), (1, 9), (4, 10), (9, 5), (7, 20)] -# define the number of each distribution -nums = [1000, 1000, 1000, 1000, 1000] -covs = [np.eye(N), np.eye(N), np.eye(N), np.eye(N), np.eye(N)] - -def GenerateData(N, nums, means, covs): - ... - GetGaussionSet(N, nums[i], means[i], covs[i]) - # concatenate the data and corresponding label - dataset[i] = np.concatenate((tmp, zeros), axis=1) - ... -``` - -`GetGaussionSet`根据给定数组生成高斯分布: - -```python -def GetGaussionSet(N, num, mean, cov): - """ - N refer to number of dimensions, mean refer to mean of Gaussion, - number refer to number of data - """ - x = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, num, 'raise') - return x -``` - -`GetGaussionSet`生成一个**以mean为均值,cov为协方差矩阵,包含num个点**的二维高斯分布的点集。 - -### **数据集分割** - -```python -# Randomly divide the data into 80% training set and 20% test set -np.random.shuffle(DataSet) -length = DataSet.shape[0] -train_len = round(length * 4 / 5) -train_data = DataSet[:train_len,:] -test_data = DataSet[train_len:,:] -``` - -打乱数据后,将数据随机划分为 80% 的训练集和 20% 的测试集。 - -## 二、KNN模型的拟合与预测 - -### 模型拟合 - -使用**交叉验证**确定合适**超参K**, 即把数据划分为训练集、验证集和测试集。一般的划分比例为6:2:2。 - -对80%的训练集进一步按6:2:2划分为60%训练集,20%验证集。 - -k值一般偏小,所以**遍历**确定正确性最高对应的k值: - -```python -v_ratio = 0.25 -length = train_data.shape[0] -label_len = data_len = round(length * (1 - v_ratio) ) -self.train_data = t_data = train_data[:data_len,:] -self.train_label = t_label = train_label[:label_len] -v_data = train_data[data_len:,:] -v_label = train_label[label_len:] - -# find the k with highest accuracy -for k in range(1, 20): - res = self._predict_by_k(t_data, t_label, v_data, k) -``` -输出如下: -``` -k : 1 acc: 0.984375 -k : 2 acc: 0.9828125 -... -k : 8 acc: 0.9890625 -k : 9 acc: 0.9890625 -k : 10 acc: 0.990625 -k : 11 acc: 0.9890625 -k : 12 acc: 0.990625 -k : 13 acc: 0.990625 -k : 14 acc: 0.9890625 -... -k : 18 acc: 0.9890625 -k : 19 acc: 0.9890625 -select k: 13 -``` - -即超参k设置为13时,在验证集上有最高准确性。 - -### **模型预测** - -```python -diff = t_data - d -dist = (np.sum(diff ** self.p, axis=1))**(1 / self.p) -topk = [t_label[x] for x in np.argsort(dist)[:k]] -``` - - 使用闵可夫斯基距离作为衡量: - -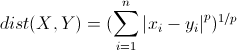 - -```python -topk = [t_label[x] for x in np.argsort(dist)[:k]] -... -i = np.random.randint(len(top_cnt)) -res.append(top_cnt[i]) -``` - -根据距离从小到大排序,去前K个label,其中出现最频繁的即为预测结果。若有结果有多个,随机选取一个作为最终结果。 - -## 三、模型结果可视化 - -> N = 2 -> -> means = [(1, 2), (1, 9), (4, 10), (9, 5), (7, 20)] -> -> nums = [1000, 1000, 1000, 1000, 1000] -> -> covs = [np.eye(N), np.eye(N), np.eye(N), np.eye(N), np.eye(N)] - -K的选取: - -``` -k : 1 acc: 0.962 -k : 2 acc: 0.964 -k : 3 acc: 0.972 -k : 4 acc: 0.971 -k : 5 acc: 0.974 -k : 6 acc: 0.971 -k : 7 acc: 0.971 -k : 8 acc: 0.97 -k : 9 acc: 0.971 -k : 10 acc: 0.971 -k : 11 acc: 0.97 -k : 12 acc: 0.971 -k : 13 acc: 0.971 -k : 14 acc: 0.969 -k : 15 acc: 0.971 -k : 16 acc: 0.972 -k : 17 acc: 0.971 -k : 18 acc: 0.971 -k : 19 acc: 0.971 -select k: 5 -``` - -预测结果:左图可视化**训练集**分布,右图可视化**测试集**分布。星星符号标记了**预测错误**的点。 - - - - -
-500 points are then split randomly into training set (80%) and testing set (20%).
-
-### 1.2 Model Accuracy with Different K and Distance Method
-
-Since a rule of thumb is to let $K = \sqrt{N}$, where $ N = N_0 + N_1 + N_2$, we first try some Ks around $\sqrt{400} = 20$ using both Euclidean and Manhattan distance.
-
-| \ | K = 10 | K = 15 | K = 20 | K = 25 | K = 30 |
-| ------------ |:------:|:------:|:------:|:------:|:------:|
-| **Euclidean** |83.0|82.0|83.0|81.0|80.0|
-| **Manhattan** |83.0|82.0|81.0|81.0|81.0|
-
-The KNN model with $K = 10$ gives the best prediction result of 83% for both distance methods, so we consider choosing $K_{0} = 10$ as a starting point for model optimization. Below is a scatter plot showing the prediction result of the chosen model ($K = 10$, Euclidean Distance). Each red dot represents a mis-classification.
-
-*Noticed model accuracy using different distance method doesn't show much difference for this dataset.
-
-
-
-500 points are then split randomly into training set (80%) and testing set (20%).
-
-### 1.2 Model Accuracy with Different K and Distance Method
-
-Since a rule of thumb is to let $K = \sqrt{N}$, where $ N = N_0 + N_1 + N_2$, we first try some Ks around $\sqrt{400} = 20$ using both Euclidean and Manhattan distance.
-
-| \ | K = 10 | K = 15 | K = 20 | K = 25 | K = 30 |
-| ------------ |:------:|:------:|:------:|:------:|:------:|
-| **Euclidean** |83.0|82.0|83.0|81.0|80.0|
-| **Manhattan** |83.0|82.0|81.0|81.0|81.0|
-
-The KNN model with $K = 10$ gives the best prediction result of 83% for both distance methods, so we consider choosing $K_{0} = 10$ as a starting point for model optimization. Below is a scatter plot showing the prediction result of the chosen model ($K = 10$, Euclidean Distance). Each red dot represents a mis-classification.
-
-*Noticed model accuracy using different distance method doesn't show much difference for this dataset.
-
- -
-### 1.3 Model Optimization
-
-General Idea: $K_{i+1} = \lceil{K_{i} + Step_{i+1}}\rceil$
-
-Detailed steps:
-
- - For each $K_{i+1}$, calculate its accuracy rate $R_{i+1}$.
- - If $R_{i+1} > R_{0}$, a better model is find. End our optimization. Else:
- - If $R_{i+1} > R_{i}$, let $Step_{i+1} = \frac{1}{C} Step_{i} $, where $C = (R_{i+1} - R_{i}) / R_{i}$.
- Which is, if model accuracy improves, continue in this direction with a smaller step. The step size is negatively related to the percentage of improvement.
- - If $R_{i+1} <= R_{i}$, let $Step_{i+1} = - \frac{1}{2} Step_{i}$.
- Which is, if the new K does not improve model accuracy, try a smaller step in reverse direction.
-
-The model from 1.2 gives K = 10 and Euclidean distance. Using this model as the starting point, define the first step $Step_{0} = \frac{1}{100}N = 5$.
-
-Optimization process:
-
-| \ | K = 10 | K = 5 | K = 8 |
-| ------------ |:------:|:------:|:------:|
-| **Accuracy rate (%)** |83.0|83.0|85.0|
-
- After three iterations, a higher accuracy rate of 85% is reached when K is adjusted to 8. Thus, our final KNN model will use K = 8 and Euclidean distance.
-
-Prediction result evaluation:
-
-
-
-### 1.3 Model Optimization
-
-General Idea: $K_{i+1} = \lceil{K_{i} + Step_{i+1}}\rceil$
-
-Detailed steps:
-
- - For each $K_{i+1}$, calculate its accuracy rate $R_{i+1}$.
- - If $R_{i+1} > R_{0}$, a better model is find. End our optimization. Else:
- - If $R_{i+1} > R_{i}$, let $Step_{i+1} = \frac{1}{C} Step_{i} $, where $C = (R_{i+1} - R_{i}) / R_{i}$.
- Which is, if model accuracy improves, continue in this direction with a smaller step. The step size is negatively related to the percentage of improvement.
- - If $R_{i+1} <= R_{i}$, let $Step_{i+1} = - \frac{1}{2} Step_{i}$.
- Which is, if the new K does not improve model accuracy, try a smaller step in reverse direction.
-
-The model from 1.2 gives K = 10 and Euclidean distance. Using this model as the starting point, define the first step $Step_{0} = \frac{1}{100}N = 5$.
-
-Optimization process:
-
-| \ | K = 10 | K = 5 | K = 8 |
-| ------------ |:------:|:------:|:------:|
-| **Accuracy rate (%)** |83.0|83.0|85.0|
-
- After three iterations, a higher accuracy rate of 85% is reached when K is adjusted to 8. Thus, our final KNN model will use K = 8 and Euclidean distance.
-
-Prediction result evaluation:
-
- -
-Compared with the model before optimization, two points on the top is now classified correctly.
-
-## 2. Distribution Parameters & Model Accuracy
-
-From inuition, we hypothesis that any change that results in a more balanced mixture of all classes will make classification harder, thereby decrease model accuracy. Below, we modify the parameters of Gaussian distributions to test our hypothesis.
-
-### 2.1 Change of Variance and Covariance
-
-Let the means stay the same. Modify the variance-covariance matrix for each class to increase overlapping between each class:
-
-$
- N_0 = 150 \hspace{1cm}
- C_0 \sim \mathcal{N}(\mu = \begin{bmatrix}50\\\\50\end{bmatrix},\sigma^{2} = \begin{bmatrix}300 & 0\\\\0 & 200\end{bmatrix})
-$
-
-$
- N_1 = 250 \hspace{1cm}
- C_1 \sim \mathcal{N}(\mu = \begin{bmatrix}60\\\\20\end{bmatrix},\sigma^{2} = \begin{bmatrix}250 & 0\\\\0 & 150\end{bmatrix})
-$
-
-$
- N_2 = 100 \hspace{1cm}
- C_2 \sim \mathcal{N}(\mu = \begin{bmatrix}20\\\\60\end{bmatrix},\sigma^{2} = \begin{bmatrix}150 & 0\\\\0 & 150\end{bmatrix})
-$
-
-Mock Data 2 Overview:
-
-
-
-Compared with the model before optimization, two points on the top is now classified correctly.
-
-## 2. Distribution Parameters & Model Accuracy
-
-From inuition, we hypothesis that any change that results in a more balanced mixture of all classes will make classification harder, thereby decrease model accuracy. Below, we modify the parameters of Gaussian distributions to test our hypothesis.
-
-### 2.1 Change of Variance and Covariance
-
-Let the means stay the same. Modify the variance-covariance matrix for each class to increase overlapping between each class:
-
-$
- N_0 = 150 \hspace{1cm}
- C_0 \sim \mathcal{N}(\mu = \begin{bmatrix}50\\\\50\end{bmatrix},\sigma^{2} = \begin{bmatrix}300 & 0\\\\0 & 200\end{bmatrix})
-$
-
-$
- N_1 = 250 \hspace{1cm}
- C_1 \sim \mathcal{N}(\mu = \begin{bmatrix}60\\\\20\end{bmatrix},\sigma^{2} = \begin{bmatrix}250 & 0\\\\0 & 150\end{bmatrix})
-$
-
-$
- N_2 = 100 \hspace{1cm}
- C_2 \sim \mathcal{N}(\mu = \begin{bmatrix}20\\\\60\end{bmatrix},\sigma^{2} = \begin{bmatrix}150 & 0\\\\0 & 150\end{bmatrix})
-$
-
-Mock Data 2 Overview:
-
- -
-Prediction result evaluation:
-
-
-
-Prediction result evaluation:
-
- -
-Accuracy of our model drop from 85% to 79% as expected.
-
-### 2.2 Change of Mean
-
-Let other parameters stay the same, decrease the distance between the means of each class to increase overlapping:
-
-$
- N_0 = 150 \hspace{1cm}
- C_0 \sim \mathcal{N}(\mu = \begin{bmatrix}50\\\\50\end{bmatrix},\sigma^{2} = \begin{bmatrix}60 & -50\\\\-50 & 140\end{bmatrix})
-$
-
-$
- N_1 = 250 \hspace{1cm}
- C_1 \sim \mathcal{N}(\mu = \begin{bmatrix}50\\\\40\end{bmatrix},\sigma^{2} = \begin{bmatrix}130 & 10\\\\10 & 100\end{bmatrix})
-$
-
-$
- N_2 = 100 \hspace{1cm}
- C_2 \sim \mathcal{N}(\mu = \begin{bmatrix}40\\\\60\end{bmatrix},\sigma^{2} = \begin{bmatrix}120 & 20\\\\20 & 90\end{bmatrix})
-$
-
-Mock Data 3 Overview:
-
-
-
-Accuracy of our model drop from 85% to 79% as expected.
-
-### 2.2 Change of Mean
-
-Let other parameters stay the same, decrease the distance between the means of each class to increase overlapping:
-
-$
- N_0 = 150 \hspace{1cm}
- C_0 \sim \mathcal{N}(\mu = \begin{bmatrix}50\\\\50\end{bmatrix},\sigma^{2} = \begin{bmatrix}60 & -50\\\\-50 & 140\end{bmatrix})
-$
-
-$
- N_1 = 250 \hspace{1cm}
- C_1 \sim \mathcal{N}(\mu = \begin{bmatrix}50\\\\40\end{bmatrix},\sigma^{2} = \begin{bmatrix}130 & 10\\\\10 & 100\end{bmatrix})
-$
-
-$
- N_2 = 100 \hspace{1cm}
- C_2 \sim \mathcal{N}(\mu = \begin{bmatrix}40\\\\60\end{bmatrix},\sigma^{2} = \begin{bmatrix}120 & 20\\\\20 & 90\end{bmatrix})
-$
-
-Mock Data 3 Overview:
-
- -
-Prediction result evaluation:
-
-
-
-Prediction result evaluation:
-
- -
-Accuracy of our model drop from 85% to 73% as expected.
-
-### 2.3 N & Model Accuracy
-
-In attempts to increase model accuracy, we try double the Ns in proportion to Data 3. With $N_{total} = 1000$, we expect some increase on model accuracy.
-
-Mock Data 4 Overview:
-
-
-
-Accuracy of our model drop from 85% to 73% as expected.
-
-### 2.3 N & Model Accuracy
-
-In attempts to increase model accuracy, we try double the Ns in proportion to Data 3. With $N_{total} = 1000$, we expect some increase on model accuracy.
-
-Mock Data 4 Overview:
-
- -
-Prediction result evaluation:
-
-
-
-Prediction result evaluation:
-
- -
-Model accuracy decreases from 73% to 62.5% even though our data size doubled. This suggests sample size contributes much less to model accuracy compared with distribution parameters. This makes sense because if the data labeled by different categories does indeed come from the same distribution, increasing N should provide more evidence of the similarity between these different categories.
-
-## Summary
-
-The main takeaways for this exercise:
-
-Model accuracy depends more on distribution parameters and the choice of K. Distance method have little influence on model accuracy, and whether an increase of N improves model accuracy or not depends on if the true distributions of all categories are significantly different (Might be able to use p-value from a statistical test to evaluate).
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 1.png b/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 32d5ded9c9d662bf7eacaede5e9316ba1d545335..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 2.png b/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index c7e7752721f808ea5ca19a56a7e642badb1617fd..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 3.png b/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 5a3fd62c0681f995d32c1ea794258095239261ee..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 4.png b/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 4.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 9c1e05f712b290be595b12c812476c72e0f0002d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 4.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 5.png b/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 5.png
deleted file mode 100644
index e49ec9595ac9c813a2e6044375c534bb669b3a7c..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 5.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 6.png b/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 6.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 11a84369882f65a2a3e46237e51fe479d4f14b88..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 6.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 7.png b/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 7.png
deleted file mode 100644
index ee33c60766eb907d5b8992c24ca3806c297d9fc8..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 7.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 8.png b/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 8.png
deleted file mode 100644
index a3f42ac859f2ef35448cb16f0412df387ba8e7a8..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 8.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 9.png b/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 9.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 0de5d1f658bdd5860681cfee20432e8074f39a1d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 9.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 410b588394c97d15227671e94f6e24e6cbb46882..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,249 +0,0 @@
-#!/usr/bin/env python
-# coding: utf-8
-
-# In[1]:
-
-
-import sys
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
-
-# ## Define Global Functions
-
-# In[139]:
-
-
-# Generate Training and Testing Sets
-def generate(Ns, Means, Covs, train_frac):
-
- # Generate 2-D data of N class
- data = list()
- label = list()
-
- for i in range(0,len(Ns)):
- Ci = np.random.multivariate_normal(Means[i], Covs[i], Ns[i])
- data.append(Ci)
- label.append([i]*Ns[i])
-
- data = np.array([v for subl in data for v in subl])
- label = np.array([v for subl in label for v in subl])
-
- #Assign random number
- idx = np.arange(sum(Ns))
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
-
- data = data[idx]
- label = label[idx]
-
- # Split into training and testing set
- split_point = int(label.size * train_frac)
- train_data, test_data = data[:split_point,], data[split_point:,]
- train_label, test_label = label[:split_point,], label[split_point:,]
-
- np.save("data.npy",((train_data, train_label),
- (test_data, test_label)))
-
- return train_data, train_label, test_data, test_label
-
-
-# Read in saved data
-def read():
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = np.load(
- "data.npy", allow_pickle = True)
- return (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
-
-
-# Create scatter plot of different categories
-def display(data, colorby, name, title):
- colors = ['red','grey','blue']
- datas =[[],[],[]]
-
- for i in range(len(data)):
- datas[colorby[i]].append(data[i])
-
- for i in range(len(datas)):
- each = np.array(datas[i])
- if len(each) == 0:
- continue
- plt.scatter(each[:, 0], each[:, 1],
- marker = 'o',
- color = colors[i],
- alpha = 0.7)
-
- plt.xlabel("X1")
- plt.ylabel("X2")
- plt.title(title)
- plt.savefig(f'img/{name}')
- plt.show()
-
-
-# ## Define Class KNN
-
-# In[140]:
-
-
-class KNN:
-
- def __init__(self):
-
- self.K = None
- self.Dist = None
- self.data = None
- self.label = None
-
-
- # Calculate distance between two given points
- def get_distance(self, x, y, dist_type = "Euclidean"):
- dist = 0.0
- if "Euclidean" == dist_type:
- distance = 0.0
- for i in range(len(x)):
- distance += (x[i] - y[i])**2
- dist = np.sqrt(distance)
-
- if "Manhattan" == dist_type:
- distance = 0.0
- for i in range(len(x)):
- distance += np.abs(x[i] - y[i])
- dist = distance
-
- return dist
-
-
- # Make a prediction for one point
- def predict_for_one(self, K, Dist, target, train_data, train_label):
- # Calculate distances between target point and other points
- dists = []
- neighbors = []
-
- for i in range(len(train_data)):
- dist = self.get_distance(target, train_data[i], Dist)
- dists.append((train_data[i], train_label[i], dist))
-
- # Get the K nearest neighbors
- dists.sort(key = lambda e: e[-1])
- neighbors = dists[1:K+1]
-
- # Make prediction based on conditional probabilities
- neighbors_class = [e[-2] for e in neighbors]
- prediction = max(neighbors_class, key = neighbors_class.count)
-
- return prediction
-
-
- # Calculate model accuracy
- def calc_accuracy(self, K, Dist, train_data, train_label):
- predictions = []
- # Make predictions for the training data
- for i in range(len(train_label)):
- target = train_data[i]
- prediction = self.predict_for_one(
- K, Dist, target, train_data, train_label
- )
- predictions.append(prediction)
-
- correct = 0
- for i in range(len(predictions)):
- if train_label[i] == predictions[i]:
- correct += 1
- accuracy = correct / len(predictions) * 100
-
- return accuracy
-
-
- # Find the Optimal K & Distance combination
- def fit(self, K_list, Dist_list, train_data, train_label):
-
- # Loop through the given options for K and distance methods
- accuracy_list = []
- for i in range(len(Dist_list)):
- Dist = Dist_list[i]
- dum_list = []
- for j in range(len(K_list)):
- K = K_list[j]
- accuracy = self.calc_accuracy(
- K, Dist, train_data, train_label
- )
- dum_list.append(accuracy)
- accuracy_list.append(dum_list)
-
- # Find the K & Distance method that gives the highest accuracy
- ac_array = np.array(accuracy_list)
- global_max = max([max(subl) for subl in accuracy_list])
- params = np.where(ac_array == global_max)
-
- # Assign the optimal parameters to KNN object
- # Randomly choice one if there exist more than one highest accuracy
- Dist_idx = np.random.choice(np.array(params[0]))
- K_idx = np.random.choice(np.array(params[1]))
-
- self.Dist = Dist_list[Dist_idx]
- self.K = K_list[K_idx]
- self.data = train_data
- self.label = train_label
-
- return ac_array
-
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- # If test data has been inputed & Model has been obtained
- predictions = []
- # For every point(target) in test data
- for i in range(len(test_data)):
- target = test_data[i]
- prediction = self.predict_for_one(
- self.K, self.Dist,
- target,
- self.data,
- self.label)
- predictions.append(prediction)
-
- return np.array(predictions)
-
-
-# ## Start of Program
-
-# In[143]:
-
-
-if __name__ == '__main__':
-
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "g":
- generate(
- Ns = [100, 250, 150],
-
- Means = [[50,50],
- [60,20],
- [20,60]],
-
- Covs = [[[60,-50],[-50,140]],
- [[130,10],[10,100]],
- [[120,20],[20,90]]],
-
- train_frac = 0.8
- )
-
- elif len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "d":
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
-
- display(train_data, train_label,
- 'train', 'Scatter Plot of Training Data')
- display(test_data, test_label,
- 'test', 'Scatter Plot of Testing Data')
- else:
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
-
- model = KNN()
-
- model.fit(
- K_list = [15, 20, 25],
- Dist_list = ["Euclidean", "Manhattan"],
- train_data = train_data,
- train_label = train_label)
-
- res = model.predict(test_data)
-
- print("acc =",np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label)))
-
-
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 6ae1a49f48c030f79bcc25f37bd717d6fe307c48..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,246 +0,0 @@
-# 课程报告
-
-## 说明
-
-我使用的包为numpy,在class KNN中:
-
-
-a.使用函数euclidean进行向量间欧式距离的计算
-
-
-b.使用closest函数进行逐个向量输入,分别计算它与全部train data的欧氏距离,并输出距它最近k个点出现次数最多train label。当最近k个点不存在出现次数最多train label(如出现次数均等),将进行label随机输出
-
-
-c.使用predict函数将全部test data逐个输入,得到预测结果
-
-
-d.使用choose函数,将预测结果与test label进行比对,结果相同取值为1,不同为0,进行准确率计算。k值选择范围根据训练与测试集数量决定(最小值为2,最大值为数据量的10%),从中选取使预测结果准确率最高k值,并输出对准确率预测
-
-
-## 数据生成 实验探究
-
-我使用以下参数生成了如下三个二维高斯分布,label分别为0,1,2
-
-
- label=0
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-10 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 10
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-20 & 25
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-
- label=1
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-23 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 22
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-16 & -5
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-
- label=2
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-10 & 5 \\\\
-5 & 10
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-20 & 25
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-这是我生成的训练集:
-
-
-
-
-Model accuracy decreases from 73% to 62.5% even though our data size doubled. This suggests sample size contributes much less to model accuracy compared with distribution parameters. This makes sense because if the data labeled by different categories does indeed come from the same distribution, increasing N should provide more evidence of the similarity between these different categories.
-
-## Summary
-
-The main takeaways for this exercise:
-
-Model accuracy depends more on distribution parameters and the choice of K. Distance method have little influence on model accuracy, and whether an increase of N improves model accuracy or not depends on if the true distributions of all categories are significantly different (Might be able to use p-value from a statistical test to evaluate).
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 1.png b/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 32d5ded9c9d662bf7eacaede5e9316ba1d545335..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 2.png b/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index c7e7752721f808ea5ca19a56a7e642badb1617fd..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 3.png b/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 5a3fd62c0681f995d32c1ea794258095239261ee..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 4.png b/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 4.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 9c1e05f712b290be595b12c812476c72e0f0002d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 4.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 5.png b/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 5.png
deleted file mode 100644
index e49ec9595ac9c813a2e6044375c534bb669b3a7c..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 5.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 6.png b/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 6.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 11a84369882f65a2a3e46237e51fe479d4f14b88..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 6.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 7.png b/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 7.png
deleted file mode 100644
index ee33c60766eb907d5b8992c24ca3806c297d9fc8..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 7.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 8.png b/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 8.png
deleted file mode 100644
index a3f42ac859f2ef35448cb16f0412df387ba8e7a8..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 8.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 9.png b/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 9.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 0de5d1f658bdd5860681cfee20432e8074f39a1d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/img/Figure 9.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 410b588394c97d15227671e94f6e24e6cbb46882..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/18340986009/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,249 +0,0 @@
-#!/usr/bin/env python
-# coding: utf-8
-
-# In[1]:
-
-
-import sys
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
-
-# ## Define Global Functions
-
-# In[139]:
-
-
-# Generate Training and Testing Sets
-def generate(Ns, Means, Covs, train_frac):
-
- # Generate 2-D data of N class
- data = list()
- label = list()
-
- for i in range(0,len(Ns)):
- Ci = np.random.multivariate_normal(Means[i], Covs[i], Ns[i])
- data.append(Ci)
- label.append([i]*Ns[i])
-
- data = np.array([v for subl in data for v in subl])
- label = np.array([v for subl in label for v in subl])
-
- #Assign random number
- idx = np.arange(sum(Ns))
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
-
- data = data[idx]
- label = label[idx]
-
- # Split into training and testing set
- split_point = int(label.size * train_frac)
- train_data, test_data = data[:split_point,], data[split_point:,]
- train_label, test_label = label[:split_point,], label[split_point:,]
-
- np.save("data.npy",((train_data, train_label),
- (test_data, test_label)))
-
- return train_data, train_label, test_data, test_label
-
-
-# Read in saved data
-def read():
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = np.load(
- "data.npy", allow_pickle = True)
- return (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
-
-
-# Create scatter plot of different categories
-def display(data, colorby, name, title):
- colors = ['red','grey','blue']
- datas =[[],[],[]]
-
- for i in range(len(data)):
- datas[colorby[i]].append(data[i])
-
- for i in range(len(datas)):
- each = np.array(datas[i])
- if len(each) == 0:
- continue
- plt.scatter(each[:, 0], each[:, 1],
- marker = 'o',
- color = colors[i],
- alpha = 0.7)
-
- plt.xlabel("X1")
- plt.ylabel("X2")
- plt.title(title)
- plt.savefig(f'img/{name}')
- plt.show()
-
-
-# ## Define Class KNN
-
-# In[140]:
-
-
-class KNN:
-
- def __init__(self):
-
- self.K = None
- self.Dist = None
- self.data = None
- self.label = None
-
-
- # Calculate distance between two given points
- def get_distance(self, x, y, dist_type = "Euclidean"):
- dist = 0.0
- if "Euclidean" == dist_type:
- distance = 0.0
- for i in range(len(x)):
- distance += (x[i] - y[i])**2
- dist = np.sqrt(distance)
-
- if "Manhattan" == dist_type:
- distance = 0.0
- for i in range(len(x)):
- distance += np.abs(x[i] - y[i])
- dist = distance
-
- return dist
-
-
- # Make a prediction for one point
- def predict_for_one(self, K, Dist, target, train_data, train_label):
- # Calculate distances between target point and other points
- dists = []
- neighbors = []
-
- for i in range(len(train_data)):
- dist = self.get_distance(target, train_data[i], Dist)
- dists.append((train_data[i], train_label[i], dist))
-
- # Get the K nearest neighbors
- dists.sort(key = lambda e: e[-1])
- neighbors = dists[1:K+1]
-
- # Make prediction based on conditional probabilities
- neighbors_class = [e[-2] for e in neighbors]
- prediction = max(neighbors_class, key = neighbors_class.count)
-
- return prediction
-
-
- # Calculate model accuracy
- def calc_accuracy(self, K, Dist, train_data, train_label):
- predictions = []
- # Make predictions for the training data
- for i in range(len(train_label)):
- target = train_data[i]
- prediction = self.predict_for_one(
- K, Dist, target, train_data, train_label
- )
- predictions.append(prediction)
-
- correct = 0
- for i in range(len(predictions)):
- if train_label[i] == predictions[i]:
- correct += 1
- accuracy = correct / len(predictions) * 100
-
- return accuracy
-
-
- # Find the Optimal K & Distance combination
- def fit(self, K_list, Dist_list, train_data, train_label):
-
- # Loop through the given options for K and distance methods
- accuracy_list = []
- for i in range(len(Dist_list)):
- Dist = Dist_list[i]
- dum_list = []
- for j in range(len(K_list)):
- K = K_list[j]
- accuracy = self.calc_accuracy(
- K, Dist, train_data, train_label
- )
- dum_list.append(accuracy)
- accuracy_list.append(dum_list)
-
- # Find the K & Distance method that gives the highest accuracy
- ac_array = np.array(accuracy_list)
- global_max = max([max(subl) for subl in accuracy_list])
- params = np.where(ac_array == global_max)
-
- # Assign the optimal parameters to KNN object
- # Randomly choice one if there exist more than one highest accuracy
- Dist_idx = np.random.choice(np.array(params[0]))
- K_idx = np.random.choice(np.array(params[1]))
-
- self.Dist = Dist_list[Dist_idx]
- self.K = K_list[K_idx]
- self.data = train_data
- self.label = train_label
-
- return ac_array
-
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- # If test data has been inputed & Model has been obtained
- predictions = []
- # For every point(target) in test data
- for i in range(len(test_data)):
- target = test_data[i]
- prediction = self.predict_for_one(
- self.K, self.Dist,
- target,
- self.data,
- self.label)
- predictions.append(prediction)
-
- return np.array(predictions)
-
-
-# ## Start of Program
-
-# In[143]:
-
-
-if __name__ == '__main__':
-
- if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "g":
- generate(
- Ns = [100, 250, 150],
-
- Means = [[50,50],
- [60,20],
- [20,60]],
-
- Covs = [[[60,-50],[-50,140]],
- [[130,10],[10,100]],
- [[120,20],[20,90]]],
-
- train_frac = 0.8
- )
-
- elif len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "d":
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
-
- display(train_data, train_label,
- 'train', 'Scatter Plot of Training Data')
- display(test_data, test_label,
- 'test', 'Scatter Plot of Testing Data')
- else:
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
-
- model = KNN()
-
- model.fit(
- K_list = [15, 20, 25],
- Dist_list = ["Euclidean", "Manhattan"],
- train_data = train_data,
- train_label = train_label)
-
- res = model.predict(test_data)
-
- print("acc =",np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label)))
-
-
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 6ae1a49f48c030f79bcc25f37bd717d6fe307c48..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,246 +0,0 @@
-# 课程报告
-
-## 说明
-
-我使用的包为numpy,在class KNN中:
-
-
-a.使用函数euclidean进行向量间欧式距离的计算
-
-
-b.使用closest函数进行逐个向量输入,分别计算它与全部train data的欧氏距离,并输出距它最近k个点出现次数最多train label。当最近k个点不存在出现次数最多train label(如出现次数均等),将进行label随机输出
-
-
-c.使用predict函数将全部test data逐个输入,得到预测结果
-
-
-d.使用choose函数,将预测结果与test label进行比对,结果相同取值为1,不同为0,进行准确率计算。k值选择范围根据训练与测试集数量决定(最小值为2,最大值为数据量的10%),从中选取使预测结果准确率最高k值,并输出对准确率预测
-
-
-## 数据生成 实验探究
-
-我使用以下参数生成了如下三个二维高斯分布,label分别为0,1,2
-
-
- label=0
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-10 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 10
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-20 & 25
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-
- label=1
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-23 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 22
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-16 & -5
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-
- label=2
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-10 & 5 \\\\
-5 & 10
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-20 & 25
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-这是我生成的训练集:
-
-
- -
-
-这是我生成的测试集:
-
-
-
-
-
-这是我生成的测试集:
-
-
- -
-
-可以通过如下表格来报告我的实验结果
-
-Algo |kvalue|Acc |
------| ---- |---- |
-KNN | 5 |0.6225 |
-
-
-
-
-由于label=0和label=2的对应高斯分布较靠近,导致训练准确性为62.25%。
-
-
-为进一步探究高斯分布距离对预测准确性影响,我使用如下参数进行分布生成:
-
- label=0
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-10 & 2.1 \\\\
-2.1 & 12
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-20 & 25
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-
- label=1
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-23 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 22
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-20 & 25
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-
- label=2
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-10 & 5 \\\\
-5 & 10
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-20 & 25
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-这是我生成的训练集:
-
-
-
-
-
-可以通过如下表格来报告我的实验结果
-
-Algo |kvalue|Acc |
------| ---- |---- |
-KNN | 5 |0.6225 |
-
-
-
-
-由于label=0和label=2的对应高斯分布较靠近,导致训练准确性为62.25%。
-
-
-为进一步探究高斯分布距离对预测准确性影响,我使用如下参数进行分布生成:
-
- label=0
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-10 & 2.1 \\\\
-2.1 & 12
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-20 & 25
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-
- label=1
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-23 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 22
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-20 & 25
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-
- label=2
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-10 & 5 \\\\
-5 & 10
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-20 & 25
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-这是我生成的训练集:
-
-
- -
-这是我生成的测试集:
-
-
-
-
-这是我生成的测试集:
-
-
- -
-
-可以通过如下表格来报告我的实验结果
-
-Algo |kvalue|Acc |
------| ---- |---- |
-KNN | 12 |0.485 |
-
-此时3个高斯分布距离彼此都很近,进行不同k值选取,实验的准确性最高达到48.5%。
-
-|k |Acc |
------ | ---- |
-| 2 | 0.4525 |
-| 3 | 0.4375 |
-| 4 | 0.4475 |
-| 5 | 0.4300 |
-| 6 | 0.4675 |
-| 7 | 0.4525 |
-| 8 | 0.4775 |
-| 9 | 0.4450 |
-| 10 | 0.4650 |
-| 11 | 0.4700 |
-| 12 | 0.4850 |
-| 13 | 0.4750 |
-| 14 | 0.4650 |
-| 15 | 0.4625 |
-| 16 | 0.4775 |
-| 17 | 0.4650 |
-| 18 | 0.4800 |
-| 19 | 0.4700 |
-| 20 | 0.4725 |
-
-
-改变高斯分布距离,我使用以下参数生成高斯分布。
-
-
- label=0
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-10 & 2.1 \\\\
-2.1 & 12
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-20 & 25
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-
- label=1
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-23 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 22
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-16 & -5
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-
- label=2
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-10 & 5 \\\\
-5 & 10
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-3 & 5
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-这是我生成的训练集:
-
-
-
-
-
-可以通过如下表格来报告我的实验结果
-
-Algo |kvalue|Acc |
------| ---- |---- |
-KNN | 12 |0.485 |
-
-此时3个高斯分布距离彼此都很近,进行不同k值选取,实验的准确性最高达到48.5%。
-
-|k |Acc |
------ | ---- |
-| 2 | 0.4525 |
-| 3 | 0.4375 |
-| 4 | 0.4475 |
-| 5 | 0.4300 |
-| 6 | 0.4675 |
-| 7 | 0.4525 |
-| 8 | 0.4775 |
-| 9 | 0.4450 |
-| 10 | 0.4650 |
-| 11 | 0.4700 |
-| 12 | 0.4850 |
-| 13 | 0.4750 |
-| 14 | 0.4650 |
-| 15 | 0.4625 |
-| 16 | 0.4775 |
-| 17 | 0.4650 |
-| 18 | 0.4800 |
-| 19 | 0.4700 |
-| 20 | 0.4725 |
-
-
-改变高斯分布距离,我使用以下参数生成高斯分布。
-
-
- label=0
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-10 & 2.1 \\\\
-2.1 & 12
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-20 & 25
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-
- label=1
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-23 & 0 \\\\
-0 & 22
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-16 & -5
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-
- label=2
-$$
-\begin{array}{l}
-\Sigma=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
-10 & 5 \\\\
-5 & 10
-\end{array}\right] \\\\
-\mu=\left[\begin{array}{ll}
-3 & 5
-\end{array}\right]
-\end{array}
-$$
-
-这是我生成的训练集:
-
-
- -
-
-这是我生成的测试集:
-
-
-
-
-
-这是我生成的测试集:
-
-
- -
-
-可以通过如下表格来报告我的实验结果
-
-Algo |kvalue|Acc |
------| ---- |---- |
-KNN | 2 |0.9975 |
-
-
-此时3个高斯分布距离较远,通过较少的k值即可得到较为准确的判断。增加高斯分布间的距离可以提升实验的准确性。
-
-## 代码使用方法
-
-```bash
-改变mode数值:
-mode=0 #数据生成
-mode=1 #数据可视化
-mode取非0-1值 #训练和测试
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/test 1.png b/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/test 1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index bf515460fd3bf6e81d027117399749a3b10c29fe..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/test 1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/test 2.png b/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/test 2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 1d962680d1019a7b4946d61b7a66ede507ad0d4c..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/test 2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/test 3.png b/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/test 3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 3ab9d8b6157ed19597c283688c34daeef54beeeb..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/test 3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/train 1.png b/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/train 1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index dbe1db24a876a4b564d98b3009aefae717ba433c..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/train 1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/train 2.png b/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/train 2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 406126994e9ac71f4a43d6d182e72d88e4eaceed..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/train 2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/train 3.png b/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/train 3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 761f9ee658095183c7c2a3925b6cbb9c51fde989..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/train 3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 0f5e2424b154e74548445bef39f513dee6b40c94..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,103 +0,0 @@
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import numpy as np
-
-class KNN():
- def euclidean(self,v1,v2):
- return np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(v1 - v2)))
- def fit(self, X_train, Y_train):
- self.train_data = train_data
- self.train_label = train_label
- def predict(self, train_data,k):
- predictions = []
- for item in train_data:
- label = self.closest(item,k)
- predictions.append(label)
- return predictions
-
- def closest(self, item,k):
- min_ind = 0
- distlst=[]
- idxlst=list(range(len(self.train_data)))
- #get distance between test_data with train_data
- for i in range(0,len(self.train_data)):
- distlst.append(self.euclidean(item, self.train_data[i]))
- #make up a dictionary with distance and index
- distdict=dict(zip(idxlst,distlst))
- distdict=dict(sorted(distdict.items(),key=lambda item:item[1]))
- #get first K nearest position
- min_ind=list(dict(list(distdict.items())[:k]).keys())
- min_dist=[self.train_label[i] for i in min_ind]
- return max(min_dist,key=min_dist.count)
-
- def choose(self,test_data,test_label):
- acclst=[]
- for k in range(2,7):
- res=self.predict(test_data,k)
- acc=np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label))
- acclst.append(acc)
- max_acc=max(acclst)
- max_k=acclst.index(max_acc)+2
- return max_k,max_acc
-
-
-def generate():
- mean = (20, 25)
- cov = np.array([[10,2.1], [2.1, 12]])
- x = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (800,))
-
- mean = (16, -5)
- cov = np.array([[23, 0], [0, 22]])
- y = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (200,))
-
- mean = (3, 5)
- cov = np.array([[10,5],[5,10]])
- z = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (1000,))
-
- idx = np.arange(2000)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- data = np.concatenate([x,y,z])
- label = np.concatenate([
- np.zeros((800,),dtype=int),
- np.ones((200,),dtype=int),
- np.ones((1000,),dtype=int)*2
- ])
- data = data[idx]
- label = label[idx]
-
- train_data, test_data = data[:1600,], data[1600:,]
- train_label, test_label = label[:1600,], label[1600:,]
- np.save("data.npy",((train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
- ))
-
-def display(data, label, name):
- datas =[[],[],[]]
- for i in range(len(data)):
- datas[label[i]].append(data[i])
-
- for each in datas:
- each = np.array(each)
- plt.scatter(each[:, 0], each[:, 1])
- label=[str(i) for i in list(range(len(datas)))]
- plt.legend(['label '+i for i in label])
- plt.show()
-
-def read():
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = np.load("data.npy",allow_pickle=True)
- return (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- mode=0
- if mode == 0:
- generate()
- if mode == 1:
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
- display(train_data, train_label, 'train')
- display(test_data, test_label, 'test')
- else:
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
-
- model = KNN()
- model.fit(train_data, train_label)
- k ,acc = model.choose(test_data,test_label)
- print("k=",k,"acc=",acc*100,"%")
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 187378e8d1e1fff3b396413ddc2e09588a505b13..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,142 +0,0 @@
-# PRML21春-HW1-KNN分类器
-
-### 简介
-
-实现KNN分类器并探索细节。本设计实现了一系列KNN算法的变种,包括:
-
-- 实现了数据的min-max标准化
-- 证明了标准化的有效性
-
-- 自动寻找较优的K值
-- 实现了两种距离(欧氏距离/曼哈顿距离)的算法
-- 比较了两种距离尺度的特性
-
-- 实现了对每个训练集中点的置信度的加权
-- 实现了对K个近邻点按距离的加权
-- 证明以上两种加权方式是有效的消融实验
-- 探索常规KNN算法对数据分布的响应
-- 验证了加权后的算法相对于常规算法对数据分布的鲁棒性
-
-
-
-### 前言
-
-本实验没有探索数据本身对于常规KNN算法的影响。
-
-我认为“点集重叠越少表现越好”之类的结论是显而易见的,不希望在数据本身上花太多时间。
-
-此外,我没有对数据可视化,因为数据的分布给定之后,大致可以预见其可视化结果。本设计中实现了许多有意义的改进,因此重点在于算法本身的探索上,与作业手册的第四条“修改数据集的属性(例如:不同高斯分布之间的距离),进行探究性实验”有出入,还望助教老师多多包涵~
-
-
-
-### min-max标准化
-
-#### 实现细节
-
-对每一个channel,都实现了
-
-`x=(x-(该channel中最小值))/((该channel中最大值)-(该channel中最小值))`
-
-的标准化,将所有的值映射到`[0,1]`上,并且会在训练集中记录训练集上每一channel的最大/最小值,并对测试集做同样的映射,以保证两者采用同一映射,如果对两个数据集分别归一化,将会有标准化方式不统一的问题。
-
-#### 正确性
-
-其带来的作用是显而易见的,在闵氏距离族中,不论采用何种距离度量,都会出现同一问题:两点之间的距离最主要受尺度最大的特征影响,这一显然的结论不需要实验便可以举出例子证明。
-
-经典的波士顿房价预测问题(尽管其原型是回归问题,仍然可以用KNN算法分析房价等级,例如高、中、低等):“历年房价中位数”的尺度是万数量级的,而“交通便利指数”、“环保指数”、“与就业中心的距离”都是十分有用的特征,然而其尺度远比房价小!
-
-如果不加处理就直接进行KNN算法,显然其他特征全部被忽略,KNN算法将完全被历年房价主导!这是不合理的。在此处尺度最大的特征恰巧是相关性极强的,算法尚能工作,如果尺度最大的恰巧是相关性低的,则算法将完全失效!
-
-
-
-### 自动寻找K值
-
-由于算法之间(自动寻找K值,置信度加权,距离加权)互相牵制,因此在搜索K值时只能采用常规KNN算法,本算法在`1~min(16,训练集样本个数)`之中搜索所有K,找到准确率最高的K值。
-
-在示例程序中,将会自动选择K=1,在自动生成的样本中,参数如下:
-
-| Distribution | Mean | Cov | Number |
-| ------------ | ------ | ----------------- | ------ |
-| Class 0 | (1,2) | [[10, 0], [0, 2]] | 100 |
-| Class 1 | (4,5) | [[7, 3], [15, 1]] | 100 |
-| Class 2 | (-2,6) | [[0, 1], [1, 2]] | 100 |
-
-将会选择K=11. 两者的寻找过程如下两图:
-
-
-
-### Euclidean & Manhattan - 两种距离尺度
-
-本设计中实现了两种距离尺度中的KNN分类器。
-
-曼哈顿距离对每一个channel都是独立的,欧氏距离对每一维度求偏导时都与当前距离相关,因此可以预见的是,在距离较远时,两者表现将接近,在距离较近的时候,需要通过实验探索两者的差异。
-
-取两个分布方差矩阵均为单位阵,令其沿y=0.5x方向上其逐渐接近,其中一个分布的均值固定在`(0,0)`,另一分布均值分别为:`(0.1,0.2),(0.6,1.2),(1.1,2.2),(1.6,3.2),(2.1,4.2),(2.6,5.2)`。
-
-可以看到如下的变化:
-
-其中蓝线是欧几里得距离,绿线是曼哈顿距离,可见欧氏距离对两分布接近时处理的更好。
-
-p.s. 以上的实验采用常规KNN算法。
-
-
-
-### 置信度加权
-
-在两个分布有较大的重叠时,训练集中的重叠点本身也不能通过KNN以很高的置信度判断自身的类别,对这类点,其置信度应该降低。
-
-置信度的算法为:`K近邻点中与自身类别相同的点数/K`。
-
-实验证明这样的改变是有益的。在如下分布中做消融实验:
-
-| Distribution | Mean | Cov | Number |
-| ------------ | ------ | ----------------- | ------ |
-| Class 0 | (1,2) | [[10, 0], [0, 2]] | 100 |
-| Class 1 | (4,5) | [[7, 3], [15, 1]] | 100 |
-| Class 2 | (-2,6) | [[0, 1], [1, 2]] | 100 |
-
-常规KNN算法:acc = 0.85
-
-带置信度加权的KNN算法: 0.8666666666666667
-
-
-
-### 距离加权
-
-在一个K近邻范围内,有些点离待监测点较近,有些较远。有理由相信距离较近的点提供的置信度更少,因此需要实现距离加权。
-
-距离加权的算法为:`每个近邻点投票的权值为:D-(该近邻点与待监测点的距离/近邻范围内最远点与待监测点的距离)`。其中D为超参。
-
-实验得到,在如上分布中,D=1.8时表现最好,消融实验如下:
-
-常规KNN算法:acc = 0.85
-
-带距离加权的KNN算法: 0.8666666666666667
-
-
-
-### 联合加权
-
-综合以上两种加权方式,此时需要引入第二个超参,该超参作用于置信度加权,并且对于仅采用置信度加权时,其不起作用,由于需要将两个计算得到的权重相乘,该超参用于调节两者起到的作用之比例。
-
-联合加权算法为:`(K近邻点中与自身类别相同的点数/K-bias)*(D-(该近邻点与待监测点的距离/近邻范围内最远点与待监测点的距离))`。其中`bias`为引入的新超参,`D`为距离加权对应的超参。
-
-实验证明,取`bias=0.2`,`D=2.1`时,可以达到较好的效果。
-
-常规KNN算法:acc = 0.85
-
-带联合加权的KNN算法:acc = 0.8833333333333333
-
-
-
-### 对数据的鲁棒性
-
-可以预见,当数据比较接近时,这样的加权会有更好的表现,因为其更好的考虑了模糊点置信程度较低的性质,并且利用了靠近待分类点与距离较远的点之间的差异。
-
-下图为实验结果,其中蓝线为联合加权结果,绿线为常规KNN算法。
-
-
-
-### 总结
-
-本设计探索了更高效的KNN算法,采用联合加权的方式对邻接范围内的点做不同的处理,取得了较好的效果。
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_1.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index b006d52cf0b89e9497b213ec044b0224a5a620a7..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_2.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index d520d40d31644714b20789c236f9976818185cab..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_3.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index c643350e0310bac079cdd179a01cff9371b27475..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_4.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_4.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 6af94b33a92ba072e05b09dc9eff0ff3c6bc0d08..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_4.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index a231c833e05fe6cb7a43b4c7fdabab987978305a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,125 +0,0 @@
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-class KNN:
- def __init__(self):
- pass
-
- def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- self.len=train_data.shape[0]
- #standardize
- train_data=train_data.astype(np.float64)
- train_data=train_data.T
- self.channel=train_data.shape[0]
- self.mins=[]
- self.maxs=[]
- for data in train_data:
- self.mins.append(np.min(data))
- self.maxs.append(np.max(data))
- for i in range(data.shape[0]):
- data[i] = (data[i] - np.min(data)) / (np.max(data) - np.min(data))
- self.train_data=train_data.T
- self.train_label=train_label
-
- #grid search for K
- maxk, maxacc=0, 0
- for k in range(1,min(17,self.len)):
- acc=0
- for d in range(self.len):
- dists = []
- indexs = np.arange(self.len)
- for i in range(self.len):
- dists.append(self.euclidean(self.train_data[d], self.train_data[i]))
- dic = dict(zip(indexs, dists))
- dic = dict(sorted(dic.items(), key=lambda item: item[1]))
- min_indexs = list(dict(list(dic.items())[1:k+1]).keys())
- min_dists = [self.train_label[i] for i in min_indexs]
- if max(min_dists, key=min_dists.count) == self.train_label[d]:
- acc+=1
- if acc>maxacc:
- maxk, maxacc=k, acc
- self.K=maxk
-
- #credibility
- self.cred=[]
- for d in range(self.len):
- dists = []
- indexs = np.arange(self.len)
- for i in range(self.len):
- dists.append(self.euclidean(self.train_data[d], self.train_data[i]))
- dic = dict(zip(indexs, dists))
- dic = dict(sorted(dic.items(), key=lambda item: item[1]))
- min_indexs = list(dict(list(dic.items())[1:self.K+1]).keys())
- min_dists = [self.train_label[i] for i in min_indexs]
- self.cred.append(float(min_dists.count(max(min_dists, key=min_dists.count)))/self.K)
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- test_data=test_data.astype(np.float64)
- test_data=test_data.T
- for i in range(self.channel):
- for j in range(test_data.shape[1]):
- test_data[i][j] = (test_data[i][j] - self.mins[i]) / (self.maxs[i] - self.mins[i])
- test_data = test_data.T
- ans=[]
- for d in range(test_data.shape[0]):
- dists = []
- indexs = np.arange(self.len)
- for i in range(self.len):
- dists.append(self.euclidean(test_data[d], self.train_data[i]))
- dic = dict(zip(indexs, dists))
- dic = dict(sorted(dic.items(), key=lambda item: item[1]))
- min_indexs = list(dict(list(dic.items())[:self.K]).keys())
- min_dict={}
- for i in min_indexs:
- min_dict[self.train_label[i]]=min_dict.get(self.train_label[i],0)+(self.cred[i]-0.2)*(2.1-dic[i]/list(dic.items())[self.K-1][1])
- ans.append(max(min_dict, key=lambda k: min_dict[k]))
- return ans
-
-
- def euclidean(self, a, b):
- return np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(a-b)))
-
- def manhattan(self, a, b):
- return np.sum(abs(a-b))
-
-
-def dataset(mean1,mean2,cov1,cov2,mean3=None,cov3=None):
- mean=mean1
- cov=cov1
- x=np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (100,))
- mean=mean2
- cov=cov2
- y=np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (100,))
- num=300
- if mean3 is not None and cov3 is not None:
- mean=mean3
- cov=cov3
- z=np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (100,))
- idx=np.arange(num)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- if mean3 is not None and cov3 is not None:
- data=np.concatenate([x, y, z])
- label=np.concatenate([np.zeros((100,), dtype=np.int8), np.ones((100,), dtype=np.int8), np.ones((100,), dtype=np.int8) * 2])
- else:
- data=np.concatenate([x, y])
- label=np.concatenate([np.zeros((100,), dtype=np.int8), np.ones((100,), dtype=np.int8)])
- data=data[idx]
- label=label[idx]
- split=int(num*0.8)
- train_data, test_data=data[:split,:], data[split:,:]
- train_label, test_label=label[:split], label[split:]
- np.save("train_data.npy",train_data)
- np.save("test_data.npy",test_data)
- np.save("train_label.npy",train_label)
- np.save("test_label.npy",test_label)
-
-def dataload():
- train_data, train_label, test_data, test_label = np.load("train_data.npy",allow_pickle=True),np.load("train_label.npy",allow_pickle=True),np.load("test_data.npy",allow_pickle=True),np.load("test_label.npy",allow_pickle=True)
- return train_data, train_label, test_data, test_label
-
-if __name__ == '__main__':
- dataset((1,2),(4,5),np.array([[10, 0], [0, 2]],dtype=np.float64),np.array([[7, 3], [15, 1]],dtype=np.float64),(-2,6),np.array([[0, 1], [1, 2]],dtype=np.float64))
- train_data, train_label, test_data, test_label=dataload()
- model=KNN()
- model.fit(train_data,train_label)
- res=model.predict(test_data)
- print("acc =",np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label)))
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/README.md
deleted file mode 100755
index 9d46bef52b53b558ad6ec716ee26dce570e77a87..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,213 +0,0 @@
-
-
-[TOC]
-
-我只使用了numpy和matplotlib两个库实现了KNN的,所以代码应该可以完成在额外的任务。
-
-#### 一、模型的实现
-
-对于单个测试数据的knn分类网络的实现:
-
-```python
-inX=test_data[i]
-#计算欧氏距离
-diffMat=np.tile(inX,(dataSetSize,1))-tra_data
-sqDifMat=diffMat**2
-sqDistances=sqDifMat.sum(axis=1)
-distances=sqDistances**0.5
-#对计算得到的距离对应的序号进行排序
-sortedDistIndicies=distances.argsort()
-#统计最近的k个点中各个类别的数量
-classCount={}
-for j in range(k):
- Label = tra_label[sortedDistIndicies[j]]
- classCount[Label] = classCount.get(Label,0) + 1
-#得到对于类别的预测
-max_count=0
-for key,value in classCount.items():
-if value >max_count :
- max_count = value
- pred_label=key
-```
-
-对与KNN fit() 部分的实现:
-
-将数据集按照8:2的比例进行划分后,对K进行拟合,多次重复在训练集上进行单次的knn分类预测,选出正确率最高的K值。
-
-~~~python
-def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- self.train_data=train_data
- self.train_label=train_label
- N=train_data.shape[0]
- cut=int(N*0.8)
-
- tra_data, test_data = train_data[:cut,], train_data[cut:,]
- tra_label, test_label = train_label[:cut,], train_label[cut:,]
-
- dataSetSize=tra_data.shape[0]
- test_number=test_data.shape[0]
-
- best_k=0
- max_score=0
- if N<6 :
- k_range=N
- else :
- k_range=20
-
- for k in range(2,k_range):
- total_correct=0
- for i in range(0,test_number):
- inX=test_data[i]
- #计算欧氏距离
- diffMat=np.tile(inX,(dataSetSize,1))-tra_data
- sqDifMat=diffMat**2
- sqDistances=sqDifMat.sum(axis=1)
- distances=sqDistances**0.5
- #对计算得到的距离对应的序号进行排序
- sortedDistIndicies=distances.argsort()
- #统计最近的k个点中各个类别的数量
- classCount={}
- for j in range(k):
- Label = tra_label[sortedDistIndicies[j]]
- classCount[Label] = classCount.get(Label,0) + 1
- #得到对于类别的预测
- max_count=0
- for key,value in classCount.items():
- if value >max_count :
- max_count = value
- pred_label=key
-
- if pred_label ==test_label[i]:
- total_correct=total_correct+1
- #选择正确率最高的K值
- score=total_correct*1.0/test_number
- if score>max_score:
- max_score=score
- best_k=k
- print("Best K: %d"%(best_k))
- self.k=best_k
-~~~
-
-#### 二、实验数据的生成
-
-通过 np.random.multivariate_normal() 生成数据集
-
-~~~python
- mean = (1, 1)
- cov = np.array([[10, 0], [0, 10]])
- x1 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (400,))
-
- mean = (1, 12)
- x2 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (400,))
-
- mean = (12, 1)
- x3 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (400,))
-
- mean = (12, 12)
- x4 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (400,))
-~~~
-
-生成的训练集:
-
-生成的测试集:
-
-训练结果:
-
-| K | 准确率 |
-| ---- | :------- |
-| 10 | 0.884375 |
-
-#### 三、探究实验
-
-##### 1. 修改mean参数
-
-首先修改成如下形式,使得四类点分布的更开
-
-~~~python
-mean = (1, 1) mean = (1, 15) mean = (15, 1) mean = (15, 15)
-~~~
-
-得到的训练集:
-
-得到的测试集:
-
-训练结果:
-
-| K | 准确率 |
-| ---- | -------- |
-| 11 | 0.978125 |
-
-可以看到不同的数据分布更开后,准确率大大提升。
-
-
-
-修改成以下的形式后,不同的数据更加集中:
-
-~~~python
-ean = (1, 1) mean = (1, 8) mean = (8, 1) mean = (8, 8)
-~~~
-
-生成的训练集:
-
-生成的测试集:
-
-训练结果:
-
-| K | 准确率 |
-| ---- | ------ |
-| 18 | 0.7 |
-
-可以看到准确率大大降低。
-
-结论:KNN分类算法的准确性依赖于数据的分布,当不同种类的数据越集中(重合的部分越多时),效果越差;
-
-反之,重合部分越少,分类结果越好。
-
-##### 2.对cov参数的修改
-
-修改cov,使得方差更大,同类数据更离散:
-
-~~~python
-cov = np.array([[30, 0], [0, 30]])
-~~~
-
-生成的训练集:
-
-生成的测试集:
-
-测试结果:
-
-| K | 准确率 |
-| ---- | -------- |
-| 18 | 0.690625 |
-
-可以看到数据更离散后,准确率下降
-
-
-
-再次修改cov,减少方差,使得同类数据更集中
-
-```python
-cov = np.array([[5, 0], [0, 5]])
-```
-
-生成的训练集:
-
-生成的测试集:
-
-训练结果:
-
-| K | 准确率 |
-| ---- | ------ |
-| 5 | 0.9875 |
-
-可以看到同类数据更集中,准确率越高。
-
-##### 探讨与结论
-
-可以和实验一得到相同的结论,不同类数据间分布的重合区域越小,KNN分类方法的准确率越高;重合区域越大,准确率越低。
-
-
-
-同时在上述实验中观察到的另一有趣现象是准确率越低时,K的最佳取指偏大;准确率越高时,K的取值偏小。但是在修改参数cov来控制正确率,希望得到准确率和K的关系时,却发现最佳K的选取还是具有一定的随机性,没有找到一般规律。
-
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_1.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_1.png
deleted file mode 100755
index e4a5d05eb4f6ccb904e8fd207fded8cf0b68b43c..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_10.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_10.png
deleted file mode 100755
index c9002a2fdce20748784f39dfaac3a0e1ca956f06..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_10.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_2.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_2.png
deleted file mode 100755
index c4cb6a263cd63039ad370eca82607f50666592b7..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_3.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_3.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 24fc664d1ea502c02c96a4deca581dc42fc465cd..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_4.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_4.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 1a3fa01d1aa274fb14dca65e961793de8f2174ca..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_4.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_5.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_5.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 4afbaeb755e3460b5f5e547d8e43e5221cd44c17..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_5.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_6.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_6.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 4dd7b5c0d0d15d0bfb3f47c5db12a5a378e17144..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_6.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_7.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_7.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 89613e8f29af003f9ad06af59112d5199da8d5a9..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_7.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_8.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_8.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 87a4ebbe6926fe0a26cc6e91c6c31e96b769736b..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_8.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_9.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_9.png
deleted file mode 100755
index dff482725b27547590be277cdba748ba1bc1305f..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_9.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/source.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 43e2a2ec214289e40b5a5c7e99b49087695fc828..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,154 +0,0 @@
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
-class KNN:
-
- def __init__(self):
- pass
-
- #def settled_knn(self,test_data,train_data,train_label) :
-
- def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- self.train_data=train_data
- self.train_label=train_label
- N=train_data.shape[0]
- cut=int(N*0.8)
-
- tra_data, test_data = train_data[:cut,], train_data[cut:,]
- tra_label, test_label = train_label[:cut,], train_label[cut:,]
-
- dataSetSize=tra_data.shape[0]
- test_number=test_data.shape[0]
-
- best_k=0
- max_score=0
- if N<6 :
- k_range=N
- else :
- k_range=20
-
- for k in range(2,k_range):
- total_correct=0
- for i in range(0,test_number):
- inX=test_data[i]
-
- diffMat=np.tile(inX,(dataSetSize,1))-tra_data
-
- sqDifMat=diffMat**2
- sqDistances=sqDifMat.sum(axis=1)
- distances=sqDistances**0.5
-
- sortedDistIndicies=distances.argsort()
-
- classCount={}
- for j in range(k):
- Label = tra_label[sortedDistIndicies[j]]
- classCount[Label] = classCount.get(Label,0) + 1
- max_count=0
- for key,value in classCount.items():
- if value >max_count :
- max_count = value
- pred_label=key
-
- if pred_label ==test_label[i]:
- total_correct=total_correct+1
-
- score=total_correct*1.0/test_number
- if score>max_score:
- max_score=score
- best_k=k
- print("Best K: %d"%(best_k))
- self.k=best_k
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- dataSetSize=self.train_data.shape[0]
- test_number=test_data.shape[0]
- ans_label=np.array([])
- for i in range(0,test_number):
- inX=test_data[i]
-
- diffMat=np.tile(inX,(dataSetSize,1))-self.train_data
-
- sqDifMat=diffMat**2
- sqDistances=sqDifMat.sum(axis=1)
- distances=sqDistances**0.5
-
- sortedDistIndicies=distances.argsort()
- classCount={}
- for j in range(self.k):
- voteIlabel = self.train_label[sortedDistIndicies[j]]
- classCount[voteIlabel] = classCount.get(voteIlabel,0) + 1
-
- max_count=0
- pred_label=self.train_label[0]
- for key,value in classCount.items():
- if value >max_count :
- max_count = value
- pred_label=key
-
- ans_label=np.append(ans_label,pred_label)
- return ans_label
-
-def generate():
- mean = (1, 1)
- cov = np.array([[10, 0], [0, 10]])
- x1 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (400,))
-
- mean = (1, 12)
- cov = np.array([[10, 0], [0, 10]])
- x2 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (400,))
-
- mean = (12, 1)
- cov = np.array([[10, 0], [0, 10]])
- x3 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (400,))
-
- mean = (12, 12)
- cov = np.array([[10, 0], [0, 10]])
- x4 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (400,))
-
- X = np.concatenate([x1, x2, x3, x4])
- Y = np.concatenate([
- np.zeros((400,),dtype=int),
- np.ones((400,),dtype=int),
- np.ones((400,),dtype=int)*2,
- np.ones((400,),dtype=int)*3
- ])
- shuffled_indices = np.random.permutation(1600)
- data=X[shuffled_indices]
- label=Y[shuffled_indices]
- total=1600
- cut=int(total*0.8)
- train_data, test_data = data[:cut,], data[cut:,]
- train_label, test_label = label[:cut,], label[cut:,]
-
- np.save("data.npy",(
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
- ))
-
-def read():
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = np.load("data.npy",allow_pickle=True)
- return (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
-
-def display(data,label,name):
- datas=[[],[],[],[]]
- for i in range(len(data)):
-
- datas[label[i]].append(data[i])
-
- for each in datas:
- each=np.array(each)
- plt.scatter(each[:,0],each[:,1])
- #plt.savefig(f'imag/{name}')
- plt.show()
-
-
-if __name__ == '__main__':
- generate()
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
- display(train_data, train_label, 'train')
- display(test_data, test_label, 'test')
-
- model = KNN()
- model.fit(train_data, train_label)
- res = model.predict(test_data)
- print("acc =",np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label)))
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/README.md b/assignment-2/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..63b9c33a1fdb2798e9e3c812c958283502b98f8d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,116 @@
+# 作业-2
+
+本次作业有两个选题,大家可以任选其一完成。
+
+## 选题1:前馈神经网络
+
+本次作业要求使用 NumPy 实现一种简单的前馈神经网络。你需要先实现 Matmul, Relu, Log, Softmax 等支持前馈计算和反向传播的算子,再利用这些算子构建一个简单的神经网络。最后,你需要使用这个模型在 MNIST 数据集上进行训练和测试,并完成实验报告。
+
+本次作业会考察你使用 NumPy 和 PyTorch 编程的能力以及对前馈神经网络背后数学知识的理解。
+
+### 更新 2021.4.25
+
+1. 修复了 torch_mnist.py 中把 softmax/log 算子输出的梯度当成了输入的梯度的问题。 现在 NumpyModel 中的 softmax_grad, log_grad 等均为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+2. 更新了 numpy_fnn.py, numpy_mnist.py, tester_demo.py 中的训练模型代码的结构,把 loss 的计算和反向传播的代码集中到 NumpyLoss 类中,便于理解。
+
+**已经完成作业的同学需要修改 numpy_fnn.py 中的 NumpyModel.backward 方法,并参考我们更新的代码来使用 NumpyLoss 类**
+
+> 以上问题的反馈来自学号尾号为 116, 154, 213 的同学
+
+### 提供材料
+
+你可以在 `handout-1/` 文件夹下找到如下文件,你需要将这些文件复制到自己的工作目录下进行作业,不过你最终只需要提交其中的部分文件。
+
+- numpy_fnn.py: 这个文件给出了你需要实现的算子和模型的框架,你只需要完成填空即可
+- tester_demo.py: 这是一个自动测试文件,它会测试你在 `numpy_fnn.py` 中实现的代码
+- torch_mnist.py: 使用 PyTorch 实现神经网络的代码,你需要按照其中定义的网络结构在 `numpy_fnn.py` 中构建网络
+- numpy_mnist.py: 使用 NumPy 搭建的神经网络进行训练测试的代码,如果 `numpy_fnn.py` 实现正确,它是可以直接运行的
+- utils.py: 实现了一些辅助性的函数,如果你想修改这些函数,请在 `numpy_mnist.py` 中重写
+
+### 提交内容
+
+- README.md: 课程作业报告
+- numpy_fnn.py: 你用 NumPy 实现的算子和模型,我们会对该代码进行自动测试
+- numpy_mnist.py: 你进行训练和测试的代码,我们会结合你的报告和代码进行评分
+
+提交方法参见[提交指南](https://gitee.com/fnlp/prml-21-spring#提交指南)
+
+### 实验环境
+
+```bash
+conda create -n assignment-2 python=3.8 -y
+conda activate assignment-2
+pip install numpy
+pip install matplotlib
+pip install torch
+pip install torchvision
+```
+
+### 实现模型
+
+你首先需要参考课内知识在 `numpy_fnn.py` 中实现 Matmul, Relu, Log, Softmax 等支持前馈计算和反向传播的算子。在实现过程中,你可以查看 `tester_demo.py` 中的测试代码,了解你需要实现的算子与 PyTorch 中的哪个算子相对应。 在安装好实验环境之后,你可以在工作目录下运行 `tester_demo.py` 来评测自己实现的算子是否符合要求。注意,在实现反向传播时,你可以使用 `self.memory` 中存下来的相关变量的值。
+
+在实现基础算子之后,你需要按照 `torch_mnist.py` 中定义的网络结构在 `numpy_fnn.py` 中补全 `NumpyModel` 的代码。注意,在反向传播时,你需要更新 `self.x1_grad`, `self.W1_grad` 等全部梯度的值。你可以查看 `tester_demo.py` 中的代码来了解评测标准,并尝试运行它进行评测。
+
+我们最终会使用自动评测代码来测试你提交的 `numpy_fnn.py` 文件,测试代码与 `tester_demo.py` 基本一致,但测试环境中会屏蔽 NumPy 之外的第三方包,你需要确保自己的 `numpy_fnn.py` 中只使用了 NumPy。
+
+除此之外,你还需要在报告中写出你实现算子反向传播的公式推导,你实现的代码需要和你推导的公式对应。
+
+### 进行实验
+
+在 `numpy_fnn.py` 中补全 `NumpyModel` 之后,你需要修改 `numpy_mnist.py` 中的代码,进行模型的训练和测试。其中,你需要使用 NumPy 实现 `mini_batch` 函数,替换 `utils.py` 中使用 PyTorch 实现的 `mini_batch` 函数。
+
+你可以使用现有模型进行若干实验,并在报告中介绍。因为这只是一个简单的作业,我们不推荐你尝试更多复杂的网络结构。如果你一定要尝试,**请勿修改 `numpy_fnn.py` 中的模型结构**,因为这样会影响你在自动测试中的得分;你可以在 `numpy_mnist.py` 中编写你的其他模型并进行实验,但这并不会让你获得更多的分数。
+
+我们提供了两个方向进行扩展探究,每个方向可以获得最多 10% 的附加分。如果你进行了拓展探究,请在报告中单独列出。
+
+探究1:实现 momentum、Adam 等其它优化方法并进行对比实验
+
+探究2:调研 PyTorch 中权重初始化的方法,并实现代码替换 `get_torch_initialization` 函数
+
+### 评分细则
+
+自动测试的七个测试点对应 `numpy_fnn.py` 中的七个空,附加分和其它部分的总和不超过 100%。
+
+- 自动测试(60%)
+ - Matmul 的反向传播 (5%)
+ - Relu 的反向传播 (5%)
+ - Log 的反向传播 (5%)
+ - Softmax 的前向计算 (5%)
+ - Softmax 的反向传播 (10%)
+ - FNN 的前向计算 (10%)
+ - FNN 的反向传播 (20%)
+- 实验与报告 (40%)
+ - 模仿 `torch_mnist.py` 的代码,在 `numpy_mnist.py` 中进行模型的训练和测试,并在报告中介绍你的实验过程与结果 (20%)
+ - 在 `numpy_mnist.py` 中只用 NumPy 实现 `mini_batch` 函数,替换 `utils.py` 中使用 PyTorch 实现的 `mini_batch` 函数 (10%)
+ - 在报告中推导 `numpy_fnn.py` 中实现算子的反向传播计算公式 (10%)
+- 附加分 (20%)
+ - 实现 momentum、Adam 等其它优化方法并进行对比实验 (10%)
+ - 调研 PyTorch 中权重初始化的方法,并实现代码替换 `get_torch_initialization` 函数 (10%)
+
+## 选题2
+
+理论和实验证明,一个两层的 ReLU 网络可以模拟任何有界闭集函数。
+
+### 提交内容
+
+- README.md: 课程作业报告
+- source.py: 你的实验代码
+
+### 具体要求
+
+你首先需要在报告中用理论证明这个结论,并给出你在证明过程中所引用定理的出处和证明过程(如果出处中有证明过程则可以省略)。
+
+其次,你需要使用 NumPy 或 PyTorch 编写实验来证明这个结论,你至少需要拟合 3 个不同类型的函数。最好可以写成可以接受任意函数做为输入,然后进行拟合的模式。
+
+### 评分细则
+
+- 课程报告 (50%)
+- 实验代码 (50%)
+ - 只使用 NumPy 实现模型 (10%)
+ - 拟合 3 个不同类型的函数的实验代码 (3*10%)
+ - 实现接受任意函数做为输入进行拟合的函数 (10%)
+- 附加分 (20%)
+ - 其它可以证明这一结论的实验,每个10%,附加分不超过20%,总分不超过 100%
+
+> 模式识别与机器学习 / 复旦大学 / 2021年春
diff --git a/assignment-2/handout-1/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/handout-1/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c2f5bf9d301a40d3390cd35eef2a9b1d0c2c4249
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/handout-1/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,162 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 1 #
+ ####################
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 2 #
+ ####################
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 3 #
+ ####################
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 4 #
+ ####################
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 5 #
+ ####################
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新。 softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ ####################
+ # code 6 #
+ ####################
+
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+
+ ####################
+ # code 7 #
+ ####################
+
+ pass
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
diff --git a/assignment-2/handout-1/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/handout-1/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c18db9439f10238e6d09b99a9e273b69f7725ff8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/handout-1/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, mini_batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+
+
+def numpy_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x.numpy())
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/handout-1/tester_demo.py b/assignment-2/handout-1/tester_demo.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..504b3eef50a6df4d0aa433113136add50835e420
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/handout-1/tester_demo.py
@@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
+import numpy as np
+import torch
+from torch import matmul as torch_matmul, relu as torch_relu, softmax as torch_softmax, log as torch_log
+
+from numpy_fnn import Matmul, Relu, Softmax, Log, NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from torch_mnist import TorchModel
+from utils import get_torch_initialization, one_hot
+
+err_epsilon = 1e-6
+err_p = 0.4
+
+
+def check_result(numpy_result, torch_result=None):
+ if isinstance(numpy_result, list) and torch_result is None:
+ flag = True
+ for (n, t) in numpy_result:
+ flag = flag and check_result(n, t)
+ return flag
+ # print((torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) - torch_result).abs().mean().item())
+ T = (torch_result * torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) < 0).sum().item()
+ direction = T / torch_result.numel() < err_p
+ return direction and ((torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) - torch_result).abs().mean() < err_epsilon).item()
+
+
+def case_1():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[5, 6])
+ W = np.random.normal(size=[6, 4])
+
+ numpy_matmul = Matmul()
+ numpy_out = numpy_matmul.forward(x, W)
+ numpy_x_grad, numpy_W_grad = numpy_matmul.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+ torch_W = torch.from_numpy(W).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_matmul(torch_x, torch_W)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ (numpy_W_grad, torch_W.grad)
+ ])
+
+
+def case_2():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[5, 6])
+
+ numpy_relu = Relu()
+ numpy_out = numpy_relu.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_relu.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_relu(torch_x)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def case_3():
+ x = np.random.uniform(low=0.0, high=1.0, size=[3, 4])
+
+ numpy_log = Log()
+ numpy_out = numpy_log.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_log.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_log(torch_x)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def case_4():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[4, 5])
+
+ numpy_softmax = Softmax()
+ numpy_out = numpy_softmax.forward(x)
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_softmax(torch_x, 1)
+
+ return check_result(numpy_out, torch_out)
+
+
+def case_5():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[20, 25])
+
+ numpy_softmax = Softmax()
+ numpy_out = numpy_softmax.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_softmax.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_softmax(torch_x, 1)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def test_model():
+ try:
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ numpy_model = NumpyModel()
+ torch_model = TorchModel()
+ torch_model.W1.data, torch_model.W2.data, torch_model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+ numpy_model.W1 = torch_model.W1.detach().clone().numpy()
+ numpy_model.W2 = torch_model.W2.detach().clone().numpy()
+ numpy_model.W3 = torch_model.W3.detach().clone().numpy()
+
+ x = torch.randn((10000, 28, 28))
+ y = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0] * 1000)
+
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+ x2 = x.numpy()
+ y_pred = torch_model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+
+ y_pred_numpy = numpy_model.forward(x2)
+ numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred_numpy, y.numpy())
+
+ check_flag_1 = check_result(y_pred_numpy, y_pred)
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("forward", 10 * check_flag_1, 10))
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in forward]")
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("forward", 0, 10))
+ return 0
+
+ try:
+
+ numpy_model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+
+ check_flag_2 = [
+ check_result(numpy_model.log_grad, torch_model.log_input.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.softmax_grad, torch_model.softmax_input.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W3_grad, torch_model.W3.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W2_grad, torch_model.W2.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W1_grad, torch_model.W1.grad)
+ ]
+ check_flag_2 = sum(check_flag_2) >= 4
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("backward", 20 * check_flag_2, 20))
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in backward]")
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("backward", 0, 20))
+ check_flag_2 = False
+
+ return 10 * check_flag_1 + 20 * check_flag_2
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ testcases = [
+ ["matmul", case_1, 5],
+ ["relu", case_2, 5],
+ ["log", case_3, 5],
+ ["softmax_1", case_4, 5],
+ ["softmax_2", case_5, 10],
+ ]
+ score = 0
+ for case in testcases:
+ try:
+ res = case[2] if case[1]() else 0
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in {}]".format(case[0]))
+ res = 0
+ score += res
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format(case[0], res, case[2]))
+ score += test_model()
+ print("{:14} {}/60".format("FINAL SCORE", score))
diff --git a/assignment-2/handout-1/torch_mnist.py b/assignment-2/handout-1/torch_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6d3e214c7606e3d43dac4b94554f942508afffb3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/handout-1/torch_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+import torch
+from utils import mini_batch, batch, download_mnist, get_torch_initialization, one_hot, plot_curve
+
+
+class TorchModel:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = torch.randn((28 * 28, 256), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W2 = torch.randn((256, 64), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W3 = torch.randn((64, 10), requires_grad=True)
+ self.softmax_input = None
+ self.log_input = None
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W1))
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W2))
+ x = torch.matmul(x, self.W3)
+
+ self.softmax_input = x
+ self.softmax_input.retain_grad()
+
+ x = torch.softmax(x, 1)
+
+ self.log_input = x
+ self.log_input.retain_grad()
+
+ x = torch.log(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ with torch.no_grad():
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1.grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2.grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3.grad
+
+ self.W1.grad = None
+ self.W2.grad = None
+ self.W3.grad = None
+
+
+def torch_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = TorchModel()
+ model.W1.data, model.W2.data, model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset, numpy=False):
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset, numpy=False)[0]
+ accuracy = model.forward(x).argmax(dim=1).eq(y).float().mean().item()
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ torch_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/handout-1/utils.py b/assignment-2/handout-1/utils.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..709220cfa7a924d914ec1c098c505f864bcd4cfc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/handout-1/utils.py
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+import torch
+import numpy as np
+from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
+
+
+def plot_curve(data):
+ plt.plot(range(len(data)), data, color='blue')
+ plt.legend(['loss_value'], loc='upper right')
+ plt.xlabel('step')
+ plt.ylabel('value')
+ plt.show()
+
+
+def download_mnist():
+ from torchvision import datasets, transforms
+
+ transform = transforms.Compose([
+ transforms.ToTensor(),
+ transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.1307,), std=(0.3081,))
+ ])
+
+ train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=True, download=True)
+ test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=False, download=True)
+
+ return train_dataset, test_dataset
+
+
+def one_hot(y, numpy=True):
+ if numpy:
+ y_ = np.zeros((y.shape[0], 10))
+ y_[np.arange(y.shape[0], dtype=np.int32), y] = 1
+ return y_
+ else:
+ y_ = torch.zeros((y.shape[0], 10))
+ y_[torch.arange(y.shape[0], dtype=torch.long), y] = 1
+ return y_
+
+
+def batch(dataset, numpy=True):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+ for each in dataset:
+ data.append(each[0])
+ label.append(each[1])
+ data = torch.stack(data)
+ label = torch.LongTensor(label)
+ if numpy:
+ return [(data.numpy(), label.numpy())]
+ else:
+ return [(data, label)]
+
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128, numpy=False):
+ return torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
+
+
+def get_torch_initialization(numpy=True):
+ fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(28 * 28, 256)
+ fc2 = torch.nn.Linear(256, 64)
+ fc3 = torch.nn.Linear(64, 10)
+
+ if numpy:
+ W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ W2 = fc2.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ W3 = fc3.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ else:
+ W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+ W2 = fc2.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+ W3 = fc3.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
diff --git a/assignment-2/handout-2/README.md b/assignment-2/handout-2/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..aa2ddddef23ca4638733a7163655be4e0739dd5f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/handout-2/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
+# 选题2 一些建议
+
+1. 如果理论证明讲不清楚可以在实验上多花一些功夫,仍然可以得到不错的分数
+2. 对于某个函数,可以在函数上采样生成训练集和测试集,使用训练集来训练神经网络,使用测试集来验证拟合效果。
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..36bd3497b1a780fc6ef92ea21a8f530133dd2d35
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,757 @@
+# 课程报告
+
+这是一个有关numpy实现前馈神经网络的实验报告,代码保存在numpy_fnn.py中,实验结果展示使用了matplotlib库。
+
+## 一、FNN算子的numpy实现
+
+### 1. Matmul
+
+Matmul是矩阵之间的乘法,输入为两个矩阵 $X$ 和 $W$ ,其中 $X\in R^{N\times d}$ , $W\in R^{d\times d'}$ ,运算结果为 $Z\in R^{N \times d'}$ 。$Z$中的每个元素 $Z_{ij}$ 由下式得到:
+$$
+\begin{equation}
+Z_{ij} = \sum_{k=1}^d X_{ik} W_{kj}
+\tag{1-1}
+\end{equation}
+$$
+用矩阵形式可以表示为:
+$$
+\begin{equation}
+Z = XW
+\tag{1-2}
+\end{equation}
+$$
+事实上,numpy提供了成熟的矩阵乘法计算函数,我们可以直接调用`numpy.matmul(X, W)`或者`numpy.dot(X, W)`使用。反向传播上,假设损失函数 $\mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})$ 到当前计算的误差项为$\delta$ ,则其关于 $W_{ij}$ 的梯度为:
+$$
+\begin{equation}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial W_{ij}} = \sum_{n=1}^{N}
+\frac{\partial Z_{nj}}{\partial W_{ij}}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial Z_{nj}}
+\tag{1-3}
+\end{equation}
+$$
+其中,根据 $(1-1)$ 式有:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac {\partial Z _ {kj}} {\partial W _ {ij}} & = X_{ni}
+\end {aligned} \tag {1-4}
+$$
+
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial Z_{nj}}=\delta_{nj}
+\end{aligned} \tag{1-5}
+$$
+
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial W_{ij}} &= \sum_{n=1}^{N}
+\frac{\partial Z_{nj}}{\partial W_{ij}}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial Z_{nj}}\\\\
+&=\sum_{n=1}^{N} X_{ni} \delta_{nj}
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{1-6}
+$$
+
+
+
+用矩阵形式可以写作:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial W} &=
+X^T \delta
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{1-7}
+$$
+对 $X_{ij}$ 的梯度为:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial X_{ij}} &= \sum_{m=1}^{d'}
+\frac{\partial Z_{im}}{\partial X_{ij}}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial Z_{im}} \\\\
+&= \sum_{m=1}^{d'}
+W_{jm} \delta_{im}
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{1-8}
+$$
+用矩阵形式可以写作:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial X} &=
+\delta W^T
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{1-9}
+$$
+
+具体代码为:
+
+```python
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ W = self.memory['W']
+ grad_W = np.matmul(x.T, grad_y)
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, W.T)
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+```
+
+### 2. ReLU
+
+ReLU函数是一类非线性激活函数,数学形式为 $ReLU(x)=max(0,x)$ 。因此,在 $x>0$ 的地方,梯度为1,其他地方梯度为0,在 $x=0$ 处,函数不可导,这时引入次梯度,使得该处的梯度为0,因此ReLU函数的反向传播可以写作:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial X_{ij}} &=
+\begin{cases}
+1, & \text{if $$x>0$$} \\\\
+0, & \text{o.w.}
+\end{cases}
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{2-1}
+$$
+
+
+矩阵形式下可以引入一个矩阵 $S$ 用来标记 $X$ 中大于0的元素的位置,其中大于0的位置数值为1,否则为0,则反向传播可以写作:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial X} &=
+S \odot\delta
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{2-2}
+$$
+
+代码为:
+
+```python
+def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ # 使用np.where起公式中S过滤矩阵的作用
+ grad_x = np.where(x > 0, grad_y, np.zeros_like(grad_y))
+
+ return grad_x
+```
+
+### 3. Log
+
+假设 $y=log(x + \epsilon)$ ,那么
+$$
+\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{1}{x + \epsilon}
+\tag{3-1}
+$$
+
+假设 $\frac{1}{X}$ 表示对矩阵 $X$ 中的元素按位取倒数得到的矩阵,则有
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial X} &=
+\left[
+\begin{matrix}
+\frac{\delta_{ij}}{X_{ij} + \epsilon}
+\end{matrix}
+\right]_{N \times d}\\\\
+&=
+\delta \odot \frac{1}{X}
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{3-2}
+$$
+
+代码为:
+
+```python
+def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ grad_x = 1 / (x + self.epsilon) * grad_y
+
+ return grad_x
+```
+
+### 4. softmax
+
+softmax是相对于argmax而言的,其优势是可导,具体形式为:
+$$
+softmax({\pmb x})=
+\left[
+\begin{matrix}
+\frac{exp(x_1)}{\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c)} & \cdots & \frac{exp(x_C)}{\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c)}
+\end{matrix}
+\right]
+\tag{4-1}
+$$
+在实际计算中,如果 $x_i$ 的值过大,很容易导致数值上溢,因此在计算时,可以在分子分母上同时除以最大值 $exp(x_{max})$ ,可以在保证数值不变的情况下防止上溢:
+$$
+softmax({\pmb x})=
+\left[
+\begin{matrix}
+\frac{exp(x_1-x_{max})}{\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c-x_{max})} & \cdots & \frac{exp(x_C-x_{max} )}{\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c-x_{max} )}
+\end{matrix}
+\right]
+\tag{4-2}
+$$
+反向传播时, $\frac {\partial softmax(x_i)} {\partial x_j}$ 需要分类讨论 $x_i$ 的情况,当 $i=j$ 时:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac {\partial softmax(x_i)} {\partial x_j} &=
+\frac{\partial}{\partial x_j}(\frac{exp(x_j-x_{max})}{\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c-x_{max})}) \\\\
+&=
+\frac{\partial}{\partial x_j}(\frac{exp(x_j)}{\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c)})\\\\
+&=
+\frac{\frac{\partial exp(x_j)}{\partial x_j}\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c) - exp(x_j)\frac{\partial \sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c)}{\partial x_j}}{(\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c))^2}\\\\
+&=
+\frac{exp(x_j)\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c) - exp(x_j)^2}{(\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c))^2}\\\\
+&=
+softmax(\pmb x)_j - (softmax(\pmb x)_j)^2\\\\
+&=softmax(\pmb x)_j(1-softmax(\pmb x)_j)
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{4-3}
+$$
+
+当 $i\neq j$ 时:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac {\partial softmax(x_i)} {\partial x_j}
+&=
+\frac{\partial}{\partial x_j}(\frac{exp(x_i)}{\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c)})\\\\
+&=
+\frac{0- exp(x_i)\frac{\partial \sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c)}{\partial x_j}}{(\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c))^2}\\\\
+&=
+\frac{- exp(x_i)exp(x_j)}{(\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c))^2}\\\\
+&=
+-softmax(\pmb x)_i softmax(\pmb x)_j
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{4-4}
+$$
+用矩阵形式表示:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac {\partial softmax(\pmb x)} {\partial {\pmb x}} &=\left[
+\begin{matrix}
+softmax(\pmb x)_1(1-softmax(\pmb x)_1) & \cdots& -softmax(\pmb x)_1 softmax(\pmb x)_C \\\\
+\vdots & \ddots & \vdots\\\\
+-softmax(\pmb x)_C softmax(\pmb x)_1 & \cdots& softmax(\pmb x)_C(1-softmax(\pmb x)_C)
+\end{matrix}
+\right] \\\\
+&=diag(softmax(\pmb x)) - softmax(\pmb x)softmax(\pmb x)^T
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{4-5}
+$$
+
+其中 $diag(softmax(\pmb x))$ 指的是将 $softmax(\pmb x)$ 元素按顺序排列在对角线上的对角阵,假设误差项为 $\delta \in R^{C}$ ,则:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial \pmb x} &=
+\frac {\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})} {\partial softmax(\pmb x)} \frac {\partial softmax(\pmb x)} {\partial {\pmb x}}\\\\
+&=\delta(diag(softmax(\pmb x)) - softmax(\pmb x)^Tsoftmax(\pmb x))
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{4-6}
+$$
+需要注意,这里的 $softmax(\pmb x)$ 是一个行向量。在numpy实现上,我们可以对 $X$ 矩阵的每一行进行softmax操作,从而得到每个样本在每个类上的预测值,记得到的结果为矩阵 $\hat Y \in R^{N \times C}$。反向传播时,我们需要将 $\hat Y$ 扩充为 $R^{N \times 1 \times C}$,并使用`numpy.matmul()`方法在最后两维上计算 $\hat Y$ 对 $X$ 的导数 $dX \in R^{N \times C \times C}$ ,在此基础上,将误差项 $\delta \in R^{N \times C}$扩充为 $R^{N \times 1 \times C}$,也在后两维上与 $dX$ 进行乘法,从而得到 $\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial X}_{temp} \in R^{N \times 1 \times C}$ ,此时再将中间的维度压缩掉,就可以得到最后的结果:$\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial X} \in R^{N \times C}$ 。
+
+代码为:
+
+```python
+def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ N, C = grad_y.shape
+ A = self.memory['A']
+ # 扩充激活值的维度,计算softmax对X导数dX
+ temp = A[:, np.newaxis, :] * np.eye(C) - np.matmul(A[:, np.newaxis, :].transpose(0, 2, 1), A[:, np.newaxis, :])
+ # 扩充误差项与dX进行乘法
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y[:, np.newaxis, :], temp).squeeze(1)
+
+ return grad_x
+```
+
+## 二、模型训练与测试
+
+### 1. 学习率调整
+
+笔者分别使用了1、0.1、0.01、0.001的学习率进行了实验,在训练集上的损失如下:
+
+
-
-
-可以通过如下表格来报告我的实验结果
-
-Algo |kvalue|Acc |
------| ---- |---- |
-KNN | 2 |0.9975 |
-
-
-此时3个高斯分布距离较远,通过较少的k值即可得到较为准确的判断。增加高斯分布间的距离可以提升实验的准确性。
-
-## 代码使用方法
-
-```bash
-改变mode数值:
-mode=0 #数据生成
-mode=1 #数据可视化
-mode取非0-1值 #训练和测试
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/test 1.png b/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/test 1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index bf515460fd3bf6e81d027117399749a3b10c29fe..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/test 1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/test 2.png b/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/test 2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 1d962680d1019a7b4946d61b7a66ede507ad0d4c..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/test 2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/test 3.png b/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/test 3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 3ab9d8b6157ed19597c283688c34daeef54beeeb..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/test 3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/train 1.png b/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/train 1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index dbe1db24a876a4b564d98b3009aefae717ba433c..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/train 1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/train 2.png b/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/train 2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 406126994e9ac71f4a43d6d182e72d88e4eaceed..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/train 2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/train 3.png b/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/train 3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 761f9ee658095183c7c2a3925b6cbb9c51fde989..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/img/train 3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 0f5e2424b154e74548445bef39f513dee6b40c94..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/19210680053/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,103 +0,0 @@
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import numpy as np
-
-class KNN():
- def euclidean(self,v1,v2):
- return np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(v1 - v2)))
- def fit(self, X_train, Y_train):
- self.train_data = train_data
- self.train_label = train_label
- def predict(self, train_data,k):
- predictions = []
- for item in train_data:
- label = self.closest(item,k)
- predictions.append(label)
- return predictions
-
- def closest(self, item,k):
- min_ind = 0
- distlst=[]
- idxlst=list(range(len(self.train_data)))
- #get distance between test_data with train_data
- for i in range(0,len(self.train_data)):
- distlst.append(self.euclidean(item, self.train_data[i]))
- #make up a dictionary with distance and index
- distdict=dict(zip(idxlst,distlst))
- distdict=dict(sorted(distdict.items(),key=lambda item:item[1]))
- #get first K nearest position
- min_ind=list(dict(list(distdict.items())[:k]).keys())
- min_dist=[self.train_label[i] for i in min_ind]
- return max(min_dist,key=min_dist.count)
-
- def choose(self,test_data,test_label):
- acclst=[]
- for k in range(2,7):
- res=self.predict(test_data,k)
- acc=np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label))
- acclst.append(acc)
- max_acc=max(acclst)
- max_k=acclst.index(max_acc)+2
- return max_k,max_acc
-
-
-def generate():
- mean = (20, 25)
- cov = np.array([[10,2.1], [2.1, 12]])
- x = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (800,))
-
- mean = (16, -5)
- cov = np.array([[23, 0], [0, 22]])
- y = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (200,))
-
- mean = (3, 5)
- cov = np.array([[10,5],[5,10]])
- z = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (1000,))
-
- idx = np.arange(2000)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- data = np.concatenate([x,y,z])
- label = np.concatenate([
- np.zeros((800,),dtype=int),
- np.ones((200,),dtype=int),
- np.ones((1000,),dtype=int)*2
- ])
- data = data[idx]
- label = label[idx]
-
- train_data, test_data = data[:1600,], data[1600:,]
- train_label, test_label = label[:1600,], label[1600:,]
- np.save("data.npy",((train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
- ))
-
-def display(data, label, name):
- datas =[[],[],[]]
- for i in range(len(data)):
- datas[label[i]].append(data[i])
-
- for each in datas:
- each = np.array(each)
- plt.scatter(each[:, 0], each[:, 1])
- label=[str(i) for i in list(range(len(datas)))]
- plt.legend(['label '+i for i in label])
- plt.show()
-
-def read():
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = np.load("data.npy",allow_pickle=True)
- return (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- mode=0
- if mode == 0:
- generate()
- if mode == 1:
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
- display(train_data, train_label, 'train')
- display(test_data, test_label, 'test')
- else:
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
-
- model = KNN()
- model.fit(train_data, train_label)
- k ,acc = model.choose(test_data,test_label)
- print("k=",k,"acc=",acc*100,"%")
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 187378e8d1e1fff3b396413ddc2e09588a505b13..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,142 +0,0 @@
-# PRML21春-HW1-KNN分类器
-
-### 简介
-
-实现KNN分类器并探索细节。本设计实现了一系列KNN算法的变种,包括:
-
-- 实现了数据的min-max标准化
-- 证明了标准化的有效性
-
-- 自动寻找较优的K值
-- 实现了两种距离(欧氏距离/曼哈顿距离)的算法
-- 比较了两种距离尺度的特性
-
-- 实现了对每个训练集中点的置信度的加权
-- 实现了对K个近邻点按距离的加权
-- 证明以上两种加权方式是有效的消融实验
-- 探索常规KNN算法对数据分布的响应
-- 验证了加权后的算法相对于常规算法对数据分布的鲁棒性
-
-
-
-### 前言
-
-本实验没有探索数据本身对于常规KNN算法的影响。
-
-我认为“点集重叠越少表现越好”之类的结论是显而易见的,不希望在数据本身上花太多时间。
-
-此外,我没有对数据可视化,因为数据的分布给定之后,大致可以预见其可视化结果。本设计中实现了许多有意义的改进,因此重点在于算法本身的探索上,与作业手册的第四条“修改数据集的属性(例如:不同高斯分布之间的距离),进行探究性实验”有出入,还望助教老师多多包涵~
-
-
-
-### min-max标准化
-
-#### 实现细节
-
-对每一个channel,都实现了
-
-`x=(x-(该channel中最小值))/((该channel中最大值)-(该channel中最小值))`
-
-的标准化,将所有的值映射到`[0,1]`上,并且会在训练集中记录训练集上每一channel的最大/最小值,并对测试集做同样的映射,以保证两者采用同一映射,如果对两个数据集分别归一化,将会有标准化方式不统一的问题。
-
-#### 正确性
-
-其带来的作用是显而易见的,在闵氏距离族中,不论采用何种距离度量,都会出现同一问题:两点之间的距离最主要受尺度最大的特征影响,这一显然的结论不需要实验便可以举出例子证明。
-
-经典的波士顿房价预测问题(尽管其原型是回归问题,仍然可以用KNN算法分析房价等级,例如高、中、低等):“历年房价中位数”的尺度是万数量级的,而“交通便利指数”、“环保指数”、“与就业中心的距离”都是十分有用的特征,然而其尺度远比房价小!
-
-如果不加处理就直接进行KNN算法,显然其他特征全部被忽略,KNN算法将完全被历年房价主导!这是不合理的。在此处尺度最大的特征恰巧是相关性极强的,算法尚能工作,如果尺度最大的恰巧是相关性低的,则算法将完全失效!
-
-
-
-### 自动寻找K值
-
-由于算法之间(自动寻找K值,置信度加权,距离加权)互相牵制,因此在搜索K值时只能采用常规KNN算法,本算法在`1~min(16,训练集样本个数)`之中搜索所有K,找到准确率最高的K值。
-
-在示例程序中,将会自动选择K=1,在自动生成的样本中,参数如下:
-
-| Distribution | Mean | Cov | Number |
-| ------------ | ------ | ----------------- | ------ |
-| Class 0 | (1,2) | [[10, 0], [0, 2]] | 100 |
-| Class 1 | (4,5) | [[7, 3], [15, 1]] | 100 |
-| Class 2 | (-2,6) | [[0, 1], [1, 2]] | 100 |
-
-将会选择K=11. 两者的寻找过程如下两图:
-
-
-
-### Euclidean & Manhattan - 两种距离尺度
-
-本设计中实现了两种距离尺度中的KNN分类器。
-
-曼哈顿距离对每一个channel都是独立的,欧氏距离对每一维度求偏导时都与当前距离相关,因此可以预见的是,在距离较远时,两者表现将接近,在距离较近的时候,需要通过实验探索两者的差异。
-
-取两个分布方差矩阵均为单位阵,令其沿y=0.5x方向上其逐渐接近,其中一个分布的均值固定在`(0,0)`,另一分布均值分别为:`(0.1,0.2),(0.6,1.2),(1.1,2.2),(1.6,3.2),(2.1,4.2),(2.6,5.2)`。
-
-可以看到如下的变化:
-
-其中蓝线是欧几里得距离,绿线是曼哈顿距离,可见欧氏距离对两分布接近时处理的更好。
-
-p.s. 以上的实验采用常规KNN算法。
-
-
-
-### 置信度加权
-
-在两个分布有较大的重叠时,训练集中的重叠点本身也不能通过KNN以很高的置信度判断自身的类别,对这类点,其置信度应该降低。
-
-置信度的算法为:`K近邻点中与自身类别相同的点数/K`。
-
-实验证明这样的改变是有益的。在如下分布中做消融实验:
-
-| Distribution | Mean | Cov | Number |
-| ------------ | ------ | ----------------- | ------ |
-| Class 0 | (1,2) | [[10, 0], [0, 2]] | 100 |
-| Class 1 | (4,5) | [[7, 3], [15, 1]] | 100 |
-| Class 2 | (-2,6) | [[0, 1], [1, 2]] | 100 |
-
-常规KNN算法:acc = 0.85
-
-带置信度加权的KNN算法: 0.8666666666666667
-
-
-
-### 距离加权
-
-在一个K近邻范围内,有些点离待监测点较近,有些较远。有理由相信距离较近的点提供的置信度更少,因此需要实现距离加权。
-
-距离加权的算法为:`每个近邻点投票的权值为:D-(该近邻点与待监测点的距离/近邻范围内最远点与待监测点的距离)`。其中D为超参。
-
-实验得到,在如上分布中,D=1.8时表现最好,消融实验如下:
-
-常规KNN算法:acc = 0.85
-
-带距离加权的KNN算法: 0.8666666666666667
-
-
-
-### 联合加权
-
-综合以上两种加权方式,此时需要引入第二个超参,该超参作用于置信度加权,并且对于仅采用置信度加权时,其不起作用,由于需要将两个计算得到的权重相乘,该超参用于调节两者起到的作用之比例。
-
-联合加权算法为:`(K近邻点中与自身类别相同的点数/K-bias)*(D-(该近邻点与待监测点的距离/近邻范围内最远点与待监测点的距离))`。其中`bias`为引入的新超参,`D`为距离加权对应的超参。
-
-实验证明,取`bias=0.2`,`D=2.1`时,可以达到较好的效果。
-
-常规KNN算法:acc = 0.85
-
-带联合加权的KNN算法:acc = 0.8833333333333333
-
-
-
-### 对数据的鲁棒性
-
-可以预见,当数据比较接近时,这样的加权会有更好的表现,因为其更好的考虑了模糊点置信程度较低的性质,并且利用了靠近待分类点与距离较远的点之间的差异。
-
-下图为实验结果,其中蓝线为联合加权结果,绿线为常规KNN算法。
-
-
-
-### 总结
-
-本设计探索了更高效的KNN算法,采用联合加权的方式对邻接范围内的点做不同的处理,取得了较好的效果。
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_1.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index b006d52cf0b89e9497b213ec044b0224a5a620a7..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_2.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_2.png
deleted file mode 100644
index d520d40d31644714b20789c236f9976818185cab..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_3.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_3.png
deleted file mode 100644
index c643350e0310bac079cdd179a01cff9371b27475..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_4.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_4.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 6af94b33a92ba072e05b09dc9eff0ff3c6bc0d08..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/img/Figure_4.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/source.py
deleted file mode 100644
index a231c833e05fe6cb7a43b4c7fdabab987978305a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/19307110020/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,125 +0,0 @@
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-class KNN:
- def __init__(self):
- pass
-
- def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- self.len=train_data.shape[0]
- #standardize
- train_data=train_data.astype(np.float64)
- train_data=train_data.T
- self.channel=train_data.shape[0]
- self.mins=[]
- self.maxs=[]
- for data in train_data:
- self.mins.append(np.min(data))
- self.maxs.append(np.max(data))
- for i in range(data.shape[0]):
- data[i] = (data[i] - np.min(data)) / (np.max(data) - np.min(data))
- self.train_data=train_data.T
- self.train_label=train_label
-
- #grid search for K
- maxk, maxacc=0, 0
- for k in range(1,min(17,self.len)):
- acc=0
- for d in range(self.len):
- dists = []
- indexs = np.arange(self.len)
- for i in range(self.len):
- dists.append(self.euclidean(self.train_data[d], self.train_data[i]))
- dic = dict(zip(indexs, dists))
- dic = dict(sorted(dic.items(), key=lambda item: item[1]))
- min_indexs = list(dict(list(dic.items())[1:k+1]).keys())
- min_dists = [self.train_label[i] for i in min_indexs]
- if max(min_dists, key=min_dists.count) == self.train_label[d]:
- acc+=1
- if acc>maxacc:
- maxk, maxacc=k, acc
- self.K=maxk
-
- #credibility
- self.cred=[]
- for d in range(self.len):
- dists = []
- indexs = np.arange(self.len)
- for i in range(self.len):
- dists.append(self.euclidean(self.train_data[d], self.train_data[i]))
- dic = dict(zip(indexs, dists))
- dic = dict(sorted(dic.items(), key=lambda item: item[1]))
- min_indexs = list(dict(list(dic.items())[1:self.K+1]).keys())
- min_dists = [self.train_label[i] for i in min_indexs]
- self.cred.append(float(min_dists.count(max(min_dists, key=min_dists.count)))/self.K)
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- test_data=test_data.astype(np.float64)
- test_data=test_data.T
- for i in range(self.channel):
- for j in range(test_data.shape[1]):
- test_data[i][j] = (test_data[i][j] - self.mins[i]) / (self.maxs[i] - self.mins[i])
- test_data = test_data.T
- ans=[]
- for d in range(test_data.shape[0]):
- dists = []
- indexs = np.arange(self.len)
- for i in range(self.len):
- dists.append(self.euclidean(test_data[d], self.train_data[i]))
- dic = dict(zip(indexs, dists))
- dic = dict(sorted(dic.items(), key=lambda item: item[1]))
- min_indexs = list(dict(list(dic.items())[:self.K]).keys())
- min_dict={}
- for i in min_indexs:
- min_dict[self.train_label[i]]=min_dict.get(self.train_label[i],0)+(self.cred[i]-0.2)*(2.1-dic[i]/list(dic.items())[self.K-1][1])
- ans.append(max(min_dict, key=lambda k: min_dict[k]))
- return ans
-
-
- def euclidean(self, a, b):
- return np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(a-b)))
-
- def manhattan(self, a, b):
- return np.sum(abs(a-b))
-
-
-def dataset(mean1,mean2,cov1,cov2,mean3=None,cov3=None):
- mean=mean1
- cov=cov1
- x=np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (100,))
- mean=mean2
- cov=cov2
- y=np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (100,))
- num=300
- if mean3 is not None and cov3 is not None:
- mean=mean3
- cov=cov3
- z=np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (100,))
- idx=np.arange(num)
- np.random.shuffle(idx)
- if mean3 is not None and cov3 is not None:
- data=np.concatenate([x, y, z])
- label=np.concatenate([np.zeros((100,), dtype=np.int8), np.ones((100,), dtype=np.int8), np.ones((100,), dtype=np.int8) * 2])
- else:
- data=np.concatenate([x, y])
- label=np.concatenate([np.zeros((100,), dtype=np.int8), np.ones((100,), dtype=np.int8)])
- data=data[idx]
- label=label[idx]
- split=int(num*0.8)
- train_data, test_data=data[:split,:], data[split:,:]
- train_label, test_label=label[:split], label[split:]
- np.save("train_data.npy",train_data)
- np.save("test_data.npy",test_data)
- np.save("train_label.npy",train_label)
- np.save("test_label.npy",test_label)
-
-def dataload():
- train_data, train_label, test_data, test_label = np.load("train_data.npy",allow_pickle=True),np.load("train_label.npy",allow_pickle=True),np.load("test_data.npy",allow_pickle=True),np.load("test_label.npy",allow_pickle=True)
- return train_data, train_label, test_data, test_label
-
-if __name__ == '__main__':
- dataset((1,2),(4,5),np.array([[10, 0], [0, 2]],dtype=np.float64),np.array([[7, 3], [15, 1]],dtype=np.float64),(-2,6),np.array([[0, 1], [1, 2]],dtype=np.float64))
- train_data, train_label, test_data, test_label=dataload()
- model=KNN()
- model.fit(train_data,train_label)
- res=model.predict(test_data)
- print("acc =",np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label)))
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/README.md b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/README.md
deleted file mode 100755
index 9d46bef52b53b558ad6ec716ee26dce570e77a87..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,213 +0,0 @@
-
-
-[TOC]
-
-我只使用了numpy和matplotlib两个库实现了KNN的,所以代码应该可以完成在额外的任务。
-
-#### 一、模型的实现
-
-对于单个测试数据的knn分类网络的实现:
-
-```python
-inX=test_data[i]
-#计算欧氏距离
-diffMat=np.tile(inX,(dataSetSize,1))-tra_data
-sqDifMat=diffMat**2
-sqDistances=sqDifMat.sum(axis=1)
-distances=sqDistances**0.5
-#对计算得到的距离对应的序号进行排序
-sortedDistIndicies=distances.argsort()
-#统计最近的k个点中各个类别的数量
-classCount={}
-for j in range(k):
- Label = tra_label[sortedDistIndicies[j]]
- classCount[Label] = classCount.get(Label,0) + 1
-#得到对于类别的预测
-max_count=0
-for key,value in classCount.items():
-if value >max_count :
- max_count = value
- pred_label=key
-```
-
-对与KNN fit() 部分的实现:
-
-将数据集按照8:2的比例进行划分后,对K进行拟合,多次重复在训练集上进行单次的knn分类预测,选出正确率最高的K值。
-
-~~~python
-def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- self.train_data=train_data
- self.train_label=train_label
- N=train_data.shape[0]
- cut=int(N*0.8)
-
- tra_data, test_data = train_data[:cut,], train_data[cut:,]
- tra_label, test_label = train_label[:cut,], train_label[cut:,]
-
- dataSetSize=tra_data.shape[0]
- test_number=test_data.shape[0]
-
- best_k=0
- max_score=0
- if N<6 :
- k_range=N
- else :
- k_range=20
-
- for k in range(2,k_range):
- total_correct=0
- for i in range(0,test_number):
- inX=test_data[i]
- #计算欧氏距离
- diffMat=np.tile(inX,(dataSetSize,1))-tra_data
- sqDifMat=diffMat**2
- sqDistances=sqDifMat.sum(axis=1)
- distances=sqDistances**0.5
- #对计算得到的距离对应的序号进行排序
- sortedDistIndicies=distances.argsort()
- #统计最近的k个点中各个类别的数量
- classCount={}
- for j in range(k):
- Label = tra_label[sortedDistIndicies[j]]
- classCount[Label] = classCount.get(Label,0) + 1
- #得到对于类别的预测
- max_count=0
- for key,value in classCount.items():
- if value >max_count :
- max_count = value
- pred_label=key
-
- if pred_label ==test_label[i]:
- total_correct=total_correct+1
- #选择正确率最高的K值
- score=total_correct*1.0/test_number
- if score>max_score:
- max_score=score
- best_k=k
- print("Best K: %d"%(best_k))
- self.k=best_k
-~~~
-
-#### 二、实验数据的生成
-
-通过 np.random.multivariate_normal() 生成数据集
-
-~~~python
- mean = (1, 1)
- cov = np.array([[10, 0], [0, 10]])
- x1 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (400,))
-
- mean = (1, 12)
- x2 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (400,))
-
- mean = (12, 1)
- x3 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (400,))
-
- mean = (12, 12)
- x4 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (400,))
-~~~
-
-生成的训练集:
-
-生成的测试集:
-
-训练结果:
-
-| K | 准确率 |
-| ---- | :------- |
-| 10 | 0.884375 |
-
-#### 三、探究实验
-
-##### 1. 修改mean参数
-
-首先修改成如下形式,使得四类点分布的更开
-
-~~~python
-mean = (1, 1) mean = (1, 15) mean = (15, 1) mean = (15, 15)
-~~~
-
-得到的训练集:
-
-得到的测试集:
-
-训练结果:
-
-| K | 准确率 |
-| ---- | -------- |
-| 11 | 0.978125 |
-
-可以看到不同的数据分布更开后,准确率大大提升。
-
-
-
-修改成以下的形式后,不同的数据更加集中:
-
-~~~python
-ean = (1, 1) mean = (1, 8) mean = (8, 1) mean = (8, 8)
-~~~
-
-生成的训练集:
-
-生成的测试集:
-
-训练结果:
-
-| K | 准确率 |
-| ---- | ------ |
-| 18 | 0.7 |
-
-可以看到准确率大大降低。
-
-结论:KNN分类算法的准确性依赖于数据的分布,当不同种类的数据越集中(重合的部分越多时),效果越差;
-
-反之,重合部分越少,分类结果越好。
-
-##### 2.对cov参数的修改
-
-修改cov,使得方差更大,同类数据更离散:
-
-~~~python
-cov = np.array([[30, 0], [0, 30]])
-~~~
-
-生成的训练集:
-
-生成的测试集:
-
-测试结果:
-
-| K | 准确率 |
-| ---- | -------- |
-| 18 | 0.690625 |
-
-可以看到数据更离散后,准确率下降
-
-
-
-再次修改cov,减少方差,使得同类数据更集中
-
-```python
-cov = np.array([[5, 0], [0, 5]])
-```
-
-生成的训练集:
-
-生成的测试集:
-
-训练结果:
-
-| K | 准确率 |
-| ---- | ------ |
-| 5 | 0.9875 |
-
-可以看到同类数据更集中,准确率越高。
-
-##### 探讨与结论
-
-可以和实验一得到相同的结论,不同类数据间分布的重合区域越小,KNN分类方法的准确率越高;重合区域越大,准确率越低。
-
-
-
-同时在上述实验中观察到的另一有趣现象是准确率越低时,K的最佳取指偏大;准确率越高时,K的取值偏小。但是在修改参数cov来控制正确率,希望得到准确率和K的关系时,却发现最佳K的选取还是具有一定的随机性,没有找到一般规律。
-
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_1.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_1.png
deleted file mode 100755
index e4a5d05eb4f6ccb904e8fd207fded8cf0b68b43c..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_10.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_10.png
deleted file mode 100755
index c9002a2fdce20748784f39dfaac3a0e1ca956f06..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_10.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_2.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_2.png
deleted file mode 100755
index c4cb6a263cd63039ad370eca82607f50666592b7..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_2.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_3.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_3.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 24fc664d1ea502c02c96a4deca581dc42fc465cd..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_3.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_4.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_4.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 1a3fa01d1aa274fb14dca65e961793de8f2174ca..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_4.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_5.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_5.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 4afbaeb755e3460b5f5e547d8e43e5221cd44c17..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_5.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_6.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_6.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 4dd7b5c0d0d15d0bfb3f47c5db12a5a378e17144..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_6.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_7.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_7.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 89613e8f29af003f9ad06af59112d5199da8d5a9..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_7.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_8.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_8.png
deleted file mode 100755
index 87a4ebbe6926fe0a26cc6e91c6c31e96b769736b..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_8.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_9.png b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_9.png
deleted file mode 100755
index dff482725b27547590be277cdba748ba1bc1305f..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Binary files a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/img/Figure_9.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/source.py b/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/source.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 43e2a2ec214289e40b5a5c7e99b49087695fc828..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/assignment-1/submission/19307130211/source.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,154 +0,0 @@
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
-class KNN:
-
- def __init__(self):
- pass
-
- #def settled_knn(self,test_data,train_data,train_label) :
-
- def fit(self, train_data, train_label):
- self.train_data=train_data
- self.train_label=train_label
- N=train_data.shape[0]
- cut=int(N*0.8)
-
- tra_data, test_data = train_data[:cut,], train_data[cut:,]
- tra_label, test_label = train_label[:cut,], train_label[cut:,]
-
- dataSetSize=tra_data.shape[0]
- test_number=test_data.shape[0]
-
- best_k=0
- max_score=0
- if N<6 :
- k_range=N
- else :
- k_range=20
-
- for k in range(2,k_range):
- total_correct=0
- for i in range(0,test_number):
- inX=test_data[i]
-
- diffMat=np.tile(inX,(dataSetSize,1))-tra_data
-
- sqDifMat=diffMat**2
- sqDistances=sqDifMat.sum(axis=1)
- distances=sqDistances**0.5
-
- sortedDistIndicies=distances.argsort()
-
- classCount={}
- for j in range(k):
- Label = tra_label[sortedDistIndicies[j]]
- classCount[Label] = classCount.get(Label,0) + 1
- max_count=0
- for key,value in classCount.items():
- if value >max_count :
- max_count = value
- pred_label=key
-
- if pred_label ==test_label[i]:
- total_correct=total_correct+1
-
- score=total_correct*1.0/test_number
- if score>max_score:
- max_score=score
- best_k=k
- print("Best K: %d"%(best_k))
- self.k=best_k
-
- def predict(self, test_data):
- dataSetSize=self.train_data.shape[0]
- test_number=test_data.shape[0]
- ans_label=np.array([])
- for i in range(0,test_number):
- inX=test_data[i]
-
- diffMat=np.tile(inX,(dataSetSize,1))-self.train_data
-
- sqDifMat=diffMat**2
- sqDistances=sqDifMat.sum(axis=1)
- distances=sqDistances**0.5
-
- sortedDistIndicies=distances.argsort()
- classCount={}
- for j in range(self.k):
- voteIlabel = self.train_label[sortedDistIndicies[j]]
- classCount[voteIlabel] = classCount.get(voteIlabel,0) + 1
-
- max_count=0
- pred_label=self.train_label[0]
- for key,value in classCount.items():
- if value >max_count :
- max_count = value
- pred_label=key
-
- ans_label=np.append(ans_label,pred_label)
- return ans_label
-
-def generate():
- mean = (1, 1)
- cov = np.array([[10, 0], [0, 10]])
- x1 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (400,))
-
- mean = (1, 12)
- cov = np.array([[10, 0], [0, 10]])
- x2 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (400,))
-
- mean = (12, 1)
- cov = np.array([[10, 0], [0, 10]])
- x3 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (400,))
-
- mean = (12, 12)
- cov = np.array([[10, 0], [0, 10]])
- x4 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, (400,))
-
- X = np.concatenate([x1, x2, x3, x4])
- Y = np.concatenate([
- np.zeros((400,),dtype=int),
- np.ones((400,),dtype=int),
- np.ones((400,),dtype=int)*2,
- np.ones((400,),dtype=int)*3
- ])
- shuffled_indices = np.random.permutation(1600)
- data=X[shuffled_indices]
- label=Y[shuffled_indices]
- total=1600
- cut=int(total*0.8)
- train_data, test_data = data[:cut,], data[cut:,]
- train_label, test_label = label[:cut,], label[cut:,]
-
- np.save("data.npy",(
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
- ))
-
-def read():
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = np.load("data.npy",allow_pickle=True)
- return (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label)
-
-def display(data,label,name):
- datas=[[],[],[],[]]
- for i in range(len(data)):
-
- datas[label[i]].append(data[i])
-
- for each in datas:
- each=np.array(each)
- plt.scatter(each[:,0],each[:,1])
- #plt.savefig(f'imag/{name}')
- plt.show()
-
-
-if __name__ == '__main__':
- generate()
- (train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = read()
- display(train_data, train_label, 'train')
- display(test_data, test_label, 'test')
-
- model = KNN()
- model.fit(train_data, train_label)
- res = model.predict(test_data)
- print("acc =",np.mean(np.equal(res, test_label)))
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/README.md b/assignment-2/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..63b9c33a1fdb2798e9e3c812c958283502b98f8d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,116 @@
+# 作业-2
+
+本次作业有两个选题,大家可以任选其一完成。
+
+## 选题1:前馈神经网络
+
+本次作业要求使用 NumPy 实现一种简单的前馈神经网络。你需要先实现 Matmul, Relu, Log, Softmax 等支持前馈计算和反向传播的算子,再利用这些算子构建一个简单的神经网络。最后,你需要使用这个模型在 MNIST 数据集上进行训练和测试,并完成实验报告。
+
+本次作业会考察你使用 NumPy 和 PyTorch 编程的能力以及对前馈神经网络背后数学知识的理解。
+
+### 更新 2021.4.25
+
+1. 修复了 torch_mnist.py 中把 softmax/log 算子输出的梯度当成了输入的梯度的问题。 现在 NumpyModel 中的 softmax_grad, log_grad 等均为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+2. 更新了 numpy_fnn.py, numpy_mnist.py, tester_demo.py 中的训练模型代码的结构,把 loss 的计算和反向传播的代码集中到 NumpyLoss 类中,便于理解。
+
+**已经完成作业的同学需要修改 numpy_fnn.py 中的 NumpyModel.backward 方法,并参考我们更新的代码来使用 NumpyLoss 类**
+
+> 以上问题的反馈来自学号尾号为 116, 154, 213 的同学
+
+### 提供材料
+
+你可以在 `handout-1/` 文件夹下找到如下文件,你需要将这些文件复制到自己的工作目录下进行作业,不过你最终只需要提交其中的部分文件。
+
+- numpy_fnn.py: 这个文件给出了你需要实现的算子和模型的框架,你只需要完成填空即可
+- tester_demo.py: 这是一个自动测试文件,它会测试你在 `numpy_fnn.py` 中实现的代码
+- torch_mnist.py: 使用 PyTorch 实现神经网络的代码,你需要按照其中定义的网络结构在 `numpy_fnn.py` 中构建网络
+- numpy_mnist.py: 使用 NumPy 搭建的神经网络进行训练测试的代码,如果 `numpy_fnn.py` 实现正确,它是可以直接运行的
+- utils.py: 实现了一些辅助性的函数,如果你想修改这些函数,请在 `numpy_mnist.py` 中重写
+
+### 提交内容
+
+- README.md: 课程作业报告
+- numpy_fnn.py: 你用 NumPy 实现的算子和模型,我们会对该代码进行自动测试
+- numpy_mnist.py: 你进行训练和测试的代码,我们会结合你的报告和代码进行评分
+
+提交方法参见[提交指南](https://gitee.com/fnlp/prml-21-spring#提交指南)
+
+### 实验环境
+
+```bash
+conda create -n assignment-2 python=3.8 -y
+conda activate assignment-2
+pip install numpy
+pip install matplotlib
+pip install torch
+pip install torchvision
+```
+
+### 实现模型
+
+你首先需要参考课内知识在 `numpy_fnn.py` 中实现 Matmul, Relu, Log, Softmax 等支持前馈计算和反向传播的算子。在实现过程中,你可以查看 `tester_demo.py` 中的测试代码,了解你需要实现的算子与 PyTorch 中的哪个算子相对应。 在安装好实验环境之后,你可以在工作目录下运行 `tester_demo.py` 来评测自己实现的算子是否符合要求。注意,在实现反向传播时,你可以使用 `self.memory` 中存下来的相关变量的值。
+
+在实现基础算子之后,你需要按照 `torch_mnist.py` 中定义的网络结构在 `numpy_fnn.py` 中补全 `NumpyModel` 的代码。注意,在反向传播时,你需要更新 `self.x1_grad`, `self.W1_grad` 等全部梯度的值。你可以查看 `tester_demo.py` 中的代码来了解评测标准,并尝试运行它进行评测。
+
+我们最终会使用自动评测代码来测试你提交的 `numpy_fnn.py` 文件,测试代码与 `tester_demo.py` 基本一致,但测试环境中会屏蔽 NumPy 之外的第三方包,你需要确保自己的 `numpy_fnn.py` 中只使用了 NumPy。
+
+除此之外,你还需要在报告中写出你实现算子反向传播的公式推导,你实现的代码需要和你推导的公式对应。
+
+### 进行实验
+
+在 `numpy_fnn.py` 中补全 `NumpyModel` 之后,你需要修改 `numpy_mnist.py` 中的代码,进行模型的训练和测试。其中,你需要使用 NumPy 实现 `mini_batch` 函数,替换 `utils.py` 中使用 PyTorch 实现的 `mini_batch` 函数。
+
+你可以使用现有模型进行若干实验,并在报告中介绍。因为这只是一个简单的作业,我们不推荐你尝试更多复杂的网络结构。如果你一定要尝试,**请勿修改 `numpy_fnn.py` 中的模型结构**,因为这样会影响你在自动测试中的得分;你可以在 `numpy_mnist.py` 中编写你的其他模型并进行实验,但这并不会让你获得更多的分数。
+
+我们提供了两个方向进行扩展探究,每个方向可以获得最多 10% 的附加分。如果你进行了拓展探究,请在报告中单独列出。
+
+探究1:实现 momentum、Adam 等其它优化方法并进行对比实验
+
+探究2:调研 PyTorch 中权重初始化的方法,并实现代码替换 `get_torch_initialization` 函数
+
+### 评分细则
+
+自动测试的七个测试点对应 `numpy_fnn.py` 中的七个空,附加分和其它部分的总和不超过 100%。
+
+- 自动测试(60%)
+ - Matmul 的反向传播 (5%)
+ - Relu 的反向传播 (5%)
+ - Log 的反向传播 (5%)
+ - Softmax 的前向计算 (5%)
+ - Softmax 的反向传播 (10%)
+ - FNN 的前向计算 (10%)
+ - FNN 的反向传播 (20%)
+- 实验与报告 (40%)
+ - 模仿 `torch_mnist.py` 的代码,在 `numpy_mnist.py` 中进行模型的训练和测试,并在报告中介绍你的实验过程与结果 (20%)
+ - 在 `numpy_mnist.py` 中只用 NumPy 实现 `mini_batch` 函数,替换 `utils.py` 中使用 PyTorch 实现的 `mini_batch` 函数 (10%)
+ - 在报告中推导 `numpy_fnn.py` 中实现算子的反向传播计算公式 (10%)
+- 附加分 (20%)
+ - 实现 momentum、Adam 等其它优化方法并进行对比实验 (10%)
+ - 调研 PyTorch 中权重初始化的方法,并实现代码替换 `get_torch_initialization` 函数 (10%)
+
+## 选题2
+
+理论和实验证明,一个两层的 ReLU 网络可以模拟任何有界闭集函数。
+
+### 提交内容
+
+- README.md: 课程作业报告
+- source.py: 你的实验代码
+
+### 具体要求
+
+你首先需要在报告中用理论证明这个结论,并给出你在证明过程中所引用定理的出处和证明过程(如果出处中有证明过程则可以省略)。
+
+其次,你需要使用 NumPy 或 PyTorch 编写实验来证明这个结论,你至少需要拟合 3 个不同类型的函数。最好可以写成可以接受任意函数做为输入,然后进行拟合的模式。
+
+### 评分细则
+
+- 课程报告 (50%)
+- 实验代码 (50%)
+ - 只使用 NumPy 实现模型 (10%)
+ - 拟合 3 个不同类型的函数的实验代码 (3*10%)
+ - 实现接受任意函数做为输入进行拟合的函数 (10%)
+- 附加分 (20%)
+ - 其它可以证明这一结论的实验,每个10%,附加分不超过20%,总分不超过 100%
+
+> 模式识别与机器学习 / 复旦大学 / 2021年春
diff --git a/assignment-2/handout-1/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/handout-1/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c2f5bf9d301a40d3390cd35eef2a9b1d0c2c4249
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/handout-1/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,162 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 1 #
+ ####################
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 2 #
+ ####################
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 3 #
+ ####################
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 4 #
+ ####################
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 5 #
+ ####################
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新。 softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ ####################
+ # code 6 #
+ ####################
+
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+
+ ####################
+ # code 7 #
+ ####################
+
+ pass
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
diff --git a/assignment-2/handout-1/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/handout-1/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c18db9439f10238e6d09b99a9e273b69f7725ff8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/handout-1/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, mini_batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+
+
+def numpy_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x.numpy())
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/handout-1/tester_demo.py b/assignment-2/handout-1/tester_demo.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..504b3eef50a6df4d0aa433113136add50835e420
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/handout-1/tester_demo.py
@@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
+import numpy as np
+import torch
+from torch import matmul as torch_matmul, relu as torch_relu, softmax as torch_softmax, log as torch_log
+
+from numpy_fnn import Matmul, Relu, Softmax, Log, NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from torch_mnist import TorchModel
+from utils import get_torch_initialization, one_hot
+
+err_epsilon = 1e-6
+err_p = 0.4
+
+
+def check_result(numpy_result, torch_result=None):
+ if isinstance(numpy_result, list) and torch_result is None:
+ flag = True
+ for (n, t) in numpy_result:
+ flag = flag and check_result(n, t)
+ return flag
+ # print((torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) - torch_result).abs().mean().item())
+ T = (torch_result * torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) < 0).sum().item()
+ direction = T / torch_result.numel() < err_p
+ return direction and ((torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) - torch_result).abs().mean() < err_epsilon).item()
+
+
+def case_1():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[5, 6])
+ W = np.random.normal(size=[6, 4])
+
+ numpy_matmul = Matmul()
+ numpy_out = numpy_matmul.forward(x, W)
+ numpy_x_grad, numpy_W_grad = numpy_matmul.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+ torch_W = torch.from_numpy(W).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_matmul(torch_x, torch_W)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ (numpy_W_grad, torch_W.grad)
+ ])
+
+
+def case_2():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[5, 6])
+
+ numpy_relu = Relu()
+ numpy_out = numpy_relu.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_relu.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_relu(torch_x)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def case_3():
+ x = np.random.uniform(low=0.0, high=1.0, size=[3, 4])
+
+ numpy_log = Log()
+ numpy_out = numpy_log.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_log.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_log(torch_x)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def case_4():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[4, 5])
+
+ numpy_softmax = Softmax()
+ numpy_out = numpy_softmax.forward(x)
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_softmax(torch_x, 1)
+
+ return check_result(numpy_out, torch_out)
+
+
+def case_5():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[20, 25])
+
+ numpy_softmax = Softmax()
+ numpy_out = numpy_softmax.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_softmax.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_softmax(torch_x, 1)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def test_model():
+ try:
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ numpy_model = NumpyModel()
+ torch_model = TorchModel()
+ torch_model.W1.data, torch_model.W2.data, torch_model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+ numpy_model.W1 = torch_model.W1.detach().clone().numpy()
+ numpy_model.W2 = torch_model.W2.detach().clone().numpy()
+ numpy_model.W3 = torch_model.W3.detach().clone().numpy()
+
+ x = torch.randn((10000, 28, 28))
+ y = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0] * 1000)
+
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+ x2 = x.numpy()
+ y_pred = torch_model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+
+ y_pred_numpy = numpy_model.forward(x2)
+ numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred_numpy, y.numpy())
+
+ check_flag_1 = check_result(y_pred_numpy, y_pred)
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("forward", 10 * check_flag_1, 10))
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in forward]")
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("forward", 0, 10))
+ return 0
+
+ try:
+
+ numpy_model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+
+ check_flag_2 = [
+ check_result(numpy_model.log_grad, torch_model.log_input.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.softmax_grad, torch_model.softmax_input.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W3_grad, torch_model.W3.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W2_grad, torch_model.W2.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W1_grad, torch_model.W1.grad)
+ ]
+ check_flag_2 = sum(check_flag_2) >= 4
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("backward", 20 * check_flag_2, 20))
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in backward]")
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("backward", 0, 20))
+ check_flag_2 = False
+
+ return 10 * check_flag_1 + 20 * check_flag_2
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ testcases = [
+ ["matmul", case_1, 5],
+ ["relu", case_2, 5],
+ ["log", case_3, 5],
+ ["softmax_1", case_4, 5],
+ ["softmax_2", case_5, 10],
+ ]
+ score = 0
+ for case in testcases:
+ try:
+ res = case[2] if case[1]() else 0
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in {}]".format(case[0]))
+ res = 0
+ score += res
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format(case[0], res, case[2]))
+ score += test_model()
+ print("{:14} {}/60".format("FINAL SCORE", score))
diff --git a/assignment-2/handout-1/torch_mnist.py b/assignment-2/handout-1/torch_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6d3e214c7606e3d43dac4b94554f942508afffb3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/handout-1/torch_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+import torch
+from utils import mini_batch, batch, download_mnist, get_torch_initialization, one_hot, plot_curve
+
+
+class TorchModel:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = torch.randn((28 * 28, 256), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W2 = torch.randn((256, 64), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W3 = torch.randn((64, 10), requires_grad=True)
+ self.softmax_input = None
+ self.log_input = None
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W1))
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W2))
+ x = torch.matmul(x, self.W3)
+
+ self.softmax_input = x
+ self.softmax_input.retain_grad()
+
+ x = torch.softmax(x, 1)
+
+ self.log_input = x
+ self.log_input.retain_grad()
+
+ x = torch.log(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ with torch.no_grad():
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1.grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2.grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3.grad
+
+ self.W1.grad = None
+ self.W2.grad = None
+ self.W3.grad = None
+
+
+def torch_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = TorchModel()
+ model.W1.data, model.W2.data, model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset, numpy=False):
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset, numpy=False)[0]
+ accuracy = model.forward(x).argmax(dim=1).eq(y).float().mean().item()
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ torch_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/handout-1/utils.py b/assignment-2/handout-1/utils.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..709220cfa7a924d914ec1c098c505f864bcd4cfc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/handout-1/utils.py
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+import torch
+import numpy as np
+from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
+
+
+def plot_curve(data):
+ plt.plot(range(len(data)), data, color='blue')
+ plt.legend(['loss_value'], loc='upper right')
+ plt.xlabel('step')
+ plt.ylabel('value')
+ plt.show()
+
+
+def download_mnist():
+ from torchvision import datasets, transforms
+
+ transform = transforms.Compose([
+ transforms.ToTensor(),
+ transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.1307,), std=(0.3081,))
+ ])
+
+ train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=True, download=True)
+ test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=False, download=True)
+
+ return train_dataset, test_dataset
+
+
+def one_hot(y, numpy=True):
+ if numpy:
+ y_ = np.zeros((y.shape[0], 10))
+ y_[np.arange(y.shape[0], dtype=np.int32), y] = 1
+ return y_
+ else:
+ y_ = torch.zeros((y.shape[0], 10))
+ y_[torch.arange(y.shape[0], dtype=torch.long), y] = 1
+ return y_
+
+
+def batch(dataset, numpy=True):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+ for each in dataset:
+ data.append(each[0])
+ label.append(each[1])
+ data = torch.stack(data)
+ label = torch.LongTensor(label)
+ if numpy:
+ return [(data.numpy(), label.numpy())]
+ else:
+ return [(data, label)]
+
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128, numpy=False):
+ return torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
+
+
+def get_torch_initialization(numpy=True):
+ fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(28 * 28, 256)
+ fc2 = torch.nn.Linear(256, 64)
+ fc3 = torch.nn.Linear(64, 10)
+
+ if numpy:
+ W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ W2 = fc2.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ W3 = fc3.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ else:
+ W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+ W2 = fc2.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+ W3 = fc3.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
diff --git a/assignment-2/handout-2/README.md b/assignment-2/handout-2/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..aa2ddddef23ca4638733a7163655be4e0739dd5f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/handout-2/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
+# 选题2 一些建议
+
+1. 如果理论证明讲不清楚可以在实验上多花一些功夫,仍然可以得到不错的分数
+2. 对于某个函数,可以在函数上采样生成训练集和测试集,使用训练集来训练神经网络,使用测试集来验证拟合效果。
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..36bd3497b1a780fc6ef92ea21a8f530133dd2d35
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,757 @@
+# 课程报告
+
+这是一个有关numpy实现前馈神经网络的实验报告,代码保存在numpy_fnn.py中,实验结果展示使用了matplotlib库。
+
+## 一、FNN算子的numpy实现
+
+### 1. Matmul
+
+Matmul是矩阵之间的乘法,输入为两个矩阵 $X$ 和 $W$ ,其中 $X\in R^{N\times d}$ , $W\in R^{d\times d'}$ ,运算结果为 $Z\in R^{N \times d'}$ 。$Z$中的每个元素 $Z_{ij}$ 由下式得到:
+$$
+\begin{equation}
+Z_{ij} = \sum_{k=1}^d X_{ik} W_{kj}
+\tag{1-1}
+\end{equation}
+$$
+用矩阵形式可以表示为:
+$$
+\begin{equation}
+Z = XW
+\tag{1-2}
+\end{equation}
+$$
+事实上,numpy提供了成熟的矩阵乘法计算函数,我们可以直接调用`numpy.matmul(X, W)`或者`numpy.dot(X, W)`使用。反向传播上,假设损失函数 $\mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})$ 到当前计算的误差项为$\delta$ ,则其关于 $W_{ij}$ 的梯度为:
+$$
+\begin{equation}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial W_{ij}} = \sum_{n=1}^{N}
+\frac{\partial Z_{nj}}{\partial W_{ij}}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial Z_{nj}}
+\tag{1-3}
+\end{equation}
+$$
+其中,根据 $(1-1)$ 式有:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac {\partial Z _ {kj}} {\partial W _ {ij}} & = X_{ni}
+\end {aligned} \tag {1-4}
+$$
+
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial Z_{nj}}=\delta_{nj}
+\end{aligned} \tag{1-5}
+$$
+
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial W_{ij}} &= \sum_{n=1}^{N}
+\frac{\partial Z_{nj}}{\partial W_{ij}}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial Z_{nj}}\\\\
+&=\sum_{n=1}^{N} X_{ni} \delta_{nj}
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{1-6}
+$$
+
+
+
+用矩阵形式可以写作:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial W} &=
+X^T \delta
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{1-7}
+$$
+对 $X_{ij}$ 的梯度为:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial X_{ij}} &= \sum_{m=1}^{d'}
+\frac{\partial Z_{im}}{\partial X_{ij}}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial Z_{im}} \\\\
+&= \sum_{m=1}^{d'}
+W_{jm} \delta_{im}
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{1-8}
+$$
+用矩阵形式可以写作:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial X} &=
+\delta W^T
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{1-9}
+$$
+
+具体代码为:
+
+```python
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ W = self.memory['W']
+ grad_W = np.matmul(x.T, grad_y)
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, W.T)
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+```
+
+### 2. ReLU
+
+ReLU函数是一类非线性激活函数,数学形式为 $ReLU(x)=max(0,x)$ 。因此,在 $x>0$ 的地方,梯度为1,其他地方梯度为0,在 $x=0$ 处,函数不可导,这时引入次梯度,使得该处的梯度为0,因此ReLU函数的反向传播可以写作:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial X_{ij}} &=
+\begin{cases}
+1, & \text{if $$x>0$$} \\\\
+0, & \text{o.w.}
+\end{cases}
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{2-1}
+$$
+
+
+矩阵形式下可以引入一个矩阵 $S$ 用来标记 $X$ 中大于0的元素的位置,其中大于0的位置数值为1,否则为0,则反向传播可以写作:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial X} &=
+S \odot\delta
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{2-2}
+$$
+
+代码为:
+
+```python
+def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ # 使用np.where起公式中S过滤矩阵的作用
+ grad_x = np.where(x > 0, grad_y, np.zeros_like(grad_y))
+
+ return grad_x
+```
+
+### 3. Log
+
+假设 $y=log(x + \epsilon)$ ,那么
+$$
+\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{1}{x + \epsilon}
+\tag{3-1}
+$$
+
+假设 $\frac{1}{X}$ 表示对矩阵 $X$ 中的元素按位取倒数得到的矩阵,则有
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial X} &=
+\left[
+\begin{matrix}
+\frac{\delta_{ij}}{X_{ij} + \epsilon}
+\end{matrix}
+\right]_{N \times d}\\\\
+&=
+\delta \odot \frac{1}{X}
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{3-2}
+$$
+
+代码为:
+
+```python
+def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ grad_x = 1 / (x + self.epsilon) * grad_y
+
+ return grad_x
+```
+
+### 4. softmax
+
+softmax是相对于argmax而言的,其优势是可导,具体形式为:
+$$
+softmax({\pmb x})=
+\left[
+\begin{matrix}
+\frac{exp(x_1)}{\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c)} & \cdots & \frac{exp(x_C)}{\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c)}
+\end{matrix}
+\right]
+\tag{4-1}
+$$
+在实际计算中,如果 $x_i$ 的值过大,很容易导致数值上溢,因此在计算时,可以在分子分母上同时除以最大值 $exp(x_{max})$ ,可以在保证数值不变的情况下防止上溢:
+$$
+softmax({\pmb x})=
+\left[
+\begin{matrix}
+\frac{exp(x_1-x_{max})}{\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c-x_{max})} & \cdots & \frac{exp(x_C-x_{max} )}{\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c-x_{max} )}
+\end{matrix}
+\right]
+\tag{4-2}
+$$
+反向传播时, $\frac {\partial softmax(x_i)} {\partial x_j}$ 需要分类讨论 $x_i$ 的情况,当 $i=j$ 时:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac {\partial softmax(x_i)} {\partial x_j} &=
+\frac{\partial}{\partial x_j}(\frac{exp(x_j-x_{max})}{\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c-x_{max})}) \\\\
+&=
+\frac{\partial}{\partial x_j}(\frac{exp(x_j)}{\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c)})\\\\
+&=
+\frac{\frac{\partial exp(x_j)}{\partial x_j}\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c) - exp(x_j)\frac{\partial \sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c)}{\partial x_j}}{(\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c))^2}\\\\
+&=
+\frac{exp(x_j)\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c) - exp(x_j)^2}{(\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c))^2}\\\\
+&=
+softmax(\pmb x)_j - (softmax(\pmb x)_j)^2\\\\
+&=softmax(\pmb x)_j(1-softmax(\pmb x)_j)
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{4-3}
+$$
+
+当 $i\neq j$ 时:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac {\partial softmax(x_i)} {\partial x_j}
+&=
+\frac{\partial}{\partial x_j}(\frac{exp(x_i)}{\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c)})\\\\
+&=
+\frac{0- exp(x_i)\frac{\partial \sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c)}{\partial x_j}}{(\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c))^2}\\\\
+&=
+\frac{- exp(x_i)exp(x_j)}{(\sum_{c=1}^C exp(x_c))^2}\\\\
+&=
+-softmax(\pmb x)_i softmax(\pmb x)_j
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{4-4}
+$$
+用矩阵形式表示:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac {\partial softmax(\pmb x)} {\partial {\pmb x}} &=\left[
+\begin{matrix}
+softmax(\pmb x)_1(1-softmax(\pmb x)_1) & \cdots& -softmax(\pmb x)_1 softmax(\pmb x)_C \\\\
+\vdots & \ddots & \vdots\\\\
+-softmax(\pmb x)_C softmax(\pmb x)_1 & \cdots& softmax(\pmb x)_C(1-softmax(\pmb x)_C)
+\end{matrix}
+\right] \\\\
+&=diag(softmax(\pmb x)) - softmax(\pmb x)softmax(\pmb x)^T
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{4-5}
+$$
+
+其中 $diag(softmax(\pmb x))$ 指的是将 $softmax(\pmb x)$ 元素按顺序排列在对角线上的对角阵,假设误差项为 $\delta \in R^{C}$ ,则:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial \pmb x} &=
+\frac {\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})} {\partial softmax(\pmb x)} \frac {\partial softmax(\pmb x)} {\partial {\pmb x}}\\\\
+&=\delta(diag(softmax(\pmb x)) - softmax(\pmb x)^Tsoftmax(\pmb x))
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{4-6}
+$$
+需要注意,这里的 $softmax(\pmb x)$ 是一个行向量。在numpy实现上,我们可以对 $X$ 矩阵的每一行进行softmax操作,从而得到每个样本在每个类上的预测值,记得到的结果为矩阵 $\hat Y \in R^{N \times C}$。反向传播时,我们需要将 $\hat Y$ 扩充为 $R^{N \times 1 \times C}$,并使用`numpy.matmul()`方法在最后两维上计算 $\hat Y$ 对 $X$ 的导数 $dX \in R^{N \times C \times C}$ ,在此基础上,将误差项 $\delta \in R^{N \times C}$扩充为 $R^{N \times 1 \times C}$,也在后两维上与 $dX$ 进行乘法,从而得到 $\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial X}_{temp} \in R^{N \times 1 \times C}$ ,此时再将中间的维度压缩掉,就可以得到最后的结果:$\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(y,\hat{y})}{\partial X} \in R^{N \times C}$ 。
+
+代码为:
+
+```python
+def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ N, C = grad_y.shape
+ A = self.memory['A']
+ # 扩充激活值的维度,计算softmax对X导数dX
+ temp = A[:, np.newaxis, :] * np.eye(C) - np.matmul(A[:, np.newaxis, :].transpose(0, 2, 1), A[:, np.newaxis, :])
+ # 扩充误差项与dX进行乘法
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y[:, np.newaxis, :], temp).squeeze(1)
+
+ return grad_x
+```
+
+## 二、模型训练与测试
+
+### 1. 学习率调整
+
+笔者分别使用了1、0.1、0.01、0.001的学习率进行了实验,在训练集上的损失如下:
+
+
+  |
+
+  |
+
 |
+  |
+
 +
+  +
+  +
+
+ .png) |
+
+ .png) |
+
+ .png) |
+
+ .png) |
+
+ .png) |
+
+ .png) |
+
+  |
+
+  |
+
+
|
+ |
+
+ |
+
 +
+输出呈现处明显地向0靠拢的趋势,当输出归0后,模型在反向传播时误差项在与其进行乘法运算后也会归零,最终导致梯度消失。如果我们调整缩放因子的大小为0.06,则会发现每一层的输出则会逐渐聚集到1和-1周围:
+
+
+
+输出呈现处明显地向0靠拢的趋势,当输出归0后,模型在反向传播时误差项在与其进行乘法运算后也会归零,最终导致梯度消失。如果我们调整缩放因子的大小为0.06,则会发现每一层的输出则会逐渐聚集到1和-1周围:
+
+ +
+这表明每一层的净输出使得 $tanh()$ 函数过饱和,而在过饱和处,激活函数的导数值趋近于0,从而也会导致梯度消失。
+
+### 2. Xavier初始化
+
+为了让神经网络每层的输出能够保持稳定,在0的周围较为均匀的分布,使得激活函数导数不为0的情况下,输出不会归0,从而保证梯度的存在,Xavier初始化方式被提出。其原理是在正态分布初始化的基础上,舍弃了常数缩放因子,而使用 $\frac{2}{\sqrt{D_{in}+D_{out}}}$ 控制其分布,其原理是尽量保证映射前后样本的方差相等(参见[深度前馈网络与Xavier初始化原理-夕小瑶](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/27919794))。
+
+对于当前层每一个神经元的输出(见公式 $(1-1)$ ),其中每一个加项的方差可以表示为:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+Var(w_ix_i)&=E[w_i]^2Var(x_i)+E[x_i]^2Var(w_i)+Var(w_i)Var(x_i)
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{5-2-1}
+$$
+如果控制 $w_i$ 和 $x_i$ 的均值为0,且假设权重与输入是独立的,并且各自属于同一分布,则神经元输出的方差可以表示为:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+Var(z)&=\sum^n_{i=1}Var(w_{i})Var(x_{i}) \\\\
+&=nVar(w)Var(x)
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{5-2-2}
+$$
+为了保证映射前后方差相等,则需要控制 $nVar(w)=1$ ,即 $Var(w)=1/n$ ,那么在前向传播时,n为 $d_{in}$ ,反向传播时n为 $d_{out}$ ,折衷起见,可以令 $std(w)$ 为 $\frac{2}{\sqrt{D_{in}+D_{out}}}$ ,从而让模型在前向和反向传播时都可以保持输入输出方差稳定,实验结果也印证了这一结论。
+
+
+
+这表明每一层的净输出使得 $tanh()$ 函数过饱和,而在过饱和处,激活函数的导数值趋近于0,从而也会导致梯度消失。
+
+### 2. Xavier初始化
+
+为了让神经网络每层的输出能够保持稳定,在0的周围较为均匀的分布,使得激活函数导数不为0的情况下,输出不会归0,从而保证梯度的存在,Xavier初始化方式被提出。其原理是在正态分布初始化的基础上,舍弃了常数缩放因子,而使用 $\frac{2}{\sqrt{D_{in}+D_{out}}}$ 控制其分布,其原理是尽量保证映射前后样本的方差相等(参见[深度前馈网络与Xavier初始化原理-夕小瑶](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/27919794))。
+
+对于当前层每一个神经元的输出(见公式 $(1-1)$ ),其中每一个加项的方差可以表示为:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+Var(w_ix_i)&=E[w_i]^2Var(x_i)+E[x_i]^2Var(w_i)+Var(w_i)Var(x_i)
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{5-2-1}
+$$
+如果控制 $w_i$ 和 $x_i$ 的均值为0,且假设权重与输入是独立的,并且各自属于同一分布,则神经元输出的方差可以表示为:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+Var(z)&=\sum^n_{i=1}Var(w_{i})Var(x_{i}) \\\\
+&=nVar(w)Var(x)
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{5-2-2}
+$$
+为了保证映射前后方差相等,则需要控制 $nVar(w)=1$ ,即 $Var(w)=1/n$ ,那么在前向传播时,n为 $d_{in}$ ,反向传播时n为 $d_{out}$ ,折衷起见,可以令 $std(w)$ 为 $\frac{2}{\sqrt{D_{in}+D_{out}}}$ ,从而让模型在前向和反向传播时都可以保持输入输出方差稳定,实验结果也印证了这一结论。
+
+ +
+### 3. kaiming
+
+Xavier初始化是针对线性函数的,但是对于部分饱和类激活函数而言也比较有效如上面使用的tanh,因为其在0附近近似成线性,但是对于非饱和类激活函数如ReLU,效果并没有那么理想,因为在ReLU网络中,输出均值并不为0。
+
+
+
+### 3. kaiming
+
+Xavier初始化是针对线性函数的,但是对于部分饱和类激活函数而言也比较有效如上面使用的tanh,因为其在0附近近似成线性,但是对于非饱和类激活函数如ReLU,效果并没有那么理想,因为在ReLU网络中,输出均值并不为0。
+
+ +
+经过ReLU函数激活后,每一层的输入还是逐渐聚拢在0周围,在这一背景下,He Kaiming提出了Kaiming初始化方法,其原理是假设每一层神经元被激活的概率为0.5,所以对公式 $(5-2-2)$ 进行修正:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+Var(z)&=\sum^n_{i=1}Var(w_{i})Var(x_{i}) \\\\
+&=\frac{n}{2}Var(w)Var(x)\\\\
+Var(w)&=\frac{2}{n}
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{5-3-1}
+$$
+在实际使用中,只需要满足前向和后向中的一个方向上的方差近似就可以起到很好的效果。从实验结果看,基本能够保证方差均值稳定。
+
+
+
+经过ReLU函数激活后,每一层的输入还是逐渐聚拢在0周围,在这一背景下,He Kaiming提出了Kaiming初始化方法,其原理是假设每一层神经元被激活的概率为0.5,所以对公式 $(5-2-2)$ 进行修正:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+Var(z)&=\sum^n_{i=1}Var(w_{i})Var(x_{i}) \\\\
+&=\frac{n}{2}Var(w)Var(x)\\\\
+Var(w)&=\frac{2}{n}
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{5-3-1}
+$$
+在实际使用中,只需要满足前向和后向中的一个方向上的方差近似就可以起到很好的效果。从实验结果看,基本能够保证方差均值稳定。
+
+ +
+一般地,针对LeakyReLU,会进行一定的修正。在`torch.nn.Linear`类中,就使用了`kaiming_uniform_()`方法进行优化,,假设参数 $W$ 的维度为 $(d_{in}, d_{out})$ ,则 $W_{ij}$ 的分布可以表示为:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+bound &= \sqrt{\frac{6}{(1+a^2)d_{in}}} \\\\
+W_{ij} &\sim U(-bound, bound)
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{5-1-1}
+$$
+其中 $a$ 是使用的ReLU函数在负半轴的斜率,torch在Linear层默认取a为 $\sqrt5$ ,则 $bound = \sqrt{\frac{1}{d_{in}}}$。因为torch与numpy随机种子不同,无法进行比较。代码如下:
+
+```python
+def get_numpy_initialization():
+ bound1 = np.sqrt(1 / (28 * 28))
+ bound2 = np.sqrt(1 / 256)
+ bound3 = np.sqrt(1 / 64)
+
+ W1 = (np.random.rand(28 * 28, 256) - .5) * 2 * bound1
+ W2 = (np.random.rand(256, 64) - .5) * 2 * bound2
+ W3 = (np.random.rand(64, 10) - .5) * 2 * bound3
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
+```
+
+损失曲线基本与torch初始化类似,
+
+
+
+一般地,针对LeakyReLU,会进行一定的修正。在`torch.nn.Linear`类中,就使用了`kaiming_uniform_()`方法进行优化,,假设参数 $W$ 的维度为 $(d_{in}, d_{out})$ ,则 $W_{ij}$ 的分布可以表示为:
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+bound &= \sqrt{\frac{6}{(1+a^2)d_{in}}} \\\\
+W_{ij} &\sim U(-bound, bound)
+\end{aligned}
+\tag{5-1-1}
+$$
+其中 $a$ 是使用的ReLU函数在负半轴的斜率,torch在Linear层默认取a为 $\sqrt5$ ,则 $bound = \sqrt{\frac{1}{d_{in}}}$。因为torch与numpy随机种子不同,无法进行比较。代码如下:
+
+```python
+def get_numpy_initialization():
+ bound1 = np.sqrt(1 / (28 * 28))
+ bound2 = np.sqrt(1 / 256)
+ bound3 = np.sqrt(1 / 64)
+
+ W1 = (np.random.rand(28 * 28, 256) - .5) * 2 * bound1
+ W2 = (np.random.rand(256, 64) - .5) * 2 * bound2
+ W3 = (np.random.rand(64, 10) - .5) * 2 * bound3
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
+```
+
+损失曲线基本与torch初始化类似,
+
+ +
+实际上,在numpy模型中,并没有使用LeakyReLU,根据torch的原则取 $bound = \sqrt{\frac{6}{d_{in}}}$ ,修改代码中对应的部分:
+
+```python
+def get_numpy_initialization():
+ bound1 = np.sqrt(6 / (28 * 28))
+ bound2 = np.sqrt(6 / 256)
+ bound3 = np.sqrt(6 / 64)
+
+ W1 = (np.random.rand(28 * 28, 256) - .5) * 2 * bound1
+ W2 = (np.random.rand(256, 64) - .5) * 2 * bound2
+ W3 = (np.random.rand(64, 10) - .5) * 2 * bound3
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
+```
+
+前三个epoch测试集准确率分别为:0.9532,0.9659,0.9734,与torch默认的初始化方式结果接近。
+
+测试模型每层经过ReLU函数激活的活性值并进行可视化处理:
+
+使用kaiming init方法:
+
+
+
+实际上,在numpy模型中,并没有使用LeakyReLU,根据torch的原则取 $bound = \sqrt{\frac{6}{d_{in}}}$ ,修改代码中对应的部分:
+
+```python
+def get_numpy_initialization():
+ bound1 = np.sqrt(6 / (28 * 28))
+ bound2 = np.sqrt(6 / 256)
+ bound3 = np.sqrt(6 / 64)
+
+ W1 = (np.random.rand(28 * 28, 256) - .5) * 2 * bound1
+ W2 = (np.random.rand(256, 64) - .5) * 2 * bound2
+ W3 = (np.random.rand(64, 10) - .5) * 2 * bound3
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
+```
+
+前三个epoch测试集准确率分别为:0.9532,0.9659,0.9734,与torch默认的初始化方式结果接近。
+
+测试模型每层经过ReLU函数激活的活性值并进行可视化处理:
+
+使用kaiming init方法:
+
+ +
+(-1,1)范围内正态分布初始化:
+
+
+
+(-1,1)范围内正态分布初始化:
+
+ +
+可以发现,kaiming初始化方法能够保持每一层的输出的均值和方差稳定,这会使得神经网络在训练的过程中出现梯度爆炸或消失的可能性减少。
+
+## 六、代码使用方法
+
+```python
+# 默认使用numpy_mini_batch与numpy_initialization
+python numpy_mnist.py v # 权重初始化比较
+python numpy_mnist.py o # 优化器比较
+python numpy_mnist.py # 默认训练与测试(SGD,epoch=3,lr=0.1)
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.0001.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.0001.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..606e56a9dc8c0a18c5ab489005b6546159b441e1
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.0001.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.001.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.001.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..960dc86d975af6b88012bef867ff92a544d33446
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.001.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.01.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.01.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..5230a0ca1902226472efa4b251b3e60606427d57
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.01.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.1.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..70edcf5abe2a755fe20b9e4f635f42f21e2d58e7
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=0.1,acc.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=0.1,acc.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f6f52dae2e3119f055ad7c15eefd32565dbc9943
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=0.1,acc.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=0.1,loss.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=0.1,loss.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..641e984914fc16fba18e1632d12b989546a56fa2
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=0.1,loss.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=0.1.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=0.1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..46e307edb61e880b41535470c9681e6b07faede8
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=0.1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=1,acc.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=1,acc.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f6f52dae2e3119f055ad7c15eefd32565dbc9943
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=1,acc.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=1,loss.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=1,loss.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..641e984914fc16fba18e1632d12b989546a56fa2
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=1,loss.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=1.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..46e307edb61e880b41535470c9681e6b07faede8
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/init2.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/init2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..813abf5d88a7b54e48d1a8ea7c00a84975a4c9e0
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/init2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/init3.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/init3.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..5a1b2b8989a76bb6fabe8a96661744975d38b216
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/init3.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/kaiming_init1.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/kaiming_init1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..edbe2c89d268711d0709752311cdbb2e7a1f8a46
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/kaiming_init1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_(1280,320).png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_(1280,320).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..87e7298570342f056190c2b991979de0b8f8b51d
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_(1280,320).png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_(254,64).png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_(254,64).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..8bad30d32f2c4ed94abe370e81e08b54f14b6e86
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_(254,64).png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_(512,128).png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_(512,128).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..366653f463fd3a69e320015bc234e41e71a16b52
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_(512,128).png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_acc_(1280,320).png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_acc_(1280,320).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6da587fc28d39bc26dfc98d7886b9e80667ffe37
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_acc_(1280,320).png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_acc_(256,64).png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_acc_(256,64).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7a8e5052e7e02b92b36427df4a1a23a98303a525
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_acc_(256,64).png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_acc_(512,128).png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_acc_(512,128).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a9a1e14089ce4a7338a26b277f9a606a28ac5308
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_acc_(512,128).png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/momentum.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/momentum.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..49cbe84c1e395b15e157df828373926a753aae7b
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/momentum.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/normal_init.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/normal_init.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b968820ee6b6323c28d6ec148c29d28c4434849f
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/normal_init.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/normal_init2.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/normal_init2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..937983cb9d5768d88cd3104a454c8c53493225dd
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/normal_init2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/numpy_init.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/numpy_init.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..df605a5d8d5c4890ddde9b11a048ce3f8cd5d356
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/numpy_init.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/optim1.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/optim1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..034e9b925200e453615bb6abd75db8b21088a2d5
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/optim1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/optim2-1.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/optim2-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b00a3bd94d29eb4486fe633c7fb1483ed0e64965
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/optim2-1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/optim2.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/optim2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..2bc60abbe4116142e57408fde28185bf3d35866d
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/optim2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/train_with_noise.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/train_with_noise.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b82edb9bea80ce1cb9c4d9530a48528665d69a54
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/train_with_noise.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/train_without_noise.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/train_without_noise.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f2213af4b5a0091350a4895a746c99b86d6d085e
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/train_without_noise.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/xavier_init.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/xavier_init.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..68669b829accf73edf59ff41cb4902414cd32b1a
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/xavier_init.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/xavier_init2.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/xavier_init2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c06e2c1a813b2007089b839771362f50ab432927
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/xavier_init2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f9bff17642d6d888ad6326c8bd7939c2e2c66502
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,279 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def __call__(self, x, W):
+ return self.forward(x, W)
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ W = self.memory['W']
+ grad_W = np.matmul(x.T, grad_y)
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, W.T)
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def __call__(self, x):
+ return self.forward(x)
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ grad_x = np.where(x > 0, grad_y, np.zeros_like(grad_y))
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def __call__(self, x):
+ return self.forward(x)
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ grad_x = 1 / (x + self.epsilon) * grad_y
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+ max = np.max(x, axis=1, keepdims=True)
+ out = np.exp(x - max) / np.sum(np.exp(x - max), axis=1).reshape(-1, 1)
+ self.memory['A'] = out
+
+ return out
+
+ def __call__(self, x):
+ return self.forward(x)
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ N, C = grad_y.shape
+ A = self.memory['A']
+ # 扩充激活值的维度,计算softmax导数
+ temp = A[:, np.newaxis, :] * np.eye(C) - np.matmul(A[:, np.newaxis, :].transpose(0, 2, 1), A[:, np.newaxis, :])
+ # 扩充误差项与dX进行乘法
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y[:, np.newaxis, :], temp).squeeze(1)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新.softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ self.memory = {}
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ x = self.relu_1(self.matmul_1(x, self.W1))
+ x = self.relu_2(self.matmul_2(x, self.W2))
+ x = self.matmul_3(x, self.W3)
+ x = self.softmax(x)
+ x = self.log(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+ grad_y = y
+
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(grad_y)
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+ self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate, mode='SGD', h_params=None):
+ """
+ 优化器,用于更新参数
+ :param learning_rate: 学习率
+ :param mode: 优化器类型,包括SGD AdaGrad RMSProp Adam
+ :param h_params: 优化器所需的超参数
+ :return: None
+ """
+ if mode == 'SGD':
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+ elif mode == 'momentum':
+ # beta 一般取0.9
+ beta = h_params[0]
+ # 获取上一时刻的动量,初始值为0
+ V1, V2, V3 = self.memory.get('V1', 0), self.memory.get('V2', 0), self.memory.get('V3', 0)
+ # 更新动量
+ V1 = beta * V1 + (1 - beta) * self.W1_grad
+ V2 = beta * V2 + (1 - beta) * self.W2_grad
+ V3 = beta * V3 + (1 - beta) * self.W3_grad
+ # 存储当前动量
+ self.memory['V1'] = V1
+ self.memory['V2'] = V2
+ self.memory['V3'] = V3
+ # 更新参数
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * V1
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * V2
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * V3
+
+ elif mode == 'AdaGrad':
+ # 学习率大于1e-2以后梯度会消失
+ epsilon = 1e-7
+ # 读取历史梯度值平方和
+ r1, r2, r3 = self.memory.get('r1', 0), self.memory.get('r2', 0), self.memory.get('r3', 0)
+ # 更新历史梯度值平方和
+ r1 += np.square(self.W1_grad)
+ r2 += np.square(self.W2_grad)
+ r3 += np.square(self.W3_grad)
+ # 存储历史梯度值平方和
+ self.memory['r1'] = r1
+ self.memory['r2'] = r2
+ self.memory['r3'] = r3
+ # 更新参数
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r1)) * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r2)) * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r3)) * self.W3_grad
+
+ elif mode == 'RMSProp':
+ # lr 1e-3, rho 0.999
+ epsilon = 1e-6
+ rho = h_params[0]
+ # 读取历史梯度值平方和
+ r1, r2, r3 = self.memory.get('r1', 0), self.memory.get('r2', 0), self.memory.get('r3', 0)
+ # 更新历史梯度值平方和
+ r1 = rho * r1 + (1 - rho) * np.square(self.W1_grad)
+ r2 = rho * r2 + (1 - rho) * np.square(self.W2_grad)
+ r3 = rho * r3 + (1 - rho) * np.square(self.W3_grad)
+ # 存储历史梯度值平方和
+ self.memory['r1'] = r1
+ self.memory['r2'] = r2
+ self.memory['r3'] = r3
+ # 更新参数
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r1)) * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r2)) * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r3)) * self.W3_grad
+
+ elif mode == 'Adam':
+ # lr=1e-3, rho1=0.9, rho2=0.999
+ epsilon = 1e-8
+ rho1, rho2 = h_params[0], h_params[1]
+ # 确定当前时刻值
+ t = self.memory.get('t', 0)
+ t += 1
+ # 读取历史梯度值平方和以及历史动量,初始值均为0
+ s1, s2, s3 = self.memory.get('s1', 0), self.memory.get('s2', 0), self.memory.get('s3', 0)
+ r1, r2, r3 = self.memory.get('r1', 0), self.memory.get('r2', 0), self.memory.get('r3', 0)
+ # 更新动量
+ s1 = rho1 * s1 + (1 - rho1) * self.W1_grad
+ s2 = rho1 * s2 + (1 - rho1) * self.W2_grad
+ s3 = rho1 * s3 + (1 - rho1) * self.W3_grad
+ # 存储动量
+ self.memory['s1'] = s1
+ self.memory['s2'] = s2
+ self.memory['s3'] = s3
+ # 更新梯度值平方和
+ r1 = rho2 * r1 + (1 - rho2) * np.square(self.W1_grad)
+ r2 = rho2 * r2 + (1 - rho2) * np.square(self.W2_grad)
+ r3 = rho2 * r3 + (1 - rho2) * np.square(self.W3_grad)
+ # 存储梯度值平方和
+ self.memory['r1'] = r1
+ self.memory['r2'] = r2
+ self.memory['r3'] = r3
+ # 修正当前动量
+ s1_hat = s1 / (1 - np.power(rho1, t))
+ s2_hat = s2 / (1 - np.power(rho1, t))
+ s3_hat = s3 / (1 - np.power(rho1, t))
+ # 修正当前梯度平方和
+ r1_hat = r1 / (1 - np.power(rho2, t))
+ r2_hat = r2 / (1 - np.power(rho2, t))
+ r3_hat = r3 / (1 - np.power(rho2, t))
+ # 更新梯度
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r1_hat)) * s1_hat
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r2_hat)) * s2_hat
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r3_hat)) * s3_hat
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f52192aedd664743252cd1d96ecdb8a8b37dc8a3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,460 @@
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss, Matmul, Relu, Log, Softmax
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, mini_batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
+
+np.random.seed(1)
+
+
+def gaussian_noise(img, mu=0.1307, std=0.3081):
+ """
+ 产生随机噪声,噪声的均值与方差与图像采样数据一致
+ :param img: 待处理的数据
+ :param mu: 噪声均值
+ :param std: 噪声方差
+ :return: 经过噪声处理后的图像
+ """
+ epsilon = 1
+ sigma = std
+ noise = np.random.normal(mu, sigma, img.shape) * epsilon
+ # 设置阈值
+ out = np.clip(img + noise, -1, 1)
+ return out
+
+
+def get_numpy_initialization(mode='kaiming', test=False, neuron_shape=(256, 64)):
+ """
+ 使用numpy模拟torch初始化
+ :param neuron_shape: 控制隐藏层神经元数量
+ :param mode: 初始化模式:normal Xavier kaiming_uniform
+ :param test: 当用来进行探究初始化实验时,设为True,此时每层均为4096个神经元,否则为False,与fnn模型结构一致
+ :return: 参数W1 W2 W3
+ """
+ # 设置神经元数量
+ if test:
+ d0 = 28 * 28
+ d1 = 4096
+ d2 = 4096
+ d3 = 4096
+ else:
+ d0 = 28 * 28
+ d1, d2 = neuron_shape
+ d3 = 10
+ # 设置初始化方式
+ if mode == 'normal':
+ factor = 0.01 # 缩放因子,用来控制参数初始化的范围
+ W1 = np.random.normal(size=(d0, d1)) * factor
+ W2 = np.random.normal(size=(d1, d2)) * factor
+ W3 = np.random.normal(size=(d2, d3)) * factor
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
+
+ if mode == 'Xavier':
+ W1 = np.random.normal(size=(d0, d1)) * (2 / (np.sqrt(d0) + np.sqrt(d1)))
+ W2 = np.random.normal(size=(d1, d2)) * (2 / (np.sqrt(d1) + np.sqrt(d2)))
+ W3 = np.random.normal(size=(d2, d3)) * (2 / (np.sqrt(d2) + np.sqrt(d3)))
+ return W1, W2, W3
+
+ elif mode == 'kaiming':
+ bound1 = np.sqrt(6 / d0)
+ bound2 = np.sqrt(6 / d1)
+ bound3 = np.sqrt(6 / d2)
+
+ W1 = (np.random.rand(d0, d1) - .5) * 2 * bound1
+ W2 = (np.random.rand(d1, d2) - .5) * 2 * bound2
+ W3 = (np.random.rand(d2, d3) - .5) * 2 * bound3
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
+
+
+def visualize_weight(mode='kaiming', act='ReLU', test=True):
+ """
+ 用来可视化每层的参数分布情况
+ :param mode: 使用的初始化方式
+ :param act: 激活函数类型:tanh ReLU
+ :param test: 当用来进行探究初始化实验时,设为True,此时每层均为4096个神经元,否则为False,与fnn模型结构一致
+ :return: None
+ """
+ print(mode, act)
+ x = np.random.rand(16, 28 * 28) # 随机初始化输入
+ W1, W2, W3 = get_numpy_initialization(mode, test) # 获取初始化参数
+ W = [0, W1, W2, W3]
+
+ # 下面这个循环模拟了一个具有三个隐藏层的神经网络
+ for i in range(1, 4):
+ if act == 'tanh':
+ x = np.tanh(x.dot(W[i]))
+ elif act == 'ReLU':
+ x = np.maximum(0, x.dot(W[i])) # 过滤掉小于0的值,模拟ReLU
+ else:
+ raise ValueError("WRONG ACTIVATION")
+ # 获取每一层经过激活后的输出
+ mean = np.mean(x)
+ std = np.std(x)
+ # 绘制分布直方图
+ plt.subplot(1, 3, i)
+ plt.hist(x.flatten())
+ if act == 'ReLU':
+ lim = 5
+ else:
+ lim = 1
+
+ plt.xlim(-lim, lim)
+ plt.title(f'layer{i}\nmean={mean:.2f}\nstd={std:.2f}')
+
+ plt.show()
+
+
+def mini_batch_numpy(dataset, batch_size=128, noise=False):
+ """
+ 使用numpy实现minibatch
+ :param dataset: torch获取的MNIST数据集
+ :param batch_size: 批大小
+ :return: 一个list,其中每个元素是一个batch(x, y)
+ """
+ # 对数据进行标准化处理 mean=(0.1307,), std=(0.3081,)
+ X = dataset.data.numpy() / 255
+ mean = 0.1307
+ std = 0.3081
+ X = (X - mean) / std
+ y = dataset.targets.numpy()
+
+ # 添加高斯噪声
+ if noise:
+ X = gaussian_noise(X)
+
+ # 打乱样本和标签
+ n = X.shape[0]
+ idx = np.arange(n)
+ np.random.shuffle(idx)
+ X = X[idx]
+ y = y[idx]
+
+ # 用于切分数据生成batches
+ iter_num = int(np.ceil(n / batch_size))
+ dataloader = \
+ [(X[i * batch_size: (i + 1) * batch_size], y[i * batch_size: (i + 1) * batch_size])
+ # 处理当最后的部分不足batch size时
+ if (i + 1) * batch_size <= n
+ else (X[i * batch_size:], y[i * batch_size:])
+ for i in range(iter_num)]
+ return dataloader
+
+
+class NumpyModel_neuron:
+ def __init__(self, neuron_shape=(256, 64)):
+ h2, h3 = neuron_shape
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, h2))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(h2, h3))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(h3, 10))
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新.softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ self.memory = {}
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ x = self.relu_1(self.matmul_1(x, self.W1))
+ x = self.relu_2(self.matmul_2(x, self.W2))
+ x = self.matmul_3(x, self.W3)
+ x = self.softmax(x)
+ x = self.log(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+ grad_y = y
+
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(grad_y)
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+ self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate, mode='SGD', h_params=None):
+ """
+ 优化器,用于更新参数
+ :param learning_rate: 学习率
+ :param mode: 优化器类型,包括SGD AdaGrad RMSProp Adam
+ :param h_params: 优化器所需的超参数
+ :return: None
+ """
+ if mode == 'SGD':
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+ elif mode == 'momentum':
+ # beta 一般取0.9
+ beta = h_params[0]
+ # 获取上一时刻的动量,初始值为0
+ V1, V2, V3 = self.memory.get('V1', 0), self.memory.get('V2', 0), self.memory.get('V3', 0)
+ # 更新动量
+ V1 = beta * V1 + (1 - beta) * self.W1_grad
+ V2 = beta * V2 + (1 - beta) * self.W2_grad
+ V3 = beta * V3 + (1 - beta) * self.W3_grad
+ # 存储当前动量
+ self.memory['V1'] = V1
+ self.memory['V2'] = V2
+ self.memory['V3'] = V3
+ # 更新参数
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * V1
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * V2
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * V3
+
+ elif mode == 'AdaGrad':
+ # 学习率大于1e-2以后梯度会消失
+ epsilon = 1e-7
+ # 读取历史梯度值平方和
+ r1, r2, r3 = self.memory.get('r1', 0), self.memory.get('r2', 0), self.memory.get('r3', 0)
+ # 更新历史梯度值平方和
+ r1 += np.square(self.W1_grad)
+ r2 += np.square(self.W2_grad)
+ r3 += np.square(self.W3_grad)
+ # 存储历史梯度值平方和
+ self.memory['r1'] = r1
+ self.memory['r2'] = r2
+ self.memory['r3'] = r3
+ # 更新参数
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r1)) * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r2)) * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r3)) * self.W3_grad
+
+ elif mode == 'RMSProp':
+ # lr 1e-3, rho 0.999
+ epsilon = 1e-6
+ rho = h_params[0]
+ # 读取历史梯度值平方和
+ r1, r2, r3 = self.memory.get('r1', 0), self.memory.get('r2', 0), self.memory.get('r3', 0)
+ # 更新历史梯度值平方和
+ r1 = rho * r1 + (1 - rho) * np.square(self.W1_grad)
+ r2 = rho * r2 + (1 - rho) * np.square(self.W2_grad)
+ r3 = rho * r3 + (1 - rho) * np.square(self.W3_grad)
+ # 存储历史梯度值平方和
+ self.memory['r1'] = r1
+ self.memory['r2'] = r2
+ self.memory['r3'] = r3
+ # 更新参数
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r1)) * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r2)) * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r3)) * self.W3_grad
+
+ elif mode == 'Adam':
+ # lr=1e-3, rho1=0.9, rho2=0.999
+ epsilon = 1e-8
+ rho1, rho2 = h_params[0], h_params[1]
+ # 确定当前时刻值
+ t = self.memory.get('t', 0)
+ t += 1
+ # 读取历史梯度值平方和以及历史动量,初始值均为0
+ s1, s2, s3 = self.memory.get('s1', 0), self.memory.get('s2', 0), self.memory.get('s3', 0)
+ r1, r2, r3 = self.memory.get('r1', 0), self.memory.get('r2', 0), self.memory.get('r3', 0)
+ # 更新动量
+ s1 = rho1 * s1 + (1 - rho1) * self.W1_grad
+ s2 = rho1 * s2 + (1 - rho1) * self.W2_grad
+ s3 = rho1 * s3 + (1 - rho1) * self.W3_grad
+ # 存储动量
+ self.memory['s1'] = s1
+ self.memory['s2'] = s2
+ self.memory['s3'] = s3
+ # 更新梯度值平方和
+ r1 = rho2 * r1 + (1 - rho2) * np.square(self.W1_grad)
+ r2 = rho2 * r2 + (1 - rho2) * np.square(self.W2_grad)
+ r3 = rho2 * r3 + (1 - rho2) * np.square(self.W3_grad)
+ # 存储梯度值平方和
+ self.memory['r1'] = r1
+ self.memory['r2'] = r2
+ self.memory['r3'] = r3
+ # 修正当前动量
+ s1_hat = s1 / (1 - np.power(rho1, t))
+ s2_hat = s2 / (1 - np.power(rho1, t))
+ s3_hat = s3 / (1 - np.power(rho1, t))
+ # 修正当前梯度平方和
+ r1_hat = r1 / (1 - np.power(rho2, t))
+ r2_hat = r2 / (1 - np.power(rho2, t))
+ r3_hat = r3 / (1 - np.power(rho2, t))
+ # 更新梯度
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r1_hat)) * s1_hat
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r2_hat)) * s2_hat
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r3_hat)) * s3_hat
+
+
+def numpy_run(arg_list, neuron_shape=(256 * 1, 64 * 1), modify=None, noise=None):
+ """
+ 训练开始
+ :param modify: 进行调整神经元实验的参数
+ :param neuron_shape: 用来控制隐藏层神经元数量
+ :param arg_list: 优化器类型与超参数列表,[1e-3, 'Adam', [0.9, 0.999]]
+ :return: None
+ """
+ # 获取超参数
+ if noise is None:
+ noise = [False, False]
+ lr = arg_list[0]
+ mode = arg_list[1]
+ print(mode)
+ h_params = arg_list[-1]
+
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ if modify == 'neuron':
+ model = NumpyModel_neuron(neuron_shape=neuron_shape)
+ elif modify == 'layer':
+ model = NumpyModel_layer(neuron_shape=neuron_shape)
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ # 初始化选择
+ # model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+ # model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_numpy_initialization()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_numpy_initialization(neuron_shape=neuron_shape)
+
+ train_loss = []
+ test_acc = []
+ test_acc_noise = []
+ test_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = lr
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ # 选择minibatch方法
+ # for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ for x, y in mini_batch_numpy(train_dataset, noise = noise[0]):
+ # print(x.numpy().shape)
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x) # 已经在mini_batch_numpy中改为numpy类型
+ # y_pred = model.forward(x.numpy()) #如果使用torch_mini_batch启用此行
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ model.optimize(learning_rate, mode, h_params)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ # x = gaussian_noise(x)
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ accuracy = np.mean((y_pred.argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ test_acc.append(accuracy)
+
+ if noise[1]:
+ x = gaussian_noise(x)
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ accuracy = np.mean((y_pred.argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ test_acc_noise.append(accuracy)
+
+ y = one_hot(y)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(axis=1).mean()
+ test_loss.append(loss)
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss, str(neuron_shape))
+ if modify is not None:
+ return test_acc
+ elif noise[1]:
+ return test_acc, test_acc_noise
+ else:
+ return train_loss
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ import sys
+
+ if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == 'v':
+ # 可视化权重
+ visualize_weight('normal', 'tanh')
+ visualize_weight('Xavier', 'tanh')
+ visualize_weight('Xavier', 'ReLU')
+ visualize_weight('kaiming', 'ReLU')
+ elif len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == 'o':
+ # 比较优化器
+ cases = [
+ [0.1, 'SGD', None],
+ [0.1, 'momentum', [0.9]],
+ [1e-2, 'AdaGrad', None],
+ [1e-4, 'RMSProp', [0.999]],
+ [1e-3, 'Adam', [0.9, 0.999]]
+ ]
+
+ loss = []
+ for case in cases:
+ loss.append(numpy_run(case))
+ step = 1
+ # loss变化图
+ color = ['k', 'y', 'c', 'b', 'r']
+ line = ['-', '-', '--', '-.', ':']
+ optim = [case[1] for case in cases]
+ for i in range(5):
+ plt.subplot(3, 2, i + 1)
+ plt.plot(range(len(loss[i]))[::step], loss[i][::step], color=color[i], linestyle=line[i], label=optim[i])
+ plt.xlabel('step')
+ plt.ylabel('value')
+ plt.legend()
+ plt.show()
+
+ # 取对数绘图
+ for i in range(5):
+ plt.plot(range(len(loss[i]))[::step], np.log(loss[i][::step]) / np.log(100), color=color[i], linestyle=line[i],
+ label=optim[i])
+ plt.legend()
+ plt.xlabel('step')
+ plt.ylabel('log_value')
+ plt.show()
+
+ elif len(sys.argv) > 1 and (sys.argv[1] == 'm' or sys.argv[1] == 'd' or sys.argv[1] == 'f'):
+ # 神经元数量实验
+ if sys.argv[1] == 'm':
+ ns = (256 * 1, 64 * 1)
+ elif sys.argv[1] == 'n':
+ ns = (256 * 2, 64 * 2)
+ elif sys.argv[1] == 'k':
+ ns = (256 * 5, 64 * 5)
+ else:
+ raise ValueError("WRONG ARGV")
+
+ acc = numpy_run([0.1, 'SGD', None], neuron_shape=ns, modify='neuron')
+ plt.plot(range(len(acc)), acc)
+ plt.title(f"test acc {ns}")
+ plt.ylabel("acc")
+ plt.xlabel("epoch")
+ plt.show()
+ elif len(sys.argv) > 1 and (sys.argv[1] == 'g' or sys.argv[1] == 'n'):
+ # 带噪声实验
+ if sys.argv[1] == 'g':
+ test_acc, test_acc_noise = numpy_run([0.1, 'SGD', None], noise=[True, True]) # noise=[训练带噪,测试带噪]
+ plt.plot(range(len(test_acc)), test_acc, linestyle='--', marker='+', color='k', label='test without noise')
+ plt.plot(range(len(test_acc_noise)), test_acc_noise, marker='o', color='y', label='test with noise')
+ plt.xlabel("epoch")
+ plt.ylabel("acc")
+ plt.title("train_with_noise")
+ plt.legend()
+ plt.show()
+ elif sys.argv[1] == 'n':
+ test_acc, test_acc_noise = numpy_run([0.1, 'SGD', None], noise=[False, True])
+ plt.plot(range(len(test_acc)), test_acc, linestyle='--', marker='+', color='k', label='test without noise')
+ plt.plot(range(len(test_acc_noise)), test_acc_noise, marker='o', color='y', label='test with noise')
+ plt.xlabel("epoch")
+ plt.ylabel("acc")
+ plt.title("train_without_noise")
+ plt.legend()
+ plt.show()
+ else:
+ numpy_run([0.1, 'SGD', None])
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..75a75c96dba24c1fe572704318d3646659659437
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,148 @@
+# 实验报告2
+
+### 1,实验结果
+
+在完成了对mini_batch函数的替换后,模型得以顺利进行:
+
+
+
+```shell
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9453
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9656
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9689
+```
+
+### 2,mini_batch的替换
+
+```python
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128, numpy=True):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+ for each in dataset:
+ data.append(np.array(each[0]))
+ label.append(each[1])
+ data = np.array(data)
+ label = np.array(label)
+
+ m = data.shape[0]
+ permutation = list(np.random.permutation(m))
+ data =data[permutation]
+ label=label[permutation]
+
+ n=m//batch_size
+ mini_batches=[]
+ for i in range(n):
+ mini_batches.append([data[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size],label[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size]])
+
+ return mini_batches
+```
+
+整体上参考了utils.py的batch函数。前半段和batch一样,将dataset中的数据分别放到data和label之中。之后,让data和label的元素顺序随机变化,再将每一个小batch的数据和标记放入对应的列表中,依次放入一个大的列表,并最终输出。
+
+### 3,反向传播公式的推导
+
+matmul:
+
+#### 
+
+设输出y为l维的向量。
+
+**dx:**对于每个x中的元素xi,它对y1,y2,y3,.....,yl的偏导为wi1,wi2......,wil.
+
+dL/dxi=(dL/dy1)·wi1+(dL/dy2)·wi2+……+(dL/dyl)·wil
+
+所以,dx=dy·WT.
+
+**dW:** 对于W的元素wij,它对yj的偏导为xi。
+
+dL/dwij=(dL/dyj)·xi
+
+所以,dW=xT*dy。对于多个样本,需要求平均值。
+
+```python
+def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+ N=grad_y.shape[0]
+
+ grad_x=np.matmul(grad_y,self.memory['W'].T)
+ grad_W=np.matmul(self.memory['x'].T,grad_y)
+
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+```
+
+
+
+2,Relu函数
+
+```python
+def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ x=self.memory['x']
+ grad_x = grad_y.copy()
+ grad_x[x<=0]=0
+ return grad_x
+
+```
+
+在xi<=0时,dyi/dxi=0,dL/dxi=0
+
+在xi>0时,dyi/dxi=1,dL/dxi=dL/dyi
+
+所以如上所示,如果xi大于0,则dx相应的位置照搬dy;如果xi小于等于0,则dx响应的位置设置为0.
+
+3,log函数
+
+```python
+def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ x=self.memory['x']
+ x[x<=self.epsilon]=self.epsilon
+ grad_x=grad_y*(1/x)
+
+ return grad_x
+```
+
+dyi/dxi=1/xi,dL/dxi=(dL/dyi)·1/xi
+
+所以,dx=dy·(1/x).
+
+4,softmax函数
+
+
+
+设x和y均为l维的向量。
+
+则对于dyj/dxi,如果i=j,则dyj/dxi=yj-(yj)^2.如果i!=j,则有dyj/dxi=-yi·yj.
+
+设D=diag(y)-yT·y,有dyj/dxi=Dij
+
+这样的话,有dL/dxi=(dL/dy1)·Di1+(dL/dy2)·Di2+……+(dL/dyl)·Dil
+
+所以,dx=dy·D
+
+```python
+def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ y=self.memory['y']
+ l=y.shape[0]
+ grad_x=[]
+ for grad_y1,y1 in zip(grad_y,y):
+ D= np.diag(y1) - np.outer(y1,y1)
+ grad_x1=np.dot(grad_y1, D)
+ grad_x.append(grad_x1)
+ grad_x=np.array(grad_x)
+ return grad_x
+```
+
+不过,在实际的实现中,要考虑到一批中不只有一个数据,要一个一个数据地逐个生成dx。
+
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/img/Figure_1.png b/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/img/Figure_1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..dab6049f889917dcbf2e93d6203b3a6579908777
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/img/Figure_1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..277f81a3f11fb44523777ef4bddcb998454bcdc3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,184 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, self.memory['W'].T)
+ grad_W = np.matmul(self.memory['x'].T, grad_y)
+
+
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ x=self.memory['x']
+ grad_x = grad_y.copy()
+ grad_x[x<=0]=0
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ x=self.memory['x']
+ x[x<=self.epsilon]=self.epsilon
+ grad_x=grad_y*(1/x)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ shift_x = x - np.max(x, axis=1).reshape(-1, 1)
+ y = np.exp(shift_x) / np.sum(np.exp(shift_x), axis=1).reshape(-1, 1)
+ #y = np.exp(x+1) / np.sum(np.exp(x+1), axis=1).reshape(-1, 1)
+ self.memory['y'] = y
+
+ return y
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ y=self.memory['y']
+ l=y.shape[0]
+ grad_x=[]
+ for grad_y1,y1 in zip(grad_y,y):
+ D= np.diag(y1) - np.outer(y1,y1)
+ grad_x1=np.dot(grad_y1, D)
+ grad_x.append(grad_x1)
+ grad_x=np.array(grad_x)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新。 softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ x=self.matmul_1.forward(x,self.W1)
+ x=self.relu_1.forward(x)
+ x=self.matmul_2.forward(x,self.W2)
+ x=self.relu_2.forward(x)
+ x=self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+
+
+ x = self.softmax.forward(x)
+ x = self.log.forward(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+
+ y = self.log.backward(y)
+ self.log_grad = y
+ y = self.softmax.backward(y)
+ self.softmax_grad = y
+ y, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(y)
+ self.x3_grad = y
+ y = self.relu_2.backward(y)
+ y, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(y)
+ self.x2_grad = y
+ y = self.relu_1.backward(y)
+ y, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(y)
+ self.x1_grad = y
+
+ pass
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a688f7c64114bf150ffff2b903dfc74688bda4ad
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, mini_batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128, numpy=True):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+ for each in dataset:
+ data.append(np.array(each[0]))
+ label.append(each[1])
+ data = np.array(data)
+ label = np.array(label)
+
+ m = data.shape[0]
+ permutation = list(np.random.permutation(m))
+ data =data[permutation]
+ label=label[permutation]
+
+ n=m//batch_size
+ mini_batches=[]
+ for i in range(n):
+ mini_batches.append([data[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size],label[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size]])
+
+ return mini_batches
+
+def numpy_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/torch_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/torch_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6a5649bbfa750b3520b4b895de7260c3aa8ea7cd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/torch_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+import torch
+from utils import mini_batch, batch, download_mnist, get_torch_initialization, one_hot, plot_curve
+
+
+class TorchModel:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = torch.randn((28 * 28, 256), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W2 = torch.randn((256, 64), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W3 = torch.randn((64, 10), requires_grad=True)
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W1))
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W2))
+ x = torch.matmul(x, self.W3)
+ self.softmax = torch.softmax(x, 1)
+ self.log = torch.log(self.softmax)
+ self.softmax.retain_grad() # for test only
+ self.log.retain_grad() # for test only
+ return self.log
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ with torch.no_grad():
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1.grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2.grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3.grad
+
+ self.W1.grad = None
+ self.W2.grad = None
+ self.W3.grad = None
+
+
+def torch_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = TorchModel()
+ model.W1.data, model.W2.data, model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset, numpy=False):
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset, numpy=False)[0]
+ accuracy = model.forward(x).argmax(dim=1).eq(y).float().mean().item()
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ torch_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..9b99779240f17d85b2217a7a0600698deb047d32
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,186 @@
+# 课程报告
+
+## 模型的训练与测试
+
+直接运行numpy_minist.py,设定batch_size =128, learning_rate = 0.1, epoch_number = 3得到如下的结果:
+
+| 轮次 | Accuracy |
+| ---- | -------- |
+| [0] | 0.9474 |
+| [1] | 0.9654 |
+| [2] | 0.9704 |
+
+得到的损失函数的变化如下图所示:
+
+
+
+可以发现,kaiming初始化方法能够保持每一层的输出的均值和方差稳定,这会使得神经网络在训练的过程中出现梯度爆炸或消失的可能性减少。
+
+## 六、代码使用方法
+
+```python
+# 默认使用numpy_mini_batch与numpy_initialization
+python numpy_mnist.py v # 权重初始化比较
+python numpy_mnist.py o # 优化器比较
+python numpy_mnist.py # 默认训练与测试(SGD,epoch=3,lr=0.1)
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.0001.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.0001.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..606e56a9dc8c0a18c5ab489005b6546159b441e1
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.0001.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.001.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.001.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..960dc86d975af6b88012bef867ff92a544d33446
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.001.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.01.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.01.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..5230a0ca1902226472efa4b251b3e60606427d57
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.01.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.1.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..70edcf5abe2a755fe20b9e4f635f42f21e2d58e7
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=3,lr=0.1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=0.1,acc.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=0.1,acc.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f6f52dae2e3119f055ad7c15eefd32565dbc9943
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=0.1,acc.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=0.1,loss.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=0.1,loss.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..641e984914fc16fba18e1632d12b989546a56fa2
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=0.1,loss.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=0.1.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=0.1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..46e307edb61e880b41535470c9681e6b07faede8
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=0.1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=1,acc.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=1,acc.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f6f52dae2e3119f055ad7c15eefd32565dbc9943
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=1,acc.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=1,loss.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=1,loss.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..641e984914fc16fba18e1632d12b989546a56fa2
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=1,loss.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=1.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..46e307edb61e880b41535470c9681e6b07faede8
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/epoch=50,lr=1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/init2.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/init2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..813abf5d88a7b54e48d1a8ea7c00a84975a4c9e0
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/init2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/init3.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/init3.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..5a1b2b8989a76bb6fabe8a96661744975d38b216
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/init3.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/kaiming_init1.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/kaiming_init1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..edbe2c89d268711d0709752311cdbb2e7a1f8a46
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/kaiming_init1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_(1280,320).png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_(1280,320).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..87e7298570342f056190c2b991979de0b8f8b51d
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_(1280,320).png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_(254,64).png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_(254,64).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..8bad30d32f2c4ed94abe370e81e08b54f14b6e86
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_(254,64).png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_(512,128).png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_(512,128).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..366653f463fd3a69e320015bc234e41e71a16b52
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_(512,128).png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_acc_(1280,320).png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_acc_(1280,320).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6da587fc28d39bc26dfc98d7886b9e80667ffe37
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_acc_(1280,320).png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_acc_(256,64).png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_acc_(256,64).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7a8e5052e7e02b92b36427df4a1a23a98303a525
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_acc_(256,64).png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_acc_(512,128).png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_acc_(512,128).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a9a1e14089ce4a7338a26b277f9a606a28ac5308
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/m_acc_(512,128).png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/momentum.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/momentum.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..49cbe84c1e395b15e157df828373926a753aae7b
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/momentum.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/normal_init.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/normal_init.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b968820ee6b6323c28d6ec148c29d28c4434849f
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/normal_init.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/normal_init2.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/normal_init2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..937983cb9d5768d88cd3104a454c8c53493225dd
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/normal_init2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/numpy_init.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/numpy_init.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..df605a5d8d5c4890ddde9b11a048ce3f8cd5d356
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/numpy_init.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/optim1.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/optim1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..034e9b925200e453615bb6abd75db8b21088a2d5
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/optim1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/optim2-1.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/optim2-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b00a3bd94d29eb4486fe633c7fb1483ed0e64965
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/optim2-1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/optim2.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/optim2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..2bc60abbe4116142e57408fde28185bf3d35866d
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/optim2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/train_with_noise.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/train_with_noise.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b82edb9bea80ce1cb9c4d9530a48528665d69a54
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/train_with_noise.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/train_without_noise.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/train_without_noise.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f2213af4b5a0091350a4895a746c99b86d6d085e
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/train_without_noise.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/xavier_init.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/xavier_init.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..68669b829accf73edf59ff41cb4902414cd32b1a
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/xavier_init.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/xavier_init2.png b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/xavier_init2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c06e2c1a813b2007089b839771362f50ab432927
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/img/xavier_init2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f9bff17642d6d888ad6326c8bd7939c2e2c66502
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,279 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def __call__(self, x, W):
+ return self.forward(x, W)
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ W = self.memory['W']
+ grad_W = np.matmul(x.T, grad_y)
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, W.T)
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def __call__(self, x):
+ return self.forward(x)
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ grad_x = np.where(x > 0, grad_y, np.zeros_like(grad_y))
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def __call__(self, x):
+ return self.forward(x)
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ grad_x = 1 / (x + self.epsilon) * grad_y
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+ max = np.max(x, axis=1, keepdims=True)
+ out = np.exp(x - max) / np.sum(np.exp(x - max), axis=1).reshape(-1, 1)
+ self.memory['A'] = out
+
+ return out
+
+ def __call__(self, x):
+ return self.forward(x)
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ N, C = grad_y.shape
+ A = self.memory['A']
+ # 扩充激活值的维度,计算softmax导数
+ temp = A[:, np.newaxis, :] * np.eye(C) - np.matmul(A[:, np.newaxis, :].transpose(0, 2, 1), A[:, np.newaxis, :])
+ # 扩充误差项与dX进行乘法
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y[:, np.newaxis, :], temp).squeeze(1)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新.softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ self.memory = {}
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ x = self.relu_1(self.matmul_1(x, self.W1))
+ x = self.relu_2(self.matmul_2(x, self.W2))
+ x = self.matmul_3(x, self.W3)
+ x = self.softmax(x)
+ x = self.log(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+ grad_y = y
+
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(grad_y)
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+ self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate, mode='SGD', h_params=None):
+ """
+ 优化器,用于更新参数
+ :param learning_rate: 学习率
+ :param mode: 优化器类型,包括SGD AdaGrad RMSProp Adam
+ :param h_params: 优化器所需的超参数
+ :return: None
+ """
+ if mode == 'SGD':
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+ elif mode == 'momentum':
+ # beta 一般取0.9
+ beta = h_params[0]
+ # 获取上一时刻的动量,初始值为0
+ V1, V2, V3 = self.memory.get('V1', 0), self.memory.get('V2', 0), self.memory.get('V3', 0)
+ # 更新动量
+ V1 = beta * V1 + (1 - beta) * self.W1_grad
+ V2 = beta * V2 + (1 - beta) * self.W2_grad
+ V3 = beta * V3 + (1 - beta) * self.W3_grad
+ # 存储当前动量
+ self.memory['V1'] = V1
+ self.memory['V2'] = V2
+ self.memory['V3'] = V3
+ # 更新参数
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * V1
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * V2
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * V3
+
+ elif mode == 'AdaGrad':
+ # 学习率大于1e-2以后梯度会消失
+ epsilon = 1e-7
+ # 读取历史梯度值平方和
+ r1, r2, r3 = self.memory.get('r1', 0), self.memory.get('r2', 0), self.memory.get('r3', 0)
+ # 更新历史梯度值平方和
+ r1 += np.square(self.W1_grad)
+ r2 += np.square(self.W2_grad)
+ r3 += np.square(self.W3_grad)
+ # 存储历史梯度值平方和
+ self.memory['r1'] = r1
+ self.memory['r2'] = r2
+ self.memory['r3'] = r3
+ # 更新参数
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r1)) * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r2)) * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r3)) * self.W3_grad
+
+ elif mode == 'RMSProp':
+ # lr 1e-3, rho 0.999
+ epsilon = 1e-6
+ rho = h_params[0]
+ # 读取历史梯度值平方和
+ r1, r2, r3 = self.memory.get('r1', 0), self.memory.get('r2', 0), self.memory.get('r3', 0)
+ # 更新历史梯度值平方和
+ r1 = rho * r1 + (1 - rho) * np.square(self.W1_grad)
+ r2 = rho * r2 + (1 - rho) * np.square(self.W2_grad)
+ r3 = rho * r3 + (1 - rho) * np.square(self.W3_grad)
+ # 存储历史梯度值平方和
+ self.memory['r1'] = r1
+ self.memory['r2'] = r2
+ self.memory['r3'] = r3
+ # 更新参数
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r1)) * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r2)) * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r3)) * self.W3_grad
+
+ elif mode == 'Adam':
+ # lr=1e-3, rho1=0.9, rho2=0.999
+ epsilon = 1e-8
+ rho1, rho2 = h_params[0], h_params[1]
+ # 确定当前时刻值
+ t = self.memory.get('t', 0)
+ t += 1
+ # 读取历史梯度值平方和以及历史动量,初始值均为0
+ s1, s2, s3 = self.memory.get('s1', 0), self.memory.get('s2', 0), self.memory.get('s3', 0)
+ r1, r2, r3 = self.memory.get('r1', 0), self.memory.get('r2', 0), self.memory.get('r3', 0)
+ # 更新动量
+ s1 = rho1 * s1 + (1 - rho1) * self.W1_grad
+ s2 = rho1 * s2 + (1 - rho1) * self.W2_grad
+ s3 = rho1 * s3 + (1 - rho1) * self.W3_grad
+ # 存储动量
+ self.memory['s1'] = s1
+ self.memory['s2'] = s2
+ self.memory['s3'] = s3
+ # 更新梯度值平方和
+ r1 = rho2 * r1 + (1 - rho2) * np.square(self.W1_grad)
+ r2 = rho2 * r2 + (1 - rho2) * np.square(self.W2_grad)
+ r3 = rho2 * r3 + (1 - rho2) * np.square(self.W3_grad)
+ # 存储梯度值平方和
+ self.memory['r1'] = r1
+ self.memory['r2'] = r2
+ self.memory['r3'] = r3
+ # 修正当前动量
+ s1_hat = s1 / (1 - np.power(rho1, t))
+ s2_hat = s2 / (1 - np.power(rho1, t))
+ s3_hat = s3 / (1 - np.power(rho1, t))
+ # 修正当前梯度平方和
+ r1_hat = r1 / (1 - np.power(rho2, t))
+ r2_hat = r2 / (1 - np.power(rho2, t))
+ r3_hat = r3 / (1 - np.power(rho2, t))
+ # 更新梯度
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r1_hat)) * s1_hat
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r2_hat)) * s2_hat
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r3_hat)) * s3_hat
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f52192aedd664743252cd1d96ecdb8a8b37dc8a3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/16300110008/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,460 @@
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss, Matmul, Relu, Log, Softmax
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, mini_batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
+
+np.random.seed(1)
+
+
+def gaussian_noise(img, mu=0.1307, std=0.3081):
+ """
+ 产生随机噪声,噪声的均值与方差与图像采样数据一致
+ :param img: 待处理的数据
+ :param mu: 噪声均值
+ :param std: 噪声方差
+ :return: 经过噪声处理后的图像
+ """
+ epsilon = 1
+ sigma = std
+ noise = np.random.normal(mu, sigma, img.shape) * epsilon
+ # 设置阈值
+ out = np.clip(img + noise, -1, 1)
+ return out
+
+
+def get_numpy_initialization(mode='kaiming', test=False, neuron_shape=(256, 64)):
+ """
+ 使用numpy模拟torch初始化
+ :param neuron_shape: 控制隐藏层神经元数量
+ :param mode: 初始化模式:normal Xavier kaiming_uniform
+ :param test: 当用来进行探究初始化实验时,设为True,此时每层均为4096个神经元,否则为False,与fnn模型结构一致
+ :return: 参数W1 W2 W3
+ """
+ # 设置神经元数量
+ if test:
+ d0 = 28 * 28
+ d1 = 4096
+ d2 = 4096
+ d3 = 4096
+ else:
+ d0 = 28 * 28
+ d1, d2 = neuron_shape
+ d3 = 10
+ # 设置初始化方式
+ if mode == 'normal':
+ factor = 0.01 # 缩放因子,用来控制参数初始化的范围
+ W1 = np.random.normal(size=(d0, d1)) * factor
+ W2 = np.random.normal(size=(d1, d2)) * factor
+ W3 = np.random.normal(size=(d2, d3)) * factor
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
+
+ if mode == 'Xavier':
+ W1 = np.random.normal(size=(d0, d1)) * (2 / (np.sqrt(d0) + np.sqrt(d1)))
+ W2 = np.random.normal(size=(d1, d2)) * (2 / (np.sqrt(d1) + np.sqrt(d2)))
+ W3 = np.random.normal(size=(d2, d3)) * (2 / (np.sqrt(d2) + np.sqrt(d3)))
+ return W1, W2, W3
+
+ elif mode == 'kaiming':
+ bound1 = np.sqrt(6 / d0)
+ bound2 = np.sqrt(6 / d1)
+ bound3 = np.sqrt(6 / d2)
+
+ W1 = (np.random.rand(d0, d1) - .5) * 2 * bound1
+ W2 = (np.random.rand(d1, d2) - .5) * 2 * bound2
+ W3 = (np.random.rand(d2, d3) - .5) * 2 * bound3
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
+
+
+def visualize_weight(mode='kaiming', act='ReLU', test=True):
+ """
+ 用来可视化每层的参数分布情况
+ :param mode: 使用的初始化方式
+ :param act: 激活函数类型:tanh ReLU
+ :param test: 当用来进行探究初始化实验时,设为True,此时每层均为4096个神经元,否则为False,与fnn模型结构一致
+ :return: None
+ """
+ print(mode, act)
+ x = np.random.rand(16, 28 * 28) # 随机初始化输入
+ W1, W2, W3 = get_numpy_initialization(mode, test) # 获取初始化参数
+ W = [0, W1, W2, W3]
+
+ # 下面这个循环模拟了一个具有三个隐藏层的神经网络
+ for i in range(1, 4):
+ if act == 'tanh':
+ x = np.tanh(x.dot(W[i]))
+ elif act == 'ReLU':
+ x = np.maximum(0, x.dot(W[i])) # 过滤掉小于0的值,模拟ReLU
+ else:
+ raise ValueError("WRONG ACTIVATION")
+ # 获取每一层经过激活后的输出
+ mean = np.mean(x)
+ std = np.std(x)
+ # 绘制分布直方图
+ plt.subplot(1, 3, i)
+ plt.hist(x.flatten())
+ if act == 'ReLU':
+ lim = 5
+ else:
+ lim = 1
+
+ plt.xlim(-lim, lim)
+ plt.title(f'layer{i}\nmean={mean:.2f}\nstd={std:.2f}')
+
+ plt.show()
+
+
+def mini_batch_numpy(dataset, batch_size=128, noise=False):
+ """
+ 使用numpy实现minibatch
+ :param dataset: torch获取的MNIST数据集
+ :param batch_size: 批大小
+ :return: 一个list,其中每个元素是一个batch(x, y)
+ """
+ # 对数据进行标准化处理 mean=(0.1307,), std=(0.3081,)
+ X = dataset.data.numpy() / 255
+ mean = 0.1307
+ std = 0.3081
+ X = (X - mean) / std
+ y = dataset.targets.numpy()
+
+ # 添加高斯噪声
+ if noise:
+ X = gaussian_noise(X)
+
+ # 打乱样本和标签
+ n = X.shape[0]
+ idx = np.arange(n)
+ np.random.shuffle(idx)
+ X = X[idx]
+ y = y[idx]
+
+ # 用于切分数据生成batches
+ iter_num = int(np.ceil(n / batch_size))
+ dataloader = \
+ [(X[i * batch_size: (i + 1) * batch_size], y[i * batch_size: (i + 1) * batch_size])
+ # 处理当最后的部分不足batch size时
+ if (i + 1) * batch_size <= n
+ else (X[i * batch_size:], y[i * batch_size:])
+ for i in range(iter_num)]
+ return dataloader
+
+
+class NumpyModel_neuron:
+ def __init__(self, neuron_shape=(256, 64)):
+ h2, h3 = neuron_shape
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, h2))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(h2, h3))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(h3, 10))
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新.softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ self.memory = {}
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ x = self.relu_1(self.matmul_1(x, self.W1))
+ x = self.relu_2(self.matmul_2(x, self.W2))
+ x = self.matmul_3(x, self.W3)
+ x = self.softmax(x)
+ x = self.log(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+ grad_y = y
+
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(grad_y)
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+ self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate, mode='SGD', h_params=None):
+ """
+ 优化器,用于更新参数
+ :param learning_rate: 学习率
+ :param mode: 优化器类型,包括SGD AdaGrad RMSProp Adam
+ :param h_params: 优化器所需的超参数
+ :return: None
+ """
+ if mode == 'SGD':
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+ elif mode == 'momentum':
+ # beta 一般取0.9
+ beta = h_params[0]
+ # 获取上一时刻的动量,初始值为0
+ V1, V2, V3 = self.memory.get('V1', 0), self.memory.get('V2', 0), self.memory.get('V3', 0)
+ # 更新动量
+ V1 = beta * V1 + (1 - beta) * self.W1_grad
+ V2 = beta * V2 + (1 - beta) * self.W2_grad
+ V3 = beta * V3 + (1 - beta) * self.W3_grad
+ # 存储当前动量
+ self.memory['V1'] = V1
+ self.memory['V2'] = V2
+ self.memory['V3'] = V3
+ # 更新参数
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * V1
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * V2
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * V3
+
+ elif mode == 'AdaGrad':
+ # 学习率大于1e-2以后梯度会消失
+ epsilon = 1e-7
+ # 读取历史梯度值平方和
+ r1, r2, r3 = self.memory.get('r1', 0), self.memory.get('r2', 0), self.memory.get('r3', 0)
+ # 更新历史梯度值平方和
+ r1 += np.square(self.W1_grad)
+ r2 += np.square(self.W2_grad)
+ r3 += np.square(self.W3_grad)
+ # 存储历史梯度值平方和
+ self.memory['r1'] = r1
+ self.memory['r2'] = r2
+ self.memory['r3'] = r3
+ # 更新参数
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r1)) * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r2)) * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r3)) * self.W3_grad
+
+ elif mode == 'RMSProp':
+ # lr 1e-3, rho 0.999
+ epsilon = 1e-6
+ rho = h_params[0]
+ # 读取历史梯度值平方和
+ r1, r2, r3 = self.memory.get('r1', 0), self.memory.get('r2', 0), self.memory.get('r3', 0)
+ # 更新历史梯度值平方和
+ r1 = rho * r1 + (1 - rho) * np.square(self.W1_grad)
+ r2 = rho * r2 + (1 - rho) * np.square(self.W2_grad)
+ r3 = rho * r3 + (1 - rho) * np.square(self.W3_grad)
+ # 存储历史梯度值平方和
+ self.memory['r1'] = r1
+ self.memory['r2'] = r2
+ self.memory['r3'] = r3
+ # 更新参数
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r1)) * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r2)) * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r3)) * self.W3_grad
+
+ elif mode == 'Adam':
+ # lr=1e-3, rho1=0.9, rho2=0.999
+ epsilon = 1e-8
+ rho1, rho2 = h_params[0], h_params[1]
+ # 确定当前时刻值
+ t = self.memory.get('t', 0)
+ t += 1
+ # 读取历史梯度值平方和以及历史动量,初始值均为0
+ s1, s2, s3 = self.memory.get('s1', 0), self.memory.get('s2', 0), self.memory.get('s3', 0)
+ r1, r2, r3 = self.memory.get('r1', 0), self.memory.get('r2', 0), self.memory.get('r3', 0)
+ # 更新动量
+ s1 = rho1 * s1 + (1 - rho1) * self.W1_grad
+ s2 = rho1 * s2 + (1 - rho1) * self.W2_grad
+ s3 = rho1 * s3 + (1 - rho1) * self.W3_grad
+ # 存储动量
+ self.memory['s1'] = s1
+ self.memory['s2'] = s2
+ self.memory['s3'] = s3
+ # 更新梯度值平方和
+ r1 = rho2 * r1 + (1 - rho2) * np.square(self.W1_grad)
+ r2 = rho2 * r2 + (1 - rho2) * np.square(self.W2_grad)
+ r3 = rho2 * r3 + (1 - rho2) * np.square(self.W3_grad)
+ # 存储梯度值平方和
+ self.memory['r1'] = r1
+ self.memory['r2'] = r2
+ self.memory['r3'] = r3
+ # 修正当前动量
+ s1_hat = s1 / (1 - np.power(rho1, t))
+ s2_hat = s2 / (1 - np.power(rho1, t))
+ s3_hat = s3 / (1 - np.power(rho1, t))
+ # 修正当前梯度平方和
+ r1_hat = r1 / (1 - np.power(rho2, t))
+ r2_hat = r2 / (1 - np.power(rho2, t))
+ r3_hat = r3 / (1 - np.power(rho2, t))
+ # 更新梯度
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r1_hat)) * s1_hat
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r2_hat)) * s2_hat
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate / (epsilon + np.sqrt(r3_hat)) * s3_hat
+
+
+def numpy_run(arg_list, neuron_shape=(256 * 1, 64 * 1), modify=None, noise=None):
+ """
+ 训练开始
+ :param modify: 进行调整神经元实验的参数
+ :param neuron_shape: 用来控制隐藏层神经元数量
+ :param arg_list: 优化器类型与超参数列表,[1e-3, 'Adam', [0.9, 0.999]]
+ :return: None
+ """
+ # 获取超参数
+ if noise is None:
+ noise = [False, False]
+ lr = arg_list[0]
+ mode = arg_list[1]
+ print(mode)
+ h_params = arg_list[-1]
+
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ if modify == 'neuron':
+ model = NumpyModel_neuron(neuron_shape=neuron_shape)
+ elif modify == 'layer':
+ model = NumpyModel_layer(neuron_shape=neuron_shape)
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ # 初始化选择
+ # model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+ # model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_numpy_initialization()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_numpy_initialization(neuron_shape=neuron_shape)
+
+ train_loss = []
+ test_acc = []
+ test_acc_noise = []
+ test_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = lr
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ # 选择minibatch方法
+ # for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ for x, y in mini_batch_numpy(train_dataset, noise = noise[0]):
+ # print(x.numpy().shape)
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x) # 已经在mini_batch_numpy中改为numpy类型
+ # y_pred = model.forward(x.numpy()) #如果使用torch_mini_batch启用此行
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ model.optimize(learning_rate, mode, h_params)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ # x = gaussian_noise(x)
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ accuracy = np.mean((y_pred.argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ test_acc.append(accuracy)
+
+ if noise[1]:
+ x = gaussian_noise(x)
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ accuracy = np.mean((y_pred.argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ test_acc_noise.append(accuracy)
+
+ y = one_hot(y)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(axis=1).mean()
+ test_loss.append(loss)
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss, str(neuron_shape))
+ if modify is not None:
+ return test_acc
+ elif noise[1]:
+ return test_acc, test_acc_noise
+ else:
+ return train_loss
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ import sys
+
+ if len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == 'v':
+ # 可视化权重
+ visualize_weight('normal', 'tanh')
+ visualize_weight('Xavier', 'tanh')
+ visualize_weight('Xavier', 'ReLU')
+ visualize_weight('kaiming', 'ReLU')
+ elif len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == 'o':
+ # 比较优化器
+ cases = [
+ [0.1, 'SGD', None],
+ [0.1, 'momentum', [0.9]],
+ [1e-2, 'AdaGrad', None],
+ [1e-4, 'RMSProp', [0.999]],
+ [1e-3, 'Adam', [0.9, 0.999]]
+ ]
+
+ loss = []
+ for case in cases:
+ loss.append(numpy_run(case))
+ step = 1
+ # loss变化图
+ color = ['k', 'y', 'c', 'b', 'r']
+ line = ['-', '-', '--', '-.', ':']
+ optim = [case[1] for case in cases]
+ for i in range(5):
+ plt.subplot(3, 2, i + 1)
+ plt.plot(range(len(loss[i]))[::step], loss[i][::step], color=color[i], linestyle=line[i], label=optim[i])
+ plt.xlabel('step')
+ plt.ylabel('value')
+ plt.legend()
+ plt.show()
+
+ # 取对数绘图
+ for i in range(5):
+ plt.plot(range(len(loss[i]))[::step], np.log(loss[i][::step]) / np.log(100), color=color[i], linestyle=line[i],
+ label=optim[i])
+ plt.legend()
+ plt.xlabel('step')
+ plt.ylabel('log_value')
+ plt.show()
+
+ elif len(sys.argv) > 1 and (sys.argv[1] == 'm' or sys.argv[1] == 'd' or sys.argv[1] == 'f'):
+ # 神经元数量实验
+ if sys.argv[1] == 'm':
+ ns = (256 * 1, 64 * 1)
+ elif sys.argv[1] == 'n':
+ ns = (256 * 2, 64 * 2)
+ elif sys.argv[1] == 'k':
+ ns = (256 * 5, 64 * 5)
+ else:
+ raise ValueError("WRONG ARGV")
+
+ acc = numpy_run([0.1, 'SGD', None], neuron_shape=ns, modify='neuron')
+ plt.plot(range(len(acc)), acc)
+ plt.title(f"test acc {ns}")
+ plt.ylabel("acc")
+ plt.xlabel("epoch")
+ plt.show()
+ elif len(sys.argv) > 1 and (sys.argv[1] == 'g' or sys.argv[1] == 'n'):
+ # 带噪声实验
+ if sys.argv[1] == 'g':
+ test_acc, test_acc_noise = numpy_run([0.1, 'SGD', None], noise=[True, True]) # noise=[训练带噪,测试带噪]
+ plt.plot(range(len(test_acc)), test_acc, linestyle='--', marker='+', color='k', label='test without noise')
+ plt.plot(range(len(test_acc_noise)), test_acc_noise, marker='o', color='y', label='test with noise')
+ plt.xlabel("epoch")
+ plt.ylabel("acc")
+ plt.title("train_with_noise")
+ plt.legend()
+ plt.show()
+ elif sys.argv[1] == 'n':
+ test_acc, test_acc_noise = numpy_run([0.1, 'SGD', None], noise=[False, True])
+ plt.plot(range(len(test_acc)), test_acc, linestyle='--', marker='+', color='k', label='test without noise')
+ plt.plot(range(len(test_acc_noise)), test_acc_noise, marker='o', color='y', label='test with noise')
+ plt.xlabel("epoch")
+ plt.ylabel("acc")
+ plt.title("train_without_noise")
+ plt.legend()
+ plt.show()
+ else:
+ numpy_run([0.1, 'SGD', None])
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..75a75c96dba24c1fe572704318d3646659659437
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,148 @@
+# 实验报告2
+
+### 1,实验结果
+
+在完成了对mini_batch函数的替换后,模型得以顺利进行:
+
+
+
+```shell
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9453
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9656
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9689
+```
+
+### 2,mini_batch的替换
+
+```python
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128, numpy=True):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+ for each in dataset:
+ data.append(np.array(each[0]))
+ label.append(each[1])
+ data = np.array(data)
+ label = np.array(label)
+
+ m = data.shape[0]
+ permutation = list(np.random.permutation(m))
+ data =data[permutation]
+ label=label[permutation]
+
+ n=m//batch_size
+ mini_batches=[]
+ for i in range(n):
+ mini_batches.append([data[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size],label[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size]])
+
+ return mini_batches
+```
+
+整体上参考了utils.py的batch函数。前半段和batch一样,将dataset中的数据分别放到data和label之中。之后,让data和label的元素顺序随机变化,再将每一个小batch的数据和标记放入对应的列表中,依次放入一个大的列表,并最终输出。
+
+### 3,反向传播公式的推导
+
+matmul:
+
+#### 
+
+设输出y为l维的向量。
+
+**dx:**对于每个x中的元素xi,它对y1,y2,y3,.....,yl的偏导为wi1,wi2......,wil.
+
+dL/dxi=(dL/dy1)·wi1+(dL/dy2)·wi2+……+(dL/dyl)·wil
+
+所以,dx=dy·WT.
+
+**dW:** 对于W的元素wij,它对yj的偏导为xi。
+
+dL/dwij=(dL/dyj)·xi
+
+所以,dW=xT*dy。对于多个样本,需要求平均值。
+
+```python
+def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+ N=grad_y.shape[0]
+
+ grad_x=np.matmul(grad_y,self.memory['W'].T)
+ grad_W=np.matmul(self.memory['x'].T,grad_y)
+
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+```
+
+
+
+2,Relu函数
+
+```python
+def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ x=self.memory['x']
+ grad_x = grad_y.copy()
+ grad_x[x<=0]=0
+ return grad_x
+
+```
+
+在xi<=0时,dyi/dxi=0,dL/dxi=0
+
+在xi>0时,dyi/dxi=1,dL/dxi=dL/dyi
+
+所以如上所示,如果xi大于0,则dx相应的位置照搬dy;如果xi小于等于0,则dx响应的位置设置为0.
+
+3,log函数
+
+```python
+def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ x=self.memory['x']
+ x[x<=self.epsilon]=self.epsilon
+ grad_x=grad_y*(1/x)
+
+ return grad_x
+```
+
+dyi/dxi=1/xi,dL/dxi=(dL/dyi)·1/xi
+
+所以,dx=dy·(1/x).
+
+4,softmax函数
+
+
+
+设x和y均为l维的向量。
+
+则对于dyj/dxi,如果i=j,则dyj/dxi=yj-(yj)^2.如果i!=j,则有dyj/dxi=-yi·yj.
+
+设D=diag(y)-yT·y,有dyj/dxi=Dij
+
+这样的话,有dL/dxi=(dL/dy1)·Di1+(dL/dy2)·Di2+……+(dL/dyl)·Dil
+
+所以,dx=dy·D
+
+```python
+def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ y=self.memory['y']
+ l=y.shape[0]
+ grad_x=[]
+ for grad_y1,y1 in zip(grad_y,y):
+ D= np.diag(y1) - np.outer(y1,y1)
+ grad_x1=np.dot(grad_y1, D)
+ grad_x.append(grad_x1)
+ grad_x=np.array(grad_x)
+ return grad_x
+```
+
+不过,在实际的实现中,要考虑到一批中不只有一个数据,要一个一个数据地逐个生成dx。
+
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/img/Figure_1.png b/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/img/Figure_1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..dab6049f889917dcbf2e93d6203b3a6579908777
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/img/Figure_1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..277f81a3f11fb44523777ef4bddcb998454bcdc3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,184 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, self.memory['W'].T)
+ grad_W = np.matmul(self.memory['x'].T, grad_y)
+
+
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ x=self.memory['x']
+ grad_x = grad_y.copy()
+ grad_x[x<=0]=0
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ x=self.memory['x']
+ x[x<=self.epsilon]=self.epsilon
+ grad_x=grad_y*(1/x)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ shift_x = x - np.max(x, axis=1).reshape(-1, 1)
+ y = np.exp(shift_x) / np.sum(np.exp(shift_x), axis=1).reshape(-1, 1)
+ #y = np.exp(x+1) / np.sum(np.exp(x+1), axis=1).reshape(-1, 1)
+ self.memory['y'] = y
+
+ return y
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ y=self.memory['y']
+ l=y.shape[0]
+ grad_x=[]
+ for grad_y1,y1 in zip(grad_y,y):
+ D= np.diag(y1) - np.outer(y1,y1)
+ grad_x1=np.dot(grad_y1, D)
+ grad_x.append(grad_x1)
+ grad_x=np.array(grad_x)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新。 softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ x=self.matmul_1.forward(x,self.W1)
+ x=self.relu_1.forward(x)
+ x=self.matmul_2.forward(x,self.W2)
+ x=self.relu_2.forward(x)
+ x=self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+
+
+ x = self.softmax.forward(x)
+ x = self.log.forward(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+
+ y = self.log.backward(y)
+ self.log_grad = y
+ y = self.softmax.backward(y)
+ self.softmax_grad = y
+ y, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(y)
+ self.x3_grad = y
+ y = self.relu_2.backward(y)
+ y, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(y)
+ self.x2_grad = y
+ y = self.relu_1.backward(y)
+ y, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(y)
+ self.x1_grad = y
+
+ pass
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a688f7c64114bf150ffff2b903dfc74688bda4ad
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, mini_batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128, numpy=True):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+ for each in dataset:
+ data.append(np.array(each[0]))
+ label.append(each[1])
+ data = np.array(data)
+ label = np.array(label)
+
+ m = data.shape[0]
+ permutation = list(np.random.permutation(m))
+ data =data[permutation]
+ label=label[permutation]
+
+ n=m//batch_size
+ mini_batches=[]
+ for i in range(n):
+ mini_batches.append([data[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size],label[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size]])
+
+ return mini_batches
+
+def numpy_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/torch_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/torch_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6a5649bbfa750b3520b4b895de7260c3aa8ea7cd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/16307130040/torch_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+import torch
+from utils import mini_batch, batch, download_mnist, get_torch_initialization, one_hot, plot_curve
+
+
+class TorchModel:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = torch.randn((28 * 28, 256), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W2 = torch.randn((256, 64), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W3 = torch.randn((64, 10), requires_grad=True)
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W1))
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W2))
+ x = torch.matmul(x, self.W3)
+ self.softmax = torch.softmax(x, 1)
+ self.log = torch.log(self.softmax)
+ self.softmax.retain_grad() # for test only
+ self.log.retain_grad() # for test only
+ return self.log
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ with torch.no_grad():
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1.grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2.grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3.grad
+
+ self.W1.grad = None
+ self.W2.grad = None
+ self.W3.grad = None
+
+
+def torch_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = TorchModel()
+ model.W1.data, model.W2.data, model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset, numpy=False):
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset, numpy=False)[0]
+ accuracy = model.forward(x).argmax(dim=1).eq(y).float().mean().item()
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ torch_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..9b99779240f17d85b2217a7a0600698deb047d32
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,186 @@
+# 课程报告
+
+## 模型的训练与测试
+
+直接运行numpy_minist.py,设定batch_size =128, learning_rate = 0.1, epoch_number = 3得到如下的结果:
+
+| 轮次 | Accuracy |
+| ---- | -------- |
+| [0] | 0.9474 |
+| [1] | 0.9654 |
+| [2] | 0.9704 |
+
+得到的损失函数的变化如下图所示:
+
+ +
+**减小batch_size的值为 64**,保持其他的参数不变进行实验,得到结果如下:
+
+| 轮次 | Accuracy |
+| ---- | -------- |
+| [0] | 0.9548 |
+| [1] | 0.9682 |
+| [2] | 0.9679 |
+
+可见当batch_size 减小时,模型准确率在每一轮中进步的幅度会变小。
+
+
+
+## mini_batch 的替换
+
+```
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128,seed=0):
+ np.random.seed(seed)
+ x_train = dataset.train_data
+ y_train = dataset.train_labels
+ m = y_train.shape[0]
+ def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128,seed=0):
+ np.random.seed(seed)
+ x_train = dataset.train_data
+ y_train = dataset.train_labels
+ m = y_train.shape[0]
+ # m为所有样本的数量
+ mini_batchs =[]
+ permutation = list(np.random.permutation(m))
+ # 打乱样本顺序
+ shuffle_X = x_train[permutation, :, :]
+ shuffle_Y = y_train[permutation]
+ num_mini_batch = int(m//batch_size)
+ # num_mini_batch为mini_batch的块数
+ for i in range(num_mini_batch):
+ mini_batch_x = shuffle_X[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size, :, :]
+ mini_batch_y = shuffle_Y[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size]
+ mini_batch = (mini_batch_x, mini_batch_y)
+ mini_batchs.append(mini_batch)
+ if m % batch_size != 0:
+ # 如果样本数不能被整除,取余下的部分
+ mini_batch_X = shuffle_X[num_mini_batch * batch_size:m, :, :]
+ mini_batch_Y = shuffle_Y[num_mini_batch * batch_size:m]
+ mini_batch = (mini_batch_X, mini_batch_Y)
+ mini_batchs.append(mini_batch)
+ return mini_batchs
+ mini_batchs =[]
+ permutation = list(np.random.permutation(m))
+ shuffle_X = x_train[permutation, :, :]
+ shuffle_Y = y_train[permutation]
+ num_mini_batch = int(m//batch_size)
+ for i in range(num_mini_batch):
+ mini_batch_x = shuffle_X[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size, :, :]
+ mini_batch_y = shuffle_Y[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size]
+ mini_batch = (mini_batch_x, mini_batch_y)
+ mini_batchs.append(mini_batch)
+ if m % batch_size != 0:
+ # 如果样本数不能被整除,取余下的部分
+ mini_batch_X = shuffle_X[num_mini_batch * batch_size:m, :, :]
+ mini_batch_Y = shuffle_Y[num_mini_batch * batch_size:m]
+ mini_batch = (mini_batch_X, mini_batch_Y)
+ mini_batchs.append(mini_batch)
+ return mini_batchs
+```
+
+整体思路是打乱样本的顺序,然后依次取出batch_size个样本的数据,作为一个mini_batch组。最后mini_batch函数返回所有的mini_batch组的集合
+
+用numpy实现mini_batch之后,运行numpy_minist.py, 设定batch_size =128, learning_rate = 0.1, epoch_number = 3, 得到的实验结果如下:
+
+| 轮次 | Accuracy |
+| ---- | -------- |
+| [0] | 0.8780 |
+| [1] | 0.8994 |
+| [2] | 0.9099 |
+
+
+
+## 反向传播公式的推导
+
+**Matmul**
+
+Matmul的计算式为
+$$
+Y = X*W
+$$
+根据矩阵的求导法则,可以推出
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial X} = W^{T}
+$$
+
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial W} = X^{T}
+$$
+
+ 对应代码段如下:
+
+```
+grad_W = np.matmul(self.memory['x'].T, grad_y)
+grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, self.memory['W'].T)
+```
+
+
+
+**Relu**
+
+Relu的计算公式为
+$$
+Y=\begin{cases}
+X&X\ge0\\\\
+0&\text{otherwise}
+\end{cases}
+$$
+所以有
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial X}=\begin{cases}
+1&X>0\\\\
+0&\text{otherwise}
+\end{cases}
+$$
+对应代码块如下:
+
+```
+grad_x = np.where(self.memory['x'] > 0, grad_y, np.zeros_like(self.memory['x']))
+```
+
+意思是说若x大于0, grad_x的结果就是传入的grad_y。否则结果为0
+
+
+
+**Log**
+
+log的计算公式为
+$$
+Y=\ln(X+\epsilon)
+$$
+因此有
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial X} = \frac1{X+\epsilon}
+$$
+对应的代码块如下:
+
+```
+grad_x = np.multiply(1./(self.memory['x'] + self.epsilon), grad_y)
+```
+
+
+
+**Softmax**
+
+Softmax的计算公式为
+$$
+Y=\frac{\exp\{X\}}{\sum_{k=1}^c\exp\{X\}}
+$$
+根据邱老师书第411~412页对该公式的导数的推导(在这里直接引用结果),有
+
+
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial X} = diag(softmax(x))-softmax(x)softmax(x)^{T}
+$$
+对应的代码块如下
+
+```
+out = self.memory['out']
+grad_x = []
+for idx in range(out.shape[0]):
+ dout = np.diag(out[idx]) - np.outer(out[idx], out[idx])
+ grad = np.matmul(dout, grad_y[idx])
+ grad_x.append(grad)
+grad_x = np.array(grad_x)
+```
+
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/img/loss_value1.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/img/loss_value1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..dbb3c56e9d1036c37ea3aa3258a7ae0acd9eb79b
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/img/loss_value1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ea2d68f88793d261f1ead5fa836c421f4b3ed140
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,173 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+ grad_W = np.matmul(self.memory['x'].T, grad_y)
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, self.memory['W'].T)
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ grad_x = np.where(self.memory['x'] > 0, grad_y, np.zeros_like(self.memory['x']))
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ grad_x = np.multiply(1./(self.memory['x'] + self.epsilon), grad_y)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+ out = []
+ for index in range(x.shape[0]):
+ temp = x[index]
+ temp = temp - max(temp)
+ temp = np.exp(temp)
+ out.append(temp/sum(temp))
+ out = np.array(out)
+ self.memory['out'] = out
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ out = self.memory['out']
+ grad_x = []
+ for idx in range(out.shape[0]):
+ dout = np.diag(out[idx]) - np.outer(out[idx], out[idx])
+ grad = np.matmul(dout, grad_y[idx])
+ grad_x.append(grad)
+ grad_x = np.array(grad_x)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新。 softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+ x = self.relu_1.forward(self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1))
+ x = self.relu_2.forward(self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2))
+ x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+ x = self.softmax.forward(x)
+ x = self.log.forward(x)
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y)
+ grad_y = self.log_grad
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(grad_y)
+ grad_y = self.softmax_grad
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(grad_y)
+ grad_y = self.x3_grad
+ self.relu_2_grad =self.relu_2.backward(grad_y)
+ grad_y = self.relu_2_grad
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad =self.matmul_2.backward(grad_y)
+ grad_y = self.x2_grad
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(grad_y)
+ grad_y = self.relu_1_grad
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(grad_y)
+ pass
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..daea871d110daf90996073d606bef96da6d2f827
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128,seed=0):
+ np.random.seed(seed)
+ x_train = dataset.train_data
+ y_train = dataset.train_labels
+ m = y_train.shape[0]
+ # m为所有样本的数量
+ mini_batchs =[]
+ permutation = list(np.random.permutation(m))
+ # 打乱样本顺序
+ shuffle_X = x_train[permutation, :, :]
+ shuffle_Y = y_train[permutation]
+ num_mini_batch = int(m//batch_size)
+ # num_mini_batch为mini_batch的块数
+ for i in range(num_mini_batch):
+ mini_batch_x = shuffle_X[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size, :, :]
+ mini_batch_y = shuffle_Y[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size]
+ mini_batch = (mini_batch_x, mini_batch_y)
+ mini_batchs.append(mini_batch)
+ if m % batch_size != 0:
+ # 如果样本数不能被整除,取余下的部分
+ mini_batch_X = shuffle_X[num_mini_batch * batch_size:m, :, :]
+ mini_batch_Y = shuffle_Y[num_mini_batch * batch_size:m]
+ mini_batch = (mini_batch_X, mini_batch_Y)
+ mini_batchs.append(mini_batch)
+ return mini_batchs
+
+def numpy_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+ y_pred = model.forward(x.numpy()/255)
+ #y_pred = model.forward(x.numpy())
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a2949d3c15d69eb19fb37c1d207072950517f373
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,128 @@
+# 选题1
+
+## 前馈神经网络的实现
+
+### Matmul
+
+forward时
+$$
+Y=XW
+$$
+backward时
+$$
+\frac {\partial L}{\partial X}=\frac {\partial L}{\partial Y}\frac {\partial Y}{\partial X}=\frac {\partial L}{\partial Y}\frac {\partial XW}{\partial X}=\frac {\partial L}{\partial Y} W^T\\\\
+\frac {\partial L}{\partial W}=\frac {\partial L}{\partial Y}\frac {\partial Y}{\partial W}=\frac {\partial L}{\partial Y}\frac {\partial XW}{\partial W}=X^T\frac {\partial L}{\partial Y}
+$$
+
+### Relu
+
+forward时
+$$
+Y_{ij}= \begin{cases} X_{ij}& X_{ij}\geq 0 \\\\
+0& otherwise \end{cases}
+$$
+backward时
+$$
+\frac{\partial L}{\partial X_{ij}}=\frac{\partial L}{\partial Y_{ij}} \frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{ij}}
+\\\\
+\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{ij}}= \begin{cases} 1 & X_{ij}\geq 0 \\\\
+0& otherwise \end{cases}\\\\
+\therefore \frac{\partial L}{\partial X_{ij}}=\begin{cases} \frac{\partial L}{\partial Y_{ij}} & X_{ij}\geq 0 \\\\
+0& otherwise \end{cases}
+$$
+
+### Log
+
+forward时
+$$
+Y_{ij}=ln(X_{ij}+\epsilon)
+$$
+backward时
+$$
+\frac{\partial L}{\partial X_{ij}}=\frac{\partial L}{\partial Y_{ij}} \frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{ij}}=\frac{\partial L}{\partial Y_{ij}}\frac {1}{X_{ij}+\epsilon}
+$$
+
+### Softmax
+
+forward时
+$$
+Y_{ij} = \frac {expX_{ij}}{\sum_k expX_{ik}}
+$$
+backward时,参考课本
+
+
+
+Softmax是对每一行进行的操作,由此可以得到每一行的Jacob矩阵为
+$$
+Jacob = diag(Y_r) - Y_rY_r^T
+$$
+
+### 补全NumpyModel
+
+forward部分根据torch_mnisy.py补全,得到网络结构为
+
+input -> matmul_1 -> relu_1 -> matmul_2 -> relu_2 -> matmul_3 -> softmax -> log
+
+根据此结构,依次反向调用之前实现的backward部分即可
+
+## 实验
+
+### 实现mini_batch
+
+有时候训练集数据过多,如果对整个数据集计算平均的损失函数值然后计算梯度进而进行反向传播,训练速度会比较慢;使用随机梯度下降则可能会导致参数无法收敛到最优值。mini_batch方法是这两种方法的折中,将数据集划分为若干批次,在提高训练速度的同时保证了较好的收敛效果。
+
+参考utils.py中mini_batch,在numpy_mnist.py中实现了mini_batch,可调参数有dataset,shuffle,batch_size。下面实验均在我实现的mini_batch上进行。
+
+### 在numpy_mnist.py中进行模型的训练和测试
+
+通过改变batch_size、学习率、是否shuffle这三个变量进行了实验。
+
+
+
+上图左边一列是batch_size为64时的情况,右边两列是batch_size为128时的情况;上面一行学习率为0.1,下面一行学习率为0.05。本次实验都进行了shuffle。可以看出,batch_size越小,在同样的step里收敛得越慢;在训练前期震荡比较大;在训练后期损失函数的震荡反而较小。
+
+
+
+上图左边一列是学习率为0.05时的情况,右边两列是学习率为0.1时的情况;同一行的数据其他实验参数相同。可以看出,学习率越小,收敛得就越慢。出乎我意料的是,学习率越小,在收敛后的实验后期,损失函数震荡比学习率大的更严重。
+
+
+
+上图左边未对训练数据进行shuffle,右边进行了shuffle,其他条件一样。可以看出未进行shuffle的模型收敛更慢,损失函数的震荡更大。这是因为在我的mini_batch的实现中,不进行shuffle的话,每次梯度的更新都是固定的total_size/batch_size组数据,相当于数据量减少了。
+
+## momentum、Adam等优化
+
+SGD会造成损失函数的震荡,可能会使最后的结果停留在一个局部最优点。为了抑制SGD的震荡,提出了SGD with Momentum的概念。SGDM在梯度下降过程中加入了一阶动量
+$$
+m_t = \beta _1m_{t-1}+(1-\beta_1)g_t
+$$
+也就是说,在梯度下降方向不变时,梯度下降的速度变快,梯度下降方向有所变化的维度上更新速度变慢。这里$\beta _1$的经验值为0.9。也就是说,梯度下降的方向主要是之前累积的下降方向,并略微偏向当前时刻的下降方向。
+
+除了一阶动量,二阶动量也被广泛使用。对于经常更新的参数,我们已经积累了大量关于它的知识,不希望被单个样本影响太大,希望学习速率慢一些;对于偶尔更新的参数,我们了解的信息太少,希望能从每个偶然出现的样本身上多学一些,即学习速率大一些。二阶动量的一种比较好的计算方法是:不累积全部历史梯度,只关注过去一段时间窗口的下降梯度,这种方法解决了学习率急剧下降的问题。这就是AdaDelta/RMSProp。
+$$
+V_t = \beta _ 2 V_{t-1}+(1-\beta_2)g_t^2
+$$
+由此,Adam自然而然地出现了,Adam把一阶动量和二阶动量都用起来,下降梯度为
+$$
+\Delta = \alpha\ m_t/\sqrt V_t
+$$
+一般为了避免分母为0,会在分母上加一个小的平滑项。$\beta _2$的经验值为0.999,Adam学习率为0.001。
+
+参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/32230623
+
+
+
+上图从左往右第一张图为不使用优化器,第二张图为使用momentum优化,第三张图为使用Adam优化,其中,前两张图学习率为0.1,最后一张图学习率为0.001。可以看出,使用momentum之后前期收敛速度加快,并且在后期损失函数震荡减少。使用Adam优化器,虽然学习率低,但是收敛速度更快,并且损失函数的震荡从训练器前期到后期一直比不使用要小。
+
+## 总结
+
+完成了自动测试 60%
+
+
+
+在numpy_minist.py中对模型进行训练和测试 20%
+
+只用NumPy实现了mini_batch函数 10%
+
+推导了numpy_fnn.py中算子的反向传播公式 10%
+
+实现了momentum、Adam等优化方法并进行了对比实验 10%
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/img/softmax.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/img/softmax.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e8ae7d1b57865a9c23e15176a13ecebaa105ec03
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/img/softmax.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/img/tester.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/img/tester.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..29246264c69d2decc2ed5f34df698fcd07481303
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/img/tester.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..67cc7bc6beac060ebe52fcee790214b1c9f1dc83
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,210 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 1 #
+ ####################
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, self.memory['W'].T)
+ grad_W = np.matmul(self.memory['x'].T, grad_y)
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 2 #
+ ####################
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ grad_x = grad_y * np.where(x > 0, np.ones_like(x), np.zeros_like(x))
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 3 #
+ ####################
+ grad_x = grad_y * np.reciprocal(self.memory['x'] + self.epsilon)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 4 #
+ ####################
+ out = np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x), axis=1, keepdims=True)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['out'] = out
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 5 #
+ ####################
+ out = self.memory['out']
+ Jacobs = np.array([np.diag(r) - np.outer(r, r) for r in out])
+ grad_y = grad_y[:, np.newaxis, :]
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, Jacobs).squeeze(axis=1)
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新。 softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ # for momentum and adam
+ self.W1_m = 0
+ self.W2_m = 0
+ self.W3_m = 0
+ self.W1_v = 0
+ self.W2_v = 0
+ self.W3_v = 0
+
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ ####################
+ # code 6 #
+ ####################
+ x = self.relu_1.forward(self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1))
+ x = self.relu_2.forward(self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2))
+ x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+ x = self.softmax.forward(x)
+ x = self.log.forward(x)
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+
+ ####################
+ # code 7 #
+ ####################
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y)
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+ self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+
+ def optimizeM(self, learning_rate, beta_1=0.9):
+ self.W1_m = beta_1 * self.W1_m + (1-beta_1)*self.W1_grad
+ self.W2_m = beta_1 * self.W2_m + (1-beta_1)*self.W2_grad
+ self.W3_m = beta_1 * self.W3_m + (1-beta_1)*self.W3_grad
+
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_m
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_m
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_m
+
+ def optimizeAM(self, learning_rate=0.001, beta_1=0.9, beta_2=0.999, epsilon=1e-8):
+ self.W1_m = beta_1 * self.W1_m + (1-beta_1) * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2_m = beta_1 * self.W2_m + (1-beta_1) * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3_m = beta_1 * self.W3_m + (1-beta_1) * self.W3_grad
+
+ self.W1_v = beta_2 * self.W1_v + (1-beta_2) * self.W1_grad * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2_v = beta_2 * self.W2_v + (1-beta_2) * self.W2_grad * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3_v = beta_2 * self.W3_v + (1-beta_2) * self.W3_grad * self.W3_grad
+
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_m / (self.W1_v**0.5 + epsilon)
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_m / (self.W2_v**0.5 + epsilon)
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_m / (self.W3_v**0.5 + epsilon)
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..5c231927da7f8c235a73f77285a6404cf7473a3c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, shuffle=True, batch_size=128):
+ data = np.array([each[0].numpy() for each in dataset])
+ label = np.array([each[1] for each in dataset])
+ data_size = data.shape[0]
+
+ index = np.arange(data_size)
+ if shuffle:
+ np.random.shuffle(index)
+
+ mini_batches = []
+
+ for i in range(0, data_size, batch_size):
+ mini_batches.append([data[index[i:i+batch_size]], label[index[i:i+batch_size]]])
+ return mini_batches
+
+
+def numpy_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 15
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ # model.optimize(learning_rate)
+ model.optimizeAM()
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..abd8de5834bacc838e1b813905da469a8d9168c3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,343 @@
+# 实验报告
+
+陈疏桐 17307130331
+
+本次实验,我用numpy实现了Matmul、log、softmax和relu四个算子的前向计算与后向计算,用四个算子构建分类模型,通过了自动测试,并实现了mini_batch函数,在mnist数据集上用不同的学习率与Batch大小进行训练和测试,讨论学习率与Batch大小对模型训练效果的影响。最后,我还实现Momentum、RMSProp与Adam三种优化方法,与传统梯度下降进行比较。
+
+## 算子的反向传播与实现
+### Matmul
+
+Matmul是矩阵的乘法,在模型中的作用相当于pytorch的一个线性层,前向传播的公式是:
+
+$$ \mathrm{Y} = \mathrm{X}\mathrm{W} $$
+
+其中,$\mathrm{X}$是形状为 $N \times d$的输入矩阵,$\mathrm{W}$是形状为$d \times d'$的矩阵, $\mathrm{Y}$是形状为$N\times d'$的输出矩阵。Matmul算子相当于输入维度为$d$、输出$d'$维的线性全连接层。
+
+Matmul分别对输入求偏导,有
+
+$$ \frac{\partial \mathrm{Y}}{\partial \mathrm{X}} = \frac{\partial \mathrm{X}\mathrm{W}}{\partial \mathrm{X}} = \mathrm{W}^T$$
+
+$$ \frac{\partial \mathrm{Y}}{\partial \mathrm{W}} = \frac{\partial \mathrm{X}\mathrm{W}}{\partial \mathrm{W}} = \mathrm{X}^T $$
+
+则根据链式法则,反向传播的计算公式为:
+
+$$ \triangledown{\mathrm{X}} = \triangledown{\mathrm{Y}} \times \mathrm{W}^T $$
+$$ \triangledown{\mathrm{W}} = \mathrm{X}^T \times \triangledown{\mathrm{Y}} $$
+
+### Relu
+
+Relu函数对输入每一个元素的公式是:
+
+$$ \mathrm{Y}_{ij}=
+\begin{cases}
+\mathrm{X}_{ij} & \mathrm{X}_{ij} \ge 0 \\\\
+0 & \text{otherwise}
+\end{cases}
+$$
+
+
+每一个输出 $\mathrm{Y}_{ij}$都只与输入$\mathrm{X}_{ij}$有关。则$\mathrm{X}$每一个元素的导数也只和对应的输出有关,为:
+
+$$ \frac{\partial \mathrm{Y}_{ij}}{\partial \mathrm{X}_{ij}} =
+\begin{cases}
+1 & \mathrm{X}_{ij} \ge 0 \\\\
+0 & \text{otherwise}
+\end{cases}$$
+
+因此,根据链式法则,输入的梯度为:
+
+$$ \triangledown{\mathrm{X}_{ij}} = \triangledown{\mathrm{Y}_{ij}} \times \frac{\partial \mathrm{Y}_{ij}}{\partial \mathrm{X}_{ij}}$$
+
+### Log
+
+Log 函数公式:
+
+$$ \mathrm{Y}_{ij} = \log(\mathrm{X}_{ij} + \epsilon)$$
+
+$$ \frac{\partial \mathrm{Y}_{ij}}{\partial \mathrm{X}_{ij}} = \frac{1}{(\mathrm{X}_{ij} + \epsilon)} $$
+
+类似地,反向传播的计算公式为:
+
+$$ \triangledown{\mathrm{X}_{ij}} = \triangledown{\mathrm{Y}_{ij}} \times \frac{\partial \mathrm{Y}_{ij}}{\partial \mathrm{X}_{ij}}$$
+
+### Softmax
+
+Softmax对输入$\mathrm{X}$的最后一个维度进行计算。前向传播的计算公式为:
+
+$$ \mathrm{Y}_{ij} = \frac{\exp^{\mathrm{X}_{ij}}}{\sum_{k} \exp ^ {\mathrm{X}_{ik}}}$$
+
+从公式可知,Softmax的每一行输出都是独立计算的,与其它行的输入无关。而对于同一行,每一个输出都与每一个输入元素有关。以行$k$为例,可推得输出元素对输入元素求导的计算公式是:
+
+$$\frac{\partial Y_{ki}}{\partial X_{kj}} = \begin{cases}
+\frac{\exp ^ {X_{kj}} \times (\sum_{t \ne j}{\exp ^ {X_{kt}}}) }{(\sum_{t}{\exp ^ {X_{kt}}})^2} = Y_{kj}(1-Y_{kj}) & i = j \\\\
+-\frac{\exp^{X_{ki} }\exp^{X_{kj} }}{(\sum_t\exp^{X_{kt}})^2}=-Y_{ki} \times Y_{kj} & i\ne j
+\end{cases}$$
+
+可得每行输出$\mathrm{Y}_{k}$与每行输入$\mathrm{X}_{k}$的Jacob矩阵$\mathrm{J}_{k}$, $\mathrm{J_{k}}_{ij} = \frac{\partial \mathrm{Y}_{ki}}{\partial \mathrm{X}_{kj}}$.
+
+输出的一行对于输入$\mathrm{X}_{kj}$的导数,是输出每一行所有元素对其导数相加,即$\sum_{i} {\frac{\partial \mathrm{Y}_{ki}}{\partial \mathrm{X}_{kj}}}$ 的结果。
+
+因此,根据链式法则,可得到反向传播的计算公式为:
+$$ \triangledown \mathrm{X}_{kj} = \sum_{i} {\frac{\partial \mathrm{Y}_{ki} \times \triangledown \mathrm{Y}_{ki}}{\partial \mathrm{X}_{kj}}}$$
+
+相当于:
+
+$$ \triangledown \mathrm{X}_{k} = \mathrm{J}_{k} \times \triangledown \mathrm{Y}_{k} $$
+
+在实现时,可以用`numpy`的`matmul`操作实现对最后两个维度的矩阵相乘,得到的矩阵堆叠起来,得到最后的结果。
+
+
+## 模型构建与训练
+### 模型构建
+
+参照`torch_mnist.py`中的`torch_model`,`numpy`模型的构建只需要将其中的算子换成我们实现的算子:
+```
+def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ x = self.relu_1.forward(self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1))
+ x = self.relu_2.forward(self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2))
+
+ x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+
+ x = self.softmax.forward(x)
+ x = self.log.forward(x)
+
+ return x
+```
+
+模型的computation graph是:
+
+
+根据计算图,可以应用链式法则,推导出各个叶子变量($\mathrm{W}_{1}, \mathrm{W}_{2}, \mathrm{W}_{3}, \mathrm{X}$)以及中间变量的计算方法。
+
+反向传播的计算图为:
+
+
+可根据计算图完成梯度的计算:
+```
+def backward(self, y):
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y)
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+ self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+```
+
+### MiniBatch
+
+在`utils`中的`mini_batch`方法,直接调用了`pytorch`的`DataLoader`。 `DataLoader`是一个负责从数据集中读取样本、组合成批次输出的方法。简单地使用`DataLoader`, 可以方便地多线程并行化预取数据,加快训练速度,且节省代码。`DataLoader`还可以自定义`Sampler`,以不同的方式从数据集中进行采样,以及`BatchSampler`以自定的方式将采集的样本组合成批,这样就可以实现在同一Batch内将数据补0、自定义Batch正负样本混合比例等操作。
+
+在这里,我们模仿`DataLoader`的默认行为实现`mini_batch`方法。
+```
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128):
+ data = np.array([each[0].numpy() for each in dataset]) # 需要先处理数据
+ label = np.array([each[1] for each in dataset])
+
+ data_size = data.shape[0]
+ idx = np.array([i for i in range(data_size)])
+ np.random.shuffle(idx) # 打乱顺序
+
+ return [(data[idx[i: i+batch_size]], label[idx[i:i+batch_size]]) for i in range(0, data_size, batch_size)] # 这里相当于DataLoader 的BatchSampler,但一次性调用
+```
+
+### 模型训练
+
+构建模型,设置`epoch=10`, `learning_rate=0.1`, `batch_size=128`后,开始训练。训练时每次fit一个batch的数据,前向传播计算输出,然后根据输出计算loss,再调用`loss.backward`计算loss对输出的求导,即模型输出的梯度,之后就可以调用模型的`backward`进行后向计算。 最后调用模型的`optimize`更新参数。
+
+训练过程:
+
+
+各个epoch的测试准确率为:
+```
+[0] Test Accuracy: 0.9437
+[1] Test Accuracy: 0.9651
+[2] Test Accuracy: 0.9684
+[3] Test Accuracy: 0.9730
+[4] Test Accuracy: 0.9755
+[5] Test Accuracy: 0.9775
+[6] Test Accuracy: 0.9778
+[7] Test Accuracy: 0.9766
+[8] Test Accuracy: 0.9768
+[9] Test Accuracy: 0.9781
+```
+
+将`learning_rate` 调整到0.2,重新训练:
+
+
+各个epoch的测试准确率为:
+```
+[0] Test Accuracy: 0.9621
+[1] Test Accuracy: 0.9703
+[2] Test Accuracy: 0.9753
+[3] Test Accuracy: 0.9740
+[4] Test Accuracy: 0.9787
+[5] Test Accuracy: 0.9756
+[6] Test Accuracy: 0.9807
+[7] Test Accuracy: 0.9795
+[8] Test Accuracy: 0.9814
+[9] Test Accuracy: 0.9825
+```
+
+可见,稍微提高学习率之后,训练前期参数更新的幅度更大,损失下降得更快,能够更早收敛。训练相同迭代数,现在的模型测试准确率更高。
+
+将`learning_rate` 提高到0.3,重新训练:
+
+
+```
+[0] Test Accuracy: 0.9554
+[1] Test Accuracy: 0.9715
+[2] Test Accuracy: 0.9744
+[3] Test Accuracy: 0.9756
+[4] Test Accuracy: 0.9782
+[5] Test Accuracy: 0.9795
+[6] Test Accuracy: 0.9801
+[7] Test Accuracy: 0.9816
+[8] Test Accuracy: 0.9828
+[9] Test Accuracy: 0.9778
+```
+
+增大学习率到0.3之后,训练前期损失下降速度与上一次训练差不多,但是到了训练后期,过大的学习率导致权重在局部最小值的附近以过大的幅度移动,难以进入最低点,模型loss表现为振荡,难以收敛。本次训练的测试准确率先提高到0.9828,后反而下降。
+
+因此,可认为对于大小为128的batch,0.2是较为合适的学习率。
+
+之后,维持学习率为0.2, 修改batch_size 为256, 重新训练:
+
+```
+[0] Test Accuracy: 0.9453
+[1] Test Accuracy: 0.9621
+[2] Test Accuracy: 0.9657
+[3] Test Accuracy: 0.9629
+[4] Test Accuracy: 0.9733
+[5] Test Accuracy: 0.9766
+[6] Test Accuracy: 0.9721
+[7] Test Accuracy: 0.9768
+[8] Test Accuracy: 0.9724
+[9] Test Accuracy: 0.9775
+```
+
+batch_size增大后,每个batch更新一次参数,参数更新的频率更低,从而收敛速度有所降低;但是对比本次实验与前几次实验loss的曲线图,可发现振荡幅度更小。
+
+将batch_size减小到64, 重新实验:
+
+```
+[0] Test Accuracy: 0.9526
+[1] Test Accuracy: 0.9674
+[2] Test Accuracy: 0.9719
+[3] Test Accuracy: 0.9759
+[4] Test Accuracy: 0.9750
+[5] Test Accuracy: 0.9748
+[6] Test Accuracy: 0.9772
+[7] Test Accuracy: 0.9791
+[8] Test Accuracy: 0.9820
+[9] Test Accuracy: 0.9823
+```
+
+loss的下降速度增加,但是振荡幅度变大了。
+
+总结:在一定范围之内,随着学习率的增大,模型收敛速度增加;随着batch_size的减小,模型收敛速度也会有一定增加,但是振荡幅度增大。 学习率过大会导致后期loss振荡、难以收敛;学习率过小则会导致loss下降速度过慢,甚至可能陷入局部最小值而错过更好的最低点。
+
+## 其他优化方式实现
+
+### momentum
+
+普通梯度下降每次更新参数仅仅取决于当前batch的梯度,这可能会让梯度方向受到某些特殊的输入影响。Momentum引入了动量,让当前更新不仅取决于当前的梯度,还考虑到先前的梯度,能够在一定程度上保持一段时间的趋势。momentum的计算方式为:
+
+$$
+\begin{align}
+& v = \alpha v - \gamma \frac{\partial L}{\partial W} \\\\
+& W = W + v
+\end{align}
+$$
+
+我们在`numpy_fnn.py`的模型中实现了Momentum的优化方法。 设置学习率为0.02,batch_size为128, 继续实验:
+
+```
+[0] Test Accuracy: 0.9586
+[1] Test Accuracy: 0.9717
+[2] Test Accuracy: 0.9743
+[3] Test Accuracy: 0.9769
+[4] Test Accuracy: 0.9778
+[5] Test Accuracy: 0.9786
+[6] Test Accuracy: 0.9782
+[7] Test Accuracy: 0.9809
+[8] Test Accuracy: 0.9790
+[9] Test Accuracy: 0.9818
+```
+
+momentum 相比传统梯度下降,不一定最后会得到更好的效果。当加入动量,当前梯度方向与动量方向相同时,参数就会得到更大幅度的调整,因此loss下降速度更快,并且前期动量基本上会积累起来,如果使用过大的学习率,很容易会溢出。所以momentum适合的学习率比普通梯度下降要小一个数量级。 而当梯度方向错误的时候,加入动量会使得参数来不及更新,从而错过最小值。
+
+### RMSProp
+
+
+RMSProp引入了自适应的学习率调节。 在训练前期,学习率应该较高,使得loss能快速下降;但随着训练迭代增加,学习率应该不断减小,使得模型能够更好地收敛。 自适应调整学习率的基本思路是根据梯度来调节,梯度越大,学习率就衰减得越快;后期梯度减小,学习率衰减就更加缓慢。
+
+而为了避免前期学习率衰减得过快,RMSProp还用了指数平均的方法,来缓慢丢弃原来的梯度历史。计算方法为:
+
+$$
+\begin{align}
+& h = \rho h + (1-\rho) \frac{\partial L}{\partial W} \odot \frac{\partial L}{\partial W} \\\\
+& W = W - \gamma \frac{1}{\sqrt{\delta + h}} \frac{\partial L}{\partial W}
+\end{align}$$
+
+设置梯度为0.001, weight_decay 为0.01, 进行训练和测试:
+
+
+```
+[0] Test Accuracy: 0.9663
+[1] Test Accuracy: 0.9701
+[2] Test Accuracy: 0.9758
+[3] Test Accuracy: 0.9701
+[4] Test Accuracy: 0.9748
+[5] Test Accuracy: 0.9813
+[6] Test Accuracy: 0.9813
+[7] Test Accuracy: 0.9819
+[8] Test Accuracy: 0.9822
+[9] Test Accuracy: 0.9808
+```
+
+可见,在训练的中间部分,loss振荡幅度比普通梯度下降更小。训练前期,模型的收敛速度更快,但到后期比起普通梯度下降并无明显优势。
+
+### Adam
+
+Adam 同时结合了动量与自适应的学习率调节。Adam首先要计算梯度的一阶和二阶矩估计,分别代表了动量与自适应的部分:
+
+$$
+\begin{align}
+& \mathrm{m} = \beta_1 \mathrm{m} + (1-\beta_1) \frac{\partial L}{\partial W} \\\\
+& \mathrm{v} = \beta_2 \mathrm{v} + (1-\beta_2) \frac{\partial L}{\partial W} \odot \frac{\partial L}{\partial W}
+\end{align}
+$$
+
+然后进行修正:
+
+$$
+\begin{align}
+& \mathrm{\hat{m}} = \frac{\mathrm{m}}{1-\beta_1 ^ t }\\\\
+& \mathrm{\hat{v}} = \frac{\mathrm{v}}{1-\beta_2 ^ t}
+\end{align}
+$$
+
+最后,参数的更新为:
+$$ W = W - \gamma \frac{\mathrm{\hat m}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{\hat v}+ \delta}}$$
+
+
+设置学习率为0.001, batch_size为128, 开始训练:
+
+```
+[0] Test Accuracy: 0.9611
+[1] Test Accuracy: 0.9701
+[2] Test Accuracy: 0.9735
+[3] Test Accuracy: 0.9752
+[4] Test Accuracy: 0.9787
+[5] Test Accuracy: 0.9788
+[6] Test Accuracy: 0.9763
+[7] Test Accuracy: 0.9790
+[8] Test Accuracy: 0.9752
+[9] Test Accuracy: 0.9806
+
+```
+
+相比传统梯度下降,loss振荡略微有所减小,前期loss下降速度略微更快,但是最后收敛的速度相当。
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/backgraph.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/backgraph.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c4a70b28e869708641bd01dba83730ed62ab9c4d
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/backgraph.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/compu_graph.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/compu_graph.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..74f02ff1b4c4795c99600fb2e358d23a170f11c1
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/compu_graph.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/momentum.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/momentum.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..152bfe4eda8bf98cb271e9e3af3801f223273ec2
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/momentum.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/rmsprop.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/rmsprop.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d4c9f6d651ea0dcac312c3a7dcb38266a477679c
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/rmsprop.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..618816332b78c4f0498444a42dd2a5028df91ef1
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train02.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train02.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a2cbc7b9ccbf2f28955902b86881d7a640f50fa7
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train02.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train03.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train03.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..41dd8fd9060e6774b983375f3b025ee6335b9f66
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train03.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train10.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train10.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a2056ba0d21f8f40fc0279e532fd6b9f1ff79cef
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train10.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train256.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train256.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..81aa1b2bcc7f708607f8c402f9f41d579793f9e1
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train256.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train64.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train64.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..8f34749c6fda428437ff3fe11292b0213eca0d7a
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train64.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train_adam.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train_adam.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..eefa8b27deb6485f895033add750f018fd14e293
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train_adam.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/trainloss.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/trainloss.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b845297f03d5d6e6ae2b026b25554519a77f471b
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/trainloss.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7b32d95b7825b4787f5d226ac058c0039aee4bba
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,208 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 1 #
+ grad_W = np.matmul(self.memory['x'].T, grad_y)
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, self.memory['W'].T)
+ ####################
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 2 #
+ ####################
+ grad_x = np.where(self.memory['x'] > 0, np.ones_like(self.memory['x']), np.zeros_like(self.memory['x'])) * grad_y # 元素乘积
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 3 #
+ ####################
+ grad_x = (1/(self.memory['x'] + self.epsilon)) * grad_y
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 4 #
+ ####################
+ exp_x = np.exp(x)
+ out = exp_x/np.sum(exp_x, axis=1, keepdims=True)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['out'] = out
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ o = self.memory['out']
+ Jacob = np.array([np.diag(r) - np.outer(r, r) for r in o])
+ # i!=j - oi* oj
+ # i==j oi*(1-oi)
+ grad_y = grad_y[:, np.newaxis, :]
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, Jacob).squeeze(1)
+ #print(grad_x.shape)
+ #print(grad_x)
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新。 softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ # 以下变量是在 momentum\rmsprop中使用的
+ self.v1 = np.zeros_like(self.W1)
+ self.v2 = np.zeros_like(self.W2)
+ self.v3 = np.zeros_like(self.W3)
+
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ x = self.relu_1.forward(self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1))
+ x = self.relu_2.forward(self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2))
+
+ x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+
+ x = self.softmax.forward(x)
+ x = self.log.forward(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y)
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+ self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+
+ def momentum(self, learning_rate, alpha=0.9):
+ self.v1 = self.v1 * alpha - learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.v2 = self.v2 * alpha - learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.v3 = self.v3 * alpha - learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+
+ self.W1 += self.v1
+ self.W2 += self.v2
+ self.W3 += self.v3
+
+ def RMSProp(self, learning_rate, weight_decay = 0.99):
+ self.v1 = self.v1 * weight_decay + (1-weight_decay) * self.W1_grad * self.W1_grad
+ self.v2 = self.v2 * weight_decay + (1-weight_decay) * self.W2_grad * self.W2_grad
+ self.v3 = self.v3 * weight_decay + (1-weight_decay) * self.W3_grad * self.W3_grad
+
+ self.W1 = self.W1 - learning_rate * self.W1_grad / np.sqrt( self.v1 + 1e-7)
+ self.W2 = self.W2 - learning_rate * self.W2_grad / np.sqrt( self.v2 + 1e-7)
+ self.W3 = self.W3 - learning_rate * self.W3_grad / np.sqrt( self.v3 + 1e-7)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..4187f01eeebbbcd6ab48bfacf8dedc37085e46e2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128):
+ data = np.array([each[0].numpy() for each in dataset])
+ label = np.array([each[1] for each in dataset])
+
+ data_size = data.shape[0]
+ idx = np.array([i for i in range(data_size)])
+ np.random.shuffle(idx)
+
+ return [(data[idx[i: i+batch_size]], label[idx[i:i+batch_size]]) for i in range(0, data_size, batch_size)]
+
+class Adam():
+ def __init__(self, param, learning_rate=0.001, beta_1=0.9, beta_2=0.999):
+ self.param = param
+ self.iter = 0
+ self.m = 0
+ self.v = 0
+ self.beta1 = beta_1
+ self.beta2 = beta_2
+ self.lr = learning_rate
+ def optimize(self, grad):
+ self.iter+=1
+ self.m = self.beta1 * self.m + (1 - self.beta1) * grad
+ self.v = self.beta2 * self.v + (1 - self.beta2) * grad * grad
+ m_hat = self.m / (1 - self.beta1 ** self.iter)
+ v_hat = self.v / (1 - self.beta2 ** self.iter)
+ self.param -= self.lr * m_hat / (v_hat ** 0.5 + 1e-8)
+ return self.param
+
+def numpy_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ W1_opt, W2_opt, W3_opt = Adam(model.W1), Adam(model.W2), Adam(model.W3)
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 10
+ learning_rate = 0.0015
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset, batch_size=128):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ #model.Adam(learning_rate)
+ W1_opt.optimize(model.W1_grad)
+ W2_opt.optimize(model.W2_grad)
+ W3_opt.optimize(model.W3_grad)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Test Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/tester_demo.py b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/tester_demo.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..515b86c1240eebad83287461548530c944f23bc8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/tester_demo.py
@@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
+import numpy as np
+import torch
+from torch import matmul as torch_matmul, relu as torch_relu, softmax as torch_softmax, log as torch_log
+
+from numpy_fnn import Matmul, Relu, Softmax, Log, NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from torch_mnist import TorchModel
+from utils import get_torch_initialization, one_hot
+
+err_epsilon = 1e-6
+err_p = 0.4
+
+
+def check_result(numpy_result, torch_result=None):
+ if isinstance(numpy_result, list) and torch_result is None:
+ flag = True
+ for (n, t) in numpy_result:
+ flag = flag and check_result(n, t)
+ return flag
+ # print((torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) - torch_result).abs().mean().item())
+ T = (torch_result * torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) < 0).sum().item()
+ direction = T / torch_result.numel() < err_p
+ return direction and ((torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) - torch_result).abs().mean() < err_epsilon).item()
+
+
+def case_1():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[5, 6])
+ W = np.random.normal(size=[6, 4])
+
+ numpy_matmul = Matmul()
+ numpy_out = numpy_matmul.forward(x, W)
+ numpy_x_grad, numpy_W_grad = numpy_matmul.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+ torch_W = torch.from_numpy(W).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_matmul(torch_x, torch_W)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ (numpy_W_grad, torch_W.grad)
+ ])
+
+
+def case_2():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[5, 6])
+
+ numpy_relu = Relu()
+ numpy_out = numpy_relu.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_relu.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_relu(torch_x)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def case_3():
+ x = np.random.uniform(low=0.0, high=1.0, size=[3, 4])
+
+ numpy_log = Log()
+ numpy_out = numpy_log.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_log.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_log(torch_x)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def case_4():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[4, 5])
+
+ numpy_softmax = Softmax()
+ numpy_out = numpy_softmax.forward(x)
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_softmax(torch_x, 1)
+
+ return check_result(numpy_out, torch_out)
+
+
+def case_5():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[20, 25])
+
+ numpy_softmax = Softmax()
+ numpy_out = numpy_softmax.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_softmax.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_softmax(torch_x, 1)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def test_model():
+ try:
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ numpy_model = NumpyModel()
+ torch_model = TorchModel()
+ torch_model.W1.data, torch_model.W2.data, torch_model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+ numpy_model.W1 = torch_model.W1.detach().clone().numpy()
+ numpy_model.W2 = torch_model.W2.detach().clone().numpy()
+ numpy_model.W3 = torch_model.W3.detach().clone().numpy()
+
+ x = torch.randn((10000, 28, 28))
+ y = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0] * 1000)
+
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+ x2 = x.numpy()
+ y_pred = torch_model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+
+ y_pred_numpy = numpy_model.forward(x2)
+ numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred_numpy, y.numpy())
+
+ check_flag_1 = check_result(y_pred_numpy, y_pred)
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("forward", 10 * check_flag_1, 10))
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in forward]")
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("forward", 0, 10))
+ return 0
+
+ try:
+
+ numpy_model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+
+ check_flag_2 = [
+ check_result(numpy_model.log_grad, torch_model.log_input.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.softmax_grad, torch_model.softmax_input.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W3_grad, torch_model.W3.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W2_grad, torch_model.W2.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W1_grad, torch_model.W1.grad)
+ ]
+ check_flag_2 = sum(check_flag_2) >= 4
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("backward", 20 * check_flag_2, 20))
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in backward]")
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("backward", 0, 20))
+ check_flag_2 = False
+
+ return 10 * check_flag_1 + 20 * check_flag_2
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ testcases = [
+ ["matmul", case_1, 5],
+ ["relu", case_2, 5],
+ ["log", case_3, 5],
+ ["softmax_1", case_4, 5],
+ ["softmax_2", case_5, 10],
+ ]
+ score = 0
+ for case in testcases:
+ try:
+ res = case[2] if case[1]() else 0
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in {}]".format(case[0]))
+ res = 0
+ score += res
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format(case[0], res, case[2]))
+ score += test_model()
+ print("{:14} {}/60".format("FINAL SCORE", score))
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/torch_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/torch_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6d3e214c7606e3d43dac4b94554f942508afffb3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/torch_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+import torch
+from utils import mini_batch, batch, download_mnist, get_torch_initialization, one_hot, plot_curve
+
+
+class TorchModel:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = torch.randn((28 * 28, 256), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W2 = torch.randn((256, 64), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W3 = torch.randn((64, 10), requires_grad=True)
+ self.softmax_input = None
+ self.log_input = None
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W1))
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W2))
+ x = torch.matmul(x, self.W3)
+
+ self.softmax_input = x
+ self.softmax_input.retain_grad()
+
+ x = torch.softmax(x, 1)
+
+ self.log_input = x
+ self.log_input.retain_grad()
+
+ x = torch.log(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ with torch.no_grad():
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1.grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2.grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3.grad
+
+ self.W1.grad = None
+ self.W2.grad = None
+ self.W3.grad = None
+
+
+def torch_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = TorchModel()
+ model.W1.data, model.W2.data, model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset, numpy=False):
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset, numpy=False)[0]
+ accuracy = model.forward(x).argmax(dim=1).eq(y).float().mean().item()
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ torch_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/utils.py b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/utils.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..709220cfa7a924d914ec1c098c505f864bcd4cfc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/utils.py
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+import torch
+import numpy as np
+from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
+
+
+def plot_curve(data):
+ plt.plot(range(len(data)), data, color='blue')
+ plt.legend(['loss_value'], loc='upper right')
+ plt.xlabel('step')
+ plt.ylabel('value')
+ plt.show()
+
+
+def download_mnist():
+ from torchvision import datasets, transforms
+
+ transform = transforms.Compose([
+ transforms.ToTensor(),
+ transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.1307,), std=(0.3081,))
+ ])
+
+ train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=True, download=True)
+ test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=False, download=True)
+
+ return train_dataset, test_dataset
+
+
+def one_hot(y, numpy=True):
+ if numpy:
+ y_ = np.zeros((y.shape[0], 10))
+ y_[np.arange(y.shape[0], dtype=np.int32), y] = 1
+ return y_
+ else:
+ y_ = torch.zeros((y.shape[0], 10))
+ y_[torch.arange(y.shape[0], dtype=torch.long), y] = 1
+ return y_
+
+
+def batch(dataset, numpy=True):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+ for each in dataset:
+ data.append(each[0])
+ label.append(each[1])
+ data = torch.stack(data)
+ label = torch.LongTensor(label)
+ if numpy:
+ return [(data.numpy(), label.numpy())]
+ else:
+ return [(data, label)]
+
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128, numpy=False):
+ return torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
+
+
+def get_torch_initialization(numpy=True):
+ fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(28 * 28, 256)
+ fc2 = torch.nn.Linear(256, 64)
+ fc3 = torch.nn.Linear(64, 10)
+
+ if numpy:
+ W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ W2 = fc2.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ W3 = fc3.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ else:
+ W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+ W2 = fc2.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+ W3 = fc3.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..647eb99d08956f5fea84c6aa563ab3e1576cfcc6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,276 @@
+# PRML-2021 Assignment2
+
+姓名:夏海淞
+
+学号:18307130090
+
+## 简述
+
+在本次实验中,我通过`NumPy`实现了一个简单的前馈神经网络,其中包括`numpy_fnn.py`中算子的反向传播以及前馈神经网络模型的构建。为了验证模型效果,我在MNIST数据集上进行了训练和测试。此外,我还实现了`Momentum`和`Adam`优化算法,并比较了它们的性能。
+
+## 算子的反向传播
+
+### `Matmul`
+
+`Matmul`的计算公式为:
+$$
+Y=X\times W
+$$
+其中$Y,X,W$分别为$n\times d',n\times d,d\times d'$的矩阵。
+
+由[神经网络与深度学习-邱锡鹏](https://nndl.github.io/nndl-book.pdf)中公式(B.20)和(B.21),有
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial W}=\frac{\partial(X\times W)}{\partial W}=X^T\\\\
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial X}=\frac{\partial(X\times W)}{\partial X}=W^T
+$$
+结合链式法则和矩阵运算法则,可得
+$$
+\nabla_X=\nabla_Y\times W^T\\\\
+\nabla_W=X^T\times \nabla_Y
+$$
+
+### `Relu`
+
+`Relu`的计算公式为:
+$$
+Y_{ij}=\begin{cases}
+X_{ij}&X_{ij}\ge0\\\\
+0&\text{otherwise}
+\end{cases}
+$$
+因此有
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{ij}}=\begin{cases}
+1&X_{ij}>0\\\\
+0&\text{otherwise}
+\end{cases}
+$$
+结合链式法则,得到反向传播的计算公式:$\nabla_{Xij}=\nabla_{Yij}\cdot\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{ij}}$
+
+### `Log`
+
+`Log`的计算公式为
+$$
+Y_{ij}=\ln(X_{ij}+\epsilon),\epsilon=10^{-12}
+$$
+因此有
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{ij}}=\frac1{X_{ij}+\epsilon}
+$$
+结合链式法则,得到反向传播的计算公式:$\nabla_{Xij}=\nabla_{Yij}\cdot\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial {X_{ij}}}$
+
+### `Softmax`
+
+`Softmax`的计算公式为
+$$
+Y_{ij}=\frac{\exp\{X_{ij} \}}{\sum_{k=1}^c\exp\{X_{ik} \}}
+$$
+其中$Y,X$均为$N\times c$的矩阵。容易发现`Softmax`以$X$的每行作为单位进行运算。因此对于$X,Y$的行分量$X_k,Y_k$,有
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y_{ki}}{\partial X_{kj}}=\begin{cases}
+\frac{\exp\{X_{kj} \}(\sum_t\exp\{X_{kt}\})-\exp\{2X_{ki}\}}{(\sum_t\exp\{X_{kt}\})^2}=Y_{ki}(1-Y_{ki})&i=j\\\\
+-\frac{\exp\{X_{ki} \}\exp\{X_{kj} \}}{(\sum_t\exp\{X_{kt}\})^2}=-Y_{ki}Y_{kj}&i\not=j
+\end{cases}
+$$
+因此可计算得到$X_k,Y_k$的Jacob矩阵,满足$J_{ij}=\frac{\partial Y_{ki}}{\partial X_{kj}}$。结合链式法则,可得
+$$
+\nabla_X=\nabla_Y\times J
+$$
+将行分量组合起来,就得到了反向传播的最终结果。
+
+## 模型构建与训练
+
+### 模型构建
+
+#### `forward`
+
+参考`torch_mnist.py`中`TorchModel`方法的模型,使用如下代码构建:
+
+```python
+def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ x = self.relu_1.forward(self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1))
+ x = self.relu_2.forward(self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2))
+ x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+
+ x = self.log.forward(self.softmax.forward(x))
+
+ return x
+```
+
+模型的计算图如下:
+
+
+
+#### `backward`
+
+根据模型的计算图,按照反向的计算顺序依次调用对应算子的反向传播算法即可。
+
+```python
+def backward(self, y):
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y)
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+ self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+
+ return self.x1_grad
+```
+
+#### `mini_batch`
+
+`mini_batch`的作用是提高模型的训练速度,同时得到较好的优化效果。传统的批处理方法对整个数据集计算平均的损失函数值,随后计算相应梯度进行反向传播。当训练数据集容量较大时,对训练速度造成严重影响;而随机方法则对数据集的每个样本计算损失函数值,随后计算相应梯度进行反向传播。此时数据集容量不对训练速度产生影响,然而由于样本的随机性,可能导致参数无法收敛到最优值,在最优值附近震荡。因此一个折中的方法是将数据集划分为若干批次,在提高训练速度的同时保证了较好的收敛效果。
+
+在本次实验中,我参照`utils.py`中的`mini_batch`,在`numpy_mnist.py`中重新实现了`mini_batch`方法:
+
+```python
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128):
+ data = np.array([np.array(each[0]) for each in dataset])
+ label = np.array([each[1] for each in dataset])
+
+ size = data.shape[0]
+ index = np.arange(size)
+ np.random.shuffle(index)
+
+ return [(data[index[i:i + batch_size]], label[index[i:i + batch_size]]) for i in range(0, size, batch_size)]
+```
+
+### 模型训练
+
+设定`learning_rate=0.1`,`batch_size=128`,`epoch_number=10`。训练结果如下:
+
+```
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9486
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9643
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9724
+[3] Accuracy: 0.9738
+[4] Accuracy: 0.9781
+[5] Accuracy: 0.9768
+[6] Accuracy: 0.9796
+[7] Accuracy: 0.9802
+[8] Accuracy: 0.9800
+[9] Accuracy: 0.9796
+```
+
+
+
+**减小batch_size的值为 64**,保持其他的参数不变进行实验,得到结果如下:
+
+| 轮次 | Accuracy |
+| ---- | -------- |
+| [0] | 0.9548 |
+| [1] | 0.9682 |
+| [2] | 0.9679 |
+
+可见当batch_size 减小时,模型准确率在每一轮中进步的幅度会变小。
+
+
+
+## mini_batch 的替换
+
+```
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128,seed=0):
+ np.random.seed(seed)
+ x_train = dataset.train_data
+ y_train = dataset.train_labels
+ m = y_train.shape[0]
+ def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128,seed=0):
+ np.random.seed(seed)
+ x_train = dataset.train_data
+ y_train = dataset.train_labels
+ m = y_train.shape[0]
+ # m为所有样本的数量
+ mini_batchs =[]
+ permutation = list(np.random.permutation(m))
+ # 打乱样本顺序
+ shuffle_X = x_train[permutation, :, :]
+ shuffle_Y = y_train[permutation]
+ num_mini_batch = int(m//batch_size)
+ # num_mini_batch为mini_batch的块数
+ for i in range(num_mini_batch):
+ mini_batch_x = shuffle_X[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size, :, :]
+ mini_batch_y = shuffle_Y[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size]
+ mini_batch = (mini_batch_x, mini_batch_y)
+ mini_batchs.append(mini_batch)
+ if m % batch_size != 0:
+ # 如果样本数不能被整除,取余下的部分
+ mini_batch_X = shuffle_X[num_mini_batch * batch_size:m, :, :]
+ mini_batch_Y = shuffle_Y[num_mini_batch * batch_size:m]
+ mini_batch = (mini_batch_X, mini_batch_Y)
+ mini_batchs.append(mini_batch)
+ return mini_batchs
+ mini_batchs =[]
+ permutation = list(np.random.permutation(m))
+ shuffle_X = x_train[permutation, :, :]
+ shuffle_Y = y_train[permutation]
+ num_mini_batch = int(m//batch_size)
+ for i in range(num_mini_batch):
+ mini_batch_x = shuffle_X[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size, :, :]
+ mini_batch_y = shuffle_Y[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size]
+ mini_batch = (mini_batch_x, mini_batch_y)
+ mini_batchs.append(mini_batch)
+ if m % batch_size != 0:
+ # 如果样本数不能被整除,取余下的部分
+ mini_batch_X = shuffle_X[num_mini_batch * batch_size:m, :, :]
+ mini_batch_Y = shuffle_Y[num_mini_batch * batch_size:m]
+ mini_batch = (mini_batch_X, mini_batch_Y)
+ mini_batchs.append(mini_batch)
+ return mini_batchs
+```
+
+整体思路是打乱样本的顺序,然后依次取出batch_size个样本的数据,作为一个mini_batch组。最后mini_batch函数返回所有的mini_batch组的集合
+
+用numpy实现mini_batch之后,运行numpy_minist.py, 设定batch_size =128, learning_rate = 0.1, epoch_number = 3, 得到的实验结果如下:
+
+| 轮次 | Accuracy |
+| ---- | -------- |
+| [0] | 0.8780 |
+| [1] | 0.8994 |
+| [2] | 0.9099 |
+
+
+
+## 反向传播公式的推导
+
+**Matmul**
+
+Matmul的计算式为
+$$
+Y = X*W
+$$
+根据矩阵的求导法则,可以推出
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial X} = W^{T}
+$$
+
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial W} = X^{T}
+$$
+
+ 对应代码段如下:
+
+```
+grad_W = np.matmul(self.memory['x'].T, grad_y)
+grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, self.memory['W'].T)
+```
+
+
+
+**Relu**
+
+Relu的计算公式为
+$$
+Y=\begin{cases}
+X&X\ge0\\\\
+0&\text{otherwise}
+\end{cases}
+$$
+所以有
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial X}=\begin{cases}
+1&X>0\\\\
+0&\text{otherwise}
+\end{cases}
+$$
+对应代码块如下:
+
+```
+grad_x = np.where(self.memory['x'] > 0, grad_y, np.zeros_like(self.memory['x']))
+```
+
+意思是说若x大于0, grad_x的结果就是传入的grad_y。否则结果为0
+
+
+
+**Log**
+
+log的计算公式为
+$$
+Y=\ln(X+\epsilon)
+$$
+因此有
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial X} = \frac1{X+\epsilon}
+$$
+对应的代码块如下:
+
+```
+grad_x = np.multiply(1./(self.memory['x'] + self.epsilon), grad_y)
+```
+
+
+
+**Softmax**
+
+Softmax的计算公式为
+$$
+Y=\frac{\exp\{X\}}{\sum_{k=1}^c\exp\{X\}}
+$$
+根据邱老师书第411~412页对该公式的导数的推导(在这里直接引用结果),有
+
+
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial X} = diag(softmax(x))-softmax(x)softmax(x)^{T}
+$$
+对应的代码块如下
+
+```
+out = self.memory['out']
+grad_x = []
+for idx in range(out.shape[0]):
+ dout = np.diag(out[idx]) - np.outer(out[idx], out[idx])
+ grad = np.matmul(dout, grad_y[idx])
+ grad_x.append(grad)
+grad_x = np.array(grad_x)
+```
+
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/img/loss_value1.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/img/loss_value1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..dbb3c56e9d1036c37ea3aa3258a7ae0acd9eb79b
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/img/loss_value1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ea2d68f88793d261f1ead5fa836c421f4b3ed140
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,173 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+ grad_W = np.matmul(self.memory['x'].T, grad_y)
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, self.memory['W'].T)
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ grad_x = np.where(self.memory['x'] > 0, grad_y, np.zeros_like(self.memory['x']))
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ grad_x = np.multiply(1./(self.memory['x'] + self.epsilon), grad_y)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+ out = []
+ for index in range(x.shape[0]):
+ temp = x[index]
+ temp = temp - max(temp)
+ temp = np.exp(temp)
+ out.append(temp/sum(temp))
+ out = np.array(out)
+ self.memory['out'] = out
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ out = self.memory['out']
+ grad_x = []
+ for idx in range(out.shape[0]):
+ dout = np.diag(out[idx]) - np.outer(out[idx], out[idx])
+ grad = np.matmul(dout, grad_y[idx])
+ grad_x.append(grad)
+ grad_x = np.array(grad_x)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新。 softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+ x = self.relu_1.forward(self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1))
+ x = self.relu_2.forward(self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2))
+ x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+ x = self.softmax.forward(x)
+ x = self.log.forward(x)
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y)
+ grad_y = self.log_grad
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(grad_y)
+ grad_y = self.softmax_grad
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(grad_y)
+ grad_y = self.x3_grad
+ self.relu_2_grad =self.relu_2.backward(grad_y)
+ grad_y = self.relu_2_grad
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad =self.matmul_2.backward(grad_y)
+ grad_y = self.x2_grad
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(grad_y)
+ grad_y = self.relu_1_grad
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(grad_y)
+ pass
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..daea871d110daf90996073d606bef96da6d2f827
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307110367/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128,seed=0):
+ np.random.seed(seed)
+ x_train = dataset.train_data
+ y_train = dataset.train_labels
+ m = y_train.shape[0]
+ # m为所有样本的数量
+ mini_batchs =[]
+ permutation = list(np.random.permutation(m))
+ # 打乱样本顺序
+ shuffle_X = x_train[permutation, :, :]
+ shuffle_Y = y_train[permutation]
+ num_mini_batch = int(m//batch_size)
+ # num_mini_batch为mini_batch的块数
+ for i in range(num_mini_batch):
+ mini_batch_x = shuffle_X[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size, :, :]
+ mini_batch_y = shuffle_Y[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size]
+ mini_batch = (mini_batch_x, mini_batch_y)
+ mini_batchs.append(mini_batch)
+ if m % batch_size != 0:
+ # 如果样本数不能被整除,取余下的部分
+ mini_batch_X = shuffle_X[num_mini_batch * batch_size:m, :, :]
+ mini_batch_Y = shuffle_Y[num_mini_batch * batch_size:m]
+ mini_batch = (mini_batch_X, mini_batch_Y)
+ mini_batchs.append(mini_batch)
+ return mini_batchs
+
+def numpy_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+ y_pred = model.forward(x.numpy()/255)
+ #y_pred = model.forward(x.numpy())
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a2949d3c15d69eb19fb37c1d207072950517f373
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,128 @@
+# 选题1
+
+## 前馈神经网络的实现
+
+### Matmul
+
+forward时
+$$
+Y=XW
+$$
+backward时
+$$
+\frac {\partial L}{\partial X}=\frac {\partial L}{\partial Y}\frac {\partial Y}{\partial X}=\frac {\partial L}{\partial Y}\frac {\partial XW}{\partial X}=\frac {\partial L}{\partial Y} W^T\\\\
+\frac {\partial L}{\partial W}=\frac {\partial L}{\partial Y}\frac {\partial Y}{\partial W}=\frac {\partial L}{\partial Y}\frac {\partial XW}{\partial W}=X^T\frac {\partial L}{\partial Y}
+$$
+
+### Relu
+
+forward时
+$$
+Y_{ij}= \begin{cases} X_{ij}& X_{ij}\geq 0 \\\\
+0& otherwise \end{cases}
+$$
+backward时
+$$
+\frac{\partial L}{\partial X_{ij}}=\frac{\partial L}{\partial Y_{ij}} \frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{ij}}
+\\\\
+\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{ij}}= \begin{cases} 1 & X_{ij}\geq 0 \\\\
+0& otherwise \end{cases}\\\\
+\therefore \frac{\partial L}{\partial X_{ij}}=\begin{cases} \frac{\partial L}{\partial Y_{ij}} & X_{ij}\geq 0 \\\\
+0& otherwise \end{cases}
+$$
+
+### Log
+
+forward时
+$$
+Y_{ij}=ln(X_{ij}+\epsilon)
+$$
+backward时
+$$
+\frac{\partial L}{\partial X_{ij}}=\frac{\partial L}{\partial Y_{ij}} \frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{ij}}=\frac{\partial L}{\partial Y_{ij}}\frac {1}{X_{ij}+\epsilon}
+$$
+
+### Softmax
+
+forward时
+$$
+Y_{ij} = \frac {expX_{ij}}{\sum_k expX_{ik}}
+$$
+backward时,参考课本
+
+
+
+Softmax是对每一行进行的操作,由此可以得到每一行的Jacob矩阵为
+$$
+Jacob = diag(Y_r) - Y_rY_r^T
+$$
+
+### 补全NumpyModel
+
+forward部分根据torch_mnisy.py补全,得到网络结构为
+
+input -> matmul_1 -> relu_1 -> matmul_2 -> relu_2 -> matmul_3 -> softmax -> log
+
+根据此结构,依次反向调用之前实现的backward部分即可
+
+## 实验
+
+### 实现mini_batch
+
+有时候训练集数据过多,如果对整个数据集计算平均的损失函数值然后计算梯度进而进行反向传播,训练速度会比较慢;使用随机梯度下降则可能会导致参数无法收敛到最优值。mini_batch方法是这两种方法的折中,将数据集划分为若干批次,在提高训练速度的同时保证了较好的收敛效果。
+
+参考utils.py中mini_batch,在numpy_mnist.py中实现了mini_batch,可调参数有dataset,shuffle,batch_size。下面实验均在我实现的mini_batch上进行。
+
+### 在numpy_mnist.py中进行模型的训练和测试
+
+通过改变batch_size、学习率、是否shuffle这三个变量进行了实验。
+
+
+
+上图左边一列是batch_size为64时的情况,右边两列是batch_size为128时的情况;上面一行学习率为0.1,下面一行学习率为0.05。本次实验都进行了shuffle。可以看出,batch_size越小,在同样的step里收敛得越慢;在训练前期震荡比较大;在训练后期损失函数的震荡反而较小。
+
+
+
+上图左边一列是学习率为0.05时的情况,右边两列是学习率为0.1时的情况;同一行的数据其他实验参数相同。可以看出,学习率越小,收敛得就越慢。出乎我意料的是,学习率越小,在收敛后的实验后期,损失函数震荡比学习率大的更严重。
+
+
+
+上图左边未对训练数据进行shuffle,右边进行了shuffle,其他条件一样。可以看出未进行shuffle的模型收敛更慢,损失函数的震荡更大。这是因为在我的mini_batch的实现中,不进行shuffle的话,每次梯度的更新都是固定的total_size/batch_size组数据,相当于数据量减少了。
+
+## momentum、Adam等优化
+
+SGD会造成损失函数的震荡,可能会使最后的结果停留在一个局部最优点。为了抑制SGD的震荡,提出了SGD with Momentum的概念。SGDM在梯度下降过程中加入了一阶动量
+$$
+m_t = \beta _1m_{t-1}+(1-\beta_1)g_t
+$$
+也就是说,在梯度下降方向不变时,梯度下降的速度变快,梯度下降方向有所变化的维度上更新速度变慢。这里$\beta _1$的经验值为0.9。也就是说,梯度下降的方向主要是之前累积的下降方向,并略微偏向当前时刻的下降方向。
+
+除了一阶动量,二阶动量也被广泛使用。对于经常更新的参数,我们已经积累了大量关于它的知识,不希望被单个样本影响太大,希望学习速率慢一些;对于偶尔更新的参数,我们了解的信息太少,希望能从每个偶然出现的样本身上多学一些,即学习速率大一些。二阶动量的一种比较好的计算方法是:不累积全部历史梯度,只关注过去一段时间窗口的下降梯度,这种方法解决了学习率急剧下降的问题。这就是AdaDelta/RMSProp。
+$$
+V_t = \beta _ 2 V_{t-1}+(1-\beta_2)g_t^2
+$$
+由此,Adam自然而然地出现了,Adam把一阶动量和二阶动量都用起来,下降梯度为
+$$
+\Delta = \alpha\ m_t/\sqrt V_t
+$$
+一般为了避免分母为0,会在分母上加一个小的平滑项。$\beta _2$的经验值为0.999,Adam学习率为0.001。
+
+参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/32230623
+
+
+
+上图从左往右第一张图为不使用优化器,第二张图为使用momentum优化,第三张图为使用Adam优化,其中,前两张图学习率为0.1,最后一张图学习率为0.001。可以看出,使用momentum之后前期收敛速度加快,并且在后期损失函数震荡减少。使用Adam优化器,虽然学习率低,但是收敛速度更快,并且损失函数的震荡从训练器前期到后期一直比不使用要小。
+
+## 总结
+
+完成了自动测试 60%
+
+
+
+在numpy_minist.py中对模型进行训练和测试 20%
+
+只用NumPy实现了mini_batch函数 10%
+
+推导了numpy_fnn.py中算子的反向传播公式 10%
+
+实现了momentum、Adam等优化方法并进行了对比实验 10%
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/img/softmax.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/img/softmax.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e8ae7d1b57865a9c23e15176a13ecebaa105ec03
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/img/softmax.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/img/tester.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/img/tester.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..29246264c69d2decc2ed5f34df698fcd07481303
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/img/tester.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..67cc7bc6beac060ebe52fcee790214b1c9f1dc83
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,210 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 1 #
+ ####################
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, self.memory['W'].T)
+ grad_W = np.matmul(self.memory['x'].T, grad_y)
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 2 #
+ ####################
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ grad_x = grad_y * np.where(x > 0, np.ones_like(x), np.zeros_like(x))
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 3 #
+ ####################
+ grad_x = grad_y * np.reciprocal(self.memory['x'] + self.epsilon)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 4 #
+ ####################
+ out = np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x), axis=1, keepdims=True)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['out'] = out
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 5 #
+ ####################
+ out = self.memory['out']
+ Jacobs = np.array([np.diag(r) - np.outer(r, r) for r in out])
+ grad_y = grad_y[:, np.newaxis, :]
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, Jacobs).squeeze(axis=1)
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新。 softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ # for momentum and adam
+ self.W1_m = 0
+ self.W2_m = 0
+ self.W3_m = 0
+ self.W1_v = 0
+ self.W2_v = 0
+ self.W3_v = 0
+
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ ####################
+ # code 6 #
+ ####################
+ x = self.relu_1.forward(self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1))
+ x = self.relu_2.forward(self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2))
+ x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+ x = self.softmax.forward(x)
+ x = self.log.forward(x)
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+
+ ####################
+ # code 7 #
+ ####################
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y)
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+ self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+
+ def optimizeM(self, learning_rate, beta_1=0.9):
+ self.W1_m = beta_1 * self.W1_m + (1-beta_1)*self.W1_grad
+ self.W2_m = beta_1 * self.W2_m + (1-beta_1)*self.W2_grad
+ self.W3_m = beta_1 * self.W3_m + (1-beta_1)*self.W3_grad
+
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_m
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_m
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_m
+
+ def optimizeAM(self, learning_rate=0.001, beta_1=0.9, beta_2=0.999, epsilon=1e-8):
+ self.W1_m = beta_1 * self.W1_m + (1-beta_1) * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2_m = beta_1 * self.W2_m + (1-beta_1) * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3_m = beta_1 * self.W3_m + (1-beta_1) * self.W3_grad
+
+ self.W1_v = beta_2 * self.W1_v + (1-beta_2) * self.W1_grad * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2_v = beta_2 * self.W2_v + (1-beta_2) * self.W2_grad * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3_v = beta_2 * self.W3_v + (1-beta_2) * self.W3_grad * self.W3_grad
+
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_m / (self.W1_v**0.5 + epsilon)
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_m / (self.W2_v**0.5 + epsilon)
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_m / (self.W3_v**0.5 + epsilon)
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..5c231927da7f8c235a73f77285a6404cf7473a3c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307130133/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, shuffle=True, batch_size=128):
+ data = np.array([each[0].numpy() for each in dataset])
+ label = np.array([each[1] for each in dataset])
+ data_size = data.shape[0]
+
+ index = np.arange(data_size)
+ if shuffle:
+ np.random.shuffle(index)
+
+ mini_batches = []
+
+ for i in range(0, data_size, batch_size):
+ mini_batches.append([data[index[i:i+batch_size]], label[index[i:i+batch_size]]])
+ return mini_batches
+
+
+def numpy_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 15
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ # model.optimize(learning_rate)
+ model.optimizeAM()
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..abd8de5834bacc838e1b813905da469a8d9168c3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,343 @@
+# 实验报告
+
+陈疏桐 17307130331
+
+本次实验,我用numpy实现了Matmul、log、softmax和relu四个算子的前向计算与后向计算,用四个算子构建分类模型,通过了自动测试,并实现了mini_batch函数,在mnist数据集上用不同的学习率与Batch大小进行训练和测试,讨论学习率与Batch大小对模型训练效果的影响。最后,我还实现Momentum、RMSProp与Adam三种优化方法,与传统梯度下降进行比较。
+
+## 算子的反向传播与实现
+### Matmul
+
+Matmul是矩阵的乘法,在模型中的作用相当于pytorch的一个线性层,前向传播的公式是:
+
+$$ \mathrm{Y} = \mathrm{X}\mathrm{W} $$
+
+其中,$\mathrm{X}$是形状为 $N \times d$的输入矩阵,$\mathrm{W}$是形状为$d \times d'$的矩阵, $\mathrm{Y}$是形状为$N\times d'$的输出矩阵。Matmul算子相当于输入维度为$d$、输出$d'$维的线性全连接层。
+
+Matmul分别对输入求偏导,有
+
+$$ \frac{\partial \mathrm{Y}}{\partial \mathrm{X}} = \frac{\partial \mathrm{X}\mathrm{W}}{\partial \mathrm{X}} = \mathrm{W}^T$$
+
+$$ \frac{\partial \mathrm{Y}}{\partial \mathrm{W}} = \frac{\partial \mathrm{X}\mathrm{W}}{\partial \mathrm{W}} = \mathrm{X}^T $$
+
+则根据链式法则,反向传播的计算公式为:
+
+$$ \triangledown{\mathrm{X}} = \triangledown{\mathrm{Y}} \times \mathrm{W}^T $$
+$$ \triangledown{\mathrm{W}} = \mathrm{X}^T \times \triangledown{\mathrm{Y}} $$
+
+### Relu
+
+Relu函数对输入每一个元素的公式是:
+
+$$ \mathrm{Y}_{ij}=
+\begin{cases}
+\mathrm{X}_{ij} & \mathrm{X}_{ij} \ge 0 \\\\
+0 & \text{otherwise}
+\end{cases}
+$$
+
+
+每一个输出 $\mathrm{Y}_{ij}$都只与输入$\mathrm{X}_{ij}$有关。则$\mathrm{X}$每一个元素的导数也只和对应的输出有关,为:
+
+$$ \frac{\partial \mathrm{Y}_{ij}}{\partial \mathrm{X}_{ij}} =
+\begin{cases}
+1 & \mathrm{X}_{ij} \ge 0 \\\\
+0 & \text{otherwise}
+\end{cases}$$
+
+因此,根据链式法则,输入的梯度为:
+
+$$ \triangledown{\mathrm{X}_{ij}} = \triangledown{\mathrm{Y}_{ij}} \times \frac{\partial \mathrm{Y}_{ij}}{\partial \mathrm{X}_{ij}}$$
+
+### Log
+
+Log 函数公式:
+
+$$ \mathrm{Y}_{ij} = \log(\mathrm{X}_{ij} + \epsilon)$$
+
+$$ \frac{\partial \mathrm{Y}_{ij}}{\partial \mathrm{X}_{ij}} = \frac{1}{(\mathrm{X}_{ij} + \epsilon)} $$
+
+类似地,反向传播的计算公式为:
+
+$$ \triangledown{\mathrm{X}_{ij}} = \triangledown{\mathrm{Y}_{ij}} \times \frac{\partial \mathrm{Y}_{ij}}{\partial \mathrm{X}_{ij}}$$
+
+### Softmax
+
+Softmax对输入$\mathrm{X}$的最后一个维度进行计算。前向传播的计算公式为:
+
+$$ \mathrm{Y}_{ij} = \frac{\exp^{\mathrm{X}_{ij}}}{\sum_{k} \exp ^ {\mathrm{X}_{ik}}}$$
+
+从公式可知,Softmax的每一行输出都是独立计算的,与其它行的输入无关。而对于同一行,每一个输出都与每一个输入元素有关。以行$k$为例,可推得输出元素对输入元素求导的计算公式是:
+
+$$\frac{\partial Y_{ki}}{\partial X_{kj}} = \begin{cases}
+\frac{\exp ^ {X_{kj}} \times (\sum_{t \ne j}{\exp ^ {X_{kt}}}) }{(\sum_{t}{\exp ^ {X_{kt}}})^2} = Y_{kj}(1-Y_{kj}) & i = j \\\\
+-\frac{\exp^{X_{ki} }\exp^{X_{kj} }}{(\sum_t\exp^{X_{kt}})^2}=-Y_{ki} \times Y_{kj} & i\ne j
+\end{cases}$$
+
+可得每行输出$\mathrm{Y}_{k}$与每行输入$\mathrm{X}_{k}$的Jacob矩阵$\mathrm{J}_{k}$, $\mathrm{J_{k}}_{ij} = \frac{\partial \mathrm{Y}_{ki}}{\partial \mathrm{X}_{kj}}$.
+
+输出的一行对于输入$\mathrm{X}_{kj}$的导数,是输出每一行所有元素对其导数相加,即$\sum_{i} {\frac{\partial \mathrm{Y}_{ki}}{\partial \mathrm{X}_{kj}}}$ 的结果。
+
+因此,根据链式法则,可得到反向传播的计算公式为:
+$$ \triangledown \mathrm{X}_{kj} = \sum_{i} {\frac{\partial \mathrm{Y}_{ki} \times \triangledown \mathrm{Y}_{ki}}{\partial \mathrm{X}_{kj}}}$$
+
+相当于:
+
+$$ \triangledown \mathrm{X}_{k} = \mathrm{J}_{k} \times \triangledown \mathrm{Y}_{k} $$
+
+在实现时,可以用`numpy`的`matmul`操作实现对最后两个维度的矩阵相乘,得到的矩阵堆叠起来,得到最后的结果。
+
+
+## 模型构建与训练
+### 模型构建
+
+参照`torch_mnist.py`中的`torch_model`,`numpy`模型的构建只需要将其中的算子换成我们实现的算子:
+```
+def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ x = self.relu_1.forward(self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1))
+ x = self.relu_2.forward(self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2))
+
+ x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+
+ x = self.softmax.forward(x)
+ x = self.log.forward(x)
+
+ return x
+```
+
+模型的computation graph是:
+
+
+根据计算图,可以应用链式法则,推导出各个叶子变量($\mathrm{W}_{1}, \mathrm{W}_{2}, \mathrm{W}_{3}, \mathrm{X}$)以及中间变量的计算方法。
+
+反向传播的计算图为:
+
+
+可根据计算图完成梯度的计算:
+```
+def backward(self, y):
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y)
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+ self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+```
+
+### MiniBatch
+
+在`utils`中的`mini_batch`方法,直接调用了`pytorch`的`DataLoader`。 `DataLoader`是一个负责从数据集中读取样本、组合成批次输出的方法。简单地使用`DataLoader`, 可以方便地多线程并行化预取数据,加快训练速度,且节省代码。`DataLoader`还可以自定义`Sampler`,以不同的方式从数据集中进行采样,以及`BatchSampler`以自定的方式将采集的样本组合成批,这样就可以实现在同一Batch内将数据补0、自定义Batch正负样本混合比例等操作。
+
+在这里,我们模仿`DataLoader`的默认行为实现`mini_batch`方法。
+```
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128):
+ data = np.array([each[0].numpy() for each in dataset]) # 需要先处理数据
+ label = np.array([each[1] for each in dataset])
+
+ data_size = data.shape[0]
+ idx = np.array([i for i in range(data_size)])
+ np.random.shuffle(idx) # 打乱顺序
+
+ return [(data[idx[i: i+batch_size]], label[idx[i:i+batch_size]]) for i in range(0, data_size, batch_size)] # 这里相当于DataLoader 的BatchSampler,但一次性调用
+```
+
+### 模型训练
+
+构建模型,设置`epoch=10`, `learning_rate=0.1`, `batch_size=128`后,开始训练。训练时每次fit一个batch的数据,前向传播计算输出,然后根据输出计算loss,再调用`loss.backward`计算loss对输出的求导,即模型输出的梯度,之后就可以调用模型的`backward`进行后向计算。 最后调用模型的`optimize`更新参数。
+
+训练过程:
+
+
+各个epoch的测试准确率为:
+```
+[0] Test Accuracy: 0.9437
+[1] Test Accuracy: 0.9651
+[2] Test Accuracy: 0.9684
+[3] Test Accuracy: 0.9730
+[4] Test Accuracy: 0.9755
+[5] Test Accuracy: 0.9775
+[6] Test Accuracy: 0.9778
+[7] Test Accuracy: 0.9766
+[8] Test Accuracy: 0.9768
+[9] Test Accuracy: 0.9781
+```
+
+将`learning_rate` 调整到0.2,重新训练:
+
+
+各个epoch的测试准确率为:
+```
+[0] Test Accuracy: 0.9621
+[1] Test Accuracy: 0.9703
+[2] Test Accuracy: 0.9753
+[3] Test Accuracy: 0.9740
+[4] Test Accuracy: 0.9787
+[5] Test Accuracy: 0.9756
+[6] Test Accuracy: 0.9807
+[7] Test Accuracy: 0.9795
+[8] Test Accuracy: 0.9814
+[9] Test Accuracy: 0.9825
+```
+
+可见,稍微提高学习率之后,训练前期参数更新的幅度更大,损失下降得更快,能够更早收敛。训练相同迭代数,现在的模型测试准确率更高。
+
+将`learning_rate` 提高到0.3,重新训练:
+
+
+```
+[0] Test Accuracy: 0.9554
+[1] Test Accuracy: 0.9715
+[2] Test Accuracy: 0.9744
+[3] Test Accuracy: 0.9756
+[4] Test Accuracy: 0.9782
+[5] Test Accuracy: 0.9795
+[6] Test Accuracy: 0.9801
+[7] Test Accuracy: 0.9816
+[8] Test Accuracy: 0.9828
+[9] Test Accuracy: 0.9778
+```
+
+增大学习率到0.3之后,训练前期损失下降速度与上一次训练差不多,但是到了训练后期,过大的学习率导致权重在局部最小值的附近以过大的幅度移动,难以进入最低点,模型loss表现为振荡,难以收敛。本次训练的测试准确率先提高到0.9828,后反而下降。
+
+因此,可认为对于大小为128的batch,0.2是较为合适的学习率。
+
+之后,维持学习率为0.2, 修改batch_size 为256, 重新训练:
+
+```
+[0] Test Accuracy: 0.9453
+[1] Test Accuracy: 0.9621
+[2] Test Accuracy: 0.9657
+[3] Test Accuracy: 0.9629
+[4] Test Accuracy: 0.9733
+[5] Test Accuracy: 0.9766
+[6] Test Accuracy: 0.9721
+[7] Test Accuracy: 0.9768
+[8] Test Accuracy: 0.9724
+[9] Test Accuracy: 0.9775
+```
+
+batch_size增大后,每个batch更新一次参数,参数更新的频率更低,从而收敛速度有所降低;但是对比本次实验与前几次实验loss的曲线图,可发现振荡幅度更小。
+
+将batch_size减小到64, 重新实验:
+
+```
+[0] Test Accuracy: 0.9526
+[1] Test Accuracy: 0.9674
+[2] Test Accuracy: 0.9719
+[3] Test Accuracy: 0.9759
+[4] Test Accuracy: 0.9750
+[5] Test Accuracy: 0.9748
+[6] Test Accuracy: 0.9772
+[7] Test Accuracy: 0.9791
+[8] Test Accuracy: 0.9820
+[9] Test Accuracy: 0.9823
+```
+
+loss的下降速度增加,但是振荡幅度变大了。
+
+总结:在一定范围之内,随着学习率的增大,模型收敛速度增加;随着batch_size的减小,模型收敛速度也会有一定增加,但是振荡幅度增大。 学习率过大会导致后期loss振荡、难以收敛;学习率过小则会导致loss下降速度过慢,甚至可能陷入局部最小值而错过更好的最低点。
+
+## 其他优化方式实现
+
+### momentum
+
+普通梯度下降每次更新参数仅仅取决于当前batch的梯度,这可能会让梯度方向受到某些特殊的输入影响。Momentum引入了动量,让当前更新不仅取决于当前的梯度,还考虑到先前的梯度,能够在一定程度上保持一段时间的趋势。momentum的计算方式为:
+
+$$
+\begin{align}
+& v = \alpha v - \gamma \frac{\partial L}{\partial W} \\\\
+& W = W + v
+\end{align}
+$$
+
+我们在`numpy_fnn.py`的模型中实现了Momentum的优化方法。 设置学习率为0.02,batch_size为128, 继续实验:
+
+```
+[0] Test Accuracy: 0.9586
+[1] Test Accuracy: 0.9717
+[2] Test Accuracy: 0.9743
+[3] Test Accuracy: 0.9769
+[4] Test Accuracy: 0.9778
+[5] Test Accuracy: 0.9786
+[6] Test Accuracy: 0.9782
+[7] Test Accuracy: 0.9809
+[8] Test Accuracy: 0.9790
+[9] Test Accuracy: 0.9818
+```
+
+momentum 相比传统梯度下降,不一定最后会得到更好的效果。当加入动量,当前梯度方向与动量方向相同时,参数就会得到更大幅度的调整,因此loss下降速度更快,并且前期动量基本上会积累起来,如果使用过大的学习率,很容易会溢出。所以momentum适合的学习率比普通梯度下降要小一个数量级。 而当梯度方向错误的时候,加入动量会使得参数来不及更新,从而错过最小值。
+
+### RMSProp
+
+
+RMSProp引入了自适应的学习率调节。 在训练前期,学习率应该较高,使得loss能快速下降;但随着训练迭代增加,学习率应该不断减小,使得模型能够更好地收敛。 自适应调整学习率的基本思路是根据梯度来调节,梯度越大,学习率就衰减得越快;后期梯度减小,学习率衰减就更加缓慢。
+
+而为了避免前期学习率衰减得过快,RMSProp还用了指数平均的方法,来缓慢丢弃原来的梯度历史。计算方法为:
+
+$$
+\begin{align}
+& h = \rho h + (1-\rho) \frac{\partial L}{\partial W} \odot \frac{\partial L}{\partial W} \\\\
+& W = W - \gamma \frac{1}{\sqrt{\delta + h}} \frac{\partial L}{\partial W}
+\end{align}$$
+
+设置梯度为0.001, weight_decay 为0.01, 进行训练和测试:
+
+
+```
+[0] Test Accuracy: 0.9663
+[1] Test Accuracy: 0.9701
+[2] Test Accuracy: 0.9758
+[3] Test Accuracy: 0.9701
+[4] Test Accuracy: 0.9748
+[5] Test Accuracy: 0.9813
+[6] Test Accuracy: 0.9813
+[7] Test Accuracy: 0.9819
+[8] Test Accuracy: 0.9822
+[9] Test Accuracy: 0.9808
+```
+
+可见,在训练的中间部分,loss振荡幅度比普通梯度下降更小。训练前期,模型的收敛速度更快,但到后期比起普通梯度下降并无明显优势。
+
+### Adam
+
+Adam 同时结合了动量与自适应的学习率调节。Adam首先要计算梯度的一阶和二阶矩估计,分别代表了动量与自适应的部分:
+
+$$
+\begin{align}
+& \mathrm{m} = \beta_1 \mathrm{m} + (1-\beta_1) \frac{\partial L}{\partial W} \\\\
+& \mathrm{v} = \beta_2 \mathrm{v} + (1-\beta_2) \frac{\partial L}{\partial W} \odot \frac{\partial L}{\partial W}
+\end{align}
+$$
+
+然后进行修正:
+
+$$
+\begin{align}
+& \mathrm{\hat{m}} = \frac{\mathrm{m}}{1-\beta_1 ^ t }\\\\
+& \mathrm{\hat{v}} = \frac{\mathrm{v}}{1-\beta_2 ^ t}
+\end{align}
+$$
+
+最后,参数的更新为:
+$$ W = W - \gamma \frac{\mathrm{\hat m}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{\hat v}+ \delta}}$$
+
+
+设置学习率为0.001, batch_size为128, 开始训练:
+
+```
+[0] Test Accuracy: 0.9611
+[1] Test Accuracy: 0.9701
+[2] Test Accuracy: 0.9735
+[3] Test Accuracy: 0.9752
+[4] Test Accuracy: 0.9787
+[5] Test Accuracy: 0.9788
+[6] Test Accuracy: 0.9763
+[7] Test Accuracy: 0.9790
+[8] Test Accuracy: 0.9752
+[9] Test Accuracy: 0.9806
+
+```
+
+相比传统梯度下降,loss振荡略微有所减小,前期loss下降速度略微更快,但是最后收敛的速度相当。
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/backgraph.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/backgraph.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c4a70b28e869708641bd01dba83730ed62ab9c4d
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/backgraph.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/compu_graph.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/compu_graph.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..74f02ff1b4c4795c99600fb2e358d23a170f11c1
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/compu_graph.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/momentum.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/momentum.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..152bfe4eda8bf98cb271e9e3af3801f223273ec2
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/momentum.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/rmsprop.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/rmsprop.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d4c9f6d651ea0dcac312c3a7dcb38266a477679c
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/rmsprop.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..618816332b78c4f0498444a42dd2a5028df91ef1
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train02.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train02.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a2cbc7b9ccbf2f28955902b86881d7a640f50fa7
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train02.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train03.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train03.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..41dd8fd9060e6774b983375f3b025ee6335b9f66
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train03.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train10.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train10.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a2056ba0d21f8f40fc0279e532fd6b9f1ff79cef
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train10.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train256.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train256.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..81aa1b2bcc7f708607f8c402f9f41d579793f9e1
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train256.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train64.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train64.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..8f34749c6fda428437ff3fe11292b0213eca0d7a
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train64.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train_adam.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train_adam.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..eefa8b27deb6485f895033add750f018fd14e293
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/train_adam.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/trainloss.png b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/trainloss.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b845297f03d5d6e6ae2b026b25554519a77f471b
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/img/trainloss.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7b32d95b7825b4787f5d226ac058c0039aee4bba
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,208 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 1 #
+ grad_W = np.matmul(self.memory['x'].T, grad_y)
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, self.memory['W'].T)
+ ####################
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 2 #
+ ####################
+ grad_x = np.where(self.memory['x'] > 0, np.ones_like(self.memory['x']), np.zeros_like(self.memory['x'])) * grad_y # 元素乘积
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 3 #
+ ####################
+ grad_x = (1/(self.memory['x'] + self.epsilon)) * grad_y
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 4 #
+ ####################
+ exp_x = np.exp(x)
+ out = exp_x/np.sum(exp_x, axis=1, keepdims=True)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['out'] = out
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ o = self.memory['out']
+ Jacob = np.array([np.diag(r) - np.outer(r, r) for r in o])
+ # i!=j - oi* oj
+ # i==j oi*(1-oi)
+ grad_y = grad_y[:, np.newaxis, :]
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, Jacob).squeeze(1)
+ #print(grad_x.shape)
+ #print(grad_x)
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新。 softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ # 以下变量是在 momentum\rmsprop中使用的
+ self.v1 = np.zeros_like(self.W1)
+ self.v2 = np.zeros_like(self.W2)
+ self.v3 = np.zeros_like(self.W3)
+
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ x = self.relu_1.forward(self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1))
+ x = self.relu_2.forward(self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2))
+
+ x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+
+ x = self.softmax.forward(x)
+ x = self.log.forward(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y)
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+ self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+
+ def momentum(self, learning_rate, alpha=0.9):
+ self.v1 = self.v1 * alpha - learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.v2 = self.v2 * alpha - learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.v3 = self.v3 * alpha - learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+
+ self.W1 += self.v1
+ self.W2 += self.v2
+ self.W3 += self.v3
+
+ def RMSProp(self, learning_rate, weight_decay = 0.99):
+ self.v1 = self.v1 * weight_decay + (1-weight_decay) * self.W1_grad * self.W1_grad
+ self.v2 = self.v2 * weight_decay + (1-weight_decay) * self.W2_grad * self.W2_grad
+ self.v3 = self.v3 * weight_decay + (1-weight_decay) * self.W3_grad * self.W3_grad
+
+ self.W1 = self.W1 - learning_rate * self.W1_grad / np.sqrt( self.v1 + 1e-7)
+ self.W2 = self.W2 - learning_rate * self.W2_grad / np.sqrt( self.v2 + 1e-7)
+ self.W3 = self.W3 - learning_rate * self.W3_grad / np.sqrt( self.v3 + 1e-7)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..4187f01eeebbbcd6ab48bfacf8dedc37085e46e2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128):
+ data = np.array([each[0].numpy() for each in dataset])
+ label = np.array([each[1] for each in dataset])
+
+ data_size = data.shape[0]
+ idx = np.array([i for i in range(data_size)])
+ np.random.shuffle(idx)
+
+ return [(data[idx[i: i+batch_size]], label[idx[i:i+batch_size]]) for i in range(0, data_size, batch_size)]
+
+class Adam():
+ def __init__(self, param, learning_rate=0.001, beta_1=0.9, beta_2=0.999):
+ self.param = param
+ self.iter = 0
+ self.m = 0
+ self.v = 0
+ self.beta1 = beta_1
+ self.beta2 = beta_2
+ self.lr = learning_rate
+ def optimize(self, grad):
+ self.iter+=1
+ self.m = self.beta1 * self.m + (1 - self.beta1) * grad
+ self.v = self.beta2 * self.v + (1 - self.beta2) * grad * grad
+ m_hat = self.m / (1 - self.beta1 ** self.iter)
+ v_hat = self.v / (1 - self.beta2 ** self.iter)
+ self.param -= self.lr * m_hat / (v_hat ** 0.5 + 1e-8)
+ return self.param
+
+def numpy_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ W1_opt, W2_opt, W3_opt = Adam(model.W1), Adam(model.W2), Adam(model.W3)
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 10
+ learning_rate = 0.0015
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset, batch_size=128):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ #model.Adam(learning_rate)
+ W1_opt.optimize(model.W1_grad)
+ W2_opt.optimize(model.W2_grad)
+ W3_opt.optimize(model.W3_grad)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Test Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/tester_demo.py b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/tester_demo.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..515b86c1240eebad83287461548530c944f23bc8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/tester_demo.py
@@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
+import numpy as np
+import torch
+from torch import matmul as torch_matmul, relu as torch_relu, softmax as torch_softmax, log as torch_log
+
+from numpy_fnn import Matmul, Relu, Softmax, Log, NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from torch_mnist import TorchModel
+from utils import get_torch_initialization, one_hot
+
+err_epsilon = 1e-6
+err_p = 0.4
+
+
+def check_result(numpy_result, torch_result=None):
+ if isinstance(numpy_result, list) and torch_result is None:
+ flag = True
+ for (n, t) in numpy_result:
+ flag = flag and check_result(n, t)
+ return flag
+ # print((torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) - torch_result).abs().mean().item())
+ T = (torch_result * torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) < 0).sum().item()
+ direction = T / torch_result.numel() < err_p
+ return direction and ((torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) - torch_result).abs().mean() < err_epsilon).item()
+
+
+def case_1():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[5, 6])
+ W = np.random.normal(size=[6, 4])
+
+ numpy_matmul = Matmul()
+ numpy_out = numpy_matmul.forward(x, W)
+ numpy_x_grad, numpy_W_grad = numpy_matmul.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+ torch_W = torch.from_numpy(W).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_matmul(torch_x, torch_W)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ (numpy_W_grad, torch_W.grad)
+ ])
+
+
+def case_2():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[5, 6])
+
+ numpy_relu = Relu()
+ numpy_out = numpy_relu.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_relu.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_relu(torch_x)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def case_3():
+ x = np.random.uniform(low=0.0, high=1.0, size=[3, 4])
+
+ numpy_log = Log()
+ numpy_out = numpy_log.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_log.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_log(torch_x)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def case_4():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[4, 5])
+
+ numpy_softmax = Softmax()
+ numpy_out = numpy_softmax.forward(x)
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_softmax(torch_x, 1)
+
+ return check_result(numpy_out, torch_out)
+
+
+def case_5():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[20, 25])
+
+ numpy_softmax = Softmax()
+ numpy_out = numpy_softmax.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_softmax.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_softmax(torch_x, 1)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def test_model():
+ try:
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ numpy_model = NumpyModel()
+ torch_model = TorchModel()
+ torch_model.W1.data, torch_model.W2.data, torch_model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+ numpy_model.W1 = torch_model.W1.detach().clone().numpy()
+ numpy_model.W2 = torch_model.W2.detach().clone().numpy()
+ numpy_model.W3 = torch_model.W3.detach().clone().numpy()
+
+ x = torch.randn((10000, 28, 28))
+ y = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0] * 1000)
+
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+ x2 = x.numpy()
+ y_pred = torch_model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+
+ y_pred_numpy = numpy_model.forward(x2)
+ numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred_numpy, y.numpy())
+
+ check_flag_1 = check_result(y_pred_numpy, y_pred)
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("forward", 10 * check_flag_1, 10))
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in forward]")
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("forward", 0, 10))
+ return 0
+
+ try:
+
+ numpy_model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+
+ check_flag_2 = [
+ check_result(numpy_model.log_grad, torch_model.log_input.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.softmax_grad, torch_model.softmax_input.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W3_grad, torch_model.W3.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W2_grad, torch_model.W2.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W1_grad, torch_model.W1.grad)
+ ]
+ check_flag_2 = sum(check_flag_2) >= 4
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("backward", 20 * check_flag_2, 20))
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in backward]")
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("backward", 0, 20))
+ check_flag_2 = False
+
+ return 10 * check_flag_1 + 20 * check_flag_2
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ testcases = [
+ ["matmul", case_1, 5],
+ ["relu", case_2, 5],
+ ["log", case_3, 5],
+ ["softmax_1", case_4, 5],
+ ["softmax_2", case_5, 10],
+ ]
+ score = 0
+ for case in testcases:
+ try:
+ res = case[2] if case[1]() else 0
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in {}]".format(case[0]))
+ res = 0
+ score += res
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format(case[0], res, case[2]))
+ score += test_model()
+ print("{:14} {}/60".format("FINAL SCORE", score))
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/torch_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/torch_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6d3e214c7606e3d43dac4b94554f942508afffb3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/torch_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+import torch
+from utils import mini_batch, batch, download_mnist, get_torch_initialization, one_hot, plot_curve
+
+
+class TorchModel:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = torch.randn((28 * 28, 256), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W2 = torch.randn((256, 64), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W3 = torch.randn((64, 10), requires_grad=True)
+ self.softmax_input = None
+ self.log_input = None
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W1))
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W2))
+ x = torch.matmul(x, self.W3)
+
+ self.softmax_input = x
+ self.softmax_input.retain_grad()
+
+ x = torch.softmax(x, 1)
+
+ self.log_input = x
+ self.log_input.retain_grad()
+
+ x = torch.log(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ with torch.no_grad():
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1.grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2.grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3.grad
+
+ self.W1.grad = None
+ self.W2.grad = None
+ self.W3.grad = None
+
+
+def torch_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = TorchModel()
+ model.W1.data, model.W2.data, model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset, numpy=False):
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset, numpy=False)[0]
+ accuracy = model.forward(x).argmax(dim=1).eq(y).float().mean().item()
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ torch_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/utils.py b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/utils.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..709220cfa7a924d914ec1c098c505f864bcd4cfc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/17307130331/utils.py
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+import torch
+import numpy as np
+from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
+
+
+def plot_curve(data):
+ plt.plot(range(len(data)), data, color='blue')
+ plt.legend(['loss_value'], loc='upper right')
+ plt.xlabel('step')
+ plt.ylabel('value')
+ plt.show()
+
+
+def download_mnist():
+ from torchvision import datasets, transforms
+
+ transform = transforms.Compose([
+ transforms.ToTensor(),
+ transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.1307,), std=(0.3081,))
+ ])
+
+ train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=True, download=True)
+ test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=False, download=True)
+
+ return train_dataset, test_dataset
+
+
+def one_hot(y, numpy=True):
+ if numpy:
+ y_ = np.zeros((y.shape[0], 10))
+ y_[np.arange(y.shape[0], dtype=np.int32), y] = 1
+ return y_
+ else:
+ y_ = torch.zeros((y.shape[0], 10))
+ y_[torch.arange(y.shape[0], dtype=torch.long), y] = 1
+ return y_
+
+
+def batch(dataset, numpy=True):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+ for each in dataset:
+ data.append(each[0])
+ label.append(each[1])
+ data = torch.stack(data)
+ label = torch.LongTensor(label)
+ if numpy:
+ return [(data.numpy(), label.numpy())]
+ else:
+ return [(data, label)]
+
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128, numpy=False):
+ return torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
+
+
+def get_torch_initialization(numpy=True):
+ fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(28 * 28, 256)
+ fc2 = torch.nn.Linear(256, 64)
+ fc3 = torch.nn.Linear(64, 10)
+
+ if numpy:
+ W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ W2 = fc2.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ W3 = fc3.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ else:
+ W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+ W2 = fc2.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+ W3 = fc3.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..647eb99d08956f5fea84c6aa563ab3e1576cfcc6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,276 @@
+# PRML-2021 Assignment2
+
+姓名:夏海淞
+
+学号:18307130090
+
+## 简述
+
+在本次实验中,我通过`NumPy`实现了一个简单的前馈神经网络,其中包括`numpy_fnn.py`中算子的反向传播以及前馈神经网络模型的构建。为了验证模型效果,我在MNIST数据集上进行了训练和测试。此外,我还实现了`Momentum`和`Adam`优化算法,并比较了它们的性能。
+
+## 算子的反向传播
+
+### `Matmul`
+
+`Matmul`的计算公式为:
+$$
+Y=X\times W
+$$
+其中$Y,X,W$分别为$n\times d',n\times d,d\times d'$的矩阵。
+
+由[神经网络与深度学习-邱锡鹏](https://nndl.github.io/nndl-book.pdf)中公式(B.20)和(B.21),有
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial W}=\frac{\partial(X\times W)}{\partial W}=X^T\\\\
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial X}=\frac{\partial(X\times W)}{\partial X}=W^T
+$$
+结合链式法则和矩阵运算法则,可得
+$$
+\nabla_X=\nabla_Y\times W^T\\\\
+\nabla_W=X^T\times \nabla_Y
+$$
+
+### `Relu`
+
+`Relu`的计算公式为:
+$$
+Y_{ij}=\begin{cases}
+X_{ij}&X_{ij}\ge0\\\\
+0&\text{otherwise}
+\end{cases}
+$$
+因此有
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{ij}}=\begin{cases}
+1&X_{ij}>0\\\\
+0&\text{otherwise}
+\end{cases}
+$$
+结合链式法则,得到反向传播的计算公式:$\nabla_{Xij}=\nabla_{Yij}\cdot\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{ij}}$
+
+### `Log`
+
+`Log`的计算公式为
+$$
+Y_{ij}=\ln(X_{ij}+\epsilon),\epsilon=10^{-12}
+$$
+因此有
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{ij}}=\frac1{X_{ij}+\epsilon}
+$$
+结合链式法则,得到反向传播的计算公式:$\nabla_{Xij}=\nabla_{Yij}\cdot\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial {X_{ij}}}$
+
+### `Softmax`
+
+`Softmax`的计算公式为
+$$
+Y_{ij}=\frac{\exp\{X_{ij} \}}{\sum_{k=1}^c\exp\{X_{ik} \}}
+$$
+其中$Y,X$均为$N\times c$的矩阵。容易发现`Softmax`以$X$的每行作为单位进行运算。因此对于$X,Y$的行分量$X_k,Y_k$,有
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y_{ki}}{\partial X_{kj}}=\begin{cases}
+\frac{\exp\{X_{kj} \}(\sum_t\exp\{X_{kt}\})-\exp\{2X_{ki}\}}{(\sum_t\exp\{X_{kt}\})^2}=Y_{ki}(1-Y_{ki})&i=j\\\\
+-\frac{\exp\{X_{ki} \}\exp\{X_{kj} \}}{(\sum_t\exp\{X_{kt}\})^2}=-Y_{ki}Y_{kj}&i\not=j
+\end{cases}
+$$
+因此可计算得到$X_k,Y_k$的Jacob矩阵,满足$J_{ij}=\frac{\partial Y_{ki}}{\partial X_{kj}}$。结合链式法则,可得
+$$
+\nabla_X=\nabla_Y\times J
+$$
+将行分量组合起来,就得到了反向传播的最终结果。
+
+## 模型构建与训练
+
+### 模型构建
+
+#### `forward`
+
+参考`torch_mnist.py`中`TorchModel`方法的模型,使用如下代码构建:
+
+```python
+def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ x = self.relu_1.forward(self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1))
+ x = self.relu_2.forward(self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2))
+ x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+
+ x = self.log.forward(self.softmax.forward(x))
+
+ return x
+```
+
+模型的计算图如下:
+
+
+
+#### `backward`
+
+根据模型的计算图,按照反向的计算顺序依次调用对应算子的反向传播算法即可。
+
+```python
+def backward(self, y):
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y)
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+ self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+
+ return self.x1_grad
+```
+
+#### `mini_batch`
+
+`mini_batch`的作用是提高模型的训练速度,同时得到较好的优化效果。传统的批处理方法对整个数据集计算平均的损失函数值,随后计算相应梯度进行反向传播。当训练数据集容量较大时,对训练速度造成严重影响;而随机方法则对数据集的每个样本计算损失函数值,随后计算相应梯度进行反向传播。此时数据集容量不对训练速度产生影响,然而由于样本的随机性,可能导致参数无法收敛到最优值,在最优值附近震荡。因此一个折中的方法是将数据集划分为若干批次,在提高训练速度的同时保证了较好的收敛效果。
+
+在本次实验中,我参照`utils.py`中的`mini_batch`,在`numpy_mnist.py`中重新实现了`mini_batch`方法:
+
+```python
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128):
+ data = np.array([np.array(each[0]) for each in dataset])
+ label = np.array([each[1] for each in dataset])
+
+ size = data.shape[0]
+ index = np.arange(size)
+ np.random.shuffle(index)
+
+ return [(data[index[i:i + batch_size]], label[index[i:i + batch_size]]) for i in range(0, size, batch_size)]
+```
+
+### 模型训练
+
+设定`learning_rate=0.1`,`batch_size=128`,`epoch_number=10`。训练结果如下:
+
+```
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9486
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9643
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9724
+[3] Accuracy: 0.9738
+[4] Accuracy: 0.9781
+[5] Accuracy: 0.9768
+[6] Accuracy: 0.9796
+[7] Accuracy: 0.9802
+[8] Accuracy: 0.9800
+[9] Accuracy: 0.9796
+```
+
+ +
+尝试缩减`batch_size`的大小,设定`batch_size=64`。训练结果如下:
+
+```
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9597
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9715
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9739
+[3] Accuracy: 0.9771
+[4] Accuracy: 0.9775
+[5] Accuracy: 0.9803
+[6] Accuracy: 0.9808
+[7] Accuracy: 0.9805
+[8] Accuracy: 0.9805
+[9] Accuracy: 0.9716
+```
+
+
+
+尝试缩减`batch_size`的大小,设定`batch_size=64`。训练结果如下:
+
+```
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9597
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9715
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9739
+[3] Accuracy: 0.9771
+[4] Accuracy: 0.9775
+[5] Accuracy: 0.9803
+[6] Accuracy: 0.9808
+[7] Accuracy: 0.9805
+[8] Accuracy: 0.9805
+[9] Accuracy: 0.9716
+```
+
+ +
+尝试降低`learning_rate`,设定`learning_rate=0.01`。训练结果如下:
+
+```
+[0] Accuracy: 0.8758
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9028
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9143
+[3] Accuracy: 0.9234
+[4] Accuracy: 0.9298
+[5] Accuracy: 0.9350
+[6] Accuracy: 0.9397
+[7] Accuracy: 0.9434
+[8] Accuracy: 0.9459
+[9] Accuracy: 0.9501
+```
+
+
+
+尝试降低`learning_rate`,设定`learning_rate=0.01`。训练结果如下:
+
+```
+[0] Accuracy: 0.8758
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9028
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9143
+[3] Accuracy: 0.9234
+[4] Accuracy: 0.9298
+[5] Accuracy: 0.9350
+[6] Accuracy: 0.9397
+[7] Accuracy: 0.9434
+[8] Accuracy: 0.9459
+[9] Accuracy: 0.9501
+```
+
+ +
+根据实验结果,可以得出以下结论:
+
+当学习率和批处理容量合适时,参数的收敛速度随着学习率的减小而减小,而参数的震荡幅度随着批处理容量的减小而增大。
+
+## 梯度下降算法的改进
+
+传统的梯度下降算法可以表述为:
+$$
+w_{t+1}=w_t-\eta\cdot\nabla f(w_t)
+$$
+尽管梯度下降作为优化算法被广泛使用,它依然存在一些缺点,主要表现为:
+
+- 参数修正方向完全由当前梯度决定,导致当学习率过高时参数可能在最优点附近震荡;
+- 学习率无法随着训练进度改变,导致训练前期收敛速度较慢,后期可能无法收敛。
+
+针对上述缺陷,产生了许多梯度下降算法的改进算法。其中较为典型的是`Momentum`算法和`Adam`算法。
+
+### `Momentum`
+
+针对“参数修正方向完全由当前梯度决定”的问题,`Momentum`引入了“动量”的概念。
+
+类比现实世界,当小球从高处向低处滚动时,其运动方向不仅与当前位置的“陡峭程度”相关,也和当前的速度,即先前位置的“陡峭程度”相关。因此在`Momentum`算法中,参数的修正值不是取决于当前梯度,而是取决于梯度的各时刻的指数移动平均值:
+$$
+m_t=\beta\cdot m_{t-1}+(1-\beta)\cdot\nabla f(w_t)\\\\
+w_{t+1}=w_t-\eta\cdot m_t
+$$
+指数移动平均值反映了参数调整时的“惯性”。当参数调整方向正确时,`Momentum`有助于加快训练速度,减少震荡的幅度;然而当参数调整方向错误时,`Momentum`会因为无法及时调整方向造成性能上的部分损失。
+
+使用`Momentum`算法的训练结果如下:
+
+```
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9444
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9627
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9681
+[3] Accuracy: 0.9731
+[4] Accuracy: 0.9765
+[5] Accuracy: 0.9755
+[6] Accuracy: 0.9768
+[7] Accuracy: 0.9790
+[8] Accuracy: 0.9794
+[9] Accuracy: 0.9819
+```
+
+
+
+根据实验结果,可以得出以下结论:
+
+当学习率和批处理容量合适时,参数的收敛速度随着学习率的减小而减小,而参数的震荡幅度随着批处理容量的减小而增大。
+
+## 梯度下降算法的改进
+
+传统的梯度下降算法可以表述为:
+$$
+w_{t+1}=w_t-\eta\cdot\nabla f(w_t)
+$$
+尽管梯度下降作为优化算法被广泛使用,它依然存在一些缺点,主要表现为:
+
+- 参数修正方向完全由当前梯度决定,导致当学习率过高时参数可能在最优点附近震荡;
+- 学习率无法随着训练进度改变,导致训练前期收敛速度较慢,后期可能无法收敛。
+
+针对上述缺陷,产生了许多梯度下降算法的改进算法。其中较为典型的是`Momentum`算法和`Adam`算法。
+
+### `Momentum`
+
+针对“参数修正方向完全由当前梯度决定”的问题,`Momentum`引入了“动量”的概念。
+
+类比现实世界,当小球从高处向低处滚动时,其运动方向不仅与当前位置的“陡峭程度”相关,也和当前的速度,即先前位置的“陡峭程度”相关。因此在`Momentum`算法中,参数的修正值不是取决于当前梯度,而是取决于梯度的各时刻的指数移动平均值:
+$$
+m_t=\beta\cdot m_{t-1}+(1-\beta)\cdot\nabla f(w_t)\\\\
+w_{t+1}=w_t-\eta\cdot m_t
+$$
+指数移动平均值反映了参数调整时的“惯性”。当参数调整方向正确时,`Momentum`有助于加快训练速度,减少震荡的幅度;然而当参数调整方向错误时,`Momentum`会因为无法及时调整方向造成性能上的部分损失。
+
+使用`Momentum`算法的训练结果如下:
+
+```
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9444
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9627
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9681
+[3] Accuracy: 0.9731
+[4] Accuracy: 0.9765
+[5] Accuracy: 0.9755
+[6] Accuracy: 0.9768
+[7] Accuracy: 0.9790
+[8] Accuracy: 0.9794
+[9] Accuracy: 0.9819
+```
+
+ +
+可以看出相较传统的梯度下降算法并无明显优势。
+
+### `Adam`
+
+针对“学习率无法随着训练进度改变”的问题,`Adam`在`Momentum`的基础上引入了“二阶动量”的概念。
+
+`Adam`的改进思路为:由于神经网络中存在大量参数,不同参数的调整频率存在差别。对于频繁更新的参数,我们希望适当降低其学习率,提高收敛概率;而对于其他参数,我们希望适当增大其学习率,加快收敛速度。同时,参数的调整频率可能发生动态改变,我们也希望学习率能够随之动态调整。
+
+因为参数的调整值与当前梯度直接相关,因此取历史梯度的平方和作为衡量参数调整频率的标准。如果历史梯度平方和较大,表明参数被频繁更新,需要降低其学习率。因此梯度下降算法改写为:
+$$
+m_t=\beta\cdot m_{t-1}+(1-\beta)\cdot\nabla f(w_t)\\\\
+V_t=V_{t-1}+\nabla^2f(w_t)\\\\
+w_{t+1}=w_t-\frac\eta{\sqrt{V_t}}\cdot m_t
+$$
+然而,由于$V_t$关于$t$单调递增,可能导致训练后期学习率过低,参数无法收敛至最优。因此将$V_t$也改为指数移动平均值,避免了上述缺陷:
+$$
+m_t=\beta_1\cdot m_{t-1}+(1-\beta_1)\cdot\nabla f(w_t)\\\\
+V_t=\beta_2\cdot V_{t-1}+(1-\beta_2)\cdot\nabla^2f(w_t)\\\\
+w_{t+1}=w_t-\frac\eta{\sqrt{V_t}}\cdot m_t
+$$
+使用`Adam`算法的训练结果如下:
+
+```
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9657
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9724
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9759
+[3] Accuracy: 0.9769
+[4] Accuracy: 0.9788
+[5] Accuracy: 0.9778
+[6] Accuracy: 0.9775
+[7] Accuracy: 0.9759
+[8] Accuracy: 0.9786
+[9] Accuracy: 0.9779
+```
+
+
+
+可以看出相较传统的梯度下降算法并无明显优势。
+
+### `Adam`
+
+针对“学习率无法随着训练进度改变”的问题,`Adam`在`Momentum`的基础上引入了“二阶动量”的概念。
+
+`Adam`的改进思路为:由于神经网络中存在大量参数,不同参数的调整频率存在差别。对于频繁更新的参数,我们希望适当降低其学习率,提高收敛概率;而对于其他参数,我们希望适当增大其学习率,加快收敛速度。同时,参数的调整频率可能发生动态改变,我们也希望学习率能够随之动态调整。
+
+因为参数的调整值与当前梯度直接相关,因此取历史梯度的平方和作为衡量参数调整频率的标准。如果历史梯度平方和较大,表明参数被频繁更新,需要降低其学习率。因此梯度下降算法改写为:
+$$
+m_t=\beta\cdot m_{t-1}+(1-\beta)\cdot\nabla f(w_t)\\\\
+V_t=V_{t-1}+\nabla^2f(w_t)\\\\
+w_{t+1}=w_t-\frac\eta{\sqrt{V_t}}\cdot m_t
+$$
+然而,由于$V_t$关于$t$单调递增,可能导致训练后期学习率过低,参数无法收敛至最优。因此将$V_t$也改为指数移动平均值,避免了上述缺陷:
+$$
+m_t=\beta_1\cdot m_{t-1}+(1-\beta_1)\cdot\nabla f(w_t)\\\\
+V_t=\beta_2\cdot V_{t-1}+(1-\beta_2)\cdot\nabla^2f(w_t)\\\\
+w_{t+1}=w_t-\frac\eta{\sqrt{V_t}}\cdot m_t
+$$
+使用`Adam`算法的训练结果如下:
+
+```
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9657
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9724
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9759
+[3] Accuracy: 0.9769
+[4] Accuracy: 0.9788
+[5] Accuracy: 0.9778
+[6] Accuracy: 0.9775
+[7] Accuracy: 0.9759
+[8] Accuracy: 0.9786
+[9] Accuracy: 0.9779
+```
+
+ +
+可以看出相较传统的梯度下降算法,损失函数值的震荡幅度有所减小,而收敛速度与传统方法相当。
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/Adam.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/Adam.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..fe0326ebad52ad9356bdd7410834d9d61e9e5152
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/Adam.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGDM.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGDM.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ba7ad91c5569f2605e7944afe3803863b8072b46
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGDM.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGD_batch_size.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGD_batch_size.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..328c4cc7bf90ef75a09f8c97ee8e9134d44a33dd
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGD_batch_size.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGD_learning_rate.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGD_learning_rate.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7bca928d1aa569b08dad43d761da1b6e27e02942
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGD_learning_rate.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGD_normal.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGD_normal.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e6f3933e1bf979fa7b3b643d8f7fe823610109e9
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGD_normal.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/fnn_model.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/fnn_model.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..29ed50732a88ed1ca38a1cb3c6e82099a3d3e087
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/fnn_model.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7010cad4609f7ae31b8bdc0b19cedc005c5b950c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,239 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+ x, W = self.memory['x'], self.memory['W']
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, W.T)
+ grad_W = np.matmul(x.T, grad_y)
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ grad_x = grad_y * np.where(x > 0, np.ones_like(x), np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ grad_x = grad_y * np.reciprocal(x + self.epsilon)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+ exp_x = np.exp(x - x.max())
+ exp_sum = np.sum(exp_x, axis=1, keepdims=True)
+ out = exp_x / exp_sum
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['out'] = out
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ sm = self.memory['out']
+ Jacobs = np.array([np.diag(r) - np.outer(r, r) for r in sm])
+
+ grad_y = grad_y[:, np.newaxis, :]
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, Jacobs).squeeze(axis=1)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新。 softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ self.beta_1 = 0.9
+ self.beta_2 = 0.999
+ self.epsilon = 1e-8
+ self.is_first = True
+
+ self.W1_grad_mean = None
+ self.W2_grad_mean = None
+ self.W3_grad_mean = None
+
+ self.W1_grad_square_mean = None
+ self.W2_grad_square_mean = None
+ self.W3_grad_square_mean = None
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ x = self.relu_1.forward(self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1))
+ x = self.relu_2.forward(self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2))
+ x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+
+ x = self.log.forward(self.softmax.forward(x))
+
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y)
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+ self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+
+ return self.x1_grad
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ def SGD():
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+
+ def SGDM():
+ if self.is_first:
+ self.is_first = False
+
+ self.W1_grad_mean = self.W1_grad
+ self.W2_grad_mean = self.W2_grad
+ self.W3_grad_mean = self.W3_grad
+ else:
+ self.W1_grad_mean = self.beta_1 * self.W1_grad_mean + (1 - self.beta_1) * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2_grad_mean = self.beta_1 * self.W2_grad_mean + (1 - self.beta_1) * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3_grad_mean = self.beta_1 * self.W3_grad_mean + (1 - self.beta_1) * self.W3_grad
+
+ delta_1 = learning_rate * self.W1_grad_mean
+ delta_2 = learning_rate * self.W2_grad_mean
+ delta_3 = learning_rate * self.W3_grad_mean
+
+ self.W1 -= delta_1
+ self.W2 -= delta_2
+ self.W3 -= delta_3
+
+ def Adam(learning_rate=0.001):
+ if self.is_first:
+ self.is_first = False
+ self.W1_grad_mean = self.W1_grad
+ self.W2_grad_mean = self.W2_grad
+ self.W3_grad_mean = self.W3_grad
+
+ self.W1_grad_square_mean = np.square(self.W1_grad)
+ self.W2_grad_square_mean = np.square(self.W2_grad)
+ self.W3_grad_square_mean = np.square(self.W3_grad)
+
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad_mean
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad_mean
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad_mean
+ else:
+ self.W1_grad_mean = self.beta_1 * self.W1_grad_mean + (1 - self.beta_1) * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2_grad_mean = self.beta_1 * self.W2_grad_mean + (1 - self.beta_1) * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3_grad_mean = self.beta_1 * self.W3_grad_mean + (1 - self.beta_1) * self.W3_grad
+
+ self.W1_grad_square_mean = self.beta_2 * self.W1_grad_square_mean + (1 - self.beta_2) * np.square(
+ self.W1_grad)
+ self.W2_grad_square_mean = self.beta_2 * self.W2_grad_square_mean + (1 - self.beta_2) * np.square(
+ self.W2_grad)
+ self.W3_grad_square_mean = self.beta_2 * self.W3_grad_square_mean + (1 - self.beta_2) * np.square(
+ self.W3_grad)
+
+ delta_1 = learning_rate * self.W1_grad_mean * np.reciprocal(
+ np.sqrt(self.W1_grad_square_mean) + np.full_like(self.W1_grad_square_mean, self.epsilon))
+ delta_2 = learning_rate * self.W2_grad_mean * np.reciprocal(
+ np.sqrt(self.W2_grad_square_mean) + np.full_like(self.W2_grad_square_mean, self.epsilon))
+ delta_3 = learning_rate * self.W3_grad_mean * np.reciprocal(
+ np.sqrt(self.W3_grad_square_mean) + np.full_like(self.W3_grad_square_mean, self.epsilon))
+
+ self.W1 -= delta_1
+ self.W2 -= delta_2
+ self.W3 -= delta_3
+
+ # SGD()
+ # SGDM()
+ Adam()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6d67f25824dabdc5791ae5cc96655affe8315e72
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128):
+ data = np.array([np.array(each[0]) for each in dataset])
+ label = np.array([each[1] for each in dataset])
+
+ size = data.shape[0]
+ index = np.arange(size)
+ np.random.shuffle(index)
+
+ return [(data[index[i:i + batch_size]], label[index[i:i + batch_size]]) for i in range(0, size, batch_size)]
+
+
+def numpy_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 10
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/tester_demo.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/tester_demo.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..504b3eef50a6df4d0aa433113136add50835e420
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/tester_demo.py
@@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
+import numpy as np
+import torch
+from torch import matmul as torch_matmul, relu as torch_relu, softmax as torch_softmax, log as torch_log
+
+from numpy_fnn import Matmul, Relu, Softmax, Log, NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from torch_mnist import TorchModel
+from utils import get_torch_initialization, one_hot
+
+err_epsilon = 1e-6
+err_p = 0.4
+
+
+def check_result(numpy_result, torch_result=None):
+ if isinstance(numpy_result, list) and torch_result is None:
+ flag = True
+ for (n, t) in numpy_result:
+ flag = flag and check_result(n, t)
+ return flag
+ # print((torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) - torch_result).abs().mean().item())
+ T = (torch_result * torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) < 0).sum().item()
+ direction = T / torch_result.numel() < err_p
+ return direction and ((torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) - torch_result).abs().mean() < err_epsilon).item()
+
+
+def case_1():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[5, 6])
+ W = np.random.normal(size=[6, 4])
+
+ numpy_matmul = Matmul()
+ numpy_out = numpy_matmul.forward(x, W)
+ numpy_x_grad, numpy_W_grad = numpy_matmul.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+ torch_W = torch.from_numpy(W).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_matmul(torch_x, torch_W)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ (numpy_W_grad, torch_W.grad)
+ ])
+
+
+def case_2():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[5, 6])
+
+ numpy_relu = Relu()
+ numpy_out = numpy_relu.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_relu.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_relu(torch_x)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def case_3():
+ x = np.random.uniform(low=0.0, high=1.0, size=[3, 4])
+
+ numpy_log = Log()
+ numpy_out = numpy_log.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_log.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_log(torch_x)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def case_4():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[4, 5])
+
+ numpy_softmax = Softmax()
+ numpy_out = numpy_softmax.forward(x)
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_softmax(torch_x, 1)
+
+ return check_result(numpy_out, torch_out)
+
+
+def case_5():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[20, 25])
+
+ numpy_softmax = Softmax()
+ numpy_out = numpy_softmax.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_softmax.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_softmax(torch_x, 1)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def test_model():
+ try:
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ numpy_model = NumpyModel()
+ torch_model = TorchModel()
+ torch_model.W1.data, torch_model.W2.data, torch_model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+ numpy_model.W1 = torch_model.W1.detach().clone().numpy()
+ numpy_model.W2 = torch_model.W2.detach().clone().numpy()
+ numpy_model.W3 = torch_model.W3.detach().clone().numpy()
+
+ x = torch.randn((10000, 28, 28))
+ y = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0] * 1000)
+
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+ x2 = x.numpy()
+ y_pred = torch_model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+
+ y_pred_numpy = numpy_model.forward(x2)
+ numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred_numpy, y.numpy())
+
+ check_flag_1 = check_result(y_pred_numpy, y_pred)
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("forward", 10 * check_flag_1, 10))
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in forward]")
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("forward", 0, 10))
+ return 0
+
+ try:
+
+ numpy_model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+
+ check_flag_2 = [
+ check_result(numpy_model.log_grad, torch_model.log_input.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.softmax_grad, torch_model.softmax_input.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W3_grad, torch_model.W3.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W2_grad, torch_model.W2.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W1_grad, torch_model.W1.grad)
+ ]
+ check_flag_2 = sum(check_flag_2) >= 4
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("backward", 20 * check_flag_2, 20))
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in backward]")
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("backward", 0, 20))
+ check_flag_2 = False
+
+ return 10 * check_flag_1 + 20 * check_flag_2
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ testcases = [
+ ["matmul", case_1, 5],
+ ["relu", case_2, 5],
+ ["log", case_3, 5],
+ ["softmax_1", case_4, 5],
+ ["softmax_2", case_5, 10],
+ ]
+ score = 0
+ for case in testcases:
+ try:
+ res = case[2] if case[1]() else 0
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in {}]".format(case[0]))
+ res = 0
+ score += res
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format(case[0], res, case[2]))
+ score += test_model()
+ print("{:14} {}/60".format("FINAL SCORE", score))
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/torch_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/torch_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6d3e214c7606e3d43dac4b94554f942508afffb3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/torch_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+import torch
+from utils import mini_batch, batch, download_mnist, get_torch_initialization, one_hot, plot_curve
+
+
+class TorchModel:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = torch.randn((28 * 28, 256), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W2 = torch.randn((256, 64), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W3 = torch.randn((64, 10), requires_grad=True)
+ self.softmax_input = None
+ self.log_input = None
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W1))
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W2))
+ x = torch.matmul(x, self.W3)
+
+ self.softmax_input = x
+ self.softmax_input.retain_grad()
+
+ x = torch.softmax(x, 1)
+
+ self.log_input = x
+ self.log_input.retain_grad()
+
+ x = torch.log(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ with torch.no_grad():
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1.grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2.grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3.grad
+
+ self.W1.grad = None
+ self.W2.grad = None
+ self.W3.grad = None
+
+
+def torch_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = TorchModel()
+ model.W1.data, model.W2.data, model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset, numpy=False):
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset, numpy=False)[0]
+ accuracy = model.forward(x).argmax(dim=1).eq(y).float().mean().item()
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ torch_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/utils.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/utils.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..709220cfa7a924d914ec1c098c505f864bcd4cfc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/utils.py
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+import torch
+import numpy as np
+from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
+
+
+def plot_curve(data):
+ plt.plot(range(len(data)), data, color='blue')
+ plt.legend(['loss_value'], loc='upper right')
+ plt.xlabel('step')
+ plt.ylabel('value')
+ plt.show()
+
+
+def download_mnist():
+ from torchvision import datasets, transforms
+
+ transform = transforms.Compose([
+ transforms.ToTensor(),
+ transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.1307,), std=(0.3081,))
+ ])
+
+ train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=True, download=True)
+ test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=False, download=True)
+
+ return train_dataset, test_dataset
+
+
+def one_hot(y, numpy=True):
+ if numpy:
+ y_ = np.zeros((y.shape[0], 10))
+ y_[np.arange(y.shape[0], dtype=np.int32), y] = 1
+ return y_
+ else:
+ y_ = torch.zeros((y.shape[0], 10))
+ y_[torch.arange(y.shape[0], dtype=torch.long), y] = 1
+ return y_
+
+
+def batch(dataset, numpy=True):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+ for each in dataset:
+ data.append(each[0])
+ label.append(each[1])
+ data = torch.stack(data)
+ label = torch.LongTensor(label)
+ if numpy:
+ return [(data.numpy(), label.numpy())]
+ else:
+ return [(data, label)]
+
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128, numpy=False):
+ return torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
+
+
+def get_torch_initialization(numpy=True):
+ fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(28 * 28, 256)
+ fc2 = torch.nn.Linear(256, 64)
+ fc3 = torch.nn.Linear(64, 10)
+
+ if numpy:
+ W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ W2 = fc2.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ W3 = fc3.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ else:
+ W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+ W2 = fc2.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+ W3 = fc3.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d1d38cfc70c1a72658e9d0fa1cf8569687ab9e45
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,179 @@
+18307130104
+
+# 课程报告
+
+这是 prml 的 assignment-2 课程报告,我的代码可以查看 numpy_fnn.py 中 code 1 ~ code 7 部分,以及 util.py 中 mini_batch 函数 numpy == True 的部分。
+
+在 assignment-2 中,完成了 numpy_fnn.py 中各种算子的反向传播,以及一个简单的前馈神经网络构建(包括正向传播和反向传播)。修改了 mini_batch,在 numpy == True 的情况下,不使用 torch 中的 dataloader 函数完成测试集的打乱和分批。
+
+## 模型实现
+
+为了区别矩阵乘法(np.matmul)和矩阵元素逐一做乘法(\*),下面用$\times$表示矩阵乘法,\*表示元素逐一相乘。
+
+### Matmul 算子的反向传播
+
+Matmul 算子输入一个 X 和权重 W,输出 $$[Y] = [X] \times [W]$$
+
+对于 Y 中的元素 $$Y_{ij}$$ 有$$Y_{ij}=\sum_{k}X_{ik} * W_{kj}$$
+
+在计算 grad_x 的时候,已知 grad_y,根据链式法则,可以得到 $gradx_{ij}=\sum_{k}\frac{\partial Y_{ik}}{\partial X_{ij}} * grady_{ik}$
+
+由 $Y_{ij}$的计算公式可以得到,$\frac{\partial Y_{ik}}{\partial X_{ij}}=W_{jk}$
+
+故 $gradx_{ij}=\sum_k W_{jk} *grady_{ik}$
+
+所以 $[gradx] = [grady] \times [W^T]$
+
+同理,可以得到$[gradW]=[x^T]\times [grady]$
+
+经过验证,矩阵的大小符合矩阵乘法规则。
+
+### Relu 算子的反向传播
+
+relu 函数的计算规则如下:
+
+$relu(x) = \begin{cases}0 & x < 0 \\\\ x & otherwise \end{cases}$
+
+求导可以得到
+
+$relu^{'}(x) = \begin{cases}0 & x < 0 \\\\ 1 & otherwise \end{cases}$
+
+故
+
+$[relugrad]=[grady]* [relu^{'}]$
+
+### Log 算子的反向传播
+
+$log(x) = \ln x$
+
+可以得到
+
+$log^{'}(x)=\frac 1 x$
+
+故
+
+$[loggrad]=[grady]* [log^{'}]$
+
+### softmax 算子的反向传播
+
+$softmax(x_i) = \frac {e^{x_i}}{\sum_j e^{x_j}}$
+
+在实现过程中,因为每一行代表一个测试数据点,所以以每一行为整体对每个元素进行 softmax 操作,从而达成对每个测试数据点进行分类的目的。
+
+采用 softmax 算子和交叉熵损失函数可以让损失函数的形式比较简单,但是遗憾的是实现的神经网络要求将两个算子的反向传播操作分开,因此没有办法投机取巧,只能分步进行计算。
+
+为了表达方便,不妨令 $a_i = softmax(x_i)$
+
+下面考虑$a_i$对$x_j$的反向传播。
+
+$a_i = \frac{e^{x_i}}{\sum_k e^{x_k}}$
+
+$\frac {\partial a_i}{\partial x_j}=\frac{\partial}{\partial x_j}(\frac{e^{x_i}}{\sum_k e^{x_k}})$
+
+接下来根据 i 和 j 是否相等分情况进行讨论。
+
+若 i == j,则 $\frac{\partial}{\partial x_j}(\frac{e^{x_i}}{\sum_k e^{x_k}})=\frac{e^{x_i}(\sum_j e^{x_j})-e^{z_i}e^{z_i}}{(\sum_k e^{x_k})^2}=a_i(1-a_i)$
+
+若 i != j,则$\frac{\partial}{\partial x_j}(\frac{e^{x_i}}{\sum_k e^{x_k}})=-\frac{e^{x_i}e^{x_j}}{(\sum_k e^{x_k})^2}=-a_ia_j$
+
+结合 grady,可以得到
+
+$gradx_{ij}=\sum_k \frac{\partial}{\partial x_j}(\frac{e^{x_k}}{\sum_w e^{x_w}}) grady_{ik}$
+
+由于这个梯度的计算需要进行分类讨论,我没有想到可以直接用 numpy 中函数进行计算的方法,所以首先计算出一个 list 再转换成 ndarray 进行返回。
+
+### 模型正向传播
+
+模型每一层的输出作为下一层的输入,最后得到的是经过 Log 计算的 softmax 结果,这样就能很方便的进行交叉熵损失函数的计算。同时经过“模型反向传播”中的分析可以知道,这样设计使反向传播时的输入也非常简便。
+
+### 模型反向传播
+
+模型进行反向传播的时候会输入一个每行为一个独热向量的矩阵,表示每个数据集的类别,初始代码中会将矩阵中所有元素都除以矩阵的大小,但是经过的尝试,需要将所有元素除以训练数据的组数才能保证结果正确。~~同时,虽然通过了测试,但是 softmax 层的输出也和 torch 中的结果有不同,而后面层的输出是正确的。我认定我理解的 softmax 层和 torch 实现的 softmax 层有一定区别。~~
+
+在更改了测试代码之后,输出和 torch 层比较接近,可以认定是正确的。
+
+接下来推导反向传播时 Log 层的输入。
+
+交叉熵损失函数的形式为
+
+$Loss = -\sum_k t_k*\ln a_k$
+
+其中 $t_k$表示是否属于第 k 个类别,$a_k$为 softmax 层的输出,Log 层的输出为$\ln a_k$,则$\frac{\partial Loss}{\partial \ln a_k}=-t_k$
+
+因此,将输入到反向传播的矩阵 T 取反作为 Log 层的反向传播输入,然后将结果作为前一层的输入逐一反向传播。
+
+## 模型训练
+
+随着训练轮数增长,训练的正确率如下
+
+learning_rate = 0.1 mini_batch = 128
+
+> [0] Accuracy: 0.9403
+
+可以看出相较传统的梯度下降算法,损失函数值的震荡幅度有所减小,而收敛速度与传统方法相当。
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/Adam.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/Adam.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..fe0326ebad52ad9356bdd7410834d9d61e9e5152
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/Adam.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGDM.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGDM.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ba7ad91c5569f2605e7944afe3803863b8072b46
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGDM.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGD_batch_size.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGD_batch_size.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..328c4cc7bf90ef75a09f8c97ee8e9134d44a33dd
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGD_batch_size.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGD_learning_rate.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGD_learning_rate.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7bca928d1aa569b08dad43d761da1b6e27e02942
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGD_learning_rate.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGD_normal.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGD_normal.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e6f3933e1bf979fa7b3b643d8f7fe823610109e9
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/SGD_normal.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/fnn_model.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/fnn_model.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..29ed50732a88ed1ca38a1cb3c6e82099a3d3e087
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/img/fnn_model.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7010cad4609f7ae31b8bdc0b19cedc005c5b950c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,239 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+ x, W = self.memory['x'], self.memory['W']
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, W.T)
+ grad_W = np.matmul(x.T, grad_y)
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ grad_x = grad_y * np.where(x > 0, np.ones_like(x), np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ grad_x = grad_y * np.reciprocal(x + self.epsilon)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+ exp_x = np.exp(x - x.max())
+ exp_sum = np.sum(exp_x, axis=1, keepdims=True)
+ out = exp_x / exp_sum
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['out'] = out
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ sm = self.memory['out']
+ Jacobs = np.array([np.diag(r) - np.outer(r, r) for r in sm])
+
+ grad_y = grad_y[:, np.newaxis, :]
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, Jacobs).squeeze(axis=1)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新。 softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ self.beta_1 = 0.9
+ self.beta_2 = 0.999
+ self.epsilon = 1e-8
+ self.is_first = True
+
+ self.W1_grad_mean = None
+ self.W2_grad_mean = None
+ self.W3_grad_mean = None
+
+ self.W1_grad_square_mean = None
+ self.W2_grad_square_mean = None
+ self.W3_grad_square_mean = None
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ x = self.relu_1.forward(self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1))
+ x = self.relu_2.forward(self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2))
+ x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+
+ x = self.log.forward(self.softmax.forward(x))
+
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y)
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+ self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+
+ return self.x1_grad
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ def SGD():
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+
+ def SGDM():
+ if self.is_first:
+ self.is_first = False
+
+ self.W1_grad_mean = self.W1_grad
+ self.W2_grad_mean = self.W2_grad
+ self.W3_grad_mean = self.W3_grad
+ else:
+ self.W1_grad_mean = self.beta_1 * self.W1_grad_mean + (1 - self.beta_1) * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2_grad_mean = self.beta_1 * self.W2_grad_mean + (1 - self.beta_1) * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3_grad_mean = self.beta_1 * self.W3_grad_mean + (1 - self.beta_1) * self.W3_grad
+
+ delta_1 = learning_rate * self.W1_grad_mean
+ delta_2 = learning_rate * self.W2_grad_mean
+ delta_3 = learning_rate * self.W3_grad_mean
+
+ self.W1 -= delta_1
+ self.W2 -= delta_2
+ self.W3 -= delta_3
+
+ def Adam(learning_rate=0.001):
+ if self.is_first:
+ self.is_first = False
+ self.W1_grad_mean = self.W1_grad
+ self.W2_grad_mean = self.W2_grad
+ self.W3_grad_mean = self.W3_grad
+
+ self.W1_grad_square_mean = np.square(self.W1_grad)
+ self.W2_grad_square_mean = np.square(self.W2_grad)
+ self.W3_grad_square_mean = np.square(self.W3_grad)
+
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad_mean
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad_mean
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad_mean
+ else:
+ self.W1_grad_mean = self.beta_1 * self.W1_grad_mean + (1 - self.beta_1) * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2_grad_mean = self.beta_1 * self.W2_grad_mean + (1 - self.beta_1) * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3_grad_mean = self.beta_1 * self.W3_grad_mean + (1 - self.beta_1) * self.W3_grad
+
+ self.W1_grad_square_mean = self.beta_2 * self.W1_grad_square_mean + (1 - self.beta_2) * np.square(
+ self.W1_grad)
+ self.W2_grad_square_mean = self.beta_2 * self.W2_grad_square_mean + (1 - self.beta_2) * np.square(
+ self.W2_grad)
+ self.W3_grad_square_mean = self.beta_2 * self.W3_grad_square_mean + (1 - self.beta_2) * np.square(
+ self.W3_grad)
+
+ delta_1 = learning_rate * self.W1_grad_mean * np.reciprocal(
+ np.sqrt(self.W1_grad_square_mean) + np.full_like(self.W1_grad_square_mean, self.epsilon))
+ delta_2 = learning_rate * self.W2_grad_mean * np.reciprocal(
+ np.sqrt(self.W2_grad_square_mean) + np.full_like(self.W2_grad_square_mean, self.epsilon))
+ delta_3 = learning_rate * self.W3_grad_mean * np.reciprocal(
+ np.sqrt(self.W3_grad_square_mean) + np.full_like(self.W3_grad_square_mean, self.epsilon))
+
+ self.W1 -= delta_1
+ self.W2 -= delta_2
+ self.W3 -= delta_3
+
+ # SGD()
+ # SGDM()
+ Adam()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6d67f25824dabdc5791ae5cc96655affe8315e72
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128):
+ data = np.array([np.array(each[0]) for each in dataset])
+ label = np.array([each[1] for each in dataset])
+
+ size = data.shape[0]
+ index = np.arange(size)
+ np.random.shuffle(index)
+
+ return [(data[index[i:i + batch_size]], label[index[i:i + batch_size]]) for i in range(0, size, batch_size)]
+
+
+def numpy_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 10
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/tester_demo.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/tester_demo.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..504b3eef50a6df4d0aa433113136add50835e420
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/tester_demo.py
@@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
+import numpy as np
+import torch
+from torch import matmul as torch_matmul, relu as torch_relu, softmax as torch_softmax, log as torch_log
+
+from numpy_fnn import Matmul, Relu, Softmax, Log, NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from torch_mnist import TorchModel
+from utils import get_torch_initialization, one_hot
+
+err_epsilon = 1e-6
+err_p = 0.4
+
+
+def check_result(numpy_result, torch_result=None):
+ if isinstance(numpy_result, list) and torch_result is None:
+ flag = True
+ for (n, t) in numpy_result:
+ flag = flag and check_result(n, t)
+ return flag
+ # print((torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) - torch_result).abs().mean().item())
+ T = (torch_result * torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) < 0).sum().item()
+ direction = T / torch_result.numel() < err_p
+ return direction and ((torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) - torch_result).abs().mean() < err_epsilon).item()
+
+
+def case_1():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[5, 6])
+ W = np.random.normal(size=[6, 4])
+
+ numpy_matmul = Matmul()
+ numpy_out = numpy_matmul.forward(x, W)
+ numpy_x_grad, numpy_W_grad = numpy_matmul.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+ torch_W = torch.from_numpy(W).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_matmul(torch_x, torch_W)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ (numpy_W_grad, torch_W.grad)
+ ])
+
+
+def case_2():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[5, 6])
+
+ numpy_relu = Relu()
+ numpy_out = numpy_relu.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_relu.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_relu(torch_x)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def case_3():
+ x = np.random.uniform(low=0.0, high=1.0, size=[3, 4])
+
+ numpy_log = Log()
+ numpy_out = numpy_log.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_log.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_log(torch_x)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def case_4():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[4, 5])
+
+ numpy_softmax = Softmax()
+ numpy_out = numpy_softmax.forward(x)
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_softmax(torch_x, 1)
+
+ return check_result(numpy_out, torch_out)
+
+
+def case_5():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[20, 25])
+
+ numpy_softmax = Softmax()
+ numpy_out = numpy_softmax.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_softmax.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_softmax(torch_x, 1)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def test_model():
+ try:
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ numpy_model = NumpyModel()
+ torch_model = TorchModel()
+ torch_model.W1.data, torch_model.W2.data, torch_model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+ numpy_model.W1 = torch_model.W1.detach().clone().numpy()
+ numpy_model.W2 = torch_model.W2.detach().clone().numpy()
+ numpy_model.W3 = torch_model.W3.detach().clone().numpy()
+
+ x = torch.randn((10000, 28, 28))
+ y = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0] * 1000)
+
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+ x2 = x.numpy()
+ y_pred = torch_model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+
+ y_pred_numpy = numpy_model.forward(x2)
+ numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred_numpy, y.numpy())
+
+ check_flag_1 = check_result(y_pred_numpy, y_pred)
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("forward", 10 * check_flag_1, 10))
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in forward]")
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("forward", 0, 10))
+ return 0
+
+ try:
+
+ numpy_model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+
+ check_flag_2 = [
+ check_result(numpy_model.log_grad, torch_model.log_input.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.softmax_grad, torch_model.softmax_input.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W3_grad, torch_model.W3.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W2_grad, torch_model.W2.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W1_grad, torch_model.W1.grad)
+ ]
+ check_flag_2 = sum(check_flag_2) >= 4
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("backward", 20 * check_flag_2, 20))
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in backward]")
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("backward", 0, 20))
+ check_flag_2 = False
+
+ return 10 * check_flag_1 + 20 * check_flag_2
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ testcases = [
+ ["matmul", case_1, 5],
+ ["relu", case_2, 5],
+ ["log", case_3, 5],
+ ["softmax_1", case_4, 5],
+ ["softmax_2", case_5, 10],
+ ]
+ score = 0
+ for case in testcases:
+ try:
+ res = case[2] if case[1]() else 0
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in {}]".format(case[0]))
+ res = 0
+ score += res
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format(case[0], res, case[2]))
+ score += test_model()
+ print("{:14} {}/60".format("FINAL SCORE", score))
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/torch_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/torch_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6d3e214c7606e3d43dac4b94554f942508afffb3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/torch_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+import torch
+from utils import mini_batch, batch, download_mnist, get_torch_initialization, one_hot, plot_curve
+
+
+class TorchModel:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = torch.randn((28 * 28, 256), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W2 = torch.randn((256, 64), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W3 = torch.randn((64, 10), requires_grad=True)
+ self.softmax_input = None
+ self.log_input = None
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W1))
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W2))
+ x = torch.matmul(x, self.W3)
+
+ self.softmax_input = x
+ self.softmax_input.retain_grad()
+
+ x = torch.softmax(x, 1)
+
+ self.log_input = x
+ self.log_input.retain_grad()
+
+ x = torch.log(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ with torch.no_grad():
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1.grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2.grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3.grad
+
+ self.W1.grad = None
+ self.W2.grad = None
+ self.W3.grad = None
+
+
+def torch_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = TorchModel()
+ model.W1.data, model.W2.data, model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset, numpy=False):
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset, numpy=False)[0]
+ accuracy = model.forward(x).argmax(dim=1).eq(y).float().mean().item()
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ torch_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/utils.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/utils.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..709220cfa7a924d914ec1c098c505f864bcd4cfc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130090/utils.py
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+import torch
+import numpy as np
+from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
+
+
+def plot_curve(data):
+ plt.plot(range(len(data)), data, color='blue')
+ plt.legend(['loss_value'], loc='upper right')
+ plt.xlabel('step')
+ plt.ylabel('value')
+ plt.show()
+
+
+def download_mnist():
+ from torchvision import datasets, transforms
+
+ transform = transforms.Compose([
+ transforms.ToTensor(),
+ transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.1307,), std=(0.3081,))
+ ])
+
+ train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=True, download=True)
+ test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=False, download=True)
+
+ return train_dataset, test_dataset
+
+
+def one_hot(y, numpy=True):
+ if numpy:
+ y_ = np.zeros((y.shape[0], 10))
+ y_[np.arange(y.shape[0], dtype=np.int32), y] = 1
+ return y_
+ else:
+ y_ = torch.zeros((y.shape[0], 10))
+ y_[torch.arange(y.shape[0], dtype=torch.long), y] = 1
+ return y_
+
+
+def batch(dataset, numpy=True):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+ for each in dataset:
+ data.append(each[0])
+ label.append(each[1])
+ data = torch.stack(data)
+ label = torch.LongTensor(label)
+ if numpy:
+ return [(data.numpy(), label.numpy())]
+ else:
+ return [(data, label)]
+
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128, numpy=False):
+ return torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
+
+
+def get_torch_initialization(numpy=True):
+ fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(28 * 28, 256)
+ fc2 = torch.nn.Linear(256, 64)
+ fc3 = torch.nn.Linear(64, 10)
+
+ if numpy:
+ W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ W2 = fc2.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ W3 = fc3.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ else:
+ W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+ W2 = fc2.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+ W3 = fc3.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d1d38cfc70c1a72658e9d0fa1cf8569687ab9e45
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,179 @@
+18307130104
+
+# 课程报告
+
+这是 prml 的 assignment-2 课程报告,我的代码可以查看 numpy_fnn.py 中 code 1 ~ code 7 部分,以及 util.py 中 mini_batch 函数 numpy == True 的部分。
+
+在 assignment-2 中,完成了 numpy_fnn.py 中各种算子的反向传播,以及一个简单的前馈神经网络构建(包括正向传播和反向传播)。修改了 mini_batch,在 numpy == True 的情况下,不使用 torch 中的 dataloader 函数完成测试集的打乱和分批。
+
+## 模型实现
+
+为了区别矩阵乘法(np.matmul)和矩阵元素逐一做乘法(\*),下面用$\times$表示矩阵乘法,\*表示元素逐一相乘。
+
+### Matmul 算子的反向传播
+
+Matmul 算子输入一个 X 和权重 W,输出 $$[Y] = [X] \times [W]$$
+
+对于 Y 中的元素 $$Y_{ij}$$ 有$$Y_{ij}=\sum_{k}X_{ik} * W_{kj}$$
+
+在计算 grad_x 的时候,已知 grad_y,根据链式法则,可以得到 $gradx_{ij}=\sum_{k}\frac{\partial Y_{ik}}{\partial X_{ij}} * grady_{ik}$
+
+由 $Y_{ij}$的计算公式可以得到,$\frac{\partial Y_{ik}}{\partial X_{ij}}=W_{jk}$
+
+故 $gradx_{ij}=\sum_k W_{jk} *grady_{ik}$
+
+所以 $[gradx] = [grady] \times [W^T]$
+
+同理,可以得到$[gradW]=[x^T]\times [grady]$
+
+经过验证,矩阵的大小符合矩阵乘法规则。
+
+### Relu 算子的反向传播
+
+relu 函数的计算规则如下:
+
+$relu(x) = \begin{cases}0 & x < 0 \\\\ x & otherwise \end{cases}$
+
+求导可以得到
+
+$relu^{'}(x) = \begin{cases}0 & x < 0 \\\\ 1 & otherwise \end{cases}$
+
+故
+
+$[relugrad]=[grady]* [relu^{'}]$
+
+### Log 算子的反向传播
+
+$log(x) = \ln x$
+
+可以得到
+
+$log^{'}(x)=\frac 1 x$
+
+故
+
+$[loggrad]=[grady]* [log^{'}]$
+
+### softmax 算子的反向传播
+
+$softmax(x_i) = \frac {e^{x_i}}{\sum_j e^{x_j}}$
+
+在实现过程中,因为每一行代表一个测试数据点,所以以每一行为整体对每个元素进行 softmax 操作,从而达成对每个测试数据点进行分类的目的。
+
+采用 softmax 算子和交叉熵损失函数可以让损失函数的形式比较简单,但是遗憾的是实现的神经网络要求将两个算子的反向传播操作分开,因此没有办法投机取巧,只能分步进行计算。
+
+为了表达方便,不妨令 $a_i = softmax(x_i)$
+
+下面考虑$a_i$对$x_j$的反向传播。
+
+$a_i = \frac{e^{x_i}}{\sum_k e^{x_k}}$
+
+$\frac {\partial a_i}{\partial x_j}=\frac{\partial}{\partial x_j}(\frac{e^{x_i}}{\sum_k e^{x_k}})$
+
+接下来根据 i 和 j 是否相等分情况进行讨论。
+
+若 i == j,则 $\frac{\partial}{\partial x_j}(\frac{e^{x_i}}{\sum_k e^{x_k}})=\frac{e^{x_i}(\sum_j e^{x_j})-e^{z_i}e^{z_i}}{(\sum_k e^{x_k})^2}=a_i(1-a_i)$
+
+若 i != j,则$\frac{\partial}{\partial x_j}(\frac{e^{x_i}}{\sum_k e^{x_k}})=-\frac{e^{x_i}e^{x_j}}{(\sum_k e^{x_k})^2}=-a_ia_j$
+
+结合 grady,可以得到
+
+$gradx_{ij}=\sum_k \frac{\partial}{\partial x_j}(\frac{e^{x_k}}{\sum_w e^{x_w}}) grady_{ik}$
+
+由于这个梯度的计算需要进行分类讨论,我没有想到可以直接用 numpy 中函数进行计算的方法,所以首先计算出一个 list 再转换成 ndarray 进行返回。
+
+### 模型正向传播
+
+模型每一层的输出作为下一层的输入,最后得到的是经过 Log 计算的 softmax 结果,这样就能很方便的进行交叉熵损失函数的计算。同时经过“模型反向传播”中的分析可以知道,这样设计使反向传播时的输入也非常简便。
+
+### 模型反向传播
+
+模型进行反向传播的时候会输入一个每行为一个独热向量的矩阵,表示每个数据集的类别,初始代码中会将矩阵中所有元素都除以矩阵的大小,但是经过的尝试,需要将所有元素除以训练数据的组数才能保证结果正确。~~同时,虽然通过了测试,但是 softmax 层的输出也和 torch 中的结果有不同,而后面层的输出是正确的。我认定我理解的 softmax 层和 torch 实现的 softmax 层有一定区别。~~
+
+在更改了测试代码之后,输出和 torch 层比较接近,可以认定是正确的。
+
+接下来推导反向传播时 Log 层的输入。
+
+交叉熵损失函数的形式为
+
+$Loss = -\sum_k t_k*\ln a_k$
+
+其中 $t_k$表示是否属于第 k 个类别,$a_k$为 softmax 层的输出,Log 层的输出为$\ln a_k$,则$\frac{\partial Loss}{\partial \ln a_k}=-t_k$
+
+因此,将输入到反向传播的矩阵 T 取反作为 Log 层的反向传播输入,然后将结果作为前一层的输入逐一反向传播。
+
+## 模型训练
+
+随着训练轮数增长,训练的正确率如下
+
+learning_rate = 0.1 mini_batch = 128
+
+> [0] Accuracy: 0.9403 +
+可以看到,正确率随着训练稳步上升,在 6 轮之后,数字基本稳定,仅仅有略微的上下波动。
+
+learning_rate = 0.1 mini_batch = 32
+
+> [0] Accuracy: 0.9646
+
+可以看到,正确率随着训练稳步上升,在 6 轮之后,数字基本稳定,仅仅有略微的上下波动。
+
+learning_rate = 0.1 mini_batch = 32
+
+> [0] Accuracy: 0.9646 +
+可以看到,由于 mini_batch 从 128 变成 32,损失随着轮数的变化会有比较大的起伏。
+
+learning_rate = 0.2 mini_batch = 128
+
+> [0] Accuracy: 0.9295
+
+可以看到,由于 mini_batch 从 128 变成 32,损失随着轮数的变化会有比较大的起伏。
+
+learning_rate = 0.2 mini_batch = 128
+
+> [0] Accuracy: 0.9295 +
+虽然调高了学习率,但是损失并没有因此产生比较大的起伏,仍然表现出非常好的效果。
+
+learning_rate = 0.05 mini_batch = 128
+
+> [0] Accuracy: 0.9310
+
+虽然调高了学习率,但是损失并没有因此产生比较大的起伏,仍然表现出非常好的效果。
+
+learning_rate = 0.05 mini_batch = 128
+
+> [0] Accuracy: 0.9310 +
+降低了学习率之后,可以看到正确率的增长比较缓慢,但是经过几轮训练之后的结果和高学习率的时候差不多。
+
+综合来看,影响最终正确率的主要还是模型本身的学习能力,一定范围内修改学习率和 mini_batch 对结果的影响不大。采用 mini_batch 的方式训练有助于降低训练过程中损失的波动。
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-1.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..11c6fba6be9d6f58a463830a5d8c006ad64af963
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-2.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..3f9aa1a2ed643f738f7d9ff59ea1923891048166
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-3.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-3.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..1e7d29f9f43741b83d6ac43ecf4b6c448c8c1141
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-3.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-4.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-4.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..2a1f550db001bdcc1d3a3b9501dba56a13028e8e
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-4.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-5.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-5.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7ee7df630e01d83559e9f316a937df107e98248d
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-5.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..0039ef8029c07eeb75caa2efd42c13aeba61ce5a
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ba780e9edb71ec687ddf7d295973be810848ce79
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 1 #
+ ####################
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, self.memory['W'].T)
+ grad_W = np.matmul(self.memory['x'].T, grad_y)
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 2 #
+ ####################
+ grad_x = grad_y * np.where(self.memory['x'] > 0, np.ones_like(self.memory['x']), np.zeros_like(self.memory['x']))
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 3 #
+ ####################
+ grad_x = grad_y * np.reciprocal(self.memory['x'] + self.epsilon)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 4 #
+ ####################
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ expx = np.exp(x)
+ sumx = np.sum(expx, axis = 1, keepdims = True)
+ return (expx / sumx)
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 5 #
+ ####################
+
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ softx = self.forward(x)
+ # print(sumx.shape)
+ [n, m] = x.shape
+ out = []
+ # print(grad_y)
+ for i in range(n):
+ out.append([])
+ for j in range(m):
+ out[i].append(0)
+ for k in range(m):
+ if j == k:
+ # print(softx[i][k], grad_y[i][k])
+ out[i][j] += (1 - softx[i][k]) * softx[i][k] * grad_y[i][k]
+ else:
+ out[i][j] += -softx[i][j] * softx[i][k] * grad_y[i][k]
+ grad_x = np.array(out)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新。 softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ ####################
+ # code 6 #
+ ####################
+ x = self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1)
+ x = self.relu_1.forward(x)
+ x = self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2)
+ x = self.relu_2.forward(x)
+ x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+ x = self.softmax.forward(x)
+ # print(x)
+ x = self.log.forward(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+
+ ####################
+ # code 7 #
+ ####################
+
+ y = self.log.backward(y)
+ self.log_grad = y
+
+ y = self.softmax.backward(y)
+ self.softmax_grad = y
+
+ y, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(y)
+ self.x3_grad = y
+
+ y = self.relu_2.backward(y)
+ self.relu_2_grad = y
+
+ y, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(y)
+ self.x2_grad = y
+
+ y = self.relu_1.backward(y)
+ self.relu_1_grad = y
+
+ y, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(y)
+ self.x1_grad = y
+ return y
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..5f7aaadd84d701b578d384df3d4976f5c76a5dfa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, mini_batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+
+
+def numpy_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset, 128, True):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/tester_demo.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/tester_demo.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..df4bb27bc0d8b9f28f5abd09faff7635d8347792
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/tester_demo.py
@@ -0,0 +1,183 @@
+import numpy as np
+import torch
+from torch import matmul as torch_matmul, relu as torch_relu, softmax as torch_softmax, log as torch_log
+
+from numpy_fnn import Matmul, Relu, Softmax, Log, NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from torch_mnist import TorchModel
+from utils import get_torch_initialization, one_hot
+
+err_epsilon = 1e-6
+err_p = 0.4
+
+
+def check_result(numpy_result, torch_result=None):
+ if isinstance(numpy_result, list) and torch_result is None:
+ flag = True
+ for (n, t) in numpy_result:
+ flag = flag and check_result(n, t)
+ return flag
+ # print((torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) - torch_result).abs().mean().item())
+ T = (torch_result * torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) < 0).sum().item()
+ direction = T / torch_result.numel() < err_p
+
+ return direction and ((torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) - torch_result).abs().mean() < err_epsilon).item()
+
+
+def case_1():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[5, 6])
+ W = np.random.normal(size=[6, 4])
+
+ numpy_matmul = Matmul()
+ numpy_out = numpy_matmul.forward(x, W)
+ numpy_x_grad, numpy_W_grad = numpy_matmul.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+ torch_W = torch.from_numpy(W).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_matmul(torch_x, torch_W)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ (numpy_W_grad, torch_W.grad)
+ ])
+
+
+def case_2():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[5, 6])
+
+ numpy_relu = Relu()
+ numpy_out = numpy_relu.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_relu.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_relu(torch_x)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def case_3():
+ x = np.random.uniform(low=0.0, high=1.0, size=[3, 4])
+
+ numpy_log = Log()
+ numpy_out = numpy_log.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_log.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_log(torch_x)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def case_4():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[4, 5])
+
+ numpy_softmax = Softmax()
+ numpy_out = numpy_softmax.forward(x)
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_softmax(torch_x, 1)
+
+ return check_result(numpy_out, torch_out)
+
+
+def case_5():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[20, 25])
+
+ numpy_softmax = Softmax()
+ numpy_out = numpy_softmax.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_softmax.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_softmax(torch_x, 1)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def test_model():
+ try:
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ numpy_model = NumpyModel()
+ torch_model = TorchModel()
+ torch_model.W1.data, torch_model.W2.data, torch_model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+ numpy_model.W1 = torch_model.W1.detach().clone().numpy()
+ numpy_model.W2 = torch_model.W2.detach().clone().numpy()
+ numpy_model.W3 = torch_model.W3.detach().clone().numpy()
+
+ x = torch.randn((10000, 28, 28))
+ y = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0] * 1000)
+
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+ x2 = x.numpy()
+ y_pred = torch_model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+
+ y_pred_numpy = numpy_model.forward(x2)
+ numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred_numpy, y.numpy())
+
+ check_flag_1 = check_result(y_pred_numpy, y_pred)
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("forward", 10 * check_flag_1, 10))
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in forward]")
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("forward", 0, 10))
+ return 0
+
+ try:
+
+ numpy_model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+
+ check_flag_2 = [
+ check_result(numpy_model.log_grad, torch_model.log_input.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.softmax_grad, torch_model.softmax_input.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W3_grad, torch_model.W3.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W2_grad, torch_model.W2.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W1_grad, torch_model.W1.grad)
+ ]
+ check_flag_2 = sum(check_flag_2) >= 4
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("backward", 20 * check_flag_2, 20))
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in backward]")
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("backward", 0, 20))
+ check_flag_2 = False
+
+ return 10 * check_flag_1 + 20 * check_flag_2
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ testcases = [
+ ["matmul", case_1, 5],
+ ["relu", case_2, 5],
+ ["log", case_3, 5],
+ ["softmax_1", case_4, 5],
+ ["softmax_2", case_5, 10],
+ ]
+ score = 0
+ for case in testcases:
+ try:
+ res = case[2] if case[1]() else 0
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in {}]".format(case[0]))
+ res = 0
+ score += res
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format(case[0], res, case[2]))
+ score += test_model()
+ print("{:14} {}/60".format("FINAL SCORE", score))
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/torch_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/torch_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6d3e214c7606e3d43dac4b94554f942508afffb3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/torch_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+import torch
+from utils import mini_batch, batch, download_mnist, get_torch_initialization, one_hot, plot_curve
+
+
+class TorchModel:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = torch.randn((28 * 28, 256), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W2 = torch.randn((256, 64), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W3 = torch.randn((64, 10), requires_grad=True)
+ self.softmax_input = None
+ self.log_input = None
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W1))
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W2))
+ x = torch.matmul(x, self.W3)
+
+ self.softmax_input = x
+ self.softmax_input.retain_grad()
+
+ x = torch.softmax(x, 1)
+
+ self.log_input = x
+ self.log_input.retain_grad()
+
+ x = torch.log(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ with torch.no_grad():
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1.grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2.grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3.grad
+
+ self.W1.grad = None
+ self.W2.grad = None
+ self.W3.grad = None
+
+
+def torch_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = TorchModel()
+ model.W1.data, model.W2.data, model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset, numpy=False):
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset, numpy=False)[0]
+ accuracy = model.forward(x).argmax(dim=1).eq(y).float().mean().item()
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ torch_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/utils.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/utils.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..274566a51dc9718158d63b6aa59546381d939223
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/utils.py
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+import torch
+import numpy as np
+from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
+
+def plot_curve(data):
+ plt.plot(range(len(data)), data, color='blue')
+ plt.legend(['loss_value'], loc='upper right')
+ plt.xlabel('step')
+ plt.ylabel('value')
+ plt.xlim(-100,5000)
+ plt.savefig('./img/result.png')
+ plt.close()
+ plt.show()
+
+
+def download_mnist():
+ from torchvision import datasets, transforms
+
+ transform = transforms.Compose([
+ transforms.ToTensor(),
+ transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.1307,), std=(0.3081,))
+ ])
+
+ train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=True, download=True)
+ test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=False, download=True)
+
+ return train_dataset, test_dataset
+
+
+def one_hot(y, numpy=True):
+ if numpy:
+ y_ = np.zeros((y.shape[0], 10))
+ y_[np.arange(y.shape[0], dtype=np.int32), y] = 1
+ return y_
+ else:
+ y_ = torch.zeros((y.shape[0], 10))
+ y_[torch.arange(y.shape[0], dtype=torch.long), y] = 1
+ return y_
+
+
+def batch(dataset, numpy=True):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+ for each in dataset:
+ data.append(each[0])
+ label.append(each[1])
+ data = torch.stack(data)
+ label = torch.LongTensor(label)
+ if numpy:
+ return [(data.numpy(), label.numpy())]
+ else:
+ return [(data, label)]
+
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128, numpy=False):
+ if numpy:
+ import random
+ datas = [(each[0].numpy(), each[1]) for each in dataset]
+ random.shuffle(datas)
+ datat = [each[0] for each in datas]
+ labelt = [each[1] for each in datas]
+ data = [np.array(datat[i: i + batch_size]) for i in range(0, len(datat), batch_size)]
+ label = [np.array(labelt[i: i + batch_size]) for i in range(0, len(datat), batch_size)]
+ return zip(data, label)
+ else:
+ return torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
+
+
+def get_torch_initialization(numpy=True):
+ fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(28 * 28, 256)
+ fc2 = torch.nn.Linear(256, 64)
+ fc3 = torch.nn.Linear(64, 10)
+
+ if numpy:
+ W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ W2 = fc2.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ W3 = fc3.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ else:
+ W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+ W2 = fc2.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+ W3 = fc3.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..60d6a7aaf412e4f028a1124ff7cc63b243e2c2d7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,160 @@
+# FNN实现
+
+[toc]
+
+## 模型实现
+
+各算子实现参考[算子导数推导部分](##算子导数推导),网络结构如下图所示
+
+
+
+根据上图对应的模型,建立顺序将算子拼接在一起,并在反向传播时从loss开始逐层回传,基本没什么难点,最终模型构建了函数
+
+$log(softmax(W_3\sigma(W_2\sigma(W_1X)))$
+
+## 模型训练
+
+在运行实现给出的`numpy_minst.py`,共运行了三个epoch,对应的准确率和loss变化情况如下
+
+| epoch | Accuracy |
+| ----- | -------- |
+| 0 | 94.49% |
+| 1 | 96.47% |
+| 2 | 96.58% |
+
+
+
+### 学习率和epoch的影响
+
+观察发现,loss下降到一定范围后开始上下抖动,推测其原因为接近极值点时学习率过大,为达到更优的性能,我调小的学习率并增大了epoch数量,得到结果如下,并做了不更改学习率仅调整epoch数量的对比实验其中i为[(i-1)*5, i\*5)中位数,20为最终结果
+
+| epoch | Accuracy(learning_rate = 0.1) | Accuracy(learning_rate = 0.05) | Accuracy(learning_rate = 0.1+0.05) |
+| ----- | ----------------------------- | ------------------------------ | ---------------------------------- |
+| 0 | 97.27% | 95.85% | 96.59% |
+| 5 | 97.93% | 97.85% | 97.91% |
+| 10 | 98.03% | 98.03% | 98.18% |
+| 15 | 98.12% | 98.09% | 98.18% |
+| 20 | 98.12% | 98.19% | 98.18% |
+
+
+
+降低了学习率之后,可以看到正确率的增长比较缓慢,但是经过几轮训练之后的结果和高学习率的时候差不多。
+
+综合来看,影响最终正确率的主要还是模型本身的学习能力,一定范围内修改学习率和 mini_batch 对结果的影响不大。采用 mini_batch 的方式训练有助于降低训练过程中损失的波动。
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-1.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..11c6fba6be9d6f58a463830a5d8c006ad64af963
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-2.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..3f9aa1a2ed643f738f7d9ff59ea1923891048166
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-3.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-3.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..1e7d29f9f43741b83d6ac43ecf4b6c448c8c1141
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-3.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-4.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-4.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..2a1f550db001bdcc1d3a3b9501dba56a13028e8e
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-4.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-5.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-5.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7ee7df630e01d83559e9f316a937df107e98248d
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result-5.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..0039ef8029c07eeb75caa2efd42c13aeba61ce5a
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/img/result.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ba780e9edb71ec687ddf7d295973be810848ce79
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 1 #
+ ####################
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, self.memory['W'].T)
+ grad_W = np.matmul(self.memory['x'].T, grad_y)
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 2 #
+ ####################
+ grad_x = grad_y * np.where(self.memory['x'] > 0, np.ones_like(self.memory['x']), np.zeros_like(self.memory['x']))
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 3 #
+ ####################
+ grad_x = grad_y * np.reciprocal(self.memory['x'] + self.epsilon)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 4 #
+ ####################
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ expx = np.exp(x)
+ sumx = np.sum(expx, axis = 1, keepdims = True)
+ return (expx / sumx)
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 5 #
+ ####################
+
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ softx = self.forward(x)
+ # print(sumx.shape)
+ [n, m] = x.shape
+ out = []
+ # print(grad_y)
+ for i in range(n):
+ out.append([])
+ for j in range(m):
+ out[i].append(0)
+ for k in range(m):
+ if j == k:
+ # print(softx[i][k], grad_y[i][k])
+ out[i][j] += (1 - softx[i][k]) * softx[i][k] * grad_y[i][k]
+ else:
+ out[i][j] += -softx[i][j] * softx[i][k] * grad_y[i][k]
+ grad_x = np.array(out)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新。 softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ ####################
+ # code 6 #
+ ####################
+ x = self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1)
+ x = self.relu_1.forward(x)
+ x = self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2)
+ x = self.relu_2.forward(x)
+ x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+ x = self.softmax.forward(x)
+ # print(x)
+ x = self.log.forward(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+
+ ####################
+ # code 7 #
+ ####################
+
+ y = self.log.backward(y)
+ self.log_grad = y
+
+ y = self.softmax.backward(y)
+ self.softmax_grad = y
+
+ y, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(y)
+ self.x3_grad = y
+
+ y = self.relu_2.backward(y)
+ self.relu_2_grad = y
+
+ y, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(y)
+ self.x2_grad = y
+
+ y = self.relu_1.backward(y)
+ self.relu_1_grad = y
+
+ y, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(y)
+ self.x1_grad = y
+ return y
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..5f7aaadd84d701b578d384df3d4976f5c76a5dfa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, mini_batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+
+
+def numpy_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset, 128, True):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/tester_demo.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/tester_demo.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..df4bb27bc0d8b9f28f5abd09faff7635d8347792
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/tester_demo.py
@@ -0,0 +1,183 @@
+import numpy as np
+import torch
+from torch import matmul as torch_matmul, relu as torch_relu, softmax as torch_softmax, log as torch_log
+
+from numpy_fnn import Matmul, Relu, Softmax, Log, NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from torch_mnist import TorchModel
+from utils import get_torch_initialization, one_hot
+
+err_epsilon = 1e-6
+err_p = 0.4
+
+
+def check_result(numpy_result, torch_result=None):
+ if isinstance(numpy_result, list) and torch_result is None:
+ flag = True
+ for (n, t) in numpy_result:
+ flag = flag and check_result(n, t)
+ return flag
+ # print((torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) - torch_result).abs().mean().item())
+ T = (torch_result * torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) < 0).sum().item()
+ direction = T / torch_result.numel() < err_p
+
+ return direction and ((torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) - torch_result).abs().mean() < err_epsilon).item()
+
+
+def case_1():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[5, 6])
+ W = np.random.normal(size=[6, 4])
+
+ numpy_matmul = Matmul()
+ numpy_out = numpy_matmul.forward(x, W)
+ numpy_x_grad, numpy_W_grad = numpy_matmul.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+ torch_W = torch.from_numpy(W).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_matmul(torch_x, torch_W)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ (numpy_W_grad, torch_W.grad)
+ ])
+
+
+def case_2():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[5, 6])
+
+ numpy_relu = Relu()
+ numpy_out = numpy_relu.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_relu.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_relu(torch_x)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def case_3():
+ x = np.random.uniform(low=0.0, high=1.0, size=[3, 4])
+
+ numpy_log = Log()
+ numpy_out = numpy_log.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_log.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_log(torch_x)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def case_4():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[4, 5])
+
+ numpy_softmax = Softmax()
+ numpy_out = numpy_softmax.forward(x)
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_softmax(torch_x, 1)
+
+ return check_result(numpy_out, torch_out)
+
+
+def case_5():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[20, 25])
+
+ numpy_softmax = Softmax()
+ numpy_out = numpy_softmax.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_softmax.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_softmax(torch_x, 1)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def test_model():
+ try:
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ numpy_model = NumpyModel()
+ torch_model = TorchModel()
+ torch_model.W1.data, torch_model.W2.data, torch_model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+ numpy_model.W1 = torch_model.W1.detach().clone().numpy()
+ numpy_model.W2 = torch_model.W2.detach().clone().numpy()
+ numpy_model.W3 = torch_model.W3.detach().clone().numpy()
+
+ x = torch.randn((10000, 28, 28))
+ y = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0] * 1000)
+
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+ x2 = x.numpy()
+ y_pred = torch_model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+
+ y_pred_numpy = numpy_model.forward(x2)
+ numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred_numpy, y.numpy())
+
+ check_flag_1 = check_result(y_pred_numpy, y_pred)
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("forward", 10 * check_flag_1, 10))
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in forward]")
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("forward", 0, 10))
+ return 0
+
+ try:
+
+ numpy_model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+
+ check_flag_2 = [
+ check_result(numpy_model.log_grad, torch_model.log_input.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.softmax_grad, torch_model.softmax_input.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W3_grad, torch_model.W3.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W2_grad, torch_model.W2.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W1_grad, torch_model.W1.grad)
+ ]
+ check_flag_2 = sum(check_flag_2) >= 4
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("backward", 20 * check_flag_2, 20))
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in backward]")
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("backward", 0, 20))
+ check_flag_2 = False
+
+ return 10 * check_flag_1 + 20 * check_flag_2
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ testcases = [
+ ["matmul", case_1, 5],
+ ["relu", case_2, 5],
+ ["log", case_3, 5],
+ ["softmax_1", case_4, 5],
+ ["softmax_2", case_5, 10],
+ ]
+ score = 0
+ for case in testcases:
+ try:
+ res = case[2] if case[1]() else 0
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in {}]".format(case[0]))
+ res = 0
+ score += res
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format(case[0], res, case[2]))
+ score += test_model()
+ print("{:14} {}/60".format("FINAL SCORE", score))
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/torch_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/torch_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6d3e214c7606e3d43dac4b94554f942508afffb3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/torch_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+import torch
+from utils import mini_batch, batch, download_mnist, get_torch_initialization, one_hot, plot_curve
+
+
+class TorchModel:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = torch.randn((28 * 28, 256), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W2 = torch.randn((256, 64), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W3 = torch.randn((64, 10), requires_grad=True)
+ self.softmax_input = None
+ self.log_input = None
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W1))
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W2))
+ x = torch.matmul(x, self.W3)
+
+ self.softmax_input = x
+ self.softmax_input.retain_grad()
+
+ x = torch.softmax(x, 1)
+
+ self.log_input = x
+ self.log_input.retain_grad()
+
+ x = torch.log(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ with torch.no_grad():
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1.grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2.grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3.grad
+
+ self.W1.grad = None
+ self.W2.grad = None
+ self.W3.grad = None
+
+
+def torch_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = TorchModel()
+ model.W1.data, model.W2.data, model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset, numpy=False):
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset, numpy=False)[0]
+ accuracy = model.forward(x).argmax(dim=1).eq(y).float().mean().item()
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ torch_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/utils.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/utils.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..274566a51dc9718158d63b6aa59546381d939223
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130104/utils.py
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+import torch
+import numpy as np
+from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
+
+def plot_curve(data):
+ plt.plot(range(len(data)), data, color='blue')
+ plt.legend(['loss_value'], loc='upper right')
+ plt.xlabel('step')
+ plt.ylabel('value')
+ plt.xlim(-100,5000)
+ plt.savefig('./img/result.png')
+ plt.close()
+ plt.show()
+
+
+def download_mnist():
+ from torchvision import datasets, transforms
+
+ transform = transforms.Compose([
+ transforms.ToTensor(),
+ transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.1307,), std=(0.3081,))
+ ])
+
+ train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=True, download=True)
+ test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=False, download=True)
+
+ return train_dataset, test_dataset
+
+
+def one_hot(y, numpy=True):
+ if numpy:
+ y_ = np.zeros((y.shape[0], 10))
+ y_[np.arange(y.shape[0], dtype=np.int32), y] = 1
+ return y_
+ else:
+ y_ = torch.zeros((y.shape[0], 10))
+ y_[torch.arange(y.shape[0], dtype=torch.long), y] = 1
+ return y_
+
+
+def batch(dataset, numpy=True):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+ for each in dataset:
+ data.append(each[0])
+ label.append(each[1])
+ data = torch.stack(data)
+ label = torch.LongTensor(label)
+ if numpy:
+ return [(data.numpy(), label.numpy())]
+ else:
+ return [(data, label)]
+
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128, numpy=False):
+ if numpy:
+ import random
+ datas = [(each[0].numpy(), each[1]) for each in dataset]
+ random.shuffle(datas)
+ datat = [each[0] for each in datas]
+ labelt = [each[1] for each in datas]
+ data = [np.array(datat[i: i + batch_size]) for i in range(0, len(datat), batch_size)]
+ label = [np.array(labelt[i: i + batch_size]) for i in range(0, len(datat), batch_size)]
+ return zip(data, label)
+ else:
+ return torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
+
+
+def get_torch_initialization(numpy=True):
+ fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(28 * 28, 256)
+ fc2 = torch.nn.Linear(256, 64)
+ fc3 = torch.nn.Linear(64, 10)
+
+ if numpy:
+ W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ W2 = fc2.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ W3 = fc3.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ else:
+ W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+ W2 = fc2.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+ W3 = fc3.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..60d6a7aaf412e4f028a1124ff7cc63b243e2c2d7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,160 @@
+# FNN实现
+
+[toc]
+
+## 模型实现
+
+各算子实现参考[算子导数推导部分](##算子导数推导),网络结构如下图所示
+
+
+
+根据上图对应的模型,建立顺序将算子拼接在一起,并在反向传播时从loss开始逐层回传,基本没什么难点,最终模型构建了函数
+
+$log(softmax(W_3\sigma(W_2\sigma(W_1X)))$
+
+## 模型训练
+
+在运行实现给出的`numpy_minst.py`,共运行了三个epoch,对应的准确率和loss变化情况如下
+
+| epoch | Accuracy |
+| ----- | -------- |
+| 0 | 94.49% |
+| 1 | 96.47% |
+| 2 | 96.58% |
+
+
+
+### 学习率和epoch的影响
+
+观察发现,loss下降到一定范围后开始上下抖动,推测其原因为接近极值点时学习率过大,为达到更优的性能,我调小的学习率并增大了epoch数量,得到结果如下,并做了不更改学习率仅调整epoch数量的对比实验其中i为[(i-1)*5, i\*5)中位数,20为最终结果
+
+| epoch | Accuracy(learning_rate = 0.1) | Accuracy(learning_rate = 0.05) | Accuracy(learning_rate = 0.1+0.05) |
+| ----- | ----------------------------- | ------------------------------ | ---------------------------------- |
+| 0 | 97.27% | 95.85% | 96.59% |
+| 5 | 97.93% | 97.85% | 97.91% |
+| 10 | 98.03% | 98.03% | 98.18% |
+| 15 | 98.12% | 98.09% | 98.18% |
+| 20 | 98.12% | 98.19% | 98.18% |
+
+ +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+
+
+## 优化器
+
+### Adam原理
+
+类似于实验部分做的对学习率的调整,Adam优化器作为一种很多情况下常常使用到的优化器,在自动调整学习率这个点较为出彩,基本已经成为了很多模型优化问题的默认优化器,另一方面初始的学习率选择也影响到了优化过程。
+
+Adam优化器的基本公式为$\theta_t = \theta_{t-1}-\alpha*\hat m_t/(\sqrt{\hat v_t}+\epsilon)$,其中$\hat m_t$以指数移动平均的方式估计样本的一阶矩,并通过超参$\beta_1$的t次方削减初始化为0导致偏差的影响,其基本公式如下,$g_t$为梯度值
+
+$\hat m_t = m_t/(1-\beta_1^t)$,$m_t = \beta_1m_{t-1}+(1-\beta_1)g_t$
+
+类似的计算$\hat v = v_t/(1-\beta_2^t),v_t = \beta_2v_{t-1}+(1-\beta_2)g_t^2$
+
+$\epsilon$目的是为了防止除数变成0
+
+### Momentum原理
+
+Momentum优化器的思路和Adam类似,但是并不考虑标准差对学习率的影响,同样利用滑动窗口机制,指数加权动量,赋给当前梯度一个较小的权重,从而平滑梯度在极值点附近的摆动,更能够接近极值点
+
+其公式如下
+
+$v_t = \beta v_{t-1}+(1-\beta)dW$
+
+$W = W - \alpha v_t$
+
+### 实现
+
+有了如上公式,我在`numpy_mnist.py`中设计了Adam类和Momentum类,由于并不能对`numpy_fnn.py`进行修改,对这两个优化器的实现大体思路变成了,针对每一个变量生成一个优化器,并通过内部变量记录上一轮迭代时参数信息,并计算后返回新的参数,例如Moment的使用呈如下格式:
+
+`model.W1 = W1_opt.optimize(model.W1, model.W1_grad)`
+
+即计算新的权值后,赋给模型
+
+### 实验比较
+
+我们将两个优化器我们同之前获得的最优结果,`lr` = 0.1+0.05方式作比较,loss和Accuracy变化如下
+
+| epoch | Accuracy(learning_rate = 0.1+0.05) | Accuracy(Adam, $\alpha = 0.001$) | Accuracy(Momentum,$\alpha = 0.1$) |
+| ----- | ---------------------------------- | ---------------------------------- | --------------------------------- |
+| 0 | 96.59% | 97.46% | 97.01% |
+| 5 | 97.91% | 97.69% | 97.95% |
+| 10 | 98.18% | 97.80% | 98.07% |
+| 15 | 98.18% | 97.98% | 98.22% |
+| 20 | 98.18% | 98.04% | 98.36% |
+
+
+
+
+
+## 优化器
+
+### Adam原理
+
+类似于实验部分做的对学习率的调整,Adam优化器作为一种很多情况下常常使用到的优化器,在自动调整学习率这个点较为出彩,基本已经成为了很多模型优化问题的默认优化器,另一方面初始的学习率选择也影响到了优化过程。
+
+Adam优化器的基本公式为$\theta_t = \theta_{t-1}-\alpha*\hat m_t/(\sqrt{\hat v_t}+\epsilon)$,其中$\hat m_t$以指数移动平均的方式估计样本的一阶矩,并通过超参$\beta_1$的t次方削减初始化为0导致偏差的影响,其基本公式如下,$g_t$为梯度值
+
+$\hat m_t = m_t/(1-\beta_1^t)$,$m_t = \beta_1m_{t-1}+(1-\beta_1)g_t$
+
+类似的计算$\hat v = v_t/(1-\beta_2^t),v_t = \beta_2v_{t-1}+(1-\beta_2)g_t^2$
+
+$\epsilon$目的是为了防止除数变成0
+
+### Momentum原理
+
+Momentum优化器的思路和Adam类似,但是并不考虑标准差对学习率的影响,同样利用滑动窗口机制,指数加权动量,赋给当前梯度一个较小的权重,从而平滑梯度在极值点附近的摆动,更能够接近极值点
+
+其公式如下
+
+$v_t = \beta v_{t-1}+(1-\beta)dW$
+
+$W = W - \alpha v_t$
+
+### 实现
+
+有了如上公式,我在`numpy_mnist.py`中设计了Adam类和Momentum类,由于并不能对`numpy_fnn.py`进行修改,对这两个优化器的实现大体思路变成了,针对每一个变量生成一个优化器,并通过内部变量记录上一轮迭代时参数信息,并计算后返回新的参数,例如Moment的使用呈如下格式:
+
+`model.W1 = W1_opt.optimize(model.W1, model.W1_grad)`
+
+即计算新的权值后,赋给模型
+
+### 实验比较
+
+我们将两个优化器我们同之前获得的最优结果,`lr` = 0.1+0.05方式作比较,loss和Accuracy变化如下
+
+| epoch | Accuracy(learning_rate = 0.1+0.05) | Accuracy(Adam, $\alpha = 0.001$) | Accuracy(Momentum,$\alpha = 0.1$) |
+| ----- | ---------------------------------- | ---------------------------------- | --------------------------------- |
+| 0 | 96.59% | 97.46% | 97.01% |
+| 5 | 97.91% | 97.69% | 97.95% |
+| 10 | 98.18% | 97.80% | 98.07% |
+| 15 | 98.18% | 97.98% | 98.22% |
+| 20 | 98.18% | 98.04% | 98.36% |
+
+
 +
+### 分析
+
+从表格和loss变化情况来看,Momentum的效果明显优于手动学习率调整,而Adam的效果甚至不如恒定学习率,查看论文中的算法后,我排除了实现错误的可能性,查找了相关资料,发现了这样的一段话:
+
+[简单认识Adam]: https://www.jianshu.com/p/aebcaf8af76e "Adam的缺陷与改进"
+
+虽然Adam算法目前成为主流的优化算法,不过在很多领域里(如计算机视觉的对象识别、NLP中的机器翻译)的最佳成果仍然是使用带动量(Momentum)的SGD来获取到的。Wilson 等人的论文结果显示,在对象识别、字符级别建模、语法成分分析等方面,自适应学习率方法(包括AdaGrad、AdaDelta、RMSProp、Adam等)通常比Momentum算法效果更差。
+
+根据该资料的说法,本次实验手写数字识别应划归为对象识别,自适应学习率方法确为效果更差,Adam的好处在于,对于不稳定目标函数,效果很好,因此,从这里可以看到,优化器选择应该针对实际问题类型综合考量
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Adam.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Adam.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..76c571e3ea0c18e00faf75a5f078350cb86a1159
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Adam.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_1.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..683414e2e126545f2a851da9a05be74eb5261b13
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..bef71ab36ae8d83504f84243e3d64082b8fcab5d
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_3.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_3.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..639051608449345a12b51083243e78dcfa6a4f70
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_3.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_4.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_4.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..fe141456a1e96e256569cdcb37a87e2d4b6f0e6b
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_4.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/matmul.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/matmul.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e3e6d769ef44203d80817a2928a5b1ea2a533e06
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/matmul.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/model.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/model.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..72c73828f7d70be8ea8d3f010b27bc7ada0a4139
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/model.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/momentum.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/momentum.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b9b0b145e362898c6a6cf5f379fe0459abb9fa28
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/momentum.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/softmax1.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/softmax1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..56c1a6c77141e66a1970dc8d7d66d00c891a74d2
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/softmax1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/softmax2.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/softmax2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..277f06da303ed92389cc7620e89ee25bf5b1c7e1
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/softmax2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..13397e1977d0b8bf530900861e08a2176816f780
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,185 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 1 #
+ ####################
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y,self.memory['W'].T)
+ grad_W = np.matmul(self.memory['x'].T, grad_y)
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 2 #
+ ####################
+ grad_x = np.where(self.memory['x'] > 0, grad_y, np.zeros_like(self.memory['x']))
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 3 #
+ ####################
+ grad_x =(1/(self.memory['x'] + self.epsilon)) *grad_y
+
+ return grad_x
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ ####################
+ # code 4 #
+ ####################
+ exp = np.exp(self.memory['x'])
+ one = np.ones((self.memory['x'].shape[1], self.memory['x'].shape[1]))
+ h = 1./np.matmul(exp,one)
+ out = h * exp
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 5 #
+ ####################
+ exp = np.exp(self.memory['x'])
+ one = np.ones((self.memory['x'].shape[1], self.memory['x'].shape[1]))
+ h = 1./np.matmul(exp,one)
+ h_grad = -h * h
+ grad_x = grad_y* exp * h + np.matmul(grad_y * exp * h_grad, one) * exp
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ ####################
+ # code 6 #
+ ####################
+ x = self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1)
+ x = self.relu_1.forward(x)
+ x = self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2)
+ x = self.relu_2.forward(x)
+ x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+ x = self.softmax.forward(x)
+ x = self.log.forward(x)
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+ ####################
+ # code 7 #
+ ####################
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y)
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+ self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+
+
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..dc5fdaa3b169f4a5ec77458993318b1b875ac400
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128, numpy=False, drop_last=False):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+ dataset_num = dataset.__len__()
+ idx = np.arange(dataset_num)
+ np.random.shuffle(idx)
+ for each in dataset:
+ data.append(each[0].numpy())
+ label.append(each[1])
+ label_numpy = np.array(label)[idx]
+ data_numpy = np.array(data)[idx]
+
+ result = []
+ for iter in range(dataset_num // batch_size):
+ result.append((data_numpy[iter*batch_size:(iter+1)*batch_size], label_numpy[iter*batch_size:(iter+1)*batch_size]))
+ if drop_last == False:
+ result.append((data_numpy[(iter+1)*batch_size:dataset_num], label_numpy[(iter+1)*batch_size:dataset_num]))
+ return result
+
+class Adam:
+ def __init__(self, weight, lr=0.0015, beta1=0.9, beta2=0.999, epsilon=1e-8):
+ self.theta = weight
+ self.lr = lr
+ self.beta1 = beta1
+ self.beta2 = beta2
+ self.epislon = epsilon
+ self.m = 0
+ self.v = 0
+ self.t = 0
+
+ def optimize(self, grad):
+ self.t += 1
+ self.m = self.beta1 * self.m + (1 - self.beta1) * grad
+ self.v = self.beta2 * self.v + (1 - self.beta2) * grad * grad
+ self.m_hat = self.m / (1 - self.beta1 ** self.t)
+ self.v_hat = self.v / (1 - self.beta2 ** self.t)
+ self.theta -= self.lr * self.m_hat / (self.v_hat ** 0.5 + self.epislon)
+ return self.theta
+
+class Momentum:
+ def __init__(self, lr=0.1, beta=0.9):
+ self.lr = lr
+ self.beta = beta
+ self.v = 0
+
+ def optimize(self, weight, grad):
+ self.v = self.beta*self.v + (1-self.beta)*grad
+ weight -= self.lr * self.v
+ return weight
+
+def numpy_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+ W1_opt = Momentum()
+ W2_opt = Momentum()
+ W3_opt = Momentum()
+
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 20
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ # if epoch >= 10:
+ # learning_rate = 0.05
+ # else:
+ # learning_rate = 0.1
+ # model.optimize(learning_rate)
+ model.W1 = W1_opt.optimize(model.W1, model.W1_grad)
+ model.W2 = W2_opt.optimize(model.W2, model.W2_grad)
+ model.W3 = W3_opt.optimize(model.W3, model.W3_grad)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b7fd7f8ae075cfb38e5157e595ddff516b3eb44e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,227 @@
+# Assignment-2 Report
+
+
+
+### 分析
+
+从表格和loss变化情况来看,Momentum的效果明显优于手动学习率调整,而Adam的效果甚至不如恒定学习率,查看论文中的算法后,我排除了实现错误的可能性,查找了相关资料,发现了这样的一段话:
+
+[简单认识Adam]: https://www.jianshu.com/p/aebcaf8af76e "Adam的缺陷与改进"
+
+虽然Adam算法目前成为主流的优化算法,不过在很多领域里(如计算机视觉的对象识别、NLP中的机器翻译)的最佳成果仍然是使用带动量(Momentum)的SGD来获取到的。Wilson 等人的论文结果显示,在对象识别、字符级别建模、语法成分分析等方面,自适应学习率方法(包括AdaGrad、AdaDelta、RMSProp、Adam等)通常比Momentum算法效果更差。
+
+根据该资料的说法,本次实验手写数字识别应划归为对象识别,自适应学习率方法确为效果更差,Adam的好处在于,对于不稳定目标函数,效果很好,因此,从这里可以看到,优化器选择应该针对实际问题类型综合考量
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Adam.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Adam.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..76c571e3ea0c18e00faf75a5f078350cb86a1159
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Adam.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_1.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..683414e2e126545f2a851da9a05be74eb5261b13
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..bef71ab36ae8d83504f84243e3d64082b8fcab5d
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_3.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_3.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..639051608449345a12b51083243e78dcfa6a4f70
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_3.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_4.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_4.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..fe141456a1e96e256569cdcb37a87e2d4b6f0e6b
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/Figure_4.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/matmul.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/matmul.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e3e6d769ef44203d80817a2928a5b1ea2a533e06
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/matmul.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/model.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/model.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..72c73828f7d70be8ea8d3f010b27bc7ada0a4139
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/model.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/momentum.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/momentum.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b9b0b145e362898c6a6cf5f379fe0459abb9fa28
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/momentum.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/softmax1.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/softmax1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..56c1a6c77141e66a1970dc8d7d66d00c891a74d2
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/softmax1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/softmax2.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/softmax2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..277f06da303ed92389cc7620e89ee25bf5b1c7e1
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/img/softmax2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..13397e1977d0b8bf530900861e08a2176816f780
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,185 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 1 #
+ ####################
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y,self.memory['W'].T)
+ grad_W = np.matmul(self.memory['x'].T, grad_y)
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 2 #
+ ####################
+ grad_x = np.where(self.memory['x'] > 0, grad_y, np.zeros_like(self.memory['x']))
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 3 #
+ ####################
+ grad_x =(1/(self.memory['x'] + self.epsilon)) *grad_y
+
+ return grad_x
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ ####################
+ # code 4 #
+ ####################
+ exp = np.exp(self.memory['x'])
+ one = np.ones((self.memory['x'].shape[1], self.memory['x'].shape[1]))
+ h = 1./np.matmul(exp,one)
+ out = h * exp
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 5 #
+ ####################
+ exp = np.exp(self.memory['x'])
+ one = np.ones((self.memory['x'].shape[1], self.memory['x'].shape[1]))
+ h = 1./np.matmul(exp,one)
+ h_grad = -h * h
+ grad_x = grad_y* exp * h + np.matmul(grad_y * exp * h_grad, one) * exp
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ ####################
+ # code 6 #
+ ####################
+ x = self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1)
+ x = self.relu_1.forward(x)
+ x = self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2)
+ x = self.relu_2.forward(x)
+ x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+ x = self.softmax.forward(x)
+ x = self.log.forward(x)
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+ ####################
+ # code 7 #
+ ####################
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y)
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+ self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+
+
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..dc5fdaa3b169f4a5ec77458993318b1b875ac400
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130116/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128, numpy=False, drop_last=False):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+ dataset_num = dataset.__len__()
+ idx = np.arange(dataset_num)
+ np.random.shuffle(idx)
+ for each in dataset:
+ data.append(each[0].numpy())
+ label.append(each[1])
+ label_numpy = np.array(label)[idx]
+ data_numpy = np.array(data)[idx]
+
+ result = []
+ for iter in range(dataset_num // batch_size):
+ result.append((data_numpy[iter*batch_size:(iter+1)*batch_size], label_numpy[iter*batch_size:(iter+1)*batch_size]))
+ if drop_last == False:
+ result.append((data_numpy[(iter+1)*batch_size:dataset_num], label_numpy[(iter+1)*batch_size:dataset_num]))
+ return result
+
+class Adam:
+ def __init__(self, weight, lr=0.0015, beta1=0.9, beta2=0.999, epsilon=1e-8):
+ self.theta = weight
+ self.lr = lr
+ self.beta1 = beta1
+ self.beta2 = beta2
+ self.epislon = epsilon
+ self.m = 0
+ self.v = 0
+ self.t = 0
+
+ def optimize(self, grad):
+ self.t += 1
+ self.m = self.beta1 * self.m + (1 - self.beta1) * grad
+ self.v = self.beta2 * self.v + (1 - self.beta2) * grad * grad
+ self.m_hat = self.m / (1 - self.beta1 ** self.t)
+ self.v_hat = self.v / (1 - self.beta2 ** self.t)
+ self.theta -= self.lr * self.m_hat / (self.v_hat ** 0.5 + self.epislon)
+ return self.theta
+
+class Momentum:
+ def __init__(self, lr=0.1, beta=0.9):
+ self.lr = lr
+ self.beta = beta
+ self.v = 0
+
+ def optimize(self, weight, grad):
+ self.v = self.beta*self.v + (1-self.beta)*grad
+ weight -= self.lr * self.v
+ return weight
+
+def numpy_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+ W1_opt = Momentum()
+ W2_opt = Momentum()
+ W3_opt = Momentum()
+
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 20
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ # if epoch >= 10:
+ # learning_rate = 0.05
+ # else:
+ # learning_rate = 0.1
+ # model.optimize(learning_rate)
+ model.W1 = W1_opt.optimize(model.W1, model.W1_grad)
+ model.W2 = W2_opt.optimize(model.W2, model.W2_grad)
+ model.W3 = W3_opt.optimize(model.W3, model.W3_grad)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b7fd7f8ae075cfb38e5157e595ddff516b3eb44e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,227 @@
+# Assignment-2 Report
+
+------李睿琛 18307130130
+## 算子实现 + +`Matmul` + +实现两个矩阵相乘。对于: +$$ +Y = X \times W +$$ +存在函数`Loss = f(Y)`,根据链式法则,求导得: + + +$$ +\frac{\partial L}{\partial W_{ij}}={\sum_{k,l}}\frac{\partial L}{\partial Y_{kl}}\times\frac{\partial Y_{kl}}{\partial W_{ij}} \\\\ +$$ + +$$ +\frac{\partial Y_{kl}}{\partial X_{ij}}=\frac{\partial {\sum_{s}(X_{ks}\times W_{sl})}}{W_{ij}}=\frac{\partial X_{ki}W_{il}}{W_{ij}}=A_{ki}{\delta_{lj}} +$$ + +$$ +\frac{\partial L}{\partial W}=X^T\frac{\partial L}{\partial Y} +$$ + +于是有: +$$ +grad\_w = X^T \times grad\_y\\\\ +同理有: grad\_x = grad\_y \times W^T +$$ +`Relu` + +作为激活函数,具有单侧抑制、宽兴奋边界等生物学合理性。 +$$ +Y_{ij}=\begin{cases} +X_{ij}&X_{ij}\ge0\\\\ +0&\text{otherwise} +\end{cases} +$$ + +求导得: +$$ +\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{mn}}=\begin{cases}1&X_{ij}>0,i=m,j=n\\\\0&\text{otherwise}\end{cases} +$$ + +`Log` + +计算公式为: +$$ +Y_{ij}=\ln(X_{ij}+\epsilon),\epsilon=10^{-12} \\\\ +$$ + +求导得: +$$ +\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{ij}}=\frac1{X_{ij}+\epsilon} +$$ + + +`Softmax` + +称为多项的Logistic回归,表达式为: +$$ +Y_{ij}=\frac{\exp\{X_{ij} \}}{\sum_{k=1}^c\exp\{X_{ik} \}}\\\\ +$$ +向量`Y_i`对向量`X_j`求导得: +$$ +\frac{\partial Y_{i}}{\partial X_{j}}=\begin{cases} +Y_{i}(1-Y_{j})&i=j\\\\ +-Y_{i}Y_{j}&\text otherwise +\end{cases} +$$ + + +## 模型搭建 + +根据`torch_mnist.py`中`TorchModel`方法搭建模型:、 + + + +根据模型计算图,即可得到如下**前馈过程:** + +```python +x = self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1) +x = self.relu_1.forward(x) +x = self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2) +x = self.relu_2.forward(x) +x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3) +x = self.softmax.forward(x) +x = self.log.forward(x) +``` + +**反向传播:** + +首先是标量Loss对向量pred的求导: +$$ +\frac{\partial L}{\partial X^T} =[\frac{\partial L}{\partial x_1},...,\frac{\partial L}{\partial x_n}]^T +$$ +于是有: + +```python +class NumpyLoss: +def backward(self): + return -self.target / self.target.shape[0] +``` + +根据计算图,继续反向传播: + +```python +self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y) +self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad) +self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad) +self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad) +self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad) +self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad) +self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad) +``` + +## mini_batch实现 + +由于数据集巨大,深度学习往往训练速度很慢,导致难以发挥最大效果。相比batch梯度下降法,mini_batch进一步分割数据集,能在一次遍历训练集的过程中做多次梯度下降,收敛到一个合适的精度。获得mini_batch过程为: + +```python +# 将数据集打乱; +sz = data.shape[0] +index = np.arange(sz) +np.random.shuffle(index) + +# 按照batch_size分割数据集; +for start in range(0, sz, batch_size): + ret.append([data[index[start: start+ batch_size]], label[index[start: start+ batch_size]]]) +``` + +## 模型参数影响 + +探究了学习率、batch_size大小对收敛速度的影响。 + +* learning_rate = 0.1,batch_size=128 + +``` +[0] Accuracy: 0.9436 +[1] Accuracy: 0.9610 +[2] Accuracy: 0.9710 +``` + + + +* learning_rate = 0.01,batch_size=128 + +``` +[0] Accuracy: 0.8730 +[1] Accuracy: 0.9047 +[2] Accuracy: 0.9142 +``` + + + +* learning_rate = 0.1,batch_size=512 + +``` +[0] Accuracy: 0.8233 +[1] Accuracy: 0.9244 +[2] Accuracy: 0.9296 +``` + + + +在一定范围内: + +随着学习率的减小,参数收敛速度减小,在相同迭代次数下准确率更低。 + +随着批处理容量的增大,迭代次数减少,震荡幅度减小,随着容量继续增大,可能达到时间上的最优。 + +## 梯度下降算法优化 + +* SGD算法。learning_rate = 0.1,batch_size=512 + +即优化前的算法。 + +* Momentum算法。learning_rate = 0.1,batch_size=512 + +SGN的损失在一个方向上快速变化而在另一个方向慢慢变化。Momentum算法将一段时间内的梯度向量进行了加权平均 ,有利于帮助SGN加速,冲破沟壑,加速收敛。引入动量能够使得在遇到局部最优的时候在动量的基础上**冲出局部最优**;另外也可使**震荡减弱**,更快运动到最优解。 + +**算法实现:** + + + +```python +# 算法实现 +self.beta1 = self.momentum * self.beta1 + (1 - self.momentum) * self.W1_grad +self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.beta1 + +``` 结果 +[0] Accuracy: 0.9058 +[1] Accuracy: 0.9293 +[2] Accuracy: 0.9391 +``` +``` + + + +* Adam算法。learning_rate = 0.1,batch_size=512 + +相比随机梯度下降中**不变**的学习率,Adam算法通过计算梯度的一阶矩估计和二阶矩估计而为不同的参数设计独立的**自适应性学习率**。 + +**算法实现:** + + + +```python +# 算法实现 +self.m1 = self.theta1 * self.m1 + (1 - self.theta1) * self.W1_grad +self.v1 = self.theta2 * self.v1 + (1 - self.theta1) * np.square(self.W1_grad) +m_ = self.m1 / (1 - np.power(self.theta1, self.n)) +v_ = self.v1 / (1 - np.power(self.theta2, self.n)) +self.W1 -= learning_rate * m_ / (np.sqrt(v_) + self.eps) + +``` 结果 +[0] Accuracy: 0.9639 +[1] Accuracy: 0.9661 +[2] Accuracy: 0.9690 +``` +``` + + + +比较三次迭代后的准确率,收敛速度:Adam > Momentum > SGD 。 \ No newline at end of file diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/Adam.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/Adam.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..cfa321ab862467b331f20692c04e66d4fd692ca0 Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/Adam.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/Adam_train.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/Adam_train.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..5fc0b816e78b331003a15c00129951be2cfae4f8 Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/Adam_train.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/Adam_train_512_01.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/Adam_train_512_01.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..2c3bc63fb7fff6797bb16d17a72359f690c133fa Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/Adam_train_512_01.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/Momentum.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/Momentum.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..6d548f77cd3d0ed85d5fbdf48439aea0a2d73955 Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/Momentum.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/Momentum_train.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/Momentum_train.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7a5d77ef53b9a9b832080deb8feae3b1fafacd2a Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/Momentum_train.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/Momentum_train_512_01.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/Momentum_train_512_01.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b33390f9ed07281e4dccba4e26c77cfea23a7238 Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/Momentum_train_512_01.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/SGD_train_128_001.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/SGD_train_128_001.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c581cfa591392a68d65dbda13c82f162f4d81cb4 Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/SGD_train_128_001.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/SGD_train_128_01.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/SGD_train_128_01.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..385a0c3d97846385dad3cbe0a95e3ac9b5b6a4f9 Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/SGD_train_128_01.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/SGD_train_512_01.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/SGD_train_512_01.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e065f65d6fee671ccb2fad718e3a8ce62c7227c5 Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/SGD_train_512_01.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/model.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/model.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e673f6710acb8d4c443cf1622f363b3e76aecbb2 Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/img/model.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/numpy_fnn.py new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..5469a9f2ba16e60bf21e5cbb009e2f2bac50263e --- /dev/null +++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/numpy_fnn.py @@ -0,0 +1,262 @@ +import os +os.environ["KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK"]="TRUE" +import numpy as np + + +class NumpyOp: + + def __init__(self): + self.memory = {} + self.epsilon = 1e-12 + + +class Matmul(NumpyOp): + + def forward(self, x, W): + """ + x: shape(N, d) + w: shape(d, d') + """ + self.memory['x'] = x + self.memory['W'] = W + h = np.matmul(x, W) + return h + + def backward(self, grad_y): + """ + grad_y: shape(N, d') + """ + + #################### + # code 1 # + #################### + + grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, self.memory['W'].T) + grad_W = np.matmul(self.memory['x'].T, grad_y) + + return grad_x, grad_W + + +class Relu(NumpyOp): + + def forward(self, x): + self.memory['x'] = x + return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x)) + + def backward(self, grad_y): + """ + grad_y: same shape as x + """ + + #################### + # code 2 # + #################### + + x = self.memory['x'] + grad_x = grad_y * np.where( x > 0, np.ones_like(x), np.zeros_like(x) ) + + return grad_x + + +class Log(NumpyOp): + + def forward(self, x): + """ + x: shape(N, c) + """ + + out = np.log(x + self.epsilon) + self.memory['x'] = x + + return out + + def backward(self, grad_y): + """ + grad_y: same shape as x + """ + + #################### + # code 3 # + #################### + + x = self.memory['x'] + grad_x = grad_y / (x + self.epsilon) + + return grad_x + + +class Softmax(NumpyOp): + """ + softmax over last dimension + """ + + def forward(self, x): + """ + x: shape(N, c) + """ + + #################### + # code 4 # + #################### + + # 得到矩阵每行的最大值,避免溢出 + row_max = np.max(x, axis=1).reshape(-1, 1) + x -= row_max + x_exp = np.exp(x) + # 每行求和 + sum_exp = np.sum(x_exp, axis=1, keepdims=True) + # out: N * c + out = x_exp / sum_exp + self.memory['out'] = out + + return out + + def backward(self, grad_y): + """ + grad_y: same shape as x + """ + + #################### + # code 5 # + #################### + + out = self.memory['out'] + # Jacobs: N * c * c + Jacobs = np.array([np.diag(x) - np.outer(x, x) for x in out]) + + # (B, n, m) * (B, m, d) = (B, n, d) + grad_y = grad_y[:, np.newaxis, :] + grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, Jacobs).squeeze(axis=1) + + return grad_x + + +class NumpyLoss: + + def __init__(self): + self.target = None + + def get_loss(self, pred, target): + self.target = target + return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean() + + def backward(self): + return -self.target / self.target.shape[0] + + +class NumpyModel: + def __init__(self): + self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256)) + self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64)) + self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10)) + + # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用 + self.matmul_1 = Matmul() + self.relu_1 = Relu() + self.matmul_2 = Matmul() + self.relu_2 = Relu() + self.matmul_3 = Matmul() + self.softmax = Softmax() + self.log = Log() + + # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新。 softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导) + self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None + self.relu_1_grad = None + self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None + self.relu_2_grad = None + self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None + self.softmax_grad = None + self.log_grad = None + + # Momentum parameters + self.beta1 = np.zeros_like(self.W1) + self.beta2 = np.zeros_like(self.W2) + self.beta3 = np.zeros_like(self.W3) + self.momentum = 0.9 + + # Adam parameters + self.theta1 = 0.9 + self.theta2 = 0.999 + self.eps = 1e-8 + self.m1 = np.zeros_like(self.W1) + self.v1 = np.zeros_like(self.W1) + self.m2 = np.zeros_like(self.W2) + self.v2 = np.zeros_like(self.W2) + self.m3 = np.zeros_like(self.W3) + self.v3 = np.zeros_like(self.W3) + self.n = 0 + + def forward(self, x): + x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28) + + #################### + # code 6 # + #################### + + x = self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1) + x = self.relu_1.forward(x) + x = self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2) + x = self.relu_2.forward(x) + x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3) + x = self.softmax.forward(x) + x = self.log.forward(x) + + return x + + def backward(self, y): + + #################### + # code 7 # + #################### + + self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y) + self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad) + self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad) + self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad) + self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad) + self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad) + self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad) + + return self.x1_grad + + def optimize(self, learning_rate): + def SGD(): + self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad + self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad + self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad + + def Momentum(): + + self.beta1 = self.momentum * self.beta1 + (1 - self.momentum) * self.W1_grad + self.beta2 = self.momentum * self.beta2 + (1 - self.momentum) * self.W2_grad + self.beta3 = self.momentum * self.beta3 + (1 - self.momentum) * self.W3_grad + self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.beta1 + self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.beta2 + self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.beta3 + + def Adam(): + + self.n += 1 + + self.m1 = self.theta1 * self.m1 + (1 - self.theta1) * self.W1_grad + self.v1 = self.theta2 * self.v1 + (1 - self.theta1) * np.square(self.W1_grad) + m_ = self.m1 / (1 - np.power(self.theta1, self.n)) + v_ = self.v1 / (1 - np.power(self.theta2, self.n)) + self.W1 -= learning_rate * m_ / (np.sqrt(v_) + self.eps) + + self.m2 = self.theta1 * self.m2 + (1 - self.theta1) * self.W2_grad + self.v2 = self.theta2 * self.v2 + (1 - self.theta1) * np.square(self.W2_grad) + m_ = self.m2 / (1 - np.power(self.theta1, self.n)) + v_ = self.v2 / (1 - np.power(self.theta2, self.n)) + self.W2 -= learning_rate * m_ / (np.sqrt(v_) + self.eps) + + self.m3 = self.theta1 * self.m3 + (1 - self.theta1) * self.W3_grad + self.v3 = self.theta2 * self.v3 + (1 - self.theta1) * np.square(self.W3_grad) + m_ = self.m3 / (1 - np.power(self.theta1, self.n)) + v_ = self.v3 / (1 - np.power(self.theta2, self.n)) + self.W3 -= learning_rate * m_ / (np.sqrt(v_) + self.eps) + + SGD() + #Momentum() + #Adam() + diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/numpy_mnist.py new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ec9d23563037904e97a1952d4a23a6b6518031bf --- /dev/null +++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130130/numpy_mnist.py @@ -0,0 +1,51 @@ +import numpy as np +from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss +from utils import download_mnist, batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot + +def mini_batch(train_dataset, batch_size=128): + data = np.array([np.array(x[0]) for x in train_dataset]) + label = np.array([np.array(x[1]) for x in train_dataset]) + + sz = data.shape[0] + index = np.arange(sz) + np.random.shuffle(index) + + ret = [] + for start in range(0, sz, batch_size): + ret.append([data[index[start: start+ batch_size]], label[index[start: start+ batch_size]]]) + return ret + + +def numpy_run(): + train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist() + + model = NumpyModel() + numpy_loss = NumpyLoss() + model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization() + + train_loss = [] + + epoch_number = 3 + learning_rate = 0.1 + + for epoch in range(epoch_number): + for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset, batch_size=512): + y = one_hot(y) + y_pred = model.forward(x) + loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y) + + # numpy_loss.backward().shape: batch_size * 10 + model.backward(numpy_loss.backward()) + model.optimize(learning_rate) + + train_loss.append(loss.item()) + + x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0] + accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y)) + print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy)) + + plot_curve(train_loss) + + +if __name__ == "__main__": + numpy_run() diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/README.md new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..51cea514496f5e1d5ba2fae3e49da09fe4afb6ca --- /dev/null +++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/README.md @@ -0,0 +1,488 @@ +# Assignment 2——选题1 报告 + +## 概述 + +本次实验实现了简单的几个Pytorch算子,包括正向计算和反向传播,同时记录了反向传播的公式推导。然后搭建了简单的模型,在Mnist手写体数据集上进行了测试。 + +**作为扩展,我调研了Pytorch的权重初始化方法——Xavier初始化和Kaiming初始化,用Numpy实现了numpyutils工具包替代utils(现在放在numpy_mnist中了)。** + +## 算子及推导 + +### Matmul + +此算子进行两个矩阵的求积运算 + +**推导** + +设反向传播的开始节点(叶节点)为 **L**,这是一个标量,下同。 + +设正向计算中两个输入矩阵为 **P(m * k) , Q(k * n)**, 输出矩阵为 **O(m * n)**; 反向传播中输入的梯度为 **G(m * n)**。 + +则有 +$$ +G_{ij} = \frac{\partial L}{\partial O_{ij}} +$$ +此公式对后面的算子同样适用。 + +**计算Q的梯度 GQ (k * n)** + +首先有 +$$ +\begin{aligned} + GQ {ts}&= \frac{\partial L}{\partial Q_{ts}} \\\\ + &=\sum_{i \leqslant m\\ j\leqslant n} \frac{\partial L}{\partial O_{ij}} \times \frac{\partial O_{ij}}{\partial Q_{ts}}\\\\ + &=\sum_{i \leqslant m\\ j = s} G_{ij} \times \frac{\partial O_{ij}}{\partial Q_{ts}} + &(其余的 \frac{\partial O_{ij}}{\partial Q_{ts}} = 0)\\\\ + &=\sum_{i \leqslant m} G_{is} \times P_{it}\\\\ + &=\sum_{i \leqslant m} P_{ti}^T \times G_{is} +\end{aligned} +$$ +所以写成矩阵乘法为 +$$ +GQ {ts} = P^T \times G +$$ +同理,**P的梯度为** +$$ +GP {ts} = G \times Q^T +$$ + +### Relu + +设输入为**X**,输出为**Y**,Relu层的输出矩阵中每个元素**只与输入矩阵中对应位置的元素有关**,设对应位置元素为**x** , **y**。 + +则有 +$$ +y = relu(x)= + \begin{cases} + 0& x \leq 0\\\\ + x& x \geq 0 + \end{cases} +$$ +和 +$$ +\frac{\partial Y_{ts}}{\partial X_{ij}} = + \begin{cases} + 1& t = i& and & s = j & and & X_{ij} > 0 \\\\ + 0& else + \end{cases} +$$ + +于是 +$$ +\frac{\partial L}{\partial X_{ij}} = \frac{\partial L}{\partial Y_{ij}} \times \frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{ij}} +$$ +设M为X的掩码矩阵,其中M中元素m定义为:当X对应位置为正数时,m为1;否则m为0。那么上面的式子写成矩阵的形式: +$$ +GX = GY * M +$$ +其中 $*$ 表示矩阵的点乘,即对应位相乘。 + +### Log + +设输入为**X**,输出为**Y**,Log层的输出矩阵中每个元素**只与输入矩阵中对应位置的元素有关**,设对应位置元素为**x** , **y**。 + +则有 +$$ +\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{1}{x} +$$ +与Relu同理,设矩阵M定义为:M和X形状相同,且 +$$ +M_{ij} = \frac{1}{X_{ij}} +$$ +则有 +$$ +GX = GY * M +$$ + +### Softmax + +设输入为**X**,输出为**Y**,其中**X**的第一维可以看成batch维,所以Softmax层的输出矩阵中每个元素只与输入矩阵中对应位置元素**所在行的元素**有关。方便起见,我们先考虑batch size为1的输入,即X (1 * n),并且用 +$$ +X_i +$$ +来简写 X 中第一行第 i 列的元素。 + +输出Y 也是 1 * n 的矩阵,我们使用和 X 相同的表示规则。那么,正向计算公式为 +$$ +Y_i = \frac{e^{X_i}}{\sum_{k=1}^n e^{X_k}} +$$ +梯度公式为: +$$ +\frac{\partial Y_i}{\partial X_j} = + \begin{cases} + Y_i \times (1 - Y_i) & i = j\\\\ + -Y_i \times Y_j & i \neq j + \end{cases} +$$ + +根据上面的公式可以计算出向量Y对向量X求导的雅各比矩阵**J (n * n)**, 定义如下 +$$ +J_{ij} = \frac{\partial Y_i}{\partial X_j} +$$ +那么 +$$ +\begin{aligned} +GX_{i} &= \frac{\partial L}{\partial X_i} \\\\ + &=\sum_{k=1}^{n}\frac{\partial L}{\partial Y_k} \times \frac{\partial Y_k}{\partial X_i}\\\\ + &=\sum_{k=1}^{n} GY_k \times J_{ki}\\\\ + &=\sum_{k=1}^{n} GY_{1k} \times J_{ki}\\\\ + &=GY \times J\\\\ + &(其中GY为Y的梯度,是这一层反向传播的输入) +\end{aligned} +$$ +我们已经推出了在输入X的第一维为1的情况下的反向传播公式,事实上,当X的第一维(batch size)大于1时,只需要添加一个最高维,扩展 X, Y, GY, J, 并利用numpy的函数: + +```python +numpy.matmul() +``` + +将自动执行张量计算,得到 GX。 + +## 模型训练与测试 + +### 模型搭建 + +首先按照 torch_mnist 搭建模型。 + +**正向传播** + +```python +x = self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1) +x = self.relu_1.forward(x) +x = self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2) +x = self.relu_2.forward(x) +x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3) +x = self.softmax.forward(x) +x = self.log.forward(x) +``` + +~~**反向传播**~~(这里由于后面测试例做了改动,这里的模型也随之变化,最终的模型在下面) + +这里有一点要注意,torch的反向传播以**标量(叶子结点)**为开始,但是我们定义的模型没有最后的激活为标量的层,所以最高层的梯度要手动计算。看到测试例中torch使用的标量(Loss)为: + +```python +loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean() +``` + +因为有一个对列求均值的操作,所以激活层的权重矩阵(也即最高层的梯度矩阵),为**- y / y.shape[0]**,但是在模型反向传播的函数中已经有这样一段代码: + +```python +for size in y.shape: + y /= size +``` + +y的符号相反,并且多除了一个y.shape[1], 所以我在反向传播一开始,把这个弥补进顶层梯度里面了,最终的code 7: + +```python +#################### +# code 7 # +#################### + +#mulgrade = mulgrade3 +#x3_grade = mulgrade2 +#x2_grade = mulgrade1 +#x1_grade = input_grad + +y *= (-y.shape[1]) +self.log_grad = y +self.softmax_grad = self.log.backward(self.log_grad) + +mulgrade = self.softmax.backward(self.softmax_grad) +self.relu_2_grad,self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(mulgrade) + +self.x3_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad) +self.relu_1_grad,self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.x3_grad) + +self.x2_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad) +self.x1_grad,self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.x2_grad) +``` + +**反向传播版本2** + +现在_grad 表示对应层的 input 的梯度,直接贴代码 + +```python +self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y) +self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad) + +mulgrade3,self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad) +self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(mulgrade3) + +mulgrade2,self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad) +self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(mulgrade2) + +self.x1_grad,self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad) +``` + +### 用numpy实现mini_batch + +将数据集打乱,并根据batch_size分割 + +```python +def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128, numpy=False): + data = [] + label = [] + for x in dataset: + data.append(np.array(x[0])) + label.append(x[1]) + data = np.array(data) + label = np.array(label) + + #索引随机打乱 + siz = data.shape[0] + ind = np.arange(siz) + np.random.shuffle(ind) + + #划分batch + res = [] + con = 0 + while con + batch_size <= siz: + data_batch = data[ind[con:con + batch_size]] + label_batch = label[ind[con:con + batch_size]] + res.append((data_batch,label_batch)) + con += batch_size + + return res +``` + +### 训练与测试 + +这部分代码助教已经给出,使用的是mnist手写体数据集。下载数据集后,对每个epoch,按照batch_size将数据读入,并使用模型进行一次正向计算、反向传播、优化。主要部分: + +```python +for epoch in range(epoch_number): + for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset): + + y = one_hot(y) + + # y_pred = model.forward(x.numpy()) + y_pred = model.forward(x) + loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(axis=1).mean() + model.backward(y) + model.optimize(learning_rate) + + train_loss.append(loss.item()) + + x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0] + accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y)) + print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy)) +``` + +### 测试结果 + +**损失函数** + + + +**每一轮epoch后正确率(共3轮)** + +``` +[0] Accuracy: 0.9459 +[1] Accuracy: 0.9635 +[2] Accuracy: 0.9713 +``` + + + +## 扩展——Pytorch权重初始化方法 + +### 结论 + +结论写在前。Pytorch线性层采取的默认初始化方式是**Kaiming**初始化,这是由我国计算机视觉领域专家**何恺明**提出的。我的探究主要包括: + +* 为什么采取Kaiming初始化? +* 考察Kaiming初始化的基础——Xavier初始化的公式 +* 考察Kaiming初始化的公式 +* 用Numpy实现一个简易的Kaiming初始化 + +### 为什么采取Kaiming初始化? + +**采取固定的分布?** + +当考虑怎么初始化权重矩阵这个问题时,可以想到应该使得初始权重具有随机性。提到随机,自然的想法是使用**均匀分布或正态分布**,那么我们如果采用**与模型无关的固定分布**(例如标准正态分布(均值为0,方差为1))怎么样?下面我们分析如果对模型本身不加考虑,采取固定的分布,会有什么问题: + +* 如果权重的绝对值太小,在多层的神经网络的每一层,输入信号的方差会不断减小;当到达最终的输出层时,可以理解为输入信号的影响已经降低到微乎其微。一方面训练效果差,另一方面可能会有梯度消失等问题。(此处从略,参考https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/25631496) +* 如果权重的绝对值太大,同样道理,随着深度的加深,可能会使输入信号的方差过大,这会造成梯度爆炸或消失的问题。 + +这里举一个例子,假如一个网络使用了多个sigmoid作为中间层(这个函数具有两边导数趋于0的特点): + +* 如果权重初始绝对值太小,随着深度的加深,输入信号的方差过小。当输入很小时,sigmoid函数接近线性,深层模型也失去了非线性性的优点。(**模型效果**) +* 如果权重初始绝对值太大,随着深度的加深,输入信号的方差过大。绝对值过大的sigmoid输入意味着激活变得饱和,梯度将开始接近零。(**梯度消失**) + +### Xavier初始化 + +前面的问题提示我们要根据模型的特点(维度,规模)决定使用的随机化方法(分布的均值、方差),**xavier初始化**应运而生,它可以使得输入值经过网络层后**方差不变**。pytorch中这一点是通过增益值gain来实现的,下面的函数用来获得特定层的gain: + +```python +torch.nn.init.calculate_gain(nonlinearity, param=None) +``` + +增益值表(图片摘自https://blog.csdn.net/winycg/article/details/86649832) + + + +Xavier初始化可以采用均匀分布 **U(-a, a)**,其中a的计算公式为: +$$ +a = gain \times \sqrt[]{\frac{6}{fan\_in+fan\_out}} +$$ +Xavier初始化可以采用正态分布 **N(0, std)**,其中std的计算公式为: +$$ +std = gain \times \sqrt[]{\frac{2}{fan\_in+fan\_out}} +$$ +其中fan_in和fan_out分别是输入神经元和输出神经元的数量,在全连接层中,就等于输入输出的feature数。 + +### Kaiming初始化 + +Xavier初始化在Relu层表现不好,主要原因是relu层会将负数映射到0,影响整体方差。所以**何恺明**在对此做了改进提出Kaiming初始化,一开始主要应用于计算机视觉、卷积网络。 + +Kaiming均匀分布的初始化采用**U(-bound, bound)**,其中bound的计算公式为:(a 的概念下面再说) +$$ +bound = \sqrt[]{\frac{6}{(1 + a ^2) \times fan\_in}} +$$ +这里补充一点,pytorch中这个公式也通过gain作为中间变量实现,也就是: +$$ +bound = gain \times \sqrt[]{\frac{3}{ fan\_in}} +$$ +其中: +$$ +gain = \sqrt{\frac{2}{1 + a^2}} +$$ +Kaiming正态分布的初始化采用**N(0,std)**,其中std的计算公式为: +$$ +std = \sqrt[]{\frac{2}{(1 + a ^2) \times fan\_in}} +$$ +这里稍微解释一下a的含义,源码中的解释为 + +``` +the negative slope of the rectifier used after this layer +``` + +简单说,是用来衡量这一层中负数比例的,负数越多,Relu层会将越多的输入“抹平”为0,a用来平衡这种“抹平”对于方差的影响。 + +### 我们使用的初始化 + +看一下我们现在使用的get_torch_initialization函数,可以看到是通过调用pytorch的线性层进行的默认初始化: + +```python +fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(28 * 28, 256) +``` + +在Linear类中通过 + +```python +self.reset_parameters() +``` + +这个函数来完成随机初始化的过程,后者使用的是 + +```python +init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight, a=math.sqrt(5)) +``` + +可见是我们前面提到的Kaiming均匀分布的初始化方式,这个函数的内容和前面的公式相符(使用gain作为中间变量): + +```python +fan = _calculate_correct_fan(tensor, mode) +gain = calculate_gain(nonlinearity, a) +std = gain / math.sqrt(fan) +bound = math.sqrt(3.0) * std # Calculate uniform bounds from standard deviation +with torch.no_grad(): + return tensor.uniform_(-bound, bound) +``` + +~~同时将参数a 的值设置为5。~~ + +同时将参数a 的值设置为根号5。 + +### ~~使用numpy完成get_torch_initialization~~ 修正 + +简单起见,我没有按照pytorch的封装方法分层实现初始化过程,后者主要为了提供多种不同的初始化方式。我直接按照线性层默认的初始方式——Kaiming均匀分布的公式用numpy实现了get_torch_initialization,其中a值取5, 代码如下: + +```python +def get_torch_initialization(numpy = True): + + a = 5 + + def Kaiming_uniform(fan_in,fan_out,a): + bound = 6.0 / (1 + a * a) / fan_in + bound = bound ** 0.5 + W = np.random.uniform(low=-bound, high=bound, size=(fan_in,fan_out)) + return W + + W1 = Kaiming_uniform(28 * 28, 256, a) + W2 = Kaiming_uniform(256, 64, a) + W3 = Kaiming_uniform(64, 10, a) + return W1,W2,W3 +``` + +顺便,我将utils其它函数(包括之前的mini_batch)转化为numpy版本,~~写在了numpyutils中~~现在全放在了numpy_mnist中。这样,使用这个工具包可以不使用torch包进行numpy_mnist。特别指出的是,download_mnist依然需要使用 torchvision这个包下载数据集。 + +### ~~测试~~ 修正 + +在numpy_mnist替换了工具包之后重新运行,正确率和之前基本一致。 + +```python +[0] Accuracy: 0.9340 +[1] Accuracy: 0.9584 +[2] Accuracy: 0.9684 +``` + +## 4月27日 对初始化方式的修正 + +之前提交的版本中采取和Linear层默认初始化方式相同的方式进行初始化,今天发现存在以下两方面的问题(特别感谢**彭润宇**同学的提醒): + +* Pytorch线性层采取默认初始化中,假定非线性层为**Leaky Relu**,并设置a值默认为**根号5**,而非5。前面我公式中采用了5,会造成很不好的效果。 +* 如**何恺明**论文中所述,a值代表leaky relu层负斜率,我们采用relu层,理论上a值应该取0才符合Kaiming初始化设计初衷。 + +本次修正针对上面两处问题进行修改,并补充探讨a值的选取。 + +### 修改 + +修改后的get_torch_initialization将a作为入参,并设置默认值为0,作为Relu层的Kaiming初始化方法。 + +```python +def get_torch_initialization(numpy = True,a = 0): + def Kaiming_uniform(fan_in,fan_out,a): + bound = 6.0 / (1 + a * a) / fan_in + bound = bound ** 0.5 + W = np.random.uniform(low=-bound, high=bound, size=(fan_in,fan_out)) + return W + + W1 = Kaiming_uniform(28 * 28, 256, a) + W2 = Kaiming_uniform(256, 64, a) + W3 = Kaiming_uniform(64, 10, a) + return W1,W2,W3 +``` + +### 对a值选取进行测试 + +Pytorch的Linear层默认非线性激活层为Leaky Relu,并将a设置为根号5的做法发人深思。为了比较a值选择对效果的影响,我选取不同的a值在原数据集上进行了测试(a从0到6,间隔为0.3,同时统计第1、2、3次迭代后的正确率)。但结果不甚理想,事实上结果中权重初始化方式对3轮迭代后的正确率影响很不明显,即使仅在第一轮迭代后。可以想见的原因包括: + +* 我们的模型及数据不会产生**梯度消失**或**神经元死亡**的问题 +* batch的随机性,测试次数少 + +我在img中保留了测试结果。但是对于我们的模型,还是按照何恺明在论文中指出的规则,对于Relu层使用a = 0。 + +### 一点问题 + +Pytorch对线性层的默认初始化中a值的选取令人困惑,按照何恺明指出,a值应该选择Leaky Relu层的**负斜率**,这个值应该是小于1 的正数(pytorch下层源码中是这样使用的,如下图) + + + +但在linear层中将其默认值设置为根号5: + +```python +init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight, a=math.sqrt(5)) +``` + +这两者存在矛盾,使得默认的线性层初始化中会将a=$\sqrt{5}$代入公式: +$$ +bound = \sqrt[]{\frac{6}{(1 + a ^2) \times fan\_in}} +$$ +得到一个较小的bound。 + +曾有多名国内外网友提及这个问题,目前我没有看到这个问题合理的解释,其中一个讨论的地址: + +https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/15314 + +我认为这有可能是Pytorch(version 3)的一处歧义甚至错误。 \ No newline at end of file diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/20190125144412278.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/20190125144412278.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..fcbc3a2982c4162900790d4e3d479717765b743f Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/20190125144412278.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210425011755375.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210425011755375.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..62a58dedaff524c0d49407a1103b4ac0d7e8d022 Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210425011755375.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210425230057530.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210425230057530.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7779533c9222baca603aab11e54f32d58054bb90 Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210425230057530.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210425230119977.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210425230119977.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..70f10047ed945ea6ac69f36d9a80195e11de4967 Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210425230119977.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427200512951.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427200512951.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..43189faca346fc18e2938d53d39691aea37c954e Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427200512951.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427203245993.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427203245993.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..52cfc7d3907638f1502a6a89866f44a6af6b73bd Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427203245993.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427203300617.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427203300617.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..24b35eed4c9f022a11991135806034b706dec21c Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427203300617.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427203337433.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427203337433.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..912b1ca130c033a9ba33e0f0b30254843241c5bc Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427203337433.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427205224362.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427205224362.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..1bb5da48837686d89da73925b935accbe5454c17 Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427205224362.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427205245840.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427205245840.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..4ec5e96e75e7987a6d12d4977a49205c03ca923a Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427205245840.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427205308848.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427205308848.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..060021006b29d7907d064146375f28b30079459e Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427205308848.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427212809776.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427212809776.png new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d0e834c5023e6ce211c264c0c386a97af8e21172 Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/img/image-20210427212809776.png differ diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/numpy_fnn.py new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..9eb8a954dc83f8c8125a655602af0cac7933c4de --- /dev/null +++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/numpy_fnn.py @@ -0,0 +1,215 @@ +import numpy as np + + +class NumpyOp: + + def __init__(self): + self.memory = {} + self.epsilon = 1e-12 + + +class Matmul(NumpyOp): + + def forward(self, x, W): + """ + x: shape(N, d) + w: shape(d, d') + """ + self.memory['x'] = x + self.memory['W'] = W + h = np.matmul(x, W) + return h + + def backward(self, grad_y): + """ + grad_y: shape(N, d') + """ + + #################### + # code 1 # + #################### + x = self.memory['x'] + W = self.memory['W'] + + grad_W = np.matmul(x.T,grad_y) + grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y,W.T) + return grad_x, grad_W + + +class Relu(NumpyOp): + + def forward(self, x): + self.memory['x'] = x + return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x)) + + def backward(self, grad_y): + """ + grad_y: same shape as x + """ + + #################### + # code 2 # + #################### + x = self.memory['x'] + x1 = np.where(x > 0, 1, 0) + grad_x = x1 * grad_y + return grad_x + + +class Log(NumpyOp): + + def forward(self, x): + """ + x: shape(N, c) + """ + + out = np.log(x + self.epsilon) + self.memory['x'] = x + + return out + + def backward(self, grad_y): + """ + grad_y: same shape as x + """ + + #################### + # code 3 # + #################### + x = self.memory['x'] + grad_x = 1/(x + self.epsilon) + grad_x = grad_x * grad_y + return grad_x + + +class Softmax(NumpyOp): + """ + softmax over last dimension + """ + + def forward(self, x): + """ + x: shape(N, c) + """ + + #################### + # code 4 # + #################### + self.memory['x'] = x + ex = np.exp(x) + rowsum = np.sum(ex,axis=1) + rowsum = rowsum[:,np.newaxis] + softmax = ex / rowsum + self.memory['softmax'] = softmax + return softmax + + + def backward(self, grad_y): + """ + grad_y: same shape as x + """ + + #################### + # code 5 # + #################### + sm = self.memory['softmax'] + Jacobs = [] + for i in range(sm.shape[0]): + r = sm[i] + #对每一行求雅各比矩阵(因为导数只与本行有关) + J = np.diag(r) - np.outer(r, r) + Jacobs.append(J) + Jacobs = np.array(Jacobs) + + grad_y = grad_y[:,np.newaxis,:] + grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y,Jacobs) + grad_x = np.squeeze(grad_x,axis=1) + + return grad_x + +class NumpyLoss: + + def __init__(self): + self.target = None + + def get_loss(self, pred, target): + self.target = target + return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean() + + def backward(self): + return -self.target / self.target.shape[0] + + +class NumpyModel: + def __init__(self): + self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256)) + self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64)) + self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10)) + + + # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用 + self.matmul_1 = Matmul() + self.relu_1 = Relu() + self.matmul_2 = Matmul() + self.relu_2 = Relu() + self.matmul_3 = Matmul() + self.softmax = Softmax() + self.log = Log() + + # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新 + self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None + self.relu_1_grad = None + self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None + self.relu_2_grad = None + self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None + self.softmax_grad = None + self.log_grad = None + + + def forward(self, x): + x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28) + + #################### + # code 6 # + #################### + x = self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1) + x = self.relu_1.forward(x) + x = self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2) + x = self.relu_2.forward(x) + x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3) + x = self.softmax.forward(x) + x = self.log.forward(x) + + return x + + def backward(self, y): + + + + #################### + # code 7 # + #################### + + self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y) + self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad) + + mulgrade3,self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad) + self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(mulgrade3) + + mulgrade2,self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad) + self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(mulgrade2) + + self.x1_grad,self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad) + + + + pass + + def optimize(self, learning_rate): + self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad + self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad + self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad + + + + \ No newline at end of file diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/numpy_mnist.py new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..1abc1e73eef32967faa94c5f1d93f20f8ae96d2d --- /dev/null +++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130154/numpy_mnist.py @@ -0,0 +1,112 @@ +from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss + +import numpy as np +from matplotlib import pyplot as plt + +def get_torch_initialization(numpy = True,a=0): + + + def Kaiming_uniform(fan_in,fan_out,a): + bound = 6.0 / (1 + a * a) / fan_in + bound = bound ** 0.5 + W = np.random.uniform(low=-bound, high=bound, size=(fan_in,fan_out)) + return W + + W1 = Kaiming_uniform(28 * 28, 256, a) + W2 = Kaiming_uniform(256, 64, a) + W3 = Kaiming_uniform(64, 10, a) + return W1,W2,W3 + +def plot_curve(data): + plt.plot(range(len(data)), data, color='blue') + plt.legend(['loss_value'], loc='upper right') + plt.xlabel('step') + plt.ylabel('value') + plt.show() + +def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128, numpy=False): + data = [] + label = [] + for x in dataset: + data.append(np.array(x[0])) + label.append(x[1]) + data = np.array(data) + label = np.array(label) + + #索引随机打乱 + siz = data.shape[0] + ind = np.arange(siz) + np.random.shuffle(ind) + + #划分batch + res = [] + con = 0 + while con + batch_size <= siz: + data_batch = data[ind[con:con + batch_size]] + label_batch = label[ind[con:con + batch_size]] + res.append((data_batch,label_batch)) + con += batch_size + + return res + +def batch(dataset, numpy=True): + data = [] + label = [] + for x in dataset: + data.append(np.array(x[0])) + label.append(x[1]) + data = np.array(data) + label = np.array(label) + return [(data, label)] + +def one_hot(y, numpy=True): + y_ = np.zeros((y.shape[0], 10)) + y_[np.arange(y.shape[0], dtype=np.int32), y] = 1 + return y_ + +def download_mnist(): + from torchvision import datasets, transforms + + transform = transforms.Compose([ + transforms.ToTensor(), + transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.1307,), std=(0.3081,)) + ]) + + train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=True, download=True) + test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=False, download=True) + + return train_dataset, test_dataset + +def numpy_run(): + train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist() + + model = NumpyModel() + numpy_loss = NumpyLoss() + model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization() + + train_loss = [] + + epoch_number = 3 + learning_rate = 0.1 + + for epoch in range(epoch_number): + for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset): + y = one_hot(y) + + y_pred = model.forward(x) + loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y) + + model.backward(numpy_loss.backward()) + model.optimize(learning_rate) + + train_loss.append(loss.item()) + + x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0] + accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y)) + print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy)) + + plot_curve(train_loss) + + +if __name__ == "__main__": + numpy_run() diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130213/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/18307130213/README.md new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..44314b9df69abb8780c981955900b82f26b376e5 --- /dev/null +++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130213/README.md @@ -0,0 +1,100 @@ +# 课程报告 + +## NumpyModel 类实现 + + `NumpyModel` 类的实现位于 [numpy_fnn.py](./numpy_fnn.py) 。 + +具体内容包括: + +1. 实现 `Matmul, Relu, Log, Softmax` 等支持前向传播和反向传播的基础算子类。 +2. 完善 `NumpyModel` 的前向传播函数 `forward` 和反向传播函数 `backward` 。 + + + +## 模型训练与测试 + +此模型应用了新的初始化方法即非 `PyTorch` 版初始化,在第一个 `epoch` 能达到更好的效果。 + +单次实验的三个 `epoch` 中,模型的准确率分别在 95.7%, 96.6%, 97.2% 附近波动,以下为某次实验的结果: + +``` +[0] Accuracy: 0.9550 +[1] Accuracy: 0.9651 +[2] Accuracy: 0.9723 +``` + +对应的图像为: + + + +可以看到,随着模型训练过程 `Loss` 逐渐收敛于某个较小值。 + + + +## 数据处理和参数初始化 + +在 `NumPy` 库基础上实现了 `mini_batch` 函数和 `get_torch_initialization` 函数,位于[numpy_mnist.py](./numpy_mnist.py) 。 + +其中 `get_torch_initialization` 函数使用了**何恺明**提出的 `Kaiming` 初始化方法。这也是 `PyTorch` 线性层默认的初始化方法。 + +究其原因可能有以下两方面的考量: + +1. 若权重初始绝对值过小,导致信号逐层衰减,激活函数趋于线性。 +2. 若权重初始绝对值过大,导致信号逐层放大,激活函数饱和,可能造成梯度消失等后果。 + +使用 `Kaiming` 初始化可以得到一个适中的随机分布值,有效地加强训练效果。 + +### Kaiming初始化公式 + + `Kaiming` 初始化方法相较于其他方法可以在使用 `relu` 或 `leaky_relu` 时取得更好的效果。 + +令 `a` 为 `leaky_relu` 的负区域所对应的的斜率且尽量保证 $a<1$,显然对于 `relu` 有 $a = 0$。 + + `Kaiming` 初始化即使用某个均匀分布 `U(-bound, bound)` 对参数矩阵进行初始化。 + +其中 `bound` 的计算公式为 +$$ +bound = \sqrt[]{\frac{6}{(1 + a ^2) \times fan\_in}} +$$ + `fan_in` 为扇入部分的参数个数。 + +此方法的具体实现见 `get_torch_initialization` 函数。 + + + +## 反向传播算子公式推导 + +在本实验中,大部分算子要求进行矩阵对矩阵求导,正确的求导方式应先将矩阵向量化,进行向量对向量的求导。 + + + + +### Matmul算子 + + + +### Relu算子 + + + +### log算子 + + + +### softmax算子 + + + +## 总结 + +已完成:自动测试 `60%` + +已完成:模仿 `torch_mnist.py` 的代码,在 `numpy_mnist.py` 中进行模型的训练和测试,并在报告中介绍你的实验过程与结果 `20%` + + 已完成:在 `numpy_mnist.py` 中只用 `NumPy` 实现 `mini_batch` 函数,替换 `utils.py` 中使用 `PyTorch` 实现的 `mini_batch` 函数 `10%` + +已完成:在报告中推导 `numpy_fnn.py` 中实现算子的反向传播计算公式 `10%` + +已完成:调研 `PyTorch` 中权重初始化的方法,并实现代码替换 `get_torch_initialization` 函数 `10%` + +已完成:相关 `bug` 查杀工作 \ No newline at end of file diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130213/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130213/numpy_fnn.py new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..13e65fbb9150c6c4643cfeec3fa0c31e3eaf4005 --- /dev/null +++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130213/numpy_fnn.py @@ -0,0 +1,161 @@ +import numpy as np + + +class NumpyOp: + + def __init__(self): + self.memory = {} + self.epsilon = 1e-12 + + +class Matmul(NumpyOp): + + def forward(self, x, W): + """ + x: shape(N, d) + w: shape(d, d') + """ + self.memory['x'] = x + self.memory['W'] = W + h = np.matmul(x, W) + return h + + def backward(self, grad_y): + """ + grad_y: shape(N, d') + """ + grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, self.memory['W'].T) + grad_W = np.matmul(self.memory['x'].T, grad_y) + return grad_x, grad_W + + +class Relu(NumpyOp): + + def forward(self, x): + self.memory['x'] = x + return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x)) + + def backward(self, grad_y): + """ + grad_y: same shape as x + """ + grad_x = np.where(self.memory['x']>0, grad_y, np.zeros_like(grad_y)) + return grad_x + + +class Log(NumpyOp): + + def forward(self, x): + """ + x: shape(N, c) + """ + out = np.log(x + self.epsilon) + self.memory['x'] = x + return out + + def backward(self, grad_y): + """ + grad_y: same shape as x + """ + grad_x = np.divide(grad_y, self.memory['x'] + self.epsilon) + return grad_x + + +class Softmax(NumpyOp): + """ + softmax over last dimension + """ + + def forward(self, x): + """ + x: shape(N, c) + """ + N, c = x.shape + e_x = np.exp(x) + sum_e_x = np.repeat(np.expand_dims(np.sum(e_x, axis=-1), axis=1), c, axis=1) + out = np.divide(e_x, sum_e_x) + self.memory['x'] = x + return out + + def backward(self, grad_y): + """ + grad_y: same shape as x + """ + N, c = self.memory['x'].shape + e_x = np.power(np.e, self.memory['x']) + sum_e_x = np.repeat(np.expand_dims(np.sum(e_x, axis=-1), axis=1), c, axis=1) + fout = np.divide(e_x, sum_e_x) + e_g = e_x * grad_y + sum_e_g = np.repeat(np.expand_dims(np.sum(e_g, axis=-1), axis=1), c, axis=1) + grad_x = fout * (grad_y - np.divide(sum_e_g, sum_e_x)) + return grad_x + +class NumpyLoss: + + def __init__(self): + self.target = None + + def get_loss(self, pred, target): + self.target = target + return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean() + + def backward(self): + return -self.target / self.target.shape[0] + + +class NumpyModel: + def __init__(self): + self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256)) + self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64)) + self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10)) + + + # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用 + self.matmul_1 = Matmul() + self.relu_1 = Relu() + self.matmul_2 = Matmul() + self.relu_2 = Relu() + self.matmul_3 = Matmul() + self.softmax = Softmax() + self.log = Log() + + # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新 + self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None + self.relu_1_grad = None + self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None + self.relu_2_grad = None + self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None + self.softmax_grad = None + self.log_grad = None + + + def forward(self, x): + x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28) + x = self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1) + x = self.relu_1.forward(x) + x = self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2) + x = self.relu_2.forward(x) + x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3) + x = self.softmax.forward(x) + x = self.log.forward(x) + return x + + + def backward(self, y): + + self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y) + self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad) + + self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad) + self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad) + + self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad) + self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad) + + self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad) + + + def optimize(self, learning_rate): + self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad + self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad + self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130213/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130213/numpy_mnist.py new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..315fbf32a5a00ec2eaaca9978fbd311f1392a0ae --- /dev/null +++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130213/numpy_mnist.py @@ -0,0 +1,68 @@ +import numpy as np +from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss +from utils import download_mnist, batch, plot_curve, one_hot + + +def get_torch_initialization(numpy=True): + + def kaiming_uniform(fan_in, fan_out, a = 0.0): + # a: the negative slope of the rectifier used after this layer, specially 0 for relu + bound = (6.0 / ((1.0 + a**2) * fan_in))**0.5 + return np.random.uniform(low = -bound, high = bound, size = (fan_in, fan_out)) + + return kaiming_uniform(28 * 28, 256), kaiming_uniform(256, 64), kaiming_uniform(64, 10) + +def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128, numpy=False): + data = [] + label = [] + for x in dataset: + data.append(np.array(x[0])) + label.append(x[1]) + data = np.array(data) + label = np.array(label) + + size = data.shape[0] + index = np.arange(size) + np.random.shuffle(index) + + batches = [] + i = 0 + while i + batch_size <= size: + batches.append((data[index[i:i + batch_size]], label[index[i:i + batch_size]])) + i += batch_size + + return batches + +def numpy_run(): + train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist() + + model = NumpyModel() + numpy_loss = NumpyLoss() + model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization() + + train_loss = [] + + epoch_number = 3 + learning_rate = 0.1 + + for epoch in range(epoch_number): + for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset): + y = one_hot(y) + + y_pred = model.forward(x) + loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y) + + model.backward(numpy_loss.backward()) + model.optimize(learning_rate) + + train_loss.append(loss.item()) + + x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0] + accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y)) + print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy)) + + plot_curve(train_loss) + + +if __name__ == "__main__": + numpy_run() diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/README.md new file mode 100644 index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a859dde38f467fbbb852f830eda2ded657e48952 --- /dev/null +++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/README.md @@ -0,0 +1,441 @@ +# 实验报告:ASS2-选题1-FNN + +18307130341 黄韵澄 + +[toc] + +### 1.实验概述 + + 实现一个前馈神经网络,利用MNIST数据集,解决手写体识别的分类问题。 + +### 2. 算子前向传播和反向传播的推导 + + 搭建的FNN中会用到Matmul、Relu、Log、Softmax这几个算子。 + +#### 2.1 Matmul层反向传播 + +$$ +loss = f(X\times W) =f(Y) +$$ + +根据链式法则: +$$ +\frac{\partial loss}{\partial X_{p,q}} = \sum_{i,j}{\frac{\partial loss}{\partial Y_{i,j}}\frac{\partial Y_{i,j}}{\partial X_{p,q}}} +$$ + 根据矩阵乘法定义: +$$ +Y_{i,j} = \sum_{k}{X_{i,k}W_{k,j}} +$$ + 所以,但$i\neq p$时,$C_{i,j}$与$A_{p,q}$无关: +$$ +\frac{\partial Y_{i,j}}{\partial X_{p,q}} =\begin{cases}W_{q,j}\quad i=p \\\\ 0 \quad i\neq p\end{cases} +$$ + 代入式子: +$$ +\frac{\partial loss}{\partial X_{p,q}} = \sum_{i,j}\frac{\partial loss}{\partial Y_{i,j}}\frac{\partial Y_{i,j}}{\partial X_{p,q}}=\sum_{j}\frac{\partial loss}{\partial Y_{p,j}}\frac{\partial Y_{p,j}}{\partial X_{p,q}}=\sum_{j}\frac{\partial loss}{\partial Y_{p,j}}W_{q,j}=\sum_{j}\frac{\partial loss}{\partial Y_{p,j}}W_{j,q}^{T} +$$ + + + 所以: +$$ +\frac{\partial loss}{\partial X} = \frac{\partial loss}{\partial Y}W^{T} +$$ + 同理: +$$ +\frac{\partial loss}{\partial W} = X^{T}\frac{\partial loss}{\partial Y} +$$ + +#### 2.2 Relu层反向传播 + +$$ +loss = f(Y) = f(Relu(X)) +$$ + +其中: +$$ +Relu(x) = \begin{cases}0 \quad x < 0 \\\\ x \quad x\geq 0\end{cases} +$$ +则: +$$ +\frac{\partial Y_{i,j}}{\partial X_{k,l}} = \begin{cases}1 \quad i=k\quad and\quad j=l\quad and\quad X_{k,l}>0 \\\\ +0\quad else \end{cases} +$$ +由链式法则: +$$ +\frac{\partial loss}{\partial X} = \frac{\partial loss}{\partial Y}\frac{\partial Y}{\partial X} +$$ +代码: + +```python +grad_x = grad_y * np.where(x > 0, 1, 0) +``` + +#### 2.3 Log层反向传播 + +$$ +loss = f(Y) = f(ln(X)) +$$ + +其中: +$$ +\frac{\partial Y_{i,j}}{\partial X_{k,l}} = \begin{cases}\frac{1}{X_{k,j}} \quad i=k\quad and\quad j=l\quad \\\\ +0\quad else \end{cases} +$$ +由链式法则: +$$ +\frac{\partial loss}{\partial X} = \frac{\partial loss}{\partial Y}\cdot \frac{\partial Y}{\partial X}=\frac{\partial loss}{\partial Y}\cdot \frac{1}{X} +$$ +代码: + +```python +grad_x = grad_y / (x + self.epsilon) +``` + +#### 2.4 Softmax层正向传播和反向传播 + +正向传播(只与行相关): + +$$ +loss = f(Y) \\ +Y_{i,j} = \frac{e^{X_{i,j}}}{\sum_{k}e^{X_{i,k}}} +$$ +反向传播: + +(1)当$j=l$时: +$$ +\frac{\partial Y_{i,j}}{\partial X_{i,l}} = \frac{\partial Y_{i,j}}{\partial X_{i,j}}=\frac{\partial \frac{e^{X_{i,j}}}{\sum_{k}e^{X_{i,k}}}}{\partial X_{i,j}} = \frac{e^{X_{i,j}}}{\sum_{k}e^{X_{i,k}}}-(\frac{e^{X_{i,j}}}{\sum_{k}e^{X_{i,k}}})^{2} = Y_{i,j}-Y_{i,j}^2 \\ +$$ +(2)当$j \neq l$时: +$$ +\frac{\partial Y_{i,j}}{\partial X_{i,l}} = \frac{\partial \frac{e^{X_{i,j}}}{\sum_{k}e^{X_{i,k}}}}{\partial X_{i,l}} = -\frac{e^{X_{i,j}}}{\sum_{k}e^{X_{i,k}}}\cdot \frac{e^{X_{i,l}}}{\sum_{k}e^{X_{i,k}}} = -Y_{i,j}\cdot Y_{i,l} \\ +$$ +(3)当$i \neq k$时,行不相关,梯度为0: +$$ +\frac{\partial Y_{i,j}}{\partial X_{k,l}} = 0 +$$ +根据链式法则(公式中的 $\cdot $ 表示点积): +$$ +\frac{\partial loss}{\partial X_{k,l}} = \sum_{j}\frac{\partial loss}{\partial Y_{k,j}}\cdot \frac{\partial Y_{k,j}}{\partial X_{k,l}} = (\sum_{j}-\frac{\partial loss}{\partial Y_{k,j}}\cdot Y_j\cdot Y_l)+ \frac{\partial loss}{\partial Y_{k,l}}\cdot Y_l \\\\ +=Y_l\cdot( \frac{\partial loss}{\partial Y_{k,l}}-\sum_{j}\frac{\partial loss}{\partial Y_{k,j}}\cdot Y_j) +$$ +简化成上式之后,可以用numpy方法的一行写完: + +```python +grad_x = y * (grad_y - (y * grad_y).sum(axis = 1).reshape(len(y),1)) +``` + +### 3.FNN模型搭建 + +#### 3.1 FNN模型 + + FNN模型搭建如图所示: + + +
+- 输入层($N\times28^2$)。与下层连接为全连接,参数为W1($28^2\times256$)。
+- 隐藏层1($N\times256$,激活函数Relu)。与下层连接为全连接,参数为W2($256\times64$)。
+- 隐藏层2($N\times64$,激活函数Relu)。与下层连接为全连接,参数为W3($64\times10$)。
+- 隐藏层3($N\times10$,激活函数Softmax)。直接输出到下层。
+- 输出层($N\times10$,激活函数Log)。
+
+ FNN模型用公式表示:
+$$
+a^{(0)} = X \\\\
+z^{(1)} = W_1\times a^{(0)} ,\quad a^{(1)} = Relu(z^{(1)}) \\\\
+z^{(2)} = W_2\times a^{(1)} ,\quad a^{(2)} = Relu(z^{(2)}) \\\\
+z^{(3)} = W_3\times a^{(2)} ,\quad a^{(3)} = Softmax(z^{(3)}) \\\\
+z^{(4)} = a^{(3)},\quad a^{(4)} = Log(z^{(4)}) \\\\
+Y = a^{(4)}
+$$
+
+ 损失值的定义:
+$$
+loss = -Y * \hat Y
+$$
+
+#### 3.2 FNN反向传播
+
+ 根据搭建的FNN模型,反方向链式求导。用上一层的求出的梯度作为下一层输入即可:
+
+```python
+self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y)
+
+self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+
+self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+
+self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+```
+
+### 3.3 FNN模型的测试结果
+
+ 直接运行`numpy_mnist.py`,即可自动下载MNIST数据集(手写体数字识别)进行自动测试。
+
+ 损失函数绘图:
+
+
+
+- 输入层($N\times28^2$)。与下层连接为全连接,参数为W1($28^2\times256$)。
+- 隐藏层1($N\times256$,激活函数Relu)。与下层连接为全连接,参数为W2($256\times64$)。
+- 隐藏层2($N\times64$,激活函数Relu)。与下层连接为全连接,参数为W3($64\times10$)。
+- 隐藏层3($N\times10$,激活函数Softmax)。直接输出到下层。
+- 输出层($N\times10$,激活函数Log)。
+
+ FNN模型用公式表示:
+$$
+a^{(0)} = X \\\\
+z^{(1)} = W_1\times a^{(0)} ,\quad a^{(1)} = Relu(z^{(1)}) \\\\
+z^{(2)} = W_2\times a^{(1)} ,\quad a^{(2)} = Relu(z^{(2)}) \\\\
+z^{(3)} = W_3\times a^{(2)} ,\quad a^{(3)} = Softmax(z^{(3)}) \\\\
+z^{(4)} = a^{(3)},\quad a^{(4)} = Log(z^{(4)}) \\\\
+Y = a^{(4)}
+$$
+
+ 损失值的定义:
+$$
+loss = -Y * \hat Y
+$$
+
+#### 3.2 FNN反向传播
+
+ 根据搭建的FNN模型,反方向链式求导。用上一层的求出的梯度作为下一层输入即可:
+
+```python
+self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y)
+
+self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+
+self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+
+self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+```
+
+### 3.3 FNN模型的测试结果
+
+ 直接运行`numpy_mnist.py`,即可自动下载MNIST数据集(手写体数字识别)进行自动测试。
+
+ 损失函数绘图:
+
+ +
+ 模型准确率:
+
+```
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9350
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9674
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9693
+```
+
+ numpy中的epoch只设置了3,但模型准确率已经相对比较高了。然而,观察损失函数的波动图像,显然模型的损失函数仍在波动,并未收敛。后续可能需要增加epoch并调节学习率使得模型的损失收敛。
+
+### 4. mini_batch函数的实现
+
+#### 4.1 mini_batch函数
+
+ `mini_batch`函数是将`dataset`分成不同批次,批处理大小为`batch_size`。
+
+ 处理步骤:
+
+- for循环提取dataset中的data和label,转换为ndarray格式:
+
+```python
+data = []
+label = []
+for x in dataset:
+ data.append(np.array(x[0]))
+ label.append(x[1])
+data = np.array(data)
+label = np.array(label)
+```
+
+- shuffle的方法有很多,我用的是`np.random.permutation`这个方法:
+
+```
+idx = np.random.permutation(len(dataset))
+data = data[idx]
+label = label[idx]
+```
+
+- 使用`np.split`方法将data和label划分。这个方法要求均等划分,为了解决dataset规模不能整除batch_size问题,代码单独处理最后一个区块:
+
+```
+split_num = len(dataset) // batch_size #均等划分的区块数量
+split_pos = split_num * batch_size # 均等划分的区块的最末位置
+# 划分data
+ret_data = np.split(data[:split_pos], split_num)
+ret_data.append(data[split_pos+1:])
+# 划分label
+ret_label = np.split(label[:split_pos], split_num)
+ret_label.append(label[split_pos+1:])
+```
+
+- 最后使用`zip`将data和label组合成tuple:
+
+```
+ret = list(zip(ret_data, ret_label))
+```
+
+#### 4.2 mini_batch函数测试
+
+使用torch方法的mini_batch:
+
+```
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9473
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9648
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9680
+time = 73.32 s
+```
+
+只使用numpy方法的mini_batch:
+
+```
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9474
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9556
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9678
+time = 66.24 s
+```
+
+ 理论上是对正确率没有影响的。速度上比torch的快了7s左右。
+
+### 5.模型优化方法
+
+#### 5.1 Momentum方法
+
+ Momentum算法又叫做动量梯度下降算法,使用原始的梯度下降有以下问题:
+
+> 梯度下降过程中有纵向波动,由于这种波动的存在,我们只能采取较小的学习率,否则波动会更大。而使用动量梯度下降法后,经过平均,抵消了上下波动,使波动趋近于零,这样就可以采用稍微大点的学习率加快梯度下降的速度。
+>
+
+ Momentum公式:
+$$
+V_{dW}= \beta \cdot V_{dW} + (1-\beta)\cdot dW \\\\
+W = W - \alpha \cdot V_{dW}
+$$
+ 其中$\alpha$为学习率,$\beta$为动量系数。在实验中$\beta$取值0.9。
+
+ 分别使用原始梯度下降(绿色线)和Momentum优化方法(蓝色线)进行测试,绘制acc-epoch图,结果如下:
+
+
+
+ 模型准确率:
+
+```
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9350
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9674
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9693
+```
+
+ numpy中的epoch只设置了3,但模型准确率已经相对比较高了。然而,观察损失函数的波动图像,显然模型的损失函数仍在波动,并未收敛。后续可能需要增加epoch并调节学习率使得模型的损失收敛。
+
+### 4. mini_batch函数的实现
+
+#### 4.1 mini_batch函数
+
+ `mini_batch`函数是将`dataset`分成不同批次,批处理大小为`batch_size`。
+
+ 处理步骤:
+
+- for循环提取dataset中的data和label,转换为ndarray格式:
+
+```python
+data = []
+label = []
+for x in dataset:
+ data.append(np.array(x[0]))
+ label.append(x[1])
+data = np.array(data)
+label = np.array(label)
+```
+
+- shuffle的方法有很多,我用的是`np.random.permutation`这个方法:
+
+```
+idx = np.random.permutation(len(dataset))
+data = data[idx]
+label = label[idx]
+```
+
+- 使用`np.split`方法将data和label划分。这个方法要求均等划分,为了解决dataset规模不能整除batch_size问题,代码单独处理最后一个区块:
+
+```
+split_num = len(dataset) // batch_size #均等划分的区块数量
+split_pos = split_num * batch_size # 均等划分的区块的最末位置
+# 划分data
+ret_data = np.split(data[:split_pos], split_num)
+ret_data.append(data[split_pos+1:])
+# 划分label
+ret_label = np.split(label[:split_pos], split_num)
+ret_label.append(label[split_pos+1:])
+```
+
+- 最后使用`zip`将data和label组合成tuple:
+
+```
+ret = list(zip(ret_data, ret_label))
+```
+
+#### 4.2 mini_batch函数测试
+
+使用torch方法的mini_batch:
+
+```
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9473
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9648
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9680
+time = 73.32 s
+```
+
+只使用numpy方法的mini_batch:
+
+```
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9474
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9556
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9678
+time = 66.24 s
+```
+
+ 理论上是对正确率没有影响的。速度上比torch的快了7s左右。
+
+### 5.模型优化方法
+
+#### 5.1 Momentum方法
+
+ Momentum算法又叫做动量梯度下降算法,使用原始的梯度下降有以下问题:
+
+> 梯度下降过程中有纵向波动,由于这种波动的存在,我们只能采取较小的学习率,否则波动会更大。而使用动量梯度下降法后,经过平均,抵消了上下波动,使波动趋近于零,这样就可以采用稍微大点的学习率加快梯度下降的速度。
+>
+
+ Momentum公式:
+$$
+V_{dW}= \beta \cdot V_{dW} + (1-\beta)\cdot dW \\\\
+W = W - \alpha \cdot V_{dW}
+$$
+ 其中$\alpha$为学习率,$\beta$为动量系数。在实验中$\beta$取值0.9。
+
+ 分别使用原始梯度下降(绿色线)和Momentum优化方法(蓝色线)进行测试,绘制acc-epoch图,结果如下:
+
+ +
+可以看到Momentum优化在前期学习速度比原始方法慢,但随着动量累计,其模型精确度很快高于原始方法的精确度,且最终精确度收敛于更高的水平。
+
+#### 5.2 Adam方法
+
+ Adam本质上实际是RMSProp优化+Momentum优化的结合:
+
+> **均方根传播(RMSProp)**:维护每个参数的学习速率,根据最近的权重梯度的平均值来调整。这意味着该算法在线上和非平稳问题上表现良好。
+
+ Adam公式:
+$$
+V_{dW} = \beta_1\cdot V_{dW} + (1-\beta_1)\cdot dW \\\\
+V_{dW}^{corrected} = \frac{V_{dW}}{1-\beta_1^t} \\\\
+S_{dW} = \beta_2\cdot S_{dW} + (1-\beta_2)\cdot dW^2 \\\\
+S_{dW}^{corrected} = \frac{S_{dW}}{1-\beta_2^t} \\\\
+W = W - \alpha \frac{V_{dW}^{corrected}}{\sqrt{S_{dW}^{corrected}}+\epsilon}
+$$
+其中$\alpha$为学习率,$\beta_1$为动量系数,$\beta_2$为自适应学习系数。
+
+ 根据典型的参数设置,$\alpha$设为0.001,$\beta_1$设为0.9,$\beta_2$设为0.999。运行20个epoch,测试结果如图(与原始optimize、Momentum方法比较):
+
+
+
+可以看到Momentum优化在前期学习速度比原始方法慢,但随着动量累计,其模型精确度很快高于原始方法的精确度,且最终精确度收敛于更高的水平。
+
+#### 5.2 Adam方法
+
+ Adam本质上实际是RMSProp优化+Momentum优化的结合:
+
+> **均方根传播(RMSProp)**:维护每个参数的学习速率,根据最近的权重梯度的平均值来调整。这意味着该算法在线上和非平稳问题上表现良好。
+
+ Adam公式:
+$$
+V_{dW} = \beta_1\cdot V_{dW} + (1-\beta_1)\cdot dW \\\\
+V_{dW}^{corrected} = \frac{V_{dW}}{1-\beta_1^t} \\\\
+S_{dW} = \beta_2\cdot S_{dW} + (1-\beta_2)\cdot dW^2 \\\\
+S_{dW}^{corrected} = \frac{S_{dW}}{1-\beta_2^t} \\\\
+W = W - \alpha \frac{V_{dW}^{corrected}}{\sqrt{S_{dW}^{corrected}}+\epsilon}
+$$
+其中$\alpha$为学习率,$\beta_1$为动量系数,$\beta_2$为自适应学习系数。
+
+ 根据典型的参数设置,$\alpha$设为0.001,$\beta_1$设为0.9,$\beta_2$设为0.999。运行20个epoch,测试结果如图(与原始optimize、Momentum方法比较):
+
+ +
+ 可以看到,Adam方法的loss波动比较大,20个epoch仍未到达收敛值。比较三种optimize方法每个epoch的acc(绿色线原始方法,蓝色线Momentum优化,紫色线Adam优化):
+
+
+
+ 可以看到,Adam方法的loss波动比较大,20个epoch仍未到达收敛值。比较三种optimize方法每个epoch的acc(绿色线原始方法,蓝色线Momentum优化,紫色线Adam优化):
+
+ +
+ 可以看到,在epoch比较小时,Adam优化并没有获得更高的精确度。在epoch结束时,acc仍处于上升趋势。可能是因为Adam方法的低学习率导致的收敛速度变慢。Momentum更适合本实验的模型。
+
+### 6. 权重初始化
+
+ 权值初始值是不能设置成0的,因为如果参数都为0,在第一遍前向计算时,所有的隐层神经元的激活值都相同。这样会导致深层神经元没有区分性。这种现象也称为对称权重现象。
+
+ 为了解决这个问题,一种比较直观的权重初始化方法就是给每个参数随机初始化一个值。然而,如果初始化的值太小,会导致神经元的输入过小,经过多层之后信号就消失了;初始化值设置过大会导致数据状态过大,激活值很快饱和了,梯度接近于0,也是不好训练的。
+
+ 因此一般而言,参数初始化的区间应该根据神经元的性质进行差异化的设置。
+
+ 下面分别介绍Xavier和Kaiming两种初始化方法。
+
+#### 6.1 Xavier初始化
+
+ Xavier Glorot,在其论文中提出一个洞见:激活值的方差是逐层递减的,这导致反向传播中的梯度也逐层递减。要解决梯度消失,就要避免激活值方差的衰减,最理想的情况是,每层的输出值(激活值)保持高斯分布。
+
+ Xavier Glorot为实现这种理想情况,设计了依托均匀分布和高斯分布两种初始化方式。分布的参数通过一个gain(增益值来计算)。
+
+ `torch.nn.init.calculate_gain(nonlinearity, param=None)`提供了对非线性函数增益值的计算:
+
+
+
+ 可以看到,在epoch比较小时,Adam优化并没有获得更高的精确度。在epoch结束时,acc仍处于上升趋势。可能是因为Adam方法的低学习率导致的收敛速度变慢。Momentum更适合本实验的模型。
+
+### 6. 权重初始化
+
+ 权值初始值是不能设置成0的,因为如果参数都为0,在第一遍前向计算时,所有的隐层神经元的激活值都相同。这样会导致深层神经元没有区分性。这种现象也称为对称权重现象。
+
+ 为了解决这个问题,一种比较直观的权重初始化方法就是给每个参数随机初始化一个值。然而,如果初始化的值太小,会导致神经元的输入过小,经过多层之后信号就消失了;初始化值设置过大会导致数据状态过大,激活值很快饱和了,梯度接近于0,也是不好训练的。
+
+ 因此一般而言,参数初始化的区间应该根据神经元的性质进行差异化的设置。
+
+ 下面分别介绍Xavier和Kaiming两种初始化方法。
+
+#### 6.1 Xavier初始化
+
+ Xavier Glorot,在其论文中提出一个洞见:激活值的方差是逐层递减的,这导致反向传播中的梯度也逐层递减。要解决梯度消失,就要避免激活值方差的衰减,最理想的情况是,每层的输出值(激活值)保持高斯分布。
+
+ Xavier Glorot为实现这种理想情况,设计了依托均匀分布和高斯分布两种初始化方式。分布的参数通过一个gain(增益值来计算)。
+
+ `torch.nn.init.calculate_gain(nonlinearity, param=None)`提供了对非线性函数增益值的计算:
+
+ +
+ 均匀分布初始化$U(-a,a)$,其中:
+$$
+a = gain\times \sqrt{\frac{6}{fan\_in+fan\_out}}
+$$
+
+
+ 正态分布初始化$N(0,std^2)$,其中:
+$$
+std = gain\times \frac{2}{fan\_in+fan\_out}
+$$
+
+
+ $fan\_in$和$fan\_out$表示输入和输出的规模。
+
+#### 6.2 Kaiming初始化
+
+> Xavier初始化的问题在于,它只适用于线性激活函数,但实际上,对于深层神经网络来说,线性激活函数是没有价值,神经网络需要非线性激活函数来构建复杂的非线性系统。今天的神经网络普遍使用relu激活函数。aiming初始化的发明人kaiming he,在其论文中提出了针对relu的kaiming初始化。
+>
+> 因为relu会抛弃掉小于0的值,对于一个均值为0的data来说,这就相当于砍掉了一半的值,这样一来,均值就会变大,前面Xavier初始化公式中E(x)=mean=0的情况就不成立了。根据新公式的推导,最终得到新的rescale系数:。
+
+ 均匀分布初始化$U(-bound,bound)$,其中:
+$$
+bound = \sqrt{\frac{6}{(1+a^2)\times fan\_in}}
+$$
+ 正态分布初始化$N(0,std^2)$,其中:
+$$
+bound = \sqrt{\frac{2}{(1+a^2)\times fan\_in}}
+$$
+ $a$为可设置的参数,$fan\_in$为输入层的规模。
+
+#### 6.3 初始化函数的实现
+
+ 首先看看`get_torch_initialization`这个函数用的是什么方式的初始化:
+
+```python
+fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(28 * 28, 256)
+W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+```
+
+ 它定义了一个Linear层,直接取其Weight的值。找到Linear这个类的定义:
+
+```python
+init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight, a=math.sqrt(5))
+```
+
+ 使用的是kaiming均匀分布,a设置为$\sqrt 5$。
+
+```python
+def kaiming_uniform_(tensor, a=0, mode='fan_in', nonlinearity='leaky_relu')
+```
+
+ 由于没有设置nonlinearity,其值为默认leaky_relu。
+
+```python
+gain = calculate_gain(nonlinearity, a)
+```
+
+ 这个传入的a即为Leaky ReLU中的`negative_slop`。
+
+```python
+gain = math.sqrt(2.0 / (1 + a ** 2))
+std = gain / math.sqrt(fan)
+bound = math.sqrt(3.0) * std
+return tensor.uniform_(-bound, bound)
+```
+
+ 代码阅读之后,可以看出,tensor中使用的是kaiming的均匀分布初始化。
+
+ 最终在代码实现均匀分布的kaiming分布,a设置为$\sqrt 5$ :
+
+```python
+def get_torch_initialization_numpy(numpy=True):
+ fan_in_1 = 28 * 28
+ fan_in_2 = 256
+ fan_in_3 = 64
+
+ bound1 = 1 / np.sqrt(fan_in_1) #bound1 = np.sqrt(6) / np.sqrt(1+np.sqrt(5)**2) /np.sqrt(fan_in_1)
+ bound2 = 1 / np.sqrt(fan_in_2)
+ bound3 = 1 / np.sqrt(fan_in_3)
+
+ W1 = np.random.uniform(-bound1, bound1, (28*28, 256))
+ W2 = np.random.uniform(-bound2, bound2, (256, 64))
+ W3 = np.random.uniform(-bound3, bound3, (64, 10))
+
+ if numpy == False:
+ W1 = torch.Tensor(W1)
+ W2 = torch.Tensor(W2)
+ W3 = torch.Tensor(W3)
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
+```
+
+ torch.mnist运行结果:
+
+
+
+ 均匀分布初始化$U(-a,a)$,其中:
+$$
+a = gain\times \sqrt{\frac{6}{fan\_in+fan\_out}}
+$$
+
+
+ 正态分布初始化$N(0,std^2)$,其中:
+$$
+std = gain\times \frac{2}{fan\_in+fan\_out}
+$$
+
+
+ $fan\_in$和$fan\_out$表示输入和输出的规模。
+
+#### 6.2 Kaiming初始化
+
+> Xavier初始化的问题在于,它只适用于线性激活函数,但实际上,对于深层神经网络来说,线性激活函数是没有价值,神经网络需要非线性激活函数来构建复杂的非线性系统。今天的神经网络普遍使用relu激活函数。aiming初始化的发明人kaiming he,在其论文中提出了针对relu的kaiming初始化。
+>
+> 因为relu会抛弃掉小于0的值,对于一个均值为0的data来说,这就相当于砍掉了一半的值,这样一来,均值就会变大,前面Xavier初始化公式中E(x)=mean=0的情况就不成立了。根据新公式的推导,最终得到新的rescale系数:。
+
+ 均匀分布初始化$U(-bound,bound)$,其中:
+$$
+bound = \sqrt{\frac{6}{(1+a^2)\times fan\_in}}
+$$
+ 正态分布初始化$N(0,std^2)$,其中:
+$$
+bound = \sqrt{\frac{2}{(1+a^2)\times fan\_in}}
+$$
+ $a$为可设置的参数,$fan\_in$为输入层的规模。
+
+#### 6.3 初始化函数的实现
+
+ 首先看看`get_torch_initialization`这个函数用的是什么方式的初始化:
+
+```python
+fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(28 * 28, 256)
+W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+```
+
+ 它定义了一个Linear层,直接取其Weight的值。找到Linear这个类的定义:
+
+```python
+init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight, a=math.sqrt(5))
+```
+
+ 使用的是kaiming均匀分布,a设置为$\sqrt 5$。
+
+```python
+def kaiming_uniform_(tensor, a=0, mode='fan_in', nonlinearity='leaky_relu')
+```
+
+ 由于没有设置nonlinearity,其值为默认leaky_relu。
+
+```python
+gain = calculate_gain(nonlinearity, a)
+```
+
+ 这个传入的a即为Leaky ReLU中的`negative_slop`。
+
+```python
+gain = math.sqrt(2.0 / (1 + a ** 2))
+std = gain / math.sqrt(fan)
+bound = math.sqrt(3.0) * std
+return tensor.uniform_(-bound, bound)
+```
+
+ 代码阅读之后,可以看出,tensor中使用的是kaiming的均匀分布初始化。
+
+ 最终在代码实现均匀分布的kaiming分布,a设置为$\sqrt 5$ :
+
+```python
+def get_torch_initialization_numpy(numpy=True):
+ fan_in_1 = 28 * 28
+ fan_in_2 = 256
+ fan_in_3 = 64
+
+ bound1 = 1 / np.sqrt(fan_in_1) #bound1 = np.sqrt(6) / np.sqrt(1+np.sqrt(5)**2) /np.sqrt(fan_in_1)
+ bound2 = 1 / np.sqrt(fan_in_2)
+ bound3 = 1 / np.sqrt(fan_in_3)
+
+ W1 = np.random.uniform(-bound1, bound1, (28*28, 256))
+ W2 = np.random.uniform(-bound2, bound2, (256, 64))
+ W3 = np.random.uniform(-bound3, bound3, (64, 10))
+
+ if numpy == False:
+ W1 = torch.Tensor(W1)
+ W2 = torch.Tensor(W2)
+ W3 = torch.Tensor(W3)
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
+```
+
+ torch.mnist运行结果:
+
+ +
+```
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9503
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9639
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9711
+```
+
+### 7.提交的代码说明
+
+- `numpy_fnn.py`:算子和FNN模型正向传播和反向传播的实现。`optimize_Momentum`方法实现Momentum优化,`optimize_Adam`方法实现Adam优化。可在`numpy_mnist.py`中修改optimize的调用改变优化方法。
+- `numpy_mnist.py`:`mini_batch_numpy`方法用numpy实现了mini_batch。
+- `utils.py`:`get_torch_initialization_numpy`方法用numpy实现了均匀分布的kaiming初始化。
+
+### 8.参考文献
+
+[1] [神经网络常见优化算法(Momentum, RMSprop, Adam)的原理及公式理解, 学习率衰减](https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42561002/article/details/88036777)
+
+[2] [深度之眼【Pytorch】-Xavier、Kaiming初始化(附keras实现)](https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42147780/article/details/103238195)
+
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig1.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..50b42797b50f8b745d7707a86e2644d84843d228
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig2.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f5dd7bdc2c2712953ddd2b990232d3a7a71b655b
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig3.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig3.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c440ff99663169e8b636ed9e3fc8b7cbdb6008f1
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig3.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig4.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig4.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..05196c545d1d6da186cd8e301eff8fec10110060
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig4.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig5.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig5.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..31658f4aa8db641225bf56c4ef54fb8c079d7ae2
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig5.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig6.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig6.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..54721b598f39cfb996bfde8986077ca64836eb76
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig6.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig7.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig7.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..1a3f1b1c91d8767838bd464ad291da558006c941
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig7.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig8.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig8.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..081717ced38314a1b250daf2f527bce99313bc71
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig8.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..bacac809951ecb357664479fa2f8f69e956fd8b8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,240 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 1 #
+ ####################
+ xT = np.transpose(self.memory['x'])
+ WT = np.transpose(self.memory['W'])
+
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, WT)
+ grad_W = np.matmul(xT, grad_y)
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 2 #
+ ####################
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ grad_x = grad_y * np.where(x > 0, 1, 0)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 3 #
+ ####################
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ grad_x = grad_y / (x + self.epsilon)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 4 #
+ ####################
+ sum = np.exp(x).sum(axis = 1)
+ sum = sum.reshape(x.shape[0], 1)
+ out = np.exp(x) / sum
+
+ self.memory['y'] = out
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 5 #
+ ####################
+ y = self.memory['y']
+
+ grad_x = y * (grad_y - (y * grad_y).sum(axis = 1).reshape(len(y),1))
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新。 softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ # Momentum优化
+ self.v_W1_grad = 0
+ self.v_W2_grad = 0
+ self.v_W3_grad = 0
+
+ # Adam优化
+ self.s_W1_grad = 0
+ self.s_W2_grad = 0
+ self.s_W3_grad = 0
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ ####################
+ # code 6 #
+ ####################
+ x = self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1)
+ x = self.relu_1.forward(x)
+
+ x = self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2)
+ x = self.relu_2.forward(x)
+
+ x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+ x = self.softmax.forward(x)
+
+ x = self.log.forward(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+
+ ####################
+ # code 7 #
+ ###################
+
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y)
+
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+
+ self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+
+ def optimize_Momentum(self, learning_rate, belta):
+ self.v_W1_grad = belta * self.v_W1_grad + (1 - belta) * self.W1_grad
+ self.v_W2_grad = belta * self.v_W2_grad + (1 - belta) * self.W2_grad
+ self.v_W3_grad = belta * self.v_W3_grad + (1 - belta) * self.W3_grad
+
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.v_W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.v_W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.v_W3_grad
+
+ def optimize_Adam(self, learning_rate, beta1, beta2, beta1_t, beta2_t, eps):
+
+ self.v_W1_grad = beta1 * self.v_W1_grad + (1 - beta1) * self.W1_grad
+ self.v_W2_grad = beta1 * self.v_W2_grad + (1 - beta1) * self.W2_grad
+ self.v_W3_grad = beta1 * self.v_W3_grad + (1 - beta1) * self.W3_grad
+
+ v_W1_corr = self.v_W1_grad / (1 - beta1_t)
+ v_W2_corr = self.v_W2_grad / (1 - beta1_t)
+ v_W3_corr = self.v_W3_grad / (1 - beta1_t)
+
+ self.s_W1_grad = beta2 * self.s_W1_grad + (1 - beta2) * (self.W1_grad ** 2)
+ self.s_W2_grad = beta2 * self.s_W2_grad + (1 - beta2) * (self.W2_grad ** 2)
+ self.s_W3_grad = beta2 * self.s_W3_grad + (1 - beta2) * (self.W3_grad ** 2)
+
+ s_W1_corr = self.s_W1_grad / (1 - beta2_t)
+ s_W2_corr = self.s_W2_grad / (1 - beta2_t)
+ s_W3_corr = self.s_W3_grad / (1 - beta2_t)
+
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * v_W1_corr / (np.sqrt(s_W1_corr) + eps)
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * v_W2_corr / (np.sqrt(s_W2_corr) + eps)
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * v_W3_corr / (np.sqrt(s_W3_corr) + eps)
+
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..87aa55fdfd8a765cbad3203b3a9082c28c5c6502
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, mini_batch, batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+
+def mini_batch_numpy(dataset, batch_size=128):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+
+ for x in dataset:
+ data.append(np.array(x[0]))
+ label.append(x[1])
+
+ data = np.array(data)
+ label = np.array(label)
+
+ idx = np.random.permutation(len(dataset))
+ data = data[idx]
+ label = label[idx]
+
+ split_num = len(dataset) // batch_size
+ split_pos = split_num * batch_size
+
+ ret_data = np.split(data[:split_pos], split_num)
+ ret_data.append(data[split_pos+1:])
+
+ ret_label = np.split(label[:split_pos], split_num)
+ ret_label.append(label[split_pos+1:])
+
+ ret = list(zip(ret_data, ret_label))
+ return ret
+
+def numpy_run():
+
+ import time
+ start = time.time()
+
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ #Adam 优化
+ beta1 = 0.9
+ beta2 = 0.999
+ beta1_t = 1
+ beta2_t = 1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ #Adam 优化
+ beta1_t *= beta1
+ beta2_t *= beta2
+
+ # for x, y in mini_batch_numpy(train_dataset): # mini_batch_numpy
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ # y_pred = model.forward(x) # mini_batch_numpy
+ y_pred = model.forward(x.numpy())
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+
+ #原始optimize
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ #Momentum 优化
+ # model.optimize_Momentum(learning_rate, 0.9)
+
+ #Adam 优化
+ # model.optimize_Adam(learning_rate, beta1, beta2, beta1_t, beta2_t, 1e-8)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ end = time.time()
+ print("time = %.2f s"%(end-start))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/tester_demo.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/tester_demo.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..504b3eef50a6df4d0aa433113136add50835e420
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/tester_demo.py
@@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
+import numpy as np
+import torch
+from torch import matmul as torch_matmul, relu as torch_relu, softmax as torch_softmax, log as torch_log
+
+from numpy_fnn import Matmul, Relu, Softmax, Log, NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from torch_mnist import TorchModel
+from utils import get_torch_initialization, one_hot
+
+err_epsilon = 1e-6
+err_p = 0.4
+
+
+def check_result(numpy_result, torch_result=None):
+ if isinstance(numpy_result, list) and torch_result is None:
+ flag = True
+ for (n, t) in numpy_result:
+ flag = flag and check_result(n, t)
+ return flag
+ # print((torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) - torch_result).abs().mean().item())
+ T = (torch_result * torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) < 0).sum().item()
+ direction = T / torch_result.numel() < err_p
+ return direction and ((torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) - torch_result).abs().mean() < err_epsilon).item()
+
+
+def case_1():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[5, 6])
+ W = np.random.normal(size=[6, 4])
+
+ numpy_matmul = Matmul()
+ numpy_out = numpy_matmul.forward(x, W)
+ numpy_x_grad, numpy_W_grad = numpy_matmul.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+ torch_W = torch.from_numpy(W).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_matmul(torch_x, torch_W)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ (numpy_W_grad, torch_W.grad)
+ ])
+
+
+def case_2():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[5, 6])
+
+ numpy_relu = Relu()
+ numpy_out = numpy_relu.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_relu.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_relu(torch_x)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def case_3():
+ x = np.random.uniform(low=0.0, high=1.0, size=[3, 4])
+
+ numpy_log = Log()
+ numpy_out = numpy_log.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_log.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_log(torch_x)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def case_4():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[4, 5])
+
+ numpy_softmax = Softmax()
+ numpy_out = numpy_softmax.forward(x)
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_softmax(torch_x, 1)
+
+ return check_result(numpy_out, torch_out)
+
+
+def case_5():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[20, 25])
+
+ numpy_softmax = Softmax()
+ numpy_out = numpy_softmax.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_softmax.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_softmax(torch_x, 1)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def test_model():
+ try:
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ numpy_model = NumpyModel()
+ torch_model = TorchModel()
+ torch_model.W1.data, torch_model.W2.data, torch_model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+ numpy_model.W1 = torch_model.W1.detach().clone().numpy()
+ numpy_model.W2 = torch_model.W2.detach().clone().numpy()
+ numpy_model.W3 = torch_model.W3.detach().clone().numpy()
+
+ x = torch.randn((10000, 28, 28))
+ y = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0] * 1000)
+
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+ x2 = x.numpy()
+ y_pred = torch_model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+
+ y_pred_numpy = numpy_model.forward(x2)
+ numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred_numpy, y.numpy())
+
+ check_flag_1 = check_result(y_pred_numpy, y_pred)
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("forward", 10 * check_flag_1, 10))
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in forward]")
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("forward", 0, 10))
+ return 0
+
+ try:
+
+ numpy_model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+
+ check_flag_2 = [
+ check_result(numpy_model.log_grad, torch_model.log_input.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.softmax_grad, torch_model.softmax_input.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W3_grad, torch_model.W3.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W2_grad, torch_model.W2.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W1_grad, torch_model.W1.grad)
+ ]
+ check_flag_2 = sum(check_flag_2) >= 4
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("backward", 20 * check_flag_2, 20))
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in backward]")
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("backward", 0, 20))
+ check_flag_2 = False
+
+ return 10 * check_flag_1 + 20 * check_flag_2
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ testcases = [
+ ["matmul", case_1, 5],
+ ["relu", case_2, 5],
+ ["log", case_3, 5],
+ ["softmax_1", case_4, 5],
+ ["softmax_2", case_5, 10],
+ ]
+ score = 0
+ for case in testcases:
+ try:
+ res = case[2] if case[1]() else 0
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in {}]".format(case[0]))
+ res = 0
+ score += res
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format(case[0], res, case[2]))
+ score += test_model()
+ print("{:14} {}/60".format("FINAL SCORE", score))
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/torch_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/torch_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7bbcedcf8108c227e09c861a761c18e99a7f9429
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/torch_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+import torch
+from utils import mini_batch, batch, download_mnist, get_torch_initialization, one_hot, plot_curve
+
+
+class TorchModel:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = torch.randn((28 * 28, 256), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W2 = torch.randn((256, 64), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W3 = torch.randn((64, 10), requires_grad=True)
+ self.softmax_input = None
+ self.log_input = None
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W1))
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W2))
+ x = torch.matmul(x, self.W3)
+
+ self.softmax_input = x
+ self.softmax_input.retain_grad()
+
+ x = torch.softmax(x, 1)
+
+ self.log_input = x
+ self.log_input.retain_grad()
+
+ x = torch.log(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ with torch.no_grad():
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1.grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2.grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3.grad
+
+ self.W1.grad = None
+ self.W2.grad = None
+ self.W3.grad = None
+
+
+def torch_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = TorchModel()
+ # model.W1.data, model.W2.data, model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+ from utils import get_torch_initialization_numpy
+ model.W1.data, model.W2.data, model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization_numpy(numpy=False)
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset, numpy=False):
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset, numpy=False)[0]
+ accuracy = model.forward(x).argmax(dim=1).eq(y).float().mean().item()
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ torch_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/utils.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/utils.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..5154f4970843623204198206ff0df1438bbee5df
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/utils.py
@@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
+import torch
+import numpy as np
+from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
+
+
+def plot_curve(data):
+ plt.plot(range(len(data)), data, color='blue')
+ plt.legend(['loss_value'], loc='upper right')
+ plt.xlabel('step')
+ plt.ylabel('value')
+ plt.show()
+
+
+def download_mnist():
+ from torchvision import datasets, transforms
+
+ transform = transforms.Compose([
+ transforms.ToTensor(),
+ transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.1307,), std=(0.3081,))
+ ])
+
+ train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=True, download=True)
+ test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=False, download=True)
+
+ return train_dataset, test_dataset
+
+
+def one_hot(y, numpy=True):
+ if numpy:
+ y_ = np.zeros((y.shape[0], 10))
+ y_[np.arange(y.shape[0], dtype=np.int32), y] = 1
+ return y_
+ else:
+ y_ = torch.zeros((y.shape[0], 10))
+ y_[torch.arange(y.shape[0], dtype=torch.long), y] = 1
+ return y_
+
+
+def batch(dataset, numpy=True):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+ for each in dataset:
+ data.append(each[0])
+ label.append(each[1])
+ data = torch.stack(data)
+ label = torch.LongTensor(label)
+ if numpy:
+ return [(data.numpy(), label.numpy())]
+ else:
+ return [(data, label)]
+
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128, numpy=False):
+ return torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
+
+
+def get_torch_initialization(numpy=True):
+ fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(28 * 28, 256)
+ fc2 = torch.nn.Linear(256, 64)
+ fc3 = torch.nn.Linear(64, 10)
+
+ if numpy:
+ W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ W2 = fc2.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ W3 = fc3.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ else:
+ W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+ W2 = fc2.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+ W3 = fc3.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
+
+def get_torch_initialization_numpy(numpy=True):
+ fan_in_1 = 28 * 28
+ fan_in_2 = 256
+ fan_in_3 = 64
+
+ bound1 = 1 / np.sqrt(fan_in_1)
+ bound2 = 1 / np.sqrt(fan_in_2)
+ bound3 = 1 / np.sqrt(fan_in_3)
+
+ W1 = np.random.uniform(-bound1, bound1, (28*28, 256))
+ W2 = np.random.uniform(-bound2, bound2, (256, 64))
+ W3 = np.random.uniform(-bound3, bound3, (64, 10))
+
+ if numpy == False:
+ W1 = torch.Tensor(W1)
+ W2 = torch.Tensor(W2)
+ W3 = torch.Tensor(W3)
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..abdc5462b52fc1d754752b8f1c3b62442d70e009
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,191 @@
+# 实验报告
+### 1.模型设计
+神经网络设计如下图所示
+### 2.算子补充
+**Matmul**
+
+**Forward**
+$$
+h=X*W
+$$
+
+**Backward**
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial X} = W^{T}
+$$
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial W} = X^{T}
+$$
+维度变化以及Python实现如下所示:
+```
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ w.T: shape(d', d)
+ """
+ grad_x=np.matmul(grad_y, W.T)
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ x.T: shape(d, N)
+ """
+ grad_W=np.matmul(x.T, grad_y)
+```
+**Relu**
+
+**Forward**
+$$
+Y=\begin{cases}
+X&X\ge0\\\\
+0&\text{otherwise}
+\end{cases}
+$$
+**Backward**
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial X}=\begin{cases}1&X\ge0\\\\
+0&\text{otherwise}
+\end{cases}
+$$
+Python实现如下所示:
+```
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ x=self.memory['x']
+ grad_x=grad_y*np.where(x>0,1,0)
+ return grad_x
+```
+**Log**
+
+Forward
+$$
+Y=Log(x+epsilon)
+$$
+**Backward**
+$$
+Y=1/(x+epsilon)
+$$
+Python实现如下所示:
+```
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ x=self.memory['x']
+ grad_x=grad_y*(1./(x+self.epsilon))
+ return grad_x
+```
+Softmax:
+
+**Forward**
+$$
+Y_i = \frac{e^{X_i}}{\sum_{k=1}^n e^{X_k}}
+$$
+
+**Backward**
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y_i}{\partial X_j} =
+ \begin{cases}
+ Y_i \times (1 - Y_i) & i = j\\\\
+ -Y_i \times Y_j & i \neq j
+ \end{cases}
+$$
+Python实现如下所示:
+
+softmax的反向传播通过逐个元素判断求导进行实现
+```
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+ ex = np.exp(x)
+ rowsum = np.sum(ex,axis=1)
+ rowsum = rowsum[:,np.newaxis]
+ softmax = ex / rowsum
+ self.memory['softmax'] = softmax
+ return softmax
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ softmax = self.memory['softmax']
+ # print(sumx.shape)
+ [ROWS, COLUMNS] = softmax.shape
+ grad_x = []
+ grad_x=[[0 for i in range(COLUMNS)] for j in range(ROWS)]
+ for i in range(len(grad_x)):
+ for j in range(len(grad_x[0])):
+ for k in range(len(grad_x[0])):
+ if j == k:
+ grad_x[i][j] += (1 - softmax[i][k]) * softmax[i][k] * grad_y[i][k]
+ else:
+ grad_x[i][j] += -softmax[i][j] * softmax[i][k] * grad_y[i][k]
+ grad_x = np.array(grad_x)
+```
+### 3.mini_batch函数优化
+原有mini_batch方法是将元素打乱重排进行训练 分别将数据和标签储存进对应list
+
+将index进行打乱
+
+根据batch_size 从乱序index中一次取出相应大小的数据及标签进行训练
+
+Python实现如下所示:
+```
+def mini_batch(dataset,batch_size=128):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+ for each in dataset:
+ data.append(np.array(each[0]))
+ label.append(each[1])
+ data = np.array(data)
+ label = np.array(label)
+ index=data.shape[0]
+ index = list(np.random.permutation(index))
+ return [(data[index[i:i + batch_size]], label[index[i:i + batch_size]]) for i in range(0, len(data), batch_size)]
+```
+### 4.实验结果
+**准确率如下**
+
+使用**更新后的mini_batch函数**
+
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9367
+
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9607
+
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9687
+
+
+
+使用**util.py中的mini_batch函数**
+
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9441
+
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9635
+
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9721
+
+
+
+经过比对,两者准确性基本相同
+
+使用**更新后的mini_batch函数**,选取更小**batch**
+
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9594
+
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9702
+
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9771
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/img/loss_value mini batch.png b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/img/loss_value mini batch.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ab0658bf3f37b62a6bf629bdd9cb5b9a42dbad80
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/img/loss_value mini batch.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/img/mini_batch_orig.png b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/img/mini_batch_orig.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c4225c0e01087cb4abe343c4c8d295cb35ec7e22
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/img/mini_batch_orig.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/img/sma_bat.png b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/img/sma_bat.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a32722a6b75cbad3c5c8765cd4a6da9830e249ac
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/img/sma_bat.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..34a4a698fb55a49f5a9e680654d62081c9d8454a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+
+
+ ####################
+ # code 1 #
+ ####################
+ x=self.memory['x']
+ W=self.memory['W']
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ w.T: shape(d', d)
+ """
+ grad_x=np.matmul(grad_y, W.T)
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ x.T: shape(d, N)
+ """
+ grad_W=np.matmul(x.T, grad_y)
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ ####################
+ # code 2 #
+ ####################
+ x=self.memory['x']
+ grad_x=grad_y*np.where(x>0,1,0)
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ ####################
+ # code 3 #
+ ####################
+ x=self.memory['x']
+ grad_x=grad_y*(1./(x+self.epsilon))
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+ ####################
+ # code 4 #
+ ####################
+# self.memory['x'] = x
+# exp_x=np.exp(x)
+# softmax=np.exp(x)/np.sum(exp_x,axis=1)
+# self.memory['softmax']=softmax
+ ex = np.exp(x)
+ rowsum = np.sum(ex,axis=1)
+ rowsum = rowsum[:,np.newaxis]
+ softmax = ex / rowsum
+ self.memory['softmax'] = softmax
+ return softmax
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ ####################
+ # code 5 #
+ ####################
+# softmax = self.memory['softmax']
+
+ softmax = self.memory['softmax']
+ # print(sumx.shape)
+ [ROWS, COLUMNS] = softmax.shape
+ grad_x = []
+ # print(grad_y)
+# grad_x=[[] for i in range(ROWS)]
+ grad_x=[[0 for i in range(COLUMNS)] for j in range(ROWS)]
+ for i in range(len(grad_x)):
+ for j in range(len(grad_x[0])):
+# for j in range(m):
+# out[i].append(0)
+ for k in range(len(grad_x[0])):
+ if j == k:
+
+ grad_x[i][j] += (1 - softmax[i][k]) * softmax[i][k] * grad_y[i][k]
+ else:
+ grad_x[i][j] += -softmax[i][j] * softmax[i][k] * grad_y[i][k]
+ grad_x = np.array(grad_x)
+
+ return grad_x
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ ####################
+ # code 6 #
+ ####################
+
+ A1 = self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1) # shape(5, 4)
+ z1 = self.relu_1.forward(A1)
+ A2 = self.matmul_2.forward(z1, self.W2)
+ z2=self.relu_2.forward(A2)
+ A3=self.matmul_3.forward(z2,self.W3)
+ z3 = self.softmax.forward(A3)
+ R = self.log.forward(z3)
+ return R
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+ ####################
+ # code 7 #
+ ####################
+ self.log_grad=self.log.backward(y)
+ self.soft_grad=self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad,self.W3_grad=self.matmul_3.backward(self.soft_grad)
+ self.relu_2_grad=self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad,self.W2_grad=self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+ self.relu_1_grad=self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad,self.W1_grad=self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+ pass
+
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..73e875088a352d2a35dc2a0e9a14357d3e5229aa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
+"""
+Created on Wed Apr 28 22:11:32 2021
+
+@author: hyt
+"""
+
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+def mini_batch(dataset,batch_size=128):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+ for each in dataset:
+ data.append(np.array(each[0]))
+ label.append(each[1])
+ data = np.array(data)
+ label = np.array(label)
+ index=data.shape[0]
+ index = list(np.random.permutation(index))
+ return [(data[index[i:i + batch_size]], label[index[i:i + batch_size]]) for i in range(0, len(data), batch_size)]
+
+
+def numpy_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+# y_pred = model.forward(x.numpy())
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..02a93eb112820dff16d39f05398e6a648fea011b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,523 @@
+# Assignment 2. 前馈神经网络
+
+- **姓名:高庆麾**
+- **学号:19307130062**
+
+
+
+## 第一部分:梯度计算公式推导
+
+### Matmul
+
+考虑 $Y = XW$,其中 $Y \in \R^{n\times d_2},\ X \in \R^{n \times d_1},\ W \in \R^{d_1 \times d_2}$
+
+设损失函数为 $\mathcal L(\boldsymbol y,\ \boldsymbol {\hat y})$ ,且 $\Delta_Y$ (即 $Y$ 相对于损失函数的梯度)已知,希望得到 $\Delta_X,\ \Delta_W$
+
+推导如下:
+
+#### $\Delta_X$ 的推导
+
+我们考虑 $Y$ 的每一位对 $X$ 贡献的偏导,即 $\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X}$
+
+由于 $Y_{ij} = \sum_{k = 1}^{d_1}X_{ik}W_{kj}$ ,$X$ 各位独立,且
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X} =
+\begin{bmatrix}
+\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{11}} & \frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{12}} & \cdots & \frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{1d_1}} \\
+\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{21}} & \frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{22}} & \cdots & \frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{2d_1}} \\
+\vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\
+\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{n1}} & \frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{n2}} & \cdots & \frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{nd_1}} \\
+\end{bmatrix}
+$$
+故 $\left[\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X}\right]_{ik} = W_{kj},\ k \in [1,\ d_1] \cap\Z$ ,其余项为 $0$
+
+由于 $\Delta_Y$ 已知,即 $\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{ij}}$ 已知,则有
+$$
+\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial X_{ij}} = \sum_{s = 1}^n\sum_{t = 1}^{d_2} \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{st}}\frac{\partial{Y_{st}}}{\partial X_{ij}} = \sum_{s = 1}^n\sum_{t = 1}^{d_2} \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{st}}\left[\frac{\partial{Y_{st}}}{\partial X}\right]_{ij} = \sum_{t = 1}^{d_2} \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{it}}\left[\frac{\partial{Y_{it}}}{\partial X}\right]_{ij} = \sum_{t = 1}^{d_2} \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{it}}W_{jt} = \sum_{t = 1}^{d_2} \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{it}}W^T_{tj}
+$$
+即
+$$
+\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial X} = \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y}W^T
+$$
+可知
+$$
+\Delta_X = \Delta_YW^T
+$$
+
+#### $\Delta_W$ 的推导
+
+其次,对于 $\Delta_W$ ,我们用类似的方法进行计算,有 $\left[\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial W}\right]_{kj} = X_{ik},\ k \in [1,\ d_1] \cap\Z$ ,其余项为 $0$ ,则有
+$$
+\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial W_{ij}} = \sum_{s = 1}^{n}\sum_{t = 1}^{d_2} \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{st}}\left[\frac{\partial{Y_{st}}}{\partial W}\right]_{ij} = \sum_{s = 1}^{n} \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{sj}}\left[\frac{\partial{Y_{sj}}}{\partial W}\right]_{ij} = \sum_{s = 1}^{n} \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{sj}}X_{si} = \sum_{s = 1}^{n} X_{is}^T\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{sj}}
+$$
+即
+$$
+\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial W} = X^T\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y}
+$$
+可知
+$$
+\Delta_W = X^T\Delta_Y
+$$
+$\square$
+
+
+
+### ReLU
+
+考虑 $Y = \mathrm{ReLU}(X)$ ,其中 $Y,\ X \in \R^{n\times m}$
+
+设损失函数为 $\mathcal L(\boldsymbol y,\ \boldsymbol {\hat y})$ ,且 $\Delta_Y$ (即 $Y$ 相对于损失函数的梯度)已知,希望得到 $\Delta_X$
+
+推导如下:
+
+#### $\Delta_X$ 的推导
+
+方法类似于上文,只要注意这里的 $\mathrm{ReLU}$ 是一个逐元素函数
+
+考虑 $Y$ 的每一位对 $X$ 贡献的导数,即 $\frac{\mathrm{d}Y_{ij}}{\mathrm{d} X}$
+
+由于 $Y_{ij} = \mathrm{ReLU}(X_{ij})$ ,故 $\left[\frac{\mathrm{d}Y_{ij}}{\mathrm{d}X}\right]_{ij} = \mathrm{ReLU}'(X_{ij})$ ,其余项为 $0$
+
+显然
+$$
+\mathrm{ReLU}'(x) = \begin{cases}
+0, & n < 0 \\
+1, & n > 0 \\
+\mathrm{Undefined}, & n = 0
+\end{cases}
+$$
+当然,在 $x = 0$ 处,由于截断误差的存在,可以认为导数为 $0$ 或 $1$
+
+则有
+$$
+\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial X_{ij}} = \sum_{s = 1}^n\sum_{t = 1}^{m} \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{st}}\frac{\mathrm{d}{Y_{st}}}{\mathrm{d} X_{ij}} = \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{ij}}\left[\frac{\partial{Y_{ij}}}{\partial X}\right]_{ij} =\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{ij}}\mathrm{ReLU}'(X_{ij})
+$$
+即(此处 $\odot$ 表示矩阵的哈达玛积,即对应位乘积)
+$$
+\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial X} = \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y}\odot\mathrm{ReLU}'(X)
+$$
+可知
+$$
+\Delta_X = \Delta_Y\odot\mathrm{ReLU}'(X)
+$$
+$\square$
+
+
+
+### Log
+
+考虑 $Y = \mathrm{Log}(X)$ ,其中 $Y,\ X \in \R^{n\times m}$
+
+设损失函数为 $\mathcal L(\boldsymbol y,\ \boldsymbol {\hat y})$ ,且 $\Delta_Y$ (即 $Y$ 相对于损失函数的梯度)已知,希望得到 $\Delta_X$
+
+推导如下:
+
+#### $\Delta_X$ 的推导
+
+方法类似于上文,只要注意这里的 $\mathrm{Log}$ 是一个逐元素函数
+
+考虑 $Y$ 的每一位对 $X$ 贡献的导数,即 $\frac{\mathrm{d}Y_{ij}}{\mathrm{d} X}$
+
+由于 $Y_{ij} = \mathrm{Log}(X_{ij})$ ,故 $\left[\frac{\mathrm{d}Y_{ij}}{\mathrm{d}X}\right]_{ij} = \mathrm{Log}'(X_{ij}) = \frac{1}{X_{ij}}$ ,其余项为 $0$
+
+则有
+$$
+\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial X_{ij}} = \sum_{s = 1}^n\sum_{t = 1}^{m} \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{st}}\frac{\mathrm{d}{Y_{st}}}{\mathrm{d} X_{ij}} = \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{ij}}\left[\frac{\partial{Y_{ij}}}{\partial X}\right]_{ij} =\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{ij}}\frac{1}{X_{ij}}
+$$
+即(其中 $\frac{1}{X}$ 表示 $X$ 的每一位取倒数后的结果)
+$$
+\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial X} = \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y}\odot\frac{1}{X}
+$$
+可知
+$$
+\Delta_X = \Delta_Y\odot\frac{1}{X}
+$$
+$\square$
+
+
+
+### Softmax
+
+考虑 $\boldsymbol y = \mathrm{Softmax}(\boldsymbol x)$ ,其中 $\boldsymbol y,\ \boldsymbol x \in \R^{1 \times c}$
+
+设损失函数为 $\mathcal L(\boldsymbol y,\ \boldsymbol {\hat y})$ ,且 $\Delta_{\boldsymbol y}$ (即 $Y$ 相对于损失函数的梯度)已知,希望得到 $\boldsymbol y$ 的表达(前向计算)及 $\Delta_{\boldsymbol x}$
+
+推导如下:
+
+#### $\boldsymbol y$ 的推导(前向计算)
+
+根据 $\mathrm{Softmax}$ 的定义,可以得到
+$$
+\boldsymbol y_i = \frac{e^{\boldsymbol x_i}}{\sum_{j = 1}^ce^{\boldsymbol x_j}}
+$$
+
+#### $\Delta_{\boldsymbol x}$ 的推导
+
+由于
+$$
+\boldsymbol y_i = \frac{e^{\boldsymbol x_i}}{\sum_{j = 1}^ce^{\boldsymbol x_j}}
+$$
+且
+$$
+\frac{\partial \boldsymbol y}{\partial\boldsymbol x} =
+\begin{bmatrix}
+\frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_1}{\partial \boldsymbol x_1} & \frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_1}{\partial \boldsymbol x_2} & \cdots & \frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_1}{\partial \boldsymbol x_c} \\
+\frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_2}{\partial \boldsymbol x_1} & \frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_2}{\partial \boldsymbol x_2} & \cdots & \frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_2}{\partial \boldsymbol x_c} \\
+\vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\
+\frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_c}{\partial \boldsymbol x_1} & \frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_c}{\partial \boldsymbol x_2} & \cdots & \frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_c}{\partial \boldsymbol x_c} \\
+\end{bmatrix}
+$$
+故当 $i = j$ 时,有
+$$
+\left[\frac{\partial \boldsymbol y}{\partial\boldsymbol x}\right]_{ii} = \frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_i}{\partial \boldsymbol x_i} = \frac{\partial\left( \frac{e^{\boldsymbol x_i}}{\sum_{j = 1}^ce^{\boldsymbol x_j}}\right)}{\partial \boldsymbol x_i} = \frac{e^{\boldsymbol x_i}(\sum_{j = 1}^ce^{\boldsymbol x_j}) - e^{\boldsymbol x_i}e^{\boldsymbol x_i}}{\left(\sum_{j = 1}^ce^{\boldsymbol x_j}\right)^2} = \frac{e^{\boldsymbol x_i}}{\sum_{j = 1}^ce^{\boldsymbol x_j}}\frac{\left(\sum_{j = 1}^ce^{\boldsymbol x_j}\right) - e^{\boldsymbol x_i}}{\sum_{j = 1}^ce^{\boldsymbol x_j}} = \boldsymbol y_i(1 - \boldsymbol y_i)
+$$
+当 $i \neq j$ 时,有
+$$
+\left[\frac{\partial \boldsymbol y}{\partial\boldsymbol x}\right]_{ij} = \frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_i}{\partial \boldsymbol x_j} = \frac{\partial\left( \frac{e^{\boldsymbol x_i}}{\sum_{j = 1}^ce^{\boldsymbol x_j}}\right)}{\partial \boldsymbol x_j} = \frac{-e^{\boldsymbol x_i}e^{\boldsymbol x_j}}{\left(\sum_{j = 1}^ce^{\boldsymbol x_j}\right)^2} = -\boldsymbol y_i\boldsymbol y_j
+$$
+则有
+$$
+\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial\boldsymbol x_{j}} = \sum_{i = 1}^c\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial\boldsymbol y_{i}}\frac{\partial\boldsymbol y_i}{\partial \boldsymbol x_j} = \sum_{i = 1}^c\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial\boldsymbol y_{i}}\left[\frac{\partial\boldsymbol y}{\partial \boldsymbol x}\right]_{ij}
+$$
+即
+$$
+\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial\boldsymbol x} = \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial \boldsymbol y}\left[\frac{\partial\boldsymbol y}{\partial \boldsymbol x}\right]
+$$
+可知(其中 $\left[\frac{\partial\boldsymbol y}{\partial \boldsymbol x}\right]$ 已经在上文中求出)
+$$
+\Delta_{\boldsymbol x} = \Delta_{\boldsymbol y}\left[\frac{\partial\boldsymbol y}{\partial \boldsymbol x}\right]
+$$
+由于原代码中给出的是一组行向量构成的矩阵,因此,我们可以对每一行分别进行如上操作,且行与行之间互不干扰,由此完成 $\mathrm{Softmax}$ 的反向传播
+
+$\square$
+
+*注意此处对应代码的写法,对于 numpy 里的 array A,A[i] 只会被认为具有一个维度(被看做是一列数而非一个行向量),因此如果希望使用其对应的行向量,需要将 A[i] 转换为 matrix 类型,此时就会带上表示行的一维
+
+
+
+### FNN
+
+由于整个 FNN 由上面推导过的许多基本层次构成,因此在 FNN 中进行前向计算,只需要类似函数嵌套的方法将模型结构的各个层次结合在一起即可
+
+设 FNN 对应的函数为 $F$ ,则
+
+#### $F$ 的推导(前向计算)
+
+$F(X) = \mathrm{Log}(\mathrm{Softmax}(\mathrm{ReLU}(\mathrm{ReLU}(X\cdot W_1)\cdot W_2)\cdot W_3))$
+
+其中 $X \in \R^{n \times 784},\ W_1 \in \R^{784\times 256},\ W_2 \in \R^{256\times 64},\ W_3 \in \R^{64\times 10},\ F(X) \in \R^{n \times 10}$ ,$n$ 为数据条数
+
+#### FNN 后向传播的推导
+
+根据代码,我们可以得到模型定义的损失函数为 $\mathcal L(\boldsymbol y,\ \boldsymbol {\hat y}) = -\boldsymbol {\hat y}\boldsymbol y^T$ ($\boldsymbol {\hat y}$ 表示预测向量),而在整个数据集上的定义为
+
+$\mathcal L(Y,\ \hat Y) = -\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i = 1}^n{\hat Y_{i:}}Y_{i:}^T = -\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i = 1}^n\sum_{j = 1}^d{\hat Y_{ij}}Y_{ij}$
+
+由此我们需要计算 $\Delta_{\hat Y}$ (即 $\hat Y$ 相对于该损失函数的梯度,$\hat Y = F(X)$ )
+
+推导如下:
+
+#### $\Delta_{\hat Y}$ 的推导
+
+根据上文对 $\mathcal L$ 的定义,我们很容易得到
+$$
+\frac{\partial\mathcal L}{\partial\hat Y_{ij}} = -\frac{1}{n}Y_{ij}
+$$
+由此即可得到最初进入反向传播过程的梯度矩阵 $\Delta_{\hat Y}$ ,其它层上的梯度可以通过逐层反向传播得到
+
+
+
+### 总结
+
+**这里希望就笔者对梯度和导数的理解,以及根据自己的理解和方法简明地推导反向传播公式的感悟,做一点总结。**
+
+对于后向传播的梯度计算,有许许多多的方法,比如迹运算技术[^1]和向量化技术[^2]即为比较通用的高维求导方法。但简单尝试后可以发现,这些方法运用起来实在过于复杂。实际上,为了正确而又简单地计算梯度,我们只需要明确所谓梯度(或者说导数)究竟有怎样的实际含义。
+
+*下面对梯度和导数的概念可能有一些混用,在本文中这两者表达的含义基本相同。
+
+对于一个非常一般的关系 $A = f(B)$ ,此处 $A,\ B$ 可视为任意维度和大小的张量。如果对线性代数比较熟悉,可以知道,其实这只是对许多多元函数关系的一种简化表达。如果我们拆开来看,若 $a$ 是 $A$ 中某一项,那么 $a$ 实际上就是一个**关于 $B$ 中所有项的多元函数**。
+
+其次,为什么要在神经网络中计算梯度?无非就是希望通过梯度下降来迭代地优化神经网络的效果(而梯度下降的方向也是损失函数值下降最快的方向,且一般而言这个损失函数的结果都是一个标量,否则难以比较大小)。既然如此,我们就需要计算出网络中每个参数的梯度,并通过将每个参数都向梯度下降的方向做一些移动,使得整个网络的损失函数在特定数据集上的表现有所优化。
+
+所以,我们可以认为,每个参数的移动都对损失函数的最终结果有一定的贡献。而链式法则告诉我们,这种贡献的正确计算方法,是考虑该参数到达损失函数的**每一条作用路径**[^3]。反向传播算法 (Back Propagation, BP) 即是利用了这种思想。如果对动态规划 (Dynamic Programming, DP) 算法比较熟悉(比如对运筹学比较熟悉或有程序设计竞赛方面的背景),可以知道 BP 实际是一个**非常显然而简单**的有向无环图 (Directed Acyclic Graph, DAG) 上 做 DP 的算法(当然这也很大程度上归功于链式法则的证明),因为神经网络中的计算图本身一定是一个 DAG,即从各个结点出发,沿着计算边行进,最终必定会到达损失函数。
+
+这样,我们在计算 $B$ 到 $\mathcal L$ 的梯度时,不再需要枚举所有作用路径,计算并累加所有的贡献,而只是需要计算从 $B$ 到以它为自变量(的一部分)的关系的象 $A$ 中所有可能的作用路径,再和先前计算好的从 $A$ 到 $\mathcal L$ 的梯度做一个“路径拼接”,实际也就是矩阵(或张量)的乘法,即可得到 $B$ 所有的贡献。关于 $A,\ B$ 的顺序,由于计算图是一个 DAG ,因此可以通过拓扑排序 (Topological Sort) 确定二者(乃至全部参数)之间合法的先后关系。
+
+回到上文的一般关系 $A = f(B)$ 中,从 $B$ 到 $A$ 的所有合法路径是怎样的?这就回到了一开始从 $A$ 中抽出的一项 $a$ (它也代表一个关于 $B$ 中所有项的多元函数) ,所谓所有的合法路径,实际也就是要考虑所有这样的 $A$ 中的项(或多元函数)对于 $B$ 中每一项的梯度,然后 $B$ 中每一项的贡献,也就是以 $\mathcal L$ 到 $A$ 中每一项的梯度作为权,乘这一 $A$ 中的项对 $B$ 中该项刚刚计算出的梯度(或称偏导)的和,这也就是先前提到的**“路径拼接”**(也是一种加权和,如此理解的意义也是非常显然的)。
+
+这样,对于日常遇到的简单情形,我们其实并不需要套用一些非常通用而繁琐的方法,只需要如上文一般,对 $A$ 中每一项求出其对 $B$ 中每一项的偏导,由此将问题转化为一个多元函数(结果是标量)对其中每个自变量的偏导问题,这显然是非常简单的(甚至不需要大学的知识)。而关于“简单情形”的定义,其实也就是指这种多元函数的形式比较一致,这样我们只需要对其中几个多元函数求出偏导,就能得到对全部情况的理解。最后模仿“路径拼接”或链式法则,将表达简化为矩阵乘法的形式,就可以非常容易地得到梯度。本文对相关常见的神经网络层反向传播的推导,全部基于这种认识和由此而来的方法,在笔者个人看来,是足够简明和容易理解的。
+
+
+
+
+
+[^1]: 来源于该式 $\mathrm{d}f = \mathrm{tr}\left(\frac{\partial f}{\partial X}^T \mathrm{d}X\right)$,用于标量对矩阵的求导。从需要求导的标量出发,套上迹运算,再结合一些迹内运算的恒等式推导得到类似形式,则迹运算内 $\mathrm{d}X$ 左侧部分的转置即为所求导数
+[^2]:来源于该式 $\mathrm{vec}(\mathrm{d}F) = \frac{\partial F}{\partial X}^T \mathrm{vec}(\mathrm{d}X)$,用于矩阵对矩阵的求导。类似地,从需要求导的矩阵出发,套上向量化运算,再结合一些向量化内运算的恒等式推导得到类似形式,则 $\mathrm{vec}(\mathrm{d}X)$ 左侧部分的转置即为所求导数
+[^3]: 对于这一点,可以举例考虑函数 $f = (x,\ y,\ z),\ x = g(u),\ y = h(u),\ z = t(u)$ 。如果可导相关的条件上没有任何障碍,那么想要求出 $\frac{\partial f}{\partial u}$ ,我们就必须计算 $\frac{\partial f}{\partial x}\frac{\partial x}{\partial u} + \frac{\partial f}{\partial y}\frac{\partial y}{\partial u} + \frac{\partial f}{\partial z}\frac{\partial z}{\partial u}$ ,也就是考虑 $u$ 到 $f$ 的每一条作用路径。
+
+
+
+
+
+## 第二部分:模型的训练和测试(先前版本)
+
+在从损失函数进行梯度回传时,发现并没有为损失函数提供 `backward` 接口,因此就去看了一下损失函数的具体形式,然后进行了一下推导,发现只需要在原来取平均的基础上加一个负号就可以,然后就通过了所有的测试。但不知道为什么初始准确率不是很高,只有 $80\%$ 多。多训练几个 epoch 后才提升得比较好。
+
+### 调整学习率
+
+#### 保守尝试
+
+根据上文的推导结果,在 `numpy_fnn.py` 中填写好有关代码,然后运行 `numpy_mnist.py` 进行训练,并尝试不同的学习率,得到结果如下:
+
+(实际顺序是先测试了原配置 $\alpha = 0.1$,后来发现损失函数后期波动较大,以为是学习率过大导致的不稳定,就尝试了更小的学习率 $\alpha = 0.05$ ,结果发现效果明显不如从前,就开始逐渐增大学习率进行试验,观察效果。最后决定将数据和损失函数图象放在一起,这样对比更加明显,且节约篇幅)
+
+| Epoch | Accuracy ($\alpha = 0.05$) | Accuracy ($\alpha = 0.1$) | Accuracy $(\alpha = 0.15$) | Accuracy $(\alpha = 0.3$) |
+| :---: | :------------------------: | :-----------------------: | :------------------------: | :-----------------------: |
+| $0$ | $80.18\%$ | $87.50\%$ | $89.20\%$ | $91.06\%$ |
+| $1$ | $87.25\%$ | $90.46\%$ | $91.22\%$ | $93.54\%$ |
+| $2$ | $89.23\%$ | $91.65\%$ | $92.46\%$ | $94.64\%$ |
+| $3$ | $90.40\%$ | $92.21\%$ | $93.19\%$ | $95.42\%$ |
+| $4$ | $91.03\%$ | $92.98\%$ | $93.67\%$ | $96.02\%$ |
+| $5$ | $91.61\%$ | $93.23\%$ | $94.45\%$ | $96.38\%$ |
+
+
+
+```
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9503
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9639
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9711
+```
+
+### 7.提交的代码说明
+
+- `numpy_fnn.py`:算子和FNN模型正向传播和反向传播的实现。`optimize_Momentum`方法实现Momentum优化,`optimize_Adam`方法实现Adam优化。可在`numpy_mnist.py`中修改optimize的调用改变优化方法。
+- `numpy_mnist.py`:`mini_batch_numpy`方法用numpy实现了mini_batch。
+- `utils.py`:`get_torch_initialization_numpy`方法用numpy实现了均匀分布的kaiming初始化。
+
+### 8.参考文献
+
+[1] [神经网络常见优化算法(Momentum, RMSprop, Adam)的原理及公式理解, 学习率衰减](https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42561002/article/details/88036777)
+
+[2] [深度之眼【Pytorch】-Xavier、Kaiming初始化(附keras实现)](https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42147780/article/details/103238195)
+
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig1.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..50b42797b50f8b745d7707a86e2644d84843d228
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig2.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f5dd7bdc2c2712953ddd2b990232d3a7a71b655b
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig3.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig3.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c440ff99663169e8b636ed9e3fc8b7cbdb6008f1
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig3.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig4.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig4.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..05196c545d1d6da186cd8e301eff8fec10110060
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig4.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig5.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig5.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..31658f4aa8db641225bf56c4ef54fb8c079d7ae2
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig5.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig6.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig6.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..54721b598f39cfb996bfde8986077ca64836eb76
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig6.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig7.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig7.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..1a3f1b1c91d8767838bd464ad291da558006c941
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig7.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig8.png b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig8.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..081717ced38314a1b250daf2f527bce99313bc71
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/img/Fig8.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..bacac809951ecb357664479fa2f8f69e956fd8b8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,240 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 1 #
+ ####################
+ xT = np.transpose(self.memory['x'])
+ WT = np.transpose(self.memory['W'])
+
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, WT)
+ grad_W = np.matmul(xT, grad_y)
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 2 #
+ ####################
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ grad_x = grad_y * np.where(x > 0, 1, 0)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 3 #
+ ####################
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ grad_x = grad_y / (x + self.epsilon)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 4 #
+ ####################
+ sum = np.exp(x).sum(axis = 1)
+ sum = sum.reshape(x.shape[0], 1)
+ out = np.exp(x) / sum
+
+ self.memory['y'] = out
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ ####################
+ # code 5 #
+ ####################
+ y = self.memory['y']
+
+ grad_x = y * (grad_y - (y * grad_y).sum(axis = 1).reshape(len(y),1))
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新。 softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ # Momentum优化
+ self.v_W1_grad = 0
+ self.v_W2_grad = 0
+ self.v_W3_grad = 0
+
+ # Adam优化
+ self.s_W1_grad = 0
+ self.s_W2_grad = 0
+ self.s_W3_grad = 0
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ ####################
+ # code 6 #
+ ####################
+ x = self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1)
+ x = self.relu_1.forward(x)
+
+ x = self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2)
+ x = self.relu_2.forward(x)
+
+ x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+ x = self.softmax.forward(x)
+
+ x = self.log.forward(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+
+ ####################
+ # code 7 #
+ ###################
+
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y)
+
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+
+ self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+
+ def optimize_Momentum(self, learning_rate, belta):
+ self.v_W1_grad = belta * self.v_W1_grad + (1 - belta) * self.W1_grad
+ self.v_W2_grad = belta * self.v_W2_grad + (1 - belta) * self.W2_grad
+ self.v_W3_grad = belta * self.v_W3_grad + (1 - belta) * self.W3_grad
+
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.v_W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.v_W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.v_W3_grad
+
+ def optimize_Adam(self, learning_rate, beta1, beta2, beta1_t, beta2_t, eps):
+
+ self.v_W1_grad = beta1 * self.v_W1_grad + (1 - beta1) * self.W1_grad
+ self.v_W2_grad = beta1 * self.v_W2_grad + (1 - beta1) * self.W2_grad
+ self.v_W3_grad = beta1 * self.v_W3_grad + (1 - beta1) * self.W3_grad
+
+ v_W1_corr = self.v_W1_grad / (1 - beta1_t)
+ v_W2_corr = self.v_W2_grad / (1 - beta1_t)
+ v_W3_corr = self.v_W3_grad / (1 - beta1_t)
+
+ self.s_W1_grad = beta2 * self.s_W1_grad + (1 - beta2) * (self.W1_grad ** 2)
+ self.s_W2_grad = beta2 * self.s_W2_grad + (1 - beta2) * (self.W2_grad ** 2)
+ self.s_W3_grad = beta2 * self.s_W3_grad + (1 - beta2) * (self.W3_grad ** 2)
+
+ s_W1_corr = self.s_W1_grad / (1 - beta2_t)
+ s_W2_corr = self.s_W2_grad / (1 - beta2_t)
+ s_W3_corr = self.s_W3_grad / (1 - beta2_t)
+
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * v_W1_corr / (np.sqrt(s_W1_corr) + eps)
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * v_W2_corr / (np.sqrt(s_W2_corr) + eps)
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * v_W3_corr / (np.sqrt(s_W3_corr) + eps)
+
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..87aa55fdfd8a765cbad3203b3a9082c28c5c6502
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, mini_batch, batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+
+def mini_batch_numpy(dataset, batch_size=128):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+
+ for x in dataset:
+ data.append(np.array(x[0]))
+ label.append(x[1])
+
+ data = np.array(data)
+ label = np.array(label)
+
+ idx = np.random.permutation(len(dataset))
+ data = data[idx]
+ label = label[idx]
+
+ split_num = len(dataset) // batch_size
+ split_pos = split_num * batch_size
+
+ ret_data = np.split(data[:split_pos], split_num)
+ ret_data.append(data[split_pos+1:])
+
+ ret_label = np.split(label[:split_pos], split_num)
+ ret_label.append(label[split_pos+1:])
+
+ ret = list(zip(ret_data, ret_label))
+ return ret
+
+def numpy_run():
+
+ import time
+ start = time.time()
+
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ #Adam 优化
+ beta1 = 0.9
+ beta2 = 0.999
+ beta1_t = 1
+ beta2_t = 1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ #Adam 优化
+ beta1_t *= beta1
+ beta2_t *= beta2
+
+ # for x, y in mini_batch_numpy(train_dataset): # mini_batch_numpy
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ # y_pred = model.forward(x) # mini_batch_numpy
+ y_pred = model.forward(x.numpy())
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+
+ #原始optimize
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ #Momentum 优化
+ # model.optimize_Momentum(learning_rate, 0.9)
+
+ #Adam 优化
+ # model.optimize_Adam(learning_rate, beta1, beta2, beta1_t, beta2_t, 1e-8)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ end = time.time()
+ print("time = %.2f s"%(end-start))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/tester_demo.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/tester_demo.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..504b3eef50a6df4d0aa433113136add50835e420
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/tester_demo.py
@@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
+import numpy as np
+import torch
+from torch import matmul as torch_matmul, relu as torch_relu, softmax as torch_softmax, log as torch_log
+
+from numpy_fnn import Matmul, Relu, Softmax, Log, NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from torch_mnist import TorchModel
+from utils import get_torch_initialization, one_hot
+
+err_epsilon = 1e-6
+err_p = 0.4
+
+
+def check_result(numpy_result, torch_result=None):
+ if isinstance(numpy_result, list) and torch_result is None:
+ flag = True
+ for (n, t) in numpy_result:
+ flag = flag and check_result(n, t)
+ return flag
+ # print((torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) - torch_result).abs().mean().item())
+ T = (torch_result * torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) < 0).sum().item()
+ direction = T / torch_result.numel() < err_p
+ return direction and ((torch.from_numpy(numpy_result) - torch_result).abs().mean() < err_epsilon).item()
+
+
+def case_1():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[5, 6])
+ W = np.random.normal(size=[6, 4])
+
+ numpy_matmul = Matmul()
+ numpy_out = numpy_matmul.forward(x, W)
+ numpy_x_grad, numpy_W_grad = numpy_matmul.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+ torch_W = torch.from_numpy(W).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_matmul(torch_x, torch_W)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ (numpy_W_grad, torch_W.grad)
+ ])
+
+
+def case_2():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[5, 6])
+
+ numpy_relu = Relu()
+ numpy_out = numpy_relu.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_relu.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_relu(torch_x)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def case_3():
+ x = np.random.uniform(low=0.0, high=1.0, size=[3, 4])
+
+ numpy_log = Log()
+ numpy_out = numpy_log.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_log.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_log(torch_x)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def case_4():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[4, 5])
+
+ numpy_softmax = Softmax()
+ numpy_out = numpy_softmax.forward(x)
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_softmax(torch_x, 1)
+
+ return check_result(numpy_out, torch_out)
+
+
+def case_5():
+ x = np.random.normal(size=[20, 25])
+
+ numpy_softmax = Softmax()
+ numpy_out = numpy_softmax.forward(x)
+ numpy_x_grad = numpy_softmax.backward(np.ones_like(numpy_out))
+
+ torch_x = torch.from_numpy(x).clone().requires_grad_()
+
+ torch_out = torch_softmax(torch_x, 1)
+ torch_out.sum().backward()
+
+ return check_result([
+ (numpy_out, torch_out),
+ (numpy_x_grad, torch_x.grad),
+ ])
+
+
+def test_model():
+ try:
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ numpy_model = NumpyModel()
+ torch_model = TorchModel()
+ torch_model.W1.data, torch_model.W2.data, torch_model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+ numpy_model.W1 = torch_model.W1.detach().clone().numpy()
+ numpy_model.W2 = torch_model.W2.detach().clone().numpy()
+ numpy_model.W3 = torch_model.W3.detach().clone().numpy()
+
+ x = torch.randn((10000, 28, 28))
+ y = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0] * 1000)
+
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+ x2 = x.numpy()
+ y_pred = torch_model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+
+ y_pred_numpy = numpy_model.forward(x2)
+ numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred_numpy, y.numpy())
+
+ check_flag_1 = check_result(y_pred_numpy, y_pred)
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("forward", 10 * check_flag_1, 10))
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in forward]")
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("forward", 0, 10))
+ return 0
+
+ try:
+
+ numpy_model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+
+ check_flag_2 = [
+ check_result(numpy_model.log_grad, torch_model.log_input.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.softmax_grad, torch_model.softmax_input.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W3_grad, torch_model.W3.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W2_grad, torch_model.W2.grad),
+ check_result(numpy_model.W1_grad, torch_model.W1.grad)
+ ]
+ check_flag_2 = sum(check_flag_2) >= 4
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("backward", 20 * check_flag_2, 20))
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in backward]")
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format("backward", 0, 20))
+ check_flag_2 = False
+
+ return 10 * check_flag_1 + 20 * check_flag_2
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ testcases = [
+ ["matmul", case_1, 5],
+ ["relu", case_2, 5],
+ ["log", case_3, 5],
+ ["softmax_1", case_4, 5],
+ ["softmax_2", case_5, 10],
+ ]
+ score = 0
+ for case in testcases:
+ try:
+ res = case[2] if case[1]() else 0
+ except:
+ print("[Runtime Error in {}]".format(case[0]))
+ res = 0
+ score += res
+ print("+ {:12} {}/{}".format(case[0], res, case[2]))
+ score += test_model()
+ print("{:14} {}/60".format("FINAL SCORE", score))
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/torch_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/torch_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7bbcedcf8108c227e09c861a761c18e99a7f9429
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/torch_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+import torch
+from utils import mini_batch, batch, download_mnist, get_torch_initialization, one_hot, plot_curve
+
+
+class TorchModel:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = torch.randn((28 * 28, 256), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W2 = torch.randn((256, 64), requires_grad=True)
+ self.W3 = torch.randn((64, 10), requires_grad=True)
+ self.softmax_input = None
+ self.log_input = None
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W1))
+ x = torch.relu(torch.matmul(x, self.W2))
+ x = torch.matmul(x, self.W3)
+
+ self.softmax_input = x
+ self.softmax_input.retain_grad()
+
+ x = torch.softmax(x, 1)
+
+ self.log_input = x
+ self.log_input.retain_grad()
+
+ x = torch.log(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ with torch.no_grad():
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1.grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2.grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3.grad
+
+ self.W1.grad = None
+ self.W2.grad = None
+ self.W3.grad = None
+
+
+def torch_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = TorchModel()
+ # model.W1.data, model.W2.data, model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization(numpy=False)
+ from utils import get_torch_initialization_numpy
+ model.W1.data, model.W2.data, model.W3.data = get_torch_initialization_numpy(numpy=False)
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset, numpy=False):
+ y = one_hot(y, numpy=False)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+ loss = (-y_pred * y).sum(dim=1).mean()
+ loss.backward()
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset, numpy=False)[0]
+ accuracy = model.forward(x).argmax(dim=1).eq(y).float().mean().item()
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ torch_run()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/utils.py b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/utils.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..5154f4970843623204198206ff0df1438bbee5df
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/18307130341/utils.py
@@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
+import torch
+import numpy as np
+from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
+
+
+def plot_curve(data):
+ plt.plot(range(len(data)), data, color='blue')
+ plt.legend(['loss_value'], loc='upper right')
+ plt.xlabel('step')
+ plt.ylabel('value')
+ plt.show()
+
+
+def download_mnist():
+ from torchvision import datasets, transforms
+
+ transform = transforms.Compose([
+ transforms.ToTensor(),
+ transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.1307,), std=(0.3081,))
+ ])
+
+ train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=True, download=True)
+ test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/", transform=transform, train=False, download=True)
+
+ return train_dataset, test_dataset
+
+
+def one_hot(y, numpy=True):
+ if numpy:
+ y_ = np.zeros((y.shape[0], 10))
+ y_[np.arange(y.shape[0], dtype=np.int32), y] = 1
+ return y_
+ else:
+ y_ = torch.zeros((y.shape[0], 10))
+ y_[torch.arange(y.shape[0], dtype=torch.long), y] = 1
+ return y_
+
+
+def batch(dataset, numpy=True):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+ for each in dataset:
+ data.append(each[0])
+ label.append(each[1])
+ data = torch.stack(data)
+ label = torch.LongTensor(label)
+ if numpy:
+ return [(data.numpy(), label.numpy())]
+ else:
+ return [(data, label)]
+
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size=128, numpy=False):
+ return torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
+
+
+def get_torch_initialization(numpy=True):
+ fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(28 * 28, 256)
+ fc2 = torch.nn.Linear(256, 64)
+ fc3 = torch.nn.Linear(64, 10)
+
+ if numpy:
+ W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ W2 = fc2.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ W3 = fc3.weight.T.detach().clone().numpy()
+ else:
+ W1 = fc1.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+ W2 = fc2.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+ W3 = fc3.weight.T.detach().clone().data
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
+
+def get_torch_initialization_numpy(numpy=True):
+ fan_in_1 = 28 * 28
+ fan_in_2 = 256
+ fan_in_3 = 64
+
+ bound1 = 1 / np.sqrt(fan_in_1)
+ bound2 = 1 / np.sqrt(fan_in_2)
+ bound3 = 1 / np.sqrt(fan_in_3)
+
+ W1 = np.random.uniform(-bound1, bound1, (28*28, 256))
+ W2 = np.random.uniform(-bound2, bound2, (256, 64))
+ W3 = np.random.uniform(-bound3, bound3, (64, 10))
+
+ if numpy == False:
+ W1 = torch.Tensor(W1)
+ W2 = torch.Tensor(W2)
+ W3 = torch.Tensor(W3)
+
+ return W1, W2, W3
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..abdc5462b52fc1d754752b8f1c3b62442d70e009
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,191 @@
+# 实验报告
+### 1.模型设计
+神经网络设计如下图所示
+### 2.算子补充
+**Matmul**
+
+**Forward**
+$$
+h=X*W
+$$
+
+**Backward**
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial X} = W^{T}
+$$
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial W} = X^{T}
+$$
+维度变化以及Python实现如下所示:
+```
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ w.T: shape(d', d)
+ """
+ grad_x=np.matmul(grad_y, W.T)
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ x.T: shape(d, N)
+ """
+ grad_W=np.matmul(x.T, grad_y)
+```
+**Relu**
+
+**Forward**
+$$
+Y=\begin{cases}
+X&X\ge0\\\\
+0&\text{otherwise}
+\end{cases}
+$$
+**Backward**
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial X}=\begin{cases}1&X\ge0\\\\
+0&\text{otherwise}
+\end{cases}
+$$
+Python实现如下所示:
+```
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ x=self.memory['x']
+ grad_x=grad_y*np.where(x>0,1,0)
+ return grad_x
+```
+**Log**
+
+Forward
+$$
+Y=Log(x+epsilon)
+$$
+**Backward**
+$$
+Y=1/(x+epsilon)
+$$
+Python实现如下所示:
+```
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ x=self.memory['x']
+ grad_x=grad_y*(1./(x+self.epsilon))
+ return grad_x
+```
+Softmax:
+
+**Forward**
+$$
+Y_i = \frac{e^{X_i}}{\sum_{k=1}^n e^{X_k}}
+$$
+
+**Backward**
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y_i}{\partial X_j} =
+ \begin{cases}
+ Y_i \times (1 - Y_i) & i = j\\\\
+ -Y_i \times Y_j & i \neq j
+ \end{cases}
+$$
+Python实现如下所示:
+
+softmax的反向传播通过逐个元素判断求导进行实现
+```
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+ ex = np.exp(x)
+ rowsum = np.sum(ex,axis=1)
+ rowsum = rowsum[:,np.newaxis]
+ softmax = ex / rowsum
+ self.memory['softmax'] = softmax
+ return softmax
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ softmax = self.memory['softmax']
+ # print(sumx.shape)
+ [ROWS, COLUMNS] = softmax.shape
+ grad_x = []
+ grad_x=[[0 for i in range(COLUMNS)] for j in range(ROWS)]
+ for i in range(len(grad_x)):
+ for j in range(len(grad_x[0])):
+ for k in range(len(grad_x[0])):
+ if j == k:
+ grad_x[i][j] += (1 - softmax[i][k]) * softmax[i][k] * grad_y[i][k]
+ else:
+ grad_x[i][j] += -softmax[i][j] * softmax[i][k] * grad_y[i][k]
+ grad_x = np.array(grad_x)
+```
+### 3.mini_batch函数优化
+原有mini_batch方法是将元素打乱重排进行训练 分别将数据和标签储存进对应list
+
+将index进行打乱
+
+根据batch_size 从乱序index中一次取出相应大小的数据及标签进行训练
+
+Python实现如下所示:
+```
+def mini_batch(dataset,batch_size=128):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+ for each in dataset:
+ data.append(np.array(each[0]))
+ label.append(each[1])
+ data = np.array(data)
+ label = np.array(label)
+ index=data.shape[0]
+ index = list(np.random.permutation(index))
+ return [(data[index[i:i + batch_size]], label[index[i:i + batch_size]]) for i in range(0, len(data), batch_size)]
+```
+### 4.实验结果
+**准确率如下**
+
+使用**更新后的mini_batch函数**
+
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9367
+
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9607
+
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9687
+
+
+
+使用**util.py中的mini_batch函数**
+
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9441
+
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9635
+
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9721
+
+
+
+经过比对,两者准确性基本相同
+
+使用**更新后的mini_batch函数**,选取更小**batch**
+
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9594
+
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9702
+
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9771
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/img/loss_value mini batch.png b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/img/loss_value mini batch.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ab0658bf3f37b62a6bf629bdd9cb5b9a42dbad80
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/img/loss_value mini batch.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/img/mini_batch_orig.png b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/img/mini_batch_orig.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c4225c0e01087cb4abe343c4c8d295cb35ec7e22
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/img/mini_batch_orig.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/img/sma_bat.png b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/img/sma_bat.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..a32722a6b75cbad3c5c8765cd4a6da9830e249ac
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/img/sma_bat.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..34a4a698fb55a49f5a9e680654d62081c9d8454a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+
+
+ ####################
+ # code 1 #
+ ####################
+ x=self.memory['x']
+ W=self.memory['W']
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ w.T: shape(d', d)
+ """
+ grad_x=np.matmul(grad_y, W.T)
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ x.T: shape(d, N)
+ """
+ grad_W=np.matmul(x.T, grad_y)
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ ####################
+ # code 2 #
+ ####################
+ x=self.memory['x']
+ grad_x=grad_y*np.where(x>0,1,0)
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ ####################
+ # code 3 #
+ ####################
+ x=self.memory['x']
+ grad_x=grad_y*(1./(x+self.epsilon))
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+ ####################
+ # code 4 #
+ ####################
+# self.memory['x'] = x
+# exp_x=np.exp(x)
+# softmax=np.exp(x)/np.sum(exp_x,axis=1)
+# self.memory['softmax']=softmax
+ ex = np.exp(x)
+ rowsum = np.sum(ex,axis=1)
+ rowsum = rowsum[:,np.newaxis]
+ softmax = ex / rowsum
+ self.memory['softmax'] = softmax
+ return softmax
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+ ####################
+ # code 5 #
+ ####################
+# softmax = self.memory['softmax']
+
+ softmax = self.memory['softmax']
+ # print(sumx.shape)
+ [ROWS, COLUMNS] = softmax.shape
+ grad_x = []
+ # print(grad_y)
+# grad_x=[[] for i in range(ROWS)]
+ grad_x=[[0 for i in range(COLUMNS)] for j in range(ROWS)]
+ for i in range(len(grad_x)):
+ for j in range(len(grad_x[0])):
+# for j in range(m):
+# out[i].append(0)
+ for k in range(len(grad_x[0])):
+ if j == k:
+
+ grad_x[i][j] += (1 - softmax[i][k]) * softmax[i][k] * grad_y[i][k]
+ else:
+ grad_x[i][j] += -softmax[i][j] * softmax[i][k] * grad_y[i][k]
+ grad_x = np.array(grad_x)
+
+ return grad_x
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ ####################
+ # code 6 #
+ ####################
+
+ A1 = self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1) # shape(5, 4)
+ z1 = self.relu_1.forward(A1)
+ A2 = self.matmul_2.forward(z1, self.W2)
+ z2=self.relu_2.forward(A2)
+ A3=self.matmul_3.forward(z2,self.W3)
+ z3 = self.softmax.forward(A3)
+ R = self.log.forward(z3)
+ return R
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+ ####################
+ # code 7 #
+ ####################
+ self.log_grad=self.log.backward(y)
+ self.soft_grad=self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad,self.W3_grad=self.matmul_3.backward(self.soft_grad)
+ self.relu_2_grad=self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad,self.W2_grad=self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+ self.relu_1_grad=self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad,self.W1_grad=self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+ pass
+
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..73e875088a352d2a35dc2a0e9a14357d3e5229aa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/19210680053/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
+"""
+Created on Wed Apr 28 22:11:32 2021
+
+@author: hyt
+"""
+
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+def mini_batch(dataset,batch_size=128):
+ data = []
+ label = []
+ for each in dataset:
+ data.append(np.array(each[0]))
+ label.append(each[1])
+ data = np.array(data)
+ label = np.array(label)
+ index=data.shape[0]
+ index = list(np.random.permutation(index))
+ return [(data[index[i:i + batch_size]], label[index[i:i + batch_size]]) for i in range(0, len(data), batch_size)]
+
+
+def numpy_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x)
+# y_pred = model.forward(x.numpy())
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..02a93eb112820dff16d39f05398e6a648fea011b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,523 @@
+# Assignment 2. 前馈神经网络
+
+- **姓名:高庆麾**
+- **学号:19307130062**
+
+
+
+## 第一部分:梯度计算公式推导
+
+### Matmul
+
+考虑 $Y = XW$,其中 $Y \in \R^{n\times d_2},\ X \in \R^{n \times d_1},\ W \in \R^{d_1 \times d_2}$
+
+设损失函数为 $\mathcal L(\boldsymbol y,\ \boldsymbol {\hat y})$ ,且 $\Delta_Y$ (即 $Y$ 相对于损失函数的梯度)已知,希望得到 $\Delta_X,\ \Delta_W$
+
+推导如下:
+
+#### $\Delta_X$ 的推导
+
+我们考虑 $Y$ 的每一位对 $X$ 贡献的偏导,即 $\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X}$
+
+由于 $Y_{ij} = \sum_{k = 1}^{d_1}X_{ik}W_{kj}$ ,$X$ 各位独立,且
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X} =
+\begin{bmatrix}
+\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{11}} & \frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{12}} & \cdots & \frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{1d_1}} \\
+\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{21}} & \frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{22}} & \cdots & \frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{2d_1}} \\
+\vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\
+\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{n1}} & \frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{n2}} & \cdots & \frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{nd_1}} \\
+\end{bmatrix}
+$$
+故 $\left[\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X}\right]_{ik} = W_{kj},\ k \in [1,\ d_1] \cap\Z$ ,其余项为 $0$
+
+由于 $\Delta_Y$ 已知,即 $\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{ij}}$ 已知,则有
+$$
+\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial X_{ij}} = \sum_{s = 1}^n\sum_{t = 1}^{d_2} \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{st}}\frac{\partial{Y_{st}}}{\partial X_{ij}} = \sum_{s = 1}^n\sum_{t = 1}^{d_2} \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{st}}\left[\frac{\partial{Y_{st}}}{\partial X}\right]_{ij} = \sum_{t = 1}^{d_2} \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{it}}\left[\frac{\partial{Y_{it}}}{\partial X}\right]_{ij} = \sum_{t = 1}^{d_2} \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{it}}W_{jt} = \sum_{t = 1}^{d_2} \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{it}}W^T_{tj}
+$$
+即
+$$
+\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial X} = \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y}W^T
+$$
+可知
+$$
+\Delta_X = \Delta_YW^T
+$$
+
+#### $\Delta_W$ 的推导
+
+其次,对于 $\Delta_W$ ,我们用类似的方法进行计算,有 $\left[\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial W}\right]_{kj} = X_{ik},\ k \in [1,\ d_1] \cap\Z$ ,其余项为 $0$ ,则有
+$$
+\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial W_{ij}} = \sum_{s = 1}^{n}\sum_{t = 1}^{d_2} \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{st}}\left[\frac{\partial{Y_{st}}}{\partial W}\right]_{ij} = \sum_{s = 1}^{n} \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{sj}}\left[\frac{\partial{Y_{sj}}}{\partial W}\right]_{ij} = \sum_{s = 1}^{n} \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{sj}}X_{si} = \sum_{s = 1}^{n} X_{is}^T\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{sj}}
+$$
+即
+$$
+\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial W} = X^T\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y}
+$$
+可知
+$$
+\Delta_W = X^T\Delta_Y
+$$
+$\square$
+
+
+
+### ReLU
+
+考虑 $Y = \mathrm{ReLU}(X)$ ,其中 $Y,\ X \in \R^{n\times m}$
+
+设损失函数为 $\mathcal L(\boldsymbol y,\ \boldsymbol {\hat y})$ ,且 $\Delta_Y$ (即 $Y$ 相对于损失函数的梯度)已知,希望得到 $\Delta_X$
+
+推导如下:
+
+#### $\Delta_X$ 的推导
+
+方法类似于上文,只要注意这里的 $\mathrm{ReLU}$ 是一个逐元素函数
+
+考虑 $Y$ 的每一位对 $X$ 贡献的导数,即 $\frac{\mathrm{d}Y_{ij}}{\mathrm{d} X}$
+
+由于 $Y_{ij} = \mathrm{ReLU}(X_{ij})$ ,故 $\left[\frac{\mathrm{d}Y_{ij}}{\mathrm{d}X}\right]_{ij} = \mathrm{ReLU}'(X_{ij})$ ,其余项为 $0$
+
+显然
+$$
+\mathrm{ReLU}'(x) = \begin{cases}
+0, & n < 0 \\
+1, & n > 0 \\
+\mathrm{Undefined}, & n = 0
+\end{cases}
+$$
+当然,在 $x = 0$ 处,由于截断误差的存在,可以认为导数为 $0$ 或 $1$
+
+则有
+$$
+\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial X_{ij}} = \sum_{s = 1}^n\sum_{t = 1}^{m} \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{st}}\frac{\mathrm{d}{Y_{st}}}{\mathrm{d} X_{ij}} = \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{ij}}\left[\frac{\partial{Y_{ij}}}{\partial X}\right]_{ij} =\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{ij}}\mathrm{ReLU}'(X_{ij})
+$$
+即(此处 $\odot$ 表示矩阵的哈达玛积,即对应位乘积)
+$$
+\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial X} = \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y}\odot\mathrm{ReLU}'(X)
+$$
+可知
+$$
+\Delta_X = \Delta_Y\odot\mathrm{ReLU}'(X)
+$$
+$\square$
+
+
+
+### Log
+
+考虑 $Y = \mathrm{Log}(X)$ ,其中 $Y,\ X \in \R^{n\times m}$
+
+设损失函数为 $\mathcal L(\boldsymbol y,\ \boldsymbol {\hat y})$ ,且 $\Delta_Y$ (即 $Y$ 相对于损失函数的梯度)已知,希望得到 $\Delta_X$
+
+推导如下:
+
+#### $\Delta_X$ 的推导
+
+方法类似于上文,只要注意这里的 $\mathrm{Log}$ 是一个逐元素函数
+
+考虑 $Y$ 的每一位对 $X$ 贡献的导数,即 $\frac{\mathrm{d}Y_{ij}}{\mathrm{d} X}$
+
+由于 $Y_{ij} = \mathrm{Log}(X_{ij})$ ,故 $\left[\frac{\mathrm{d}Y_{ij}}{\mathrm{d}X}\right]_{ij} = \mathrm{Log}'(X_{ij}) = \frac{1}{X_{ij}}$ ,其余项为 $0$
+
+则有
+$$
+\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial X_{ij}} = \sum_{s = 1}^n\sum_{t = 1}^{m} \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{st}}\frac{\mathrm{d}{Y_{st}}}{\mathrm{d} X_{ij}} = \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{ij}}\left[\frac{\partial{Y_{ij}}}{\partial X}\right]_{ij} =\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y_{ij}}\frac{1}{X_{ij}}
+$$
+即(其中 $\frac{1}{X}$ 表示 $X$ 的每一位取倒数后的结果)
+$$
+\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial X} = \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial Y}\odot\frac{1}{X}
+$$
+可知
+$$
+\Delta_X = \Delta_Y\odot\frac{1}{X}
+$$
+$\square$
+
+
+
+### Softmax
+
+考虑 $\boldsymbol y = \mathrm{Softmax}(\boldsymbol x)$ ,其中 $\boldsymbol y,\ \boldsymbol x \in \R^{1 \times c}$
+
+设损失函数为 $\mathcal L(\boldsymbol y,\ \boldsymbol {\hat y})$ ,且 $\Delta_{\boldsymbol y}$ (即 $Y$ 相对于损失函数的梯度)已知,希望得到 $\boldsymbol y$ 的表达(前向计算)及 $\Delta_{\boldsymbol x}$
+
+推导如下:
+
+#### $\boldsymbol y$ 的推导(前向计算)
+
+根据 $\mathrm{Softmax}$ 的定义,可以得到
+$$
+\boldsymbol y_i = \frac{e^{\boldsymbol x_i}}{\sum_{j = 1}^ce^{\boldsymbol x_j}}
+$$
+
+#### $\Delta_{\boldsymbol x}$ 的推导
+
+由于
+$$
+\boldsymbol y_i = \frac{e^{\boldsymbol x_i}}{\sum_{j = 1}^ce^{\boldsymbol x_j}}
+$$
+且
+$$
+\frac{\partial \boldsymbol y}{\partial\boldsymbol x} =
+\begin{bmatrix}
+\frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_1}{\partial \boldsymbol x_1} & \frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_1}{\partial \boldsymbol x_2} & \cdots & \frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_1}{\partial \boldsymbol x_c} \\
+\frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_2}{\partial \boldsymbol x_1} & \frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_2}{\partial \boldsymbol x_2} & \cdots & \frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_2}{\partial \boldsymbol x_c} \\
+\vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\
+\frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_c}{\partial \boldsymbol x_1} & \frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_c}{\partial \boldsymbol x_2} & \cdots & \frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_c}{\partial \boldsymbol x_c} \\
+\end{bmatrix}
+$$
+故当 $i = j$ 时,有
+$$
+\left[\frac{\partial \boldsymbol y}{\partial\boldsymbol x}\right]_{ii} = \frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_i}{\partial \boldsymbol x_i} = \frac{\partial\left( \frac{e^{\boldsymbol x_i}}{\sum_{j = 1}^ce^{\boldsymbol x_j}}\right)}{\partial \boldsymbol x_i} = \frac{e^{\boldsymbol x_i}(\sum_{j = 1}^ce^{\boldsymbol x_j}) - e^{\boldsymbol x_i}e^{\boldsymbol x_i}}{\left(\sum_{j = 1}^ce^{\boldsymbol x_j}\right)^2} = \frac{e^{\boldsymbol x_i}}{\sum_{j = 1}^ce^{\boldsymbol x_j}}\frac{\left(\sum_{j = 1}^ce^{\boldsymbol x_j}\right) - e^{\boldsymbol x_i}}{\sum_{j = 1}^ce^{\boldsymbol x_j}} = \boldsymbol y_i(1 - \boldsymbol y_i)
+$$
+当 $i \neq j$ 时,有
+$$
+\left[\frac{\partial \boldsymbol y}{\partial\boldsymbol x}\right]_{ij} = \frac{\partial \boldsymbol y_i}{\partial \boldsymbol x_j} = \frac{\partial\left( \frac{e^{\boldsymbol x_i}}{\sum_{j = 1}^ce^{\boldsymbol x_j}}\right)}{\partial \boldsymbol x_j} = \frac{-e^{\boldsymbol x_i}e^{\boldsymbol x_j}}{\left(\sum_{j = 1}^ce^{\boldsymbol x_j}\right)^2} = -\boldsymbol y_i\boldsymbol y_j
+$$
+则有
+$$
+\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial\boldsymbol x_{j}} = \sum_{i = 1}^c\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial\boldsymbol y_{i}}\frac{\partial\boldsymbol y_i}{\partial \boldsymbol x_j} = \sum_{i = 1}^c\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial\boldsymbol y_{i}}\left[\frac{\partial\boldsymbol y}{\partial \boldsymbol x}\right]_{ij}
+$$
+即
+$$
+\frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial\boldsymbol x} = \frac{\partial{\mathcal L}}{\partial \boldsymbol y}\left[\frac{\partial\boldsymbol y}{\partial \boldsymbol x}\right]
+$$
+可知(其中 $\left[\frac{\partial\boldsymbol y}{\partial \boldsymbol x}\right]$ 已经在上文中求出)
+$$
+\Delta_{\boldsymbol x} = \Delta_{\boldsymbol y}\left[\frac{\partial\boldsymbol y}{\partial \boldsymbol x}\right]
+$$
+由于原代码中给出的是一组行向量构成的矩阵,因此,我们可以对每一行分别进行如上操作,且行与行之间互不干扰,由此完成 $\mathrm{Softmax}$ 的反向传播
+
+$\square$
+
+*注意此处对应代码的写法,对于 numpy 里的 array A,A[i] 只会被认为具有一个维度(被看做是一列数而非一个行向量),因此如果希望使用其对应的行向量,需要将 A[i] 转换为 matrix 类型,此时就会带上表示行的一维
+
+
+
+### FNN
+
+由于整个 FNN 由上面推导过的许多基本层次构成,因此在 FNN 中进行前向计算,只需要类似函数嵌套的方法将模型结构的各个层次结合在一起即可
+
+设 FNN 对应的函数为 $F$ ,则
+
+#### $F$ 的推导(前向计算)
+
+$F(X) = \mathrm{Log}(\mathrm{Softmax}(\mathrm{ReLU}(\mathrm{ReLU}(X\cdot W_1)\cdot W_2)\cdot W_3))$
+
+其中 $X \in \R^{n \times 784},\ W_1 \in \R^{784\times 256},\ W_2 \in \R^{256\times 64},\ W_3 \in \R^{64\times 10},\ F(X) \in \R^{n \times 10}$ ,$n$ 为数据条数
+
+#### FNN 后向传播的推导
+
+根据代码,我们可以得到模型定义的损失函数为 $\mathcal L(\boldsymbol y,\ \boldsymbol {\hat y}) = -\boldsymbol {\hat y}\boldsymbol y^T$ ($\boldsymbol {\hat y}$ 表示预测向量),而在整个数据集上的定义为
+
+$\mathcal L(Y,\ \hat Y) = -\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i = 1}^n{\hat Y_{i:}}Y_{i:}^T = -\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i = 1}^n\sum_{j = 1}^d{\hat Y_{ij}}Y_{ij}$
+
+由此我们需要计算 $\Delta_{\hat Y}$ (即 $\hat Y$ 相对于该损失函数的梯度,$\hat Y = F(X)$ )
+
+推导如下:
+
+#### $\Delta_{\hat Y}$ 的推导
+
+根据上文对 $\mathcal L$ 的定义,我们很容易得到
+$$
+\frac{\partial\mathcal L}{\partial\hat Y_{ij}} = -\frac{1}{n}Y_{ij}
+$$
+由此即可得到最初进入反向传播过程的梯度矩阵 $\Delta_{\hat Y}$ ,其它层上的梯度可以通过逐层反向传播得到
+
+
+
+### 总结
+
+**这里希望就笔者对梯度和导数的理解,以及根据自己的理解和方法简明地推导反向传播公式的感悟,做一点总结。**
+
+对于后向传播的梯度计算,有许许多多的方法,比如迹运算技术[^1]和向量化技术[^2]即为比较通用的高维求导方法。但简单尝试后可以发现,这些方法运用起来实在过于复杂。实际上,为了正确而又简单地计算梯度,我们只需要明确所谓梯度(或者说导数)究竟有怎样的实际含义。
+
+*下面对梯度和导数的概念可能有一些混用,在本文中这两者表达的含义基本相同。
+
+对于一个非常一般的关系 $A = f(B)$ ,此处 $A,\ B$ 可视为任意维度和大小的张量。如果对线性代数比较熟悉,可以知道,其实这只是对许多多元函数关系的一种简化表达。如果我们拆开来看,若 $a$ 是 $A$ 中某一项,那么 $a$ 实际上就是一个**关于 $B$ 中所有项的多元函数**。
+
+其次,为什么要在神经网络中计算梯度?无非就是希望通过梯度下降来迭代地优化神经网络的效果(而梯度下降的方向也是损失函数值下降最快的方向,且一般而言这个损失函数的结果都是一个标量,否则难以比较大小)。既然如此,我们就需要计算出网络中每个参数的梯度,并通过将每个参数都向梯度下降的方向做一些移动,使得整个网络的损失函数在特定数据集上的表现有所优化。
+
+所以,我们可以认为,每个参数的移动都对损失函数的最终结果有一定的贡献。而链式法则告诉我们,这种贡献的正确计算方法,是考虑该参数到达损失函数的**每一条作用路径**[^3]。反向传播算法 (Back Propagation, BP) 即是利用了这种思想。如果对动态规划 (Dynamic Programming, DP) 算法比较熟悉(比如对运筹学比较熟悉或有程序设计竞赛方面的背景),可以知道 BP 实际是一个**非常显然而简单**的有向无环图 (Directed Acyclic Graph, DAG) 上 做 DP 的算法(当然这也很大程度上归功于链式法则的证明),因为神经网络中的计算图本身一定是一个 DAG,即从各个结点出发,沿着计算边行进,最终必定会到达损失函数。
+
+这样,我们在计算 $B$ 到 $\mathcal L$ 的梯度时,不再需要枚举所有作用路径,计算并累加所有的贡献,而只是需要计算从 $B$ 到以它为自变量(的一部分)的关系的象 $A$ 中所有可能的作用路径,再和先前计算好的从 $A$ 到 $\mathcal L$ 的梯度做一个“路径拼接”,实际也就是矩阵(或张量)的乘法,即可得到 $B$ 所有的贡献。关于 $A,\ B$ 的顺序,由于计算图是一个 DAG ,因此可以通过拓扑排序 (Topological Sort) 确定二者(乃至全部参数)之间合法的先后关系。
+
+回到上文的一般关系 $A = f(B)$ 中,从 $B$ 到 $A$ 的所有合法路径是怎样的?这就回到了一开始从 $A$ 中抽出的一项 $a$ (它也代表一个关于 $B$ 中所有项的多元函数) ,所谓所有的合法路径,实际也就是要考虑所有这样的 $A$ 中的项(或多元函数)对于 $B$ 中每一项的梯度,然后 $B$ 中每一项的贡献,也就是以 $\mathcal L$ 到 $A$ 中每一项的梯度作为权,乘这一 $A$ 中的项对 $B$ 中该项刚刚计算出的梯度(或称偏导)的和,这也就是先前提到的**“路径拼接”**(也是一种加权和,如此理解的意义也是非常显然的)。
+
+这样,对于日常遇到的简单情形,我们其实并不需要套用一些非常通用而繁琐的方法,只需要如上文一般,对 $A$ 中每一项求出其对 $B$ 中每一项的偏导,由此将问题转化为一个多元函数(结果是标量)对其中每个自变量的偏导问题,这显然是非常简单的(甚至不需要大学的知识)。而关于“简单情形”的定义,其实也就是指这种多元函数的形式比较一致,这样我们只需要对其中几个多元函数求出偏导,就能得到对全部情况的理解。最后模仿“路径拼接”或链式法则,将表达简化为矩阵乘法的形式,就可以非常容易地得到梯度。本文对相关常见的神经网络层反向传播的推导,全部基于这种认识和由此而来的方法,在笔者个人看来,是足够简明和容易理解的。
+
+
+
+
+
+[^1]: 来源于该式 $\mathrm{d}f = \mathrm{tr}\left(\frac{\partial f}{\partial X}^T \mathrm{d}X\right)$,用于标量对矩阵的求导。从需要求导的标量出发,套上迹运算,再结合一些迹内运算的恒等式推导得到类似形式,则迹运算内 $\mathrm{d}X$ 左侧部分的转置即为所求导数
+[^2]:来源于该式 $\mathrm{vec}(\mathrm{d}F) = \frac{\partial F}{\partial X}^T \mathrm{vec}(\mathrm{d}X)$,用于矩阵对矩阵的求导。类似地,从需要求导的矩阵出发,套上向量化运算,再结合一些向量化内运算的恒等式推导得到类似形式,则 $\mathrm{vec}(\mathrm{d}X)$ 左侧部分的转置即为所求导数
+[^3]: 对于这一点,可以举例考虑函数 $f = (x,\ y,\ z),\ x = g(u),\ y = h(u),\ z = t(u)$ 。如果可导相关的条件上没有任何障碍,那么想要求出 $\frac{\partial f}{\partial u}$ ,我们就必须计算 $\frac{\partial f}{\partial x}\frac{\partial x}{\partial u} + \frac{\partial f}{\partial y}\frac{\partial y}{\partial u} + \frac{\partial f}{\partial z}\frac{\partial z}{\partial u}$ ,也就是考虑 $u$ 到 $f$ 的每一条作用路径。
+
+
+
+
+
+## 第二部分:模型的训练和测试(先前版本)
+
+在从损失函数进行梯度回传时,发现并没有为损失函数提供 `backward` 接口,因此就去看了一下损失函数的具体形式,然后进行了一下推导,发现只需要在原来取平均的基础上加一个负号就可以,然后就通过了所有的测试。但不知道为什么初始准确率不是很高,只有 $80\%$ 多。多训练几个 epoch 后才提升得比较好。
+
+### 调整学习率
+
+#### 保守尝试
+
+根据上文的推导结果,在 `numpy_fnn.py` 中填写好有关代码,然后运行 `numpy_mnist.py` 进行训练,并尝试不同的学习率,得到结果如下:
+
+(实际顺序是先测试了原配置 $\alpha = 0.1$,后来发现损失函数后期波动较大,以为是学习率过大导致的不稳定,就尝试了更小的学习率 $\alpha = 0.05$ ,结果发现效果明显不如从前,就开始逐渐增大学习率进行试验,观察效果。最后决定将数据和损失函数图象放在一起,这样对比更加明显,且节约篇幅)
+
+| Epoch | Accuracy ($\alpha = 0.05$) | Accuracy ($\alpha = 0.1$) | Accuracy $(\alpha = 0.15$) | Accuracy $(\alpha = 0.3$) |
+| :---: | :------------------------: | :-----------------------: | :------------------------: | :-----------------------: |
+| $0$ | $80.18\%$ | $87.50\%$ | $89.20\%$ | $91.06\%$ |
+| $1$ | $87.25\%$ | $90.46\%$ | $91.22\%$ | $93.54\%$ |
+| $2$ | $89.23\%$ | $91.65\%$ | $92.46\%$ | $94.64\%$ |
+| $3$ | $90.40\%$ | $92.21\%$ | $93.19\%$ | $95.42\%$ |
+| $4$ | $91.03\%$ | $92.98\%$ | $93.67\%$ | $96.02\%$ |
+| $5$ | $91.61\%$ | $93.23\%$ | $94.45\%$ | $96.38\%$ |
+
+


 +
+(上四图从左到右分别是 $\alpha = 0.05,\ 0.1,\ 0.15,\ 0.3$ 的情况,可以看到损失函数下降的速度明显不同)
+
+设置这几个 $\alpha$ 也是为了比较在 $\mathrm{epoch}\times \alpha$ 相同时的模型训练效果,结果如下:
+
+| condition | accuracy |
+| :----------------------------------: | :-------: |
+| $\alpha = 0.05,\ \mathrm{epoch} = 6$ | $91.61\%$ |
+| $\alpha = 0.1,\ \mathrm{epoch} = 3$ | $91.65\%$ |
+| $\alpha = 0.15,\ \mathrm{epoch} = 2$ | $91.22\%$ |
+| $\alpha = 0.3,\ \mathrm{epoch} = 1$ | $91.06\%$ |
+
+可以发现,在保持模型训练效果大体不变的情况下,可以**适当增加**学习率,减少训练的 $\mathrm{epoch}$ 次数,从而提高训练效率
+
+那么,既然提到了适当,那何时是不太适当的呢?这将在下一节中进行探索。
+
+#### 过大的 $\alpha$
+
+显然一切都不能太极端,我们也不能一昧地提升学习率而不计后果。过大的学习率容易造成模型训练的不稳定,以及数值计算上的严重问题,于是希望在这一节探索怎样的 $\alpha$ 是过大的
+
+| Epoch | Accuracy ($\alpha = 1.0$) | Accuracy ($\alpha = 5.0$) | Accuracy ($\alpha = 8.0$) |
+| :---: | :-----------------------: | :-----------------------: | :-----------------------: |
+| $0$ | $94.64\%$ | $96.36\%$ | $9.80\%$ |
+| $1$ | $96.28\%$ | $96.99\%$ | $9.80\%$ |
+| $2$ | $97.08\%$ | $97.14\%$ | $9.80\%$ |
+| $3$ | $97.39\%$ | $97.73\%$ | $9.80\%$ |
+| $4$ | $97.57\%$ | $97.52\%$ | $9.80\%$ |
+| $5$ | $97.82\%$ | $97.84\%$ | $9.80\%$ |
+
+
+
+(上四图从左到右分别是 $\alpha = 0.05,\ 0.1,\ 0.15,\ 0.3$ 的情况,可以看到损失函数下降的速度明显不同)
+
+设置这几个 $\alpha$ 也是为了比较在 $\mathrm{epoch}\times \alpha$ 相同时的模型训练效果,结果如下:
+
+| condition | accuracy |
+| :----------------------------------: | :-------: |
+| $\alpha = 0.05,\ \mathrm{epoch} = 6$ | $91.61\%$ |
+| $\alpha = 0.1,\ \mathrm{epoch} = 3$ | $91.65\%$ |
+| $\alpha = 0.15,\ \mathrm{epoch} = 2$ | $91.22\%$ |
+| $\alpha = 0.3,\ \mathrm{epoch} = 1$ | $91.06\%$ |
+
+可以发现,在保持模型训练效果大体不变的情况下,可以**适当增加**学习率,减少训练的 $\mathrm{epoch}$ 次数,从而提高训练效率
+
+那么,既然提到了适当,那何时是不太适当的呢?这将在下一节中进行探索。
+
+#### 过大的 $\alpha$
+
+显然一切都不能太极端,我们也不能一昧地提升学习率而不计后果。过大的学习率容易造成模型训练的不稳定,以及数值计算上的严重问题,于是希望在这一节探索怎样的 $\alpha$ 是过大的
+
+| Epoch | Accuracy ($\alpha = 1.0$) | Accuracy ($\alpha = 5.0$) | Accuracy ($\alpha = 8.0$) |
+| :---: | :-----------------------: | :-----------------------: | :-----------------------: |
+| $0$ | $94.64\%$ | $96.36\%$ | $9.80\%$ |
+| $1$ | $96.28\%$ | $96.99\%$ | $9.80\%$ |
+| $2$ | $97.08\%$ | $97.14\%$ | $9.80\%$ |
+| $3$ | $97.39\%$ | $97.73\%$ | $9.80\%$ |
+| $4$ | $97.57\%$ | $97.52\%$ | $9.80\%$ |
+| $5$ | $97.82\%$ | $97.84\%$ | $9.80\%$ |
+
+

 +
+(上三图分别对应 $\alpha = 1.0,\ 5.0,\ 8.0$ 情况)
+
+可以看到 $\alpha = 1.0$ 的效果还非常好,$\alpha = 5.0$ 时损失函数已经出现相对明显大幅度的波动,而 $\alpha = 8.0$ 时在训练过程中出现了数值问题,模型优化失效
+
+#### 总结
+
+- 可以发现,在 $\alpha$ 一定的范围内(合理范围内),epoch $\times\ \alpha$ 相同时,训练模型的精度也大体相近。总体看来在这个模型中,$0.1$ 的学习率确实还不太合适,迭代速度太慢
+- 增大 $\alpha$ 时,损失函数下降的速度也有非常明显的提升,可以看到损失函数近于直线下降的部分,随着 $\alpha$ 增大其倾斜程度也有非常明显的增大
+- 合理增大 $\alpha$ 对模型精度的提升非常明显,如 $\alpha = 1.0$ 在第 $6$ 个 epoch 时的精度甚至达到了近 $98\%$(但和 torch 下的模型训练效率相比,差距仍然很明显)
+
+
+
+
+
+## 第二部分:模型的训练和测试(修改后版本)
+
+然后听说对 `numpy_fnn.py` 作了不少修改,然后就 pull 了一下,发现给损失函数加上了 `backward`,并在模型 `backward` 时传入了,这样就不需要再手动处理什么,直接从 `ReLU` 开始反向传播就好。然而,这次在 MNIST 上的测试准确率变得很好,初始就是 $90\%$ 以上,训练几个 epoch 以后也显著地变得更好。所以这一部分就是把之前的结果重新做一遍,然后更新一下实验数据。
+
+### 调整学习率
+
+#### 保守尝试
+
+根据上文的推导结果,在 `numpy_fnn.py` 中填写好有关代码,然后运行 `numpy_mnist.py` 进行训练,并尝试不同的学习率,得到结果如下:
+
+| Epoch | Accuracy ($\alpha = 0.05$) | Accuracy ($\alpha = 0.1$) | Accuracy $(\alpha = 0.15$) | Accuracy $(\alpha = 0.3$) |
+| :---: | :------------------------: | :-----------------------: | :------------------------: | :-----------------------: |
+| $0$ | $92.51\%$ | $94.56\%$ | $95.47\%$ | $96.09\%$ |
+| $1$ | $94.96\%$ | $96.12\%$ | $95.89\%$ | $95.97\%$ |
+| $2$ | $96.15\%$ | $96.96\%$ | $97.27\%$ | $96.94\%$ |
+| $3$ | $96.28\%$ | $97.28\%$ | $97.52\%$ | $97.78\%$ |
+| $4$ | $96.93\%$ | $97.23\%$ | $97.54\%$ | $98.05\%$ |
+| $5$ | $97.14\%$ | $97.55\%$ | $98.08\%$ | $97.91\%$ |
+
+
+
+(上三图分别对应 $\alpha = 1.0,\ 5.0,\ 8.0$ 情况)
+
+可以看到 $\alpha = 1.0$ 的效果还非常好,$\alpha = 5.0$ 时损失函数已经出现相对明显大幅度的波动,而 $\alpha = 8.0$ 时在训练过程中出现了数值问题,模型优化失效
+
+#### 总结
+
+- 可以发现,在 $\alpha$ 一定的范围内(合理范围内),epoch $\times\ \alpha$ 相同时,训练模型的精度也大体相近。总体看来在这个模型中,$0.1$ 的学习率确实还不太合适,迭代速度太慢
+- 增大 $\alpha$ 时,损失函数下降的速度也有非常明显的提升,可以看到损失函数近于直线下降的部分,随着 $\alpha$ 增大其倾斜程度也有非常明显的增大
+- 合理增大 $\alpha$ 对模型精度的提升非常明显,如 $\alpha = 1.0$ 在第 $6$ 个 epoch 时的精度甚至达到了近 $98\%$(但和 torch 下的模型训练效率相比,差距仍然很明显)
+
+
+
+
+
+## 第二部分:模型的训练和测试(修改后版本)
+
+然后听说对 `numpy_fnn.py` 作了不少修改,然后就 pull 了一下,发现给损失函数加上了 `backward`,并在模型 `backward` 时传入了,这样就不需要再手动处理什么,直接从 `ReLU` 开始反向传播就好。然而,这次在 MNIST 上的测试准确率变得很好,初始就是 $90\%$ 以上,训练几个 epoch 以后也显著地变得更好。所以这一部分就是把之前的结果重新做一遍,然后更新一下实验数据。
+
+### 调整学习率
+
+#### 保守尝试
+
+根据上文的推导结果,在 `numpy_fnn.py` 中填写好有关代码,然后运行 `numpy_mnist.py` 进行训练,并尝试不同的学习率,得到结果如下:
+
+| Epoch | Accuracy ($\alpha = 0.05$) | Accuracy ($\alpha = 0.1$) | Accuracy $(\alpha = 0.15$) | Accuracy $(\alpha = 0.3$) |
+| :---: | :------------------------: | :-----------------------: | :------------------------: | :-----------------------: |
+| $0$ | $92.51\%$ | $94.56\%$ | $95.47\%$ | $96.09\%$ |
+| $1$ | $94.96\%$ | $96.12\%$ | $95.89\%$ | $95.97\%$ |
+| $2$ | $96.15\%$ | $96.96\%$ | $97.27\%$ | $96.94\%$ |
+| $3$ | $96.28\%$ | $97.28\%$ | $97.52\%$ | $97.78\%$ |
+| $4$ | $96.93\%$ | $97.23\%$ | $97.54\%$ | $98.05\%$ |
+| $5$ | $97.14\%$ | $97.55\%$ | $98.08\%$ | $97.91\%$ |
+
+


 +
+(上四图从左到右分别是 $\alpha = 0.05,\ 0.1,\ 0.15,\ 0.3$ 的情况,可以看到损失函数下降的速度明显不同)
+
+设置这几个 $\alpha$ 也是为了比较在 $\mathrm{epoch}\times \alpha$ 相同时的模型训练效果,结果如下:
+
+| condition | accuracy |
+| :----------------------------------: | :-------: |
+| $\alpha = 0.05,\ \mathrm{epoch} = 6$ | $97.1\%$ |
+| $\alpha = 0.1,\ \mathrm{epoch} = 3$ | $96.96\%$ |
+| $\alpha = 0.15,\ \mathrm{epoch} = 2$ | $95.89\%$ |
+| $\alpha = 0.3,\ \mathrm{epoch} = 1$ | $96.09\%$ |
+
+#### 过大的 $\alpha$
+
+上一节中,我们就看到,在采用较大学习率时,模型学习效果会出现明显的波动,且最终学习效果会有所下降。那么当采用更大学习率时,会出现什么结果呢?
+
+| Epoch | Accuracy ($\alpha = 1.0$) |
+| :---: | :-----------------------: |
+| $0$ | $9.80\%$ |
+| $1$ | $9.80\%$ |
+| $2$ | $9.80\%$ |
+| $3$ | $9.80\%$ |
+| $4$ | $9.80\%$ |
+| $5$ | $9.80\%$ |
+
+
+
+(上四图从左到右分别是 $\alpha = 0.05,\ 0.1,\ 0.15,\ 0.3$ 的情况,可以看到损失函数下降的速度明显不同)
+
+设置这几个 $\alpha$ 也是为了比较在 $\mathrm{epoch}\times \alpha$ 相同时的模型训练效果,结果如下:
+
+| condition | accuracy |
+| :----------------------------------: | :-------: |
+| $\alpha = 0.05,\ \mathrm{epoch} = 6$ | $97.1\%$ |
+| $\alpha = 0.1,\ \mathrm{epoch} = 3$ | $96.96\%$ |
+| $\alpha = 0.15,\ \mathrm{epoch} = 2$ | $95.89\%$ |
+| $\alpha = 0.3,\ \mathrm{epoch} = 1$ | $96.09\%$ |
+
+#### 过大的 $\alpha$
+
+上一节中,我们就看到,在采用较大学习率时,模型学习效果会出现明显的波动,且最终学习效果会有所下降。那么当采用更大学习率时,会出现什么结果呢?
+
+| Epoch | Accuracy ($\alpha = 1.0$) |
+| :---: | :-----------------------: |
+| $0$ | $9.80\%$ |
+| $1$ | $9.80\%$ |
+| $2$ | $9.80\%$ |
+| $3$ | $9.80\%$ |
+| $4$ | $9.80\%$ |
+| $5$ | $9.80\%$ |
+
+ +
+(上三图分别对应 $\alpha = 1.0,\ 5.0,\ 8.0$ 情况)
+
+和先前不同, $\alpha = 1.0$ 时模型就出现了数值问题,导致优化失效
+
+
+
+## 第三部分:自定义 mini_batch
+
+用 numpy 手写 mini_batch 函数,其实原理很简单,算法大概分为如下步骤(写在代码中):
+
+```python
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size = 128, numpy = False):
+ if batch_size <= 0 or not isinstance(batch_size, int):
+ return None
+ # 1. 判断传入的 batch_size 是否合法,需要为正整数,不合法返回空
+
+ data, label = batch(dataset)[0]
+ # 2. 用 batch 方法将 torchvision 下的 MNIST 数据集转换为 numpy 的 array
+
+ datanum = len(data)
+ idx = np.arange(datanum)
+ np.random.shuffle(idx)
+ data, label = data[idx], label[idx]
+ # 3. 对 data 和 label 进行 random shuffle,具体来说,可以先对一个指示下标的数组做 random shuffle,然后用这个下标数组配合 slice 机制对 data 和 label 进行对应的 random shuffle,从而防止 data 和 label 错误匹配
+
+ batchnum = (datanum - 1) // batch_size + 1 # datanum 对 batch_size 下取整
+ batches = []
+ # 4. 计算 batch 数量,初始化 batches 列表
+
+ for i in range(batchnum):
+ batches.append((data[i * batch_size: min(datanum, (i + 1) * batch_size)], label[i * batch_size: min(datanum, (i + 1) * batch_size)]))
+ # 5. 通过 slice 机制选出第 i 个 batch 对应的 data 和 label 子集,放入 batches 列表中
+
+ return batches
+```
+
+
+
+## 第四部分:额外探究
+
+### 其他基于梯度的优化方法对比实验
+
+在代码中 ( numpy_fnn.py 和 numpy_mnist.py ) 实现了十种优化方法,有
+
+- Momentum, 动量法
+- Nesterov Accelerated Gradient, NAG, Nesterov 加速梯度 或称 Nesterov 动量法
+- Adaptive Moment Estimation Algorithm, Adam 算法
+- Inverse Time Decay, 逆时衰减
+- Exponential Decay, 指数衰减
+- Natural Exponential Decay, 自然指数衰减
+- Cosine Decay, 余弦衰减
+- Adaptive Gradient Algorithm, AdaGrad 算法
+- RMSprop 算法
+- AdaDelta 算法
+
+包括无优化的版本,共有十一种不同的对比实验
+
+#### $\mathrm{epoch} = 3,\ \alpha = 0.1$
+
+这里设定 $\mathrm{epoch} = 3,\ \alpha = 0.1$ ,当然,对于调整学习率的算法,$\alpha$ 是不固定的,提供的只是一个初始值
+
+| Epoch | None | Momentum | Nesterov | Adam |
+| :---: | :-------: | :-------: | :-------: | :-------: |
+| $0$ | $92.15\%$ | $96.72\%$ | $96.42\%$ | $95.43\%$ |
+| $1$ | $96.21\%$ | $97.00\%$ | $96.88\%$ | $96.87\%$ |
+| $2$ | $96.81\%$ | $97.54\%$ | $97.09\%$ | $97.55\%$ |
+
+| Epoch | Inverse Time Decay | Exponential Decay | Natural Exponential Decay | Cosine Decay |
+| :---: | :----------------: | :---------------: | :-----------------------: | :----------: |
+| $0$ | $86.71\%$ | $81.10\%$ | $81.05\%$ | $94.17\%$ |
+| $1$ | $87.93\%$ | $81.10\%$ | $81.05\%$ | $95.91\%$ |
+| $2$ | $88.49\%$ | $81.10\%$ | $81.05\%$ | $96.08\%$ |
+
+| Epoch | AdaGrad | RMSprop | AdaDelta |
+| :---: | :-------: | :-------: | :-------: |
+| $0$ | $95.04\%$ | $95.47\%$ | $76.42\%$ |
+| $1$ | $96.28\%$ | $96.45\%$ | $86.86\%$ |
+| $2$ | $97.24\%$ | $97.43\%$ | $89.22\%$ |
+
+
+
+*其实这时候忘了把 RMSprop 加进去了,但是对比也是很丰富的...
+
+
+
+#### $\mathrm{epoch} = 3,\ \alpha = 0.05$
+
+为了更好地突出各个算法的不同,将学习率 $\alpha$ 降低为 $0.05$
+
+| Epoch | None | Momentum | Nesterov | Adam |
+| :---: | :-------: | :-------: | :-------: | :-------: |
+| $0$ | $92.47\%$ | $96.20\%$ | $96.65\%$ | $93.67\%$ |
+| $1$ | $94.43\%$ | $97.38\%$ | $97.13\%$ | $96.11\%$ |
+| $2$ | $95.67\%$ | $97.70\%$ | $97.70\%$ | $96.69\%$ |
+
+| Epoch | Inverse Time Decay | Exponential Decay | Natural Exponential Decay | Cosine Decay |
+| :---: | :----------------: | :---------------: | :-----------------------: | :----------: |
+| $0$ | $77.18\%$ | $67.31\%$ | $64.09\%$ | $92.47\%$ |
+| $1$ | $80.42\%$ | $67.31\%$ | $64.09\%$ | $94.07\%$ |
+| $2$ | $81.90\%$ | $67.31\%$ | $64.09\%$ | $94.35\%$ |
+
+| Epoch | AdaGrad | RMSprop | AdaDelta |
+| :---: | :-------: | :-------: | :-------: |
+| $0$ | $93.29\%$ | $93.74\%$ | $75.09\%$ |
+| $1$ | $95.47\%$ | $95.17\%$ | $87.09\%$ |
+| $2$ | $96.49\%$ | $96.71\%$ | $89.76\%$ |
+
+
+
+*这时候仍然忘了把 RMSprop 加进去了...
+
+
+
+#### $\mathrm{epoch} = 3,\ \alpha = 0.01$
+
+为了更好地突出各个算法的不同,将学习率 $\alpha$ 进一步降低为 $0.01$,同时加上 RMSprop 算法
+
+| Epoch | None | Momentum | Nesterov | Adam |
+| :---: | :-------: | :-------: | :-------: | :-------: |
+| $0$ | $87.89\%$ | $94.37\%$ | $94.51\%$ | $89.81\%$ |
+| $1$ | $90.47\%$ | $96.32\%$ | $95.82\%$ | $91.76\%$ |
+| $2$ | $91.98\%$ | $97.12\%$ | $96.85\%$ | $92.96\%$ |
+
+| Epoch | Inverse Time Decay | Exponential Decay | Natural Exponential Decay | Cosine Decay |
+| :---: | :----------------: | :---------------: | :-----------------------: | :----------: |
+| $0$ | $36.83\%$ | $21.94\%$ | $29.31\%$ | $87.22\%$ |
+| $1$ | $45.39\%$ | $21.94\%$ | $29.31\%$ | $89.67\%$ |
+| $2$ | $50.02\%$ | $21.94\%$ | $29.31\%$ | $89.85\%$ |
+
+| Epoch | AdaGrad | RMSprop | AdaDelta |
+| :---: | :-------: | :-----: | :-------: |
+| $0$ | $89.44\%$ | $89.56\%$ | $77.58\%$ |
+| $1$ | $91.83\%$ | $91.85\%$ | $86.84\%$ |
+| $2$ | $92.76\%$ | $92.90\%$ | $89.26\%$ |
+
+
+
+#### 总结
+
+- 可以发现 Momentum 和 Nesterov 效果一直不错,且表现接近,这可能是因为本作业的模型比较简单,而 Momentum 和 Nesterov 总体来看做的事情比较相似,所以没有体现出 Nesterov 对梯度更新的修正。Adam 在 $\alpha$ 较大时表现也很好
+- 对于以某种方式衰减 $\alpha$ 的优化,初始 $\alpha$ 必须足够大才能体现出较好的效果,毕竟 $\alpha$ 太小的话,衰减到最后已经不足以对参数产生实质性的更新从而导致停滞(如 Exponential Decay 和 Natural Exponential Decay)
+- AdaGrad 和 RMSprop 表现比较接近,这可能也是因为本作业的模型比较简单,所以没有体现出 RMSprop 中指数衰减移动平均的优势,且这两者也会受到学习率减小的影响
+
+
+
+### 权重初始化
+
+留坑待补...
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/1.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..76e24ca85c7ce4d93a478588b5bb4c56712f55f8
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.2.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..dcd73246ee7c55075b77254e662b29c73b388479
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.3.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.3.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..52dc358d56961c0b88b78c4be37f09d6cf0ff73f
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.3.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.4.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.4.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b1887ce4f8daf51fb7f0b83c31e8fc7af2edb333
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.4.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.5.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.5.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..0bfb996933564302164fef6ef8f81ccff226b261
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.5.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.8.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.8.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..25fbb117e3043af4ee3c0971e0df2f86e235002f
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.8.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..50493ce463016089ef27bd53da94fb037f1a11da
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/3.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/3.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ff604f17eb61b62e9f093adf749a1f9e300f183b
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/3.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/4.1.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/4.1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..06c1a99c134d02ef2198b12330e1fae207a0c88a
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/4.1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/4.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/4.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..517a871080f592d5bdf8b0d16ce2fb1851c0b0a8
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/4.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.1.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..3649baecd02c1fa828f201b1220fcf81a2d11131
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.2.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7706ab7fefd7672d262ef8e8781bc97d3d749401
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.3.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.3.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..3f8c5876a1a72ebdbccf057b776ec5b9be91f296
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.3.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.4.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.4.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e8ca3f58c0149ffd66c0510e30da28c4f2751ff4
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.4.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d1698795bf9cd724b32984a43585b0ffcece7dad
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/6.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/6.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f3246e39870e14e383f18c231d30c5f22e2c637d
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/6.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/7.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/7.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b4fbff12bdc4a177d7fd555580ac7312fabf1d06
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/7.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/8.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/8.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c8568213cf5f72bfe57b28c7bdb9e2a8cc2bcfe4
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/8.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c5c95457e32cddf3ea2cb9effb780331e632d2bd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,340 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+
+ # code1
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, self.memory['W'].T)
+ grad_W = np.matmul(self.memory['x'].T, grad_y)
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ # code2
+ grad_x = grad_y * (self.memory['x'] >= 0)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ # code3
+ grad_x = grad_y * (1.0 / self.memory['x'])
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ # code4
+ mx = x.max(axis = 1).reshape(x.shape[0], -1) # 防止上溢和下溢
+ ex = np.exp(x - mx)
+ out = (ex.T / (ex.sum(axis = 1))).T
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['y'] = out
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ # code5
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ y = self.memory['y']
+ grad_x = np.zeros(x.shape)
+ for i in range(x.shape[0]):
+ grad_x[i] = np.matmul(grad_y[i], -np.matmul(np.matrix(y[i]).T, np.matrix(y[i])) + np.diag(np.array(y[i])))
+ return grad_x
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self, learning_rate = 0.1, update_type = None, iter_times = 1407):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新。 softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ # 以下变量指定了梯度回传所用的优化方法,并完成了有关的初始化
+ self.update_type = update_type
+ self.learning_rate = learning_rate
+ self.iter_times = iter_times
+ if update_type == 'Momentum':
+ self.rho = 0.9
+ self.W1_delta = np.zeros(self.W1.shape)
+ self.W2_delta = np.zeros(self.W2.shape)
+ self.W3_delta = np.zeros(self.W3.shape)
+
+ elif update_type == 'Nesterov':
+ self.rho = 0.9
+ self.W1_delta = np.zeros(self.W1.shape)
+ self.W2_delta = np.zeros(self.W2.shape)
+ self.W3_delta = np.zeros(self.W3.shape)
+
+ elif update_type == 'Adam':
+ self.epsilon = 1e-7
+ self.beta1, self.beta2 = 0.9, 0.99
+ self.M1 = np.zeros(self.W1.shape)
+ self.M2 = np.zeros(self.W2.shape)
+ self.M3 = np.zeros(self.W3.shape)
+ self.G1, self.G2, self.G3 = .0, .0, .0
+
+ elif update_type == 'Inverse Time Decay':
+ self.beta = 0.1
+ self.t = 0
+
+ elif update_type == 'Exponential Decay':
+ self.beta = 0.96
+ self.t = 0
+
+ elif update_type == 'Natural Exponential Decay':
+ self.beta = 0.04
+ self.t = 0
+
+ elif update_type == 'Cosine Decay':
+ self.t = 0
+
+ elif update_type == 'AdaGrad':
+ self.epsilon = 1e-7
+
+ elif update_type == 'RMSprop':
+ self.beta = 0.9
+ self.epsilon = 1e-7
+ self.G1, self.G2, self.G3 = .0, .0, .0
+
+ elif update_type == 'AdaDelta':
+ self.beta = 0.9
+ self.epsilon = 1e-7
+ self.W1_delta = np.zeros(self.W1.shape)
+ self.W2_delta = np.zeros(self.W2.shape)
+ self.W3_delta = np.zeros(self.W3.shape)
+ self.X1, self.X2, self.X3 = .0, .0, .0
+ self.G1, self.G2, self.G3 = .0, .0, .0
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ # code6
+ if self.update_type == 'Nesterov':
+ # 在前向传播之前进行 Nesterov 算法的第一阶段
+ self.W1_delta = self.rho * self.W1_delta
+ self.W2_delta = self.rho * self.W2_delta
+ self.W3_delta = self.rho * self.W3_delta
+ self.W1 += self.W1_delta
+ self.W2 += self.W2_delta
+ self.W3 += self.W3_delta
+
+ x = self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1)
+ x = self.relu_1.forward(x)
+ x = self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2)
+ x = self.relu_2.forward(x)
+ x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+ x = self.softmax.forward(x)
+ x = self.log.forward(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+ # for size in y.shape:
+ # y /= size
+
+
+ # code7
+ #self.log_grad = self.log.backward(-y)
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y)
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+ self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+
+
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ if not self.update_type:
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+
+ elif self.update_type == 'Momentum':
+ self.W1_delta = self.rho * self.W1_delta - learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2_delta = self.rho * self.W2_delta - learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3_delta = self.rho * self.W3_delta - learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+ self.W1 += self.W1_delta
+ self.W2 += self.W2_delta
+ self.W3 += self.W3_delta
+
+ elif self.update_type == 'Nesterov':
+ # 在参数更新时进行 Nesterov 第二阶段
+ self.W1_delta -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2_delta -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3_delta -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+
+ elif self.update_type == 'Adam':
+ self.M1 = self.beta1 * self.M1 + (1 - self.beta1) * self.W1_grad
+ self.G1 = self.beta2 * self.G1 + (1 - self.beta2) * (self.W1_grad * self.W1_grad).sum()
+ _M1 = self.M1 / (1 - self.beta1)
+ _G1 = self.G1 / (1 - self.beta2)
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate / np.sqrt(_G1 + self.epsilon) * _M1
+
+ self.M2 = self.beta1 * self.M2 + (1 - self.beta1) * self.W2_grad
+ self.G2 = self.beta2 * self.G2 + (1 - self.beta2) * (self.W2_grad * self.W2_grad).sum()
+ _M2 = self.M2 / (1 - self.beta1)
+ _G2 = self.G2 / (1 - self.beta2)
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate / np.sqrt(_G2 + self.epsilon) * _M2
+
+ self.M3 = self.beta1 * self.M3 + (1 - self.beta1) * self.W3_grad
+ self.G3 = self.beta2 * self.G3 + (1 - self.beta2) * (self.W3_grad * self.W3_grad).sum()
+ _M3 = self.M3 / (1 - self.beta1)
+ _G3 = self.G3 / (1 - self.beta2)
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate / np.sqrt(_G3 + self.epsilon) * _M3
+
+ elif self.update_type == 'Inverse Time Decay':
+ learning_rate = self.learning_rate / (1.0 + self.beta * self.t)
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+ self.t += 1
+
+ elif self.update_type == 'Exponential Decay':
+ learning_rate = self.learning_rate * pow(self.beta, self.t)
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+ self.t += 1
+
+ elif self.update_type == 'Natural Exponential Decay':
+ learning_rate = self.learning_rate * np.exp(-self.beta * self.t)
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+ self.t += 1
+
+ elif self.update_type == 'Cosine Decay':
+ learning_rate = self.learning_rate / 2.0 * (1.0 + np.cos(self.t * np.pi / self.iter_times))
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+ self.t += 1
+
+ elif self.update_type == 'AdaGrad':
+ G = (self.W1_grad * self.W1_grad).sum()
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate / np.sqrt(G + self.epsilon) * self.W1_grad
+ G = (self.W2_grad * self.W2_grad).sum()
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate / np.sqrt(G + self.epsilon) * self.W2_grad
+ G = (self.W3_grad * self.W3_grad).sum()
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate / np.sqrt(G + self.epsilon) * self.W3_grad
+
+ elif self.update_type == 'RMSprop':
+ self.G1 = self.beta * self.G1 + (1 - self.beta) * (self.W1_grad * self.W1_grad).sum()
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate / np.sqrt(self.G1 + self.epsilon) * self.W1_grad
+ self.G2 = self.beta * self.G2 + (1 - self.beta) * (self.W2_grad * self.W2_grad).sum()
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate / np.sqrt(self.G2 + self.epsilon) * self.W2_grad
+ self.G3 = self.beta * self.G3 + (1 - self.beta) * (self.W3_grad * self.W3_grad).sum()
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate / np.sqrt(self.G3 + self.epsilon) * self.W3_grad
+
+ elif self.update_type == 'AdaDelta':
+ self.X1 = self.beta * self.X1 + (1 - self.beta) * (self.W1_delta * self.W1_delta).sum()
+ self.G1 = self.beta * self.G1 + (1 - self.beta) * (self.W1_grad * self.W1_grad).sum()
+ self.W1_delta = -np.sqrt(self.X1 + self.epsilon) / np.sqrt(self.G1 + self.epsilon) * self.W1_grad
+ self.W1 += self.W1_delta
+
+ self.X2 = self.beta * self.X2 + (1 - self.beta) * (self.W2_delta * self.W2_delta).sum()
+ self.G2 = self.beta * self.G2 + (1 - self.beta) * (self.W2_grad * self.W2_grad).sum()
+ self.W2_delta = -np.sqrt(self.X2 + self.epsilon) / np.sqrt(self.G2 + self.epsilon) * self.W2_grad
+ self.W2 += self.W2_delta
+
+ self.X3 = self.beta * self.X3 + (1 - self.beta) * (self.W3_delta * self.W3_delta).sum()
+ self.G3 = self.beta * self.G3 + (1 - self.beta) * (self.W3_grad * self.W3_grad).sum()
+ self.W3_delta = -np.sqrt(self.X3 + self.epsilon) / np.sqrt(self.G3 + self.epsilon) * self.W3_grad
+ self.W3 += self.W3_delta
+
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..4e2bf7a7f624444ede1e6b317d46b0052f1ac675
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,143 @@
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, mini_batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size = 128, numpy = False):
+ if batch_size <= 0 or not isinstance(batch_size, int):
+ return None
+ # 1. 判断传入的 batch_size 是否合法,需要为正整数,不合法返回空
+
+ data, label = batch(dataset)[0]
+ # 2. 用 batch 方法将 torchvision 下的 MNIST 数据集转换为 numpy 的 array
+
+ datanum = len(data)
+ idx = np.arange(datanum)
+ np.random.shuffle(idx)
+ data, label = data[idx], label[idx]
+ # 3. 对 data 和 label 进行 random shuffle,具体来说,可以先对一个指示下标的数组做 random shuffle,然后用这个下标数组配合 slice 机制对 data 和 label 进行对应的 random shuffle,从而防止 data 和 label 错误匹配
+
+ batchnum = (datanum - 1) // batch_size + 1 # datanum 对 batch_size 下取整
+ batches = []
+ # 4. 计算 batch 数量,初始化 batches 列表
+
+ for i in range(batchnum):
+ batches.append((data[i * batch_size: min(datanum, (i + 1) * batch_size)], label[i * batch_size: min(datanum, (i + 1) * batch_size)]))
+ # 5. 通过 slice 机制选出第 i 个 batch 对应的 data 和 label 子集,放入 batches 列表中
+ return batches
+
+def numpy_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ # y_pred = model.forward(x.numpy()) # minibatch from pytorch
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x) # now x is a numpy array, so x.numpy() is not needed
+
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+
+def my_numpy_run(learning_rate = 0.01, epoch_number = 3, update_type = None):
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel(learning_rate, update_type, iter_times = 1407)
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ # y_pred = model.forward(x.numpy()) # minibatch from pytorch
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x) # now x is a numpy array, so x.numpy() is not needed
+
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ return train_loss
+ # plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+def multi_test():
+ from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
+ cases = [ None,
+ 'Momentum',
+ 'Nesterov',
+ 'Adam',
+ 'Inverse Time Decay',
+ 'Exponential Decay',
+ 'Natural Exponential Decay',
+ 'Cosine Decay',
+ 'AdaGrad',
+ 'RMSprop',
+ 'AdaDelta',
+ ]
+
+ colors = ['#1f77b4',
+ '#ff7f0e',
+ '#2ca02c',
+ '#d62728',
+ '#9467bd',
+ '#8c564b',
+ '#e377c2',
+ '#7f7f7f',
+ '#bcbd22',
+ '#17becf',
+ '#1a55FF']
+
+ # Configure rcParams axes.prop_cycle to simultaneously cycle cases and colors.
+ # mpl.rcParams['axes.prop_cycle'] = cycler(markevery=cases, color=colors)
+ # Set the plot curve with markers and a title
+ plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (10.0, 4.0) # 设置figure_size尺寸
+ fig = plt.figure()
+ ax = fig.add_axes([0.1, 0.1, 0.6, 0.75])
+ plt.xlabel('step')
+ plt.ylabel('loss value')
+ for i in range(len(cases)):
+ print('Test ' + str(cases[i]) + ' :')
+ data = my_numpy_run(update_type = cases[i])
+ print('-------------\n')
+ ax.plot(range(len(data)), data, linewidth = 0.5, label = str(cases[i]))
+ ax.legend(bbox_to_anchor = (1.05, 1), loc = 'upper left', borderaxespad = 0.)
+
+ plt.savefig("5.4.png", format = 'png', dpi = 1000)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
+ # my_numpy_run(learning_rate = 0.05, update_type = 'RMSprop')
+ # multi_test()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130211/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/19307130211/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..bcbe1fc6a17e98a4a5fd9ec9df13c372ac4455da
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/19307130211/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,255 @@
+# Assignment2
+
+姓名:陈洋
+
+学号:19307130211
+
+
+
+### 1.算子推算:
+
+首先先推算得到FNN网络需要的算子,并编写相应代码。
+
+##### Matmul:
+
+对于Matmul的计算公式为:
+$$
+Y_{ij}=\sum_{1\leq k\leq d} W_{ik}\times X{kj}
+$$
+又因为[神经网络与深度学习-邱锡鹏](https://nndl.github.io/nndl-book.pdf)书中公式B.21
+
+得到
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial X}=\frac{\partial(W\times X)}{\partial X}=W^T\\\\
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial X}=\frac{\partial(W\times X)}{\partial W}=X^T
+$$
+又因为链式法则,grad_y已知,所以:
+
+$grad\_x=grad\_y\times W^T $ 即`grad_x=np.matmul(grad_y,W.T) `
+
+$grad\_w=X^T\times grad\_y$ 即`grad_W=np.matmul(x.T,grad_y)`
+
+##### ReLU:
+
+对于ReLU的计算公式:
+$$
+Y_{ij}= \begin{cases} X{ij}, X{ij}\geq 0 \\\\ 0, X{ij}<0 \end{cases}
+$$
+所以
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X{ij}}= \begin{cases} 1, X{ij}\geq 0 \\\\ 0, X{ij}<0 \end{cases}
+$$
+又因为grad_y已知,所以得到:
+
+
+
+##### Log:
+
+Log 的计算公式为
+$$
+Y_{ij}=\ln(X_{ij}+\epsilon)
+$$
+所以
+$$
+\frac {\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{ij}}= \frac {1}{(X_{ij}+\epsilon)}
+$$
+已知grad_y,所以:
+
+
+
+即对应于代码:
+
+~~~python
+mask=1/(x+self.epsilon) #求1/(X+e)
+grad_x=mask*grad_y
+~~~
+
+##### Softmax:
+
+softmax的计算公式为
+$$
+Y_{ij}=\frac{\exp\{X_{ij}\}}{\sum_{k=1}^d\exp\{X_{ik} \}}
+$$
+所以对应的代码为
+
+~~~python
+x_exp=np.exp(x) #先对X中每个元素求e^Xij,
+out=x_exp / np.sum(x_exp,axis=1,keepdims=True)#axis=1,压缩列,将矩阵的每一行相加,并保持x的维度
+~~~
+
+其导数的推导:
+
+对于每一行的softmax是单独的,所以这里一行为例,证明过程参考了[神经网络与深度学习-邱锡鹏](https://nndl.github.io/nndl-book.pdf)书中推导:
+
+
+
+所以对于每一行的softmax的Jacobs矩阵为:
+$$
+J=diag(Y_i)-Y_i\times Y_i^T
+$$
+所以对应的代码为
+
+~~~Python
+J=np.diag(temp)-np.outer(temp,temp)
+#每一行的导数为grad_Yi*J,所以grad_Xi计算代码如下:
+t=np.dot(grad_y[i],Jacobs[i])
+~~~
+
+### 2.网络的完善与实现
+
+通过对torch_mnist.py的阅读得到网络的结构:
+
+`input->全连接层->激活函数ReLU->全连接层->激活函数ReLU->全连接层->softmax->Log`
+
+所以其实只要按照同样的顺序调用之前实现好的算子,就可以完成实验的要求。
+
+##### 1.实验
+
+填写完代码后,初次运行numpy_mnist.py,结果如下:
+
+其中 epoch=3,learning_rate=0.1。
+
+~~~shell
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9487
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9647
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9690
+~~~
+
+
+
+##### 2.mini_batch 的实现
+
+mini_batch()函数源代码就是使用pytorch包里面的dataloader实现了对数据分组和打乱,所以我们实现的mini_batch()需要实现这两个功能。
+
+首先将data和label分别取出放在list中,通过numpy.random.choice()函数得到一个用来随机打乱的index。
+
+~~~python
+idx=np.random.choice(Num,Num,replace=False)
+~~~
+
+因为需要使用index作为索引,所以原先为list的数据需要使用np.array()进行转换,所以在训练过程中需要修改代码,如下。
+
+~~~python
+#y_pred = model.forward(x.numpy())
+y_pred = model.forward(x)
+~~~
+
+##### 3.对模型的进一步讨论
+
+增大epoch,使epoch=10,15,20:
+
+
+
+(上三图分别对应 $\alpha = 1.0,\ 5.0,\ 8.0$ 情况)
+
+和先前不同, $\alpha = 1.0$ 时模型就出现了数值问题,导致优化失效
+
+
+
+## 第三部分:自定义 mini_batch
+
+用 numpy 手写 mini_batch 函数,其实原理很简单,算法大概分为如下步骤(写在代码中):
+
+```python
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size = 128, numpy = False):
+ if batch_size <= 0 or not isinstance(batch_size, int):
+ return None
+ # 1. 判断传入的 batch_size 是否合法,需要为正整数,不合法返回空
+
+ data, label = batch(dataset)[0]
+ # 2. 用 batch 方法将 torchvision 下的 MNIST 数据集转换为 numpy 的 array
+
+ datanum = len(data)
+ idx = np.arange(datanum)
+ np.random.shuffle(idx)
+ data, label = data[idx], label[idx]
+ # 3. 对 data 和 label 进行 random shuffle,具体来说,可以先对一个指示下标的数组做 random shuffle,然后用这个下标数组配合 slice 机制对 data 和 label 进行对应的 random shuffle,从而防止 data 和 label 错误匹配
+
+ batchnum = (datanum - 1) // batch_size + 1 # datanum 对 batch_size 下取整
+ batches = []
+ # 4. 计算 batch 数量,初始化 batches 列表
+
+ for i in range(batchnum):
+ batches.append((data[i * batch_size: min(datanum, (i + 1) * batch_size)], label[i * batch_size: min(datanum, (i + 1) * batch_size)]))
+ # 5. 通过 slice 机制选出第 i 个 batch 对应的 data 和 label 子集,放入 batches 列表中
+
+ return batches
+```
+
+
+
+## 第四部分:额外探究
+
+### 其他基于梯度的优化方法对比实验
+
+在代码中 ( numpy_fnn.py 和 numpy_mnist.py ) 实现了十种优化方法,有
+
+- Momentum, 动量法
+- Nesterov Accelerated Gradient, NAG, Nesterov 加速梯度 或称 Nesterov 动量法
+- Adaptive Moment Estimation Algorithm, Adam 算法
+- Inverse Time Decay, 逆时衰减
+- Exponential Decay, 指数衰减
+- Natural Exponential Decay, 自然指数衰减
+- Cosine Decay, 余弦衰减
+- Adaptive Gradient Algorithm, AdaGrad 算法
+- RMSprop 算法
+- AdaDelta 算法
+
+包括无优化的版本,共有十一种不同的对比实验
+
+#### $\mathrm{epoch} = 3,\ \alpha = 0.1$
+
+这里设定 $\mathrm{epoch} = 3,\ \alpha = 0.1$ ,当然,对于调整学习率的算法,$\alpha$ 是不固定的,提供的只是一个初始值
+
+| Epoch | None | Momentum | Nesterov | Adam |
+| :---: | :-------: | :-------: | :-------: | :-------: |
+| $0$ | $92.15\%$ | $96.72\%$ | $96.42\%$ | $95.43\%$ |
+| $1$ | $96.21\%$ | $97.00\%$ | $96.88\%$ | $96.87\%$ |
+| $2$ | $96.81\%$ | $97.54\%$ | $97.09\%$ | $97.55\%$ |
+
+| Epoch | Inverse Time Decay | Exponential Decay | Natural Exponential Decay | Cosine Decay |
+| :---: | :----------------: | :---------------: | :-----------------------: | :----------: |
+| $0$ | $86.71\%$ | $81.10\%$ | $81.05\%$ | $94.17\%$ |
+| $1$ | $87.93\%$ | $81.10\%$ | $81.05\%$ | $95.91\%$ |
+| $2$ | $88.49\%$ | $81.10\%$ | $81.05\%$ | $96.08\%$ |
+
+| Epoch | AdaGrad | RMSprop | AdaDelta |
+| :---: | :-------: | :-------: | :-------: |
+| $0$ | $95.04\%$ | $95.47\%$ | $76.42\%$ |
+| $1$ | $96.28\%$ | $96.45\%$ | $86.86\%$ |
+| $2$ | $97.24\%$ | $97.43\%$ | $89.22\%$ |
+
+
+
+*其实这时候忘了把 RMSprop 加进去了,但是对比也是很丰富的...
+
+
+
+#### $\mathrm{epoch} = 3,\ \alpha = 0.05$
+
+为了更好地突出各个算法的不同,将学习率 $\alpha$ 降低为 $0.05$
+
+| Epoch | None | Momentum | Nesterov | Adam |
+| :---: | :-------: | :-------: | :-------: | :-------: |
+| $0$ | $92.47\%$ | $96.20\%$ | $96.65\%$ | $93.67\%$ |
+| $1$ | $94.43\%$ | $97.38\%$ | $97.13\%$ | $96.11\%$ |
+| $2$ | $95.67\%$ | $97.70\%$ | $97.70\%$ | $96.69\%$ |
+
+| Epoch | Inverse Time Decay | Exponential Decay | Natural Exponential Decay | Cosine Decay |
+| :---: | :----------------: | :---------------: | :-----------------------: | :----------: |
+| $0$ | $77.18\%$ | $67.31\%$ | $64.09\%$ | $92.47\%$ |
+| $1$ | $80.42\%$ | $67.31\%$ | $64.09\%$ | $94.07\%$ |
+| $2$ | $81.90\%$ | $67.31\%$ | $64.09\%$ | $94.35\%$ |
+
+| Epoch | AdaGrad | RMSprop | AdaDelta |
+| :---: | :-------: | :-------: | :-------: |
+| $0$ | $93.29\%$ | $93.74\%$ | $75.09\%$ |
+| $1$ | $95.47\%$ | $95.17\%$ | $87.09\%$ |
+| $2$ | $96.49\%$ | $96.71\%$ | $89.76\%$ |
+
+
+
+*这时候仍然忘了把 RMSprop 加进去了...
+
+
+
+#### $\mathrm{epoch} = 3,\ \alpha = 0.01$
+
+为了更好地突出各个算法的不同,将学习率 $\alpha$ 进一步降低为 $0.01$,同时加上 RMSprop 算法
+
+| Epoch | None | Momentum | Nesterov | Adam |
+| :---: | :-------: | :-------: | :-------: | :-------: |
+| $0$ | $87.89\%$ | $94.37\%$ | $94.51\%$ | $89.81\%$ |
+| $1$ | $90.47\%$ | $96.32\%$ | $95.82\%$ | $91.76\%$ |
+| $2$ | $91.98\%$ | $97.12\%$ | $96.85\%$ | $92.96\%$ |
+
+| Epoch | Inverse Time Decay | Exponential Decay | Natural Exponential Decay | Cosine Decay |
+| :---: | :----------------: | :---------------: | :-----------------------: | :----------: |
+| $0$ | $36.83\%$ | $21.94\%$ | $29.31\%$ | $87.22\%$ |
+| $1$ | $45.39\%$ | $21.94\%$ | $29.31\%$ | $89.67\%$ |
+| $2$ | $50.02\%$ | $21.94\%$ | $29.31\%$ | $89.85\%$ |
+
+| Epoch | AdaGrad | RMSprop | AdaDelta |
+| :---: | :-------: | :-----: | :-------: |
+| $0$ | $89.44\%$ | $89.56\%$ | $77.58\%$ |
+| $1$ | $91.83\%$ | $91.85\%$ | $86.84\%$ |
+| $2$ | $92.76\%$ | $92.90\%$ | $89.26\%$ |
+
+
+
+#### 总结
+
+- 可以发现 Momentum 和 Nesterov 效果一直不错,且表现接近,这可能是因为本作业的模型比较简单,而 Momentum 和 Nesterov 总体来看做的事情比较相似,所以没有体现出 Nesterov 对梯度更新的修正。Adam 在 $\alpha$ 较大时表现也很好
+- 对于以某种方式衰减 $\alpha$ 的优化,初始 $\alpha$ 必须足够大才能体现出较好的效果,毕竟 $\alpha$ 太小的话,衰减到最后已经不足以对参数产生实质性的更新从而导致停滞(如 Exponential Decay 和 Natural Exponential Decay)
+- AdaGrad 和 RMSprop 表现比较接近,这可能也是因为本作业的模型比较简单,所以没有体现出 RMSprop 中指数衰减移动平均的优势,且这两者也会受到学习率减小的影响
+
+
+
+### 权重初始化
+
+留坑待补...
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/1.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..76e24ca85c7ce4d93a478588b5bb4c56712f55f8
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.2.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..dcd73246ee7c55075b77254e662b29c73b388479
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.3.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.3.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..52dc358d56961c0b88b78c4be37f09d6cf0ff73f
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.3.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.4.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.4.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b1887ce4f8daf51fb7f0b83c31e8fc7af2edb333
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.4.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.5.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.5.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..0bfb996933564302164fef6ef8f81ccff226b261
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.5.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.8.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.8.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..25fbb117e3043af4ee3c0971e0df2f86e235002f
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.8.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..50493ce463016089ef27bd53da94fb037f1a11da
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/3.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/3.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ff604f17eb61b62e9f093adf749a1f9e300f183b
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/3.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/4.1.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/4.1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..06c1a99c134d02ef2198b12330e1fae207a0c88a
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/4.1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/4.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/4.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..517a871080f592d5bdf8b0d16ce2fb1851c0b0a8
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/4.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.1.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..3649baecd02c1fa828f201b1220fcf81a2d11131
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.1.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.2.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..7706ab7fefd7672d262ef8e8781bc97d3d749401
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.2.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.3.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.3.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..3f8c5876a1a72ebdbccf057b776ec5b9be91f296
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.3.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.4.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.4.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e8ca3f58c0149ffd66c0510e30da28c4f2751ff4
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.4.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..d1698795bf9cd724b32984a43585b0ffcece7dad
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/5.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/6.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/6.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..f3246e39870e14e383f18c231d30c5f22e2c637d
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/6.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/7.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/7.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..b4fbff12bdc4a177d7fd555580ac7312fabf1d06
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/7.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/8.png b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/8.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c8568213cf5f72bfe57b28c7bdb9e2a8cc2bcfe4
Binary files /dev/null and b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/img/8.png differ
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/numpy_fnn.py b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/numpy_fnn.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..c5c95457e32cddf3ea2cb9effb780331e632d2bd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/numpy_fnn.py
@@ -0,0 +1,340 @@
+import numpy as np
+
+class NumpyOp:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.memory = {}
+ self.epsilon = 1e-12
+
+
+class Matmul(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x, W):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, d)
+ w: shape(d, d')
+ """
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['W'] = W
+ h = np.matmul(x, W)
+ return h
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: shape(N, d')
+ """
+
+ # code1
+ grad_x = np.matmul(grad_y, self.memory['W'].T)
+ grad_W = np.matmul(self.memory['x'].T, grad_y)
+
+ return grad_x, grad_W
+
+
+class Relu(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ return np.where(x > 0, x, np.zeros_like(x))
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ # code2
+ grad_x = grad_y * (self.memory['x'] >= 0)
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Log(NumpyOp):
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ out = np.log(x + self.epsilon)
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ # code3
+ grad_x = grad_y * (1.0 / self.memory['x'])
+
+ return grad_x
+
+
+class Softmax(NumpyOp):
+ """
+ softmax over last dimension
+ """
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ """
+ x: shape(N, c)
+ """
+
+ # code4
+ mx = x.max(axis = 1).reshape(x.shape[0], -1) # 防止上溢和下溢
+ ex = np.exp(x - mx)
+ out = (ex.T / (ex.sum(axis = 1))).T
+ self.memory['x'] = x
+ self.memory['y'] = out
+
+ return out
+
+ def backward(self, grad_y):
+ """
+ grad_y: same shape as x
+ """
+
+ # code5
+ x = self.memory['x']
+ y = self.memory['y']
+ grad_x = np.zeros(x.shape)
+ for i in range(x.shape[0]):
+ grad_x[i] = np.matmul(grad_y[i], -np.matmul(np.matrix(y[i]).T, np.matrix(y[i])) + np.diag(np.array(y[i])))
+ return grad_x
+
+class NumpyLoss:
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.target = None
+
+ def get_loss(self, pred, target):
+ self.target = target
+ return (-pred * target).sum(axis=1).mean()
+
+ def backward(self):
+ return -self.target / self.target.shape[0]
+
+class NumpyModel:
+ def __init__(self, learning_rate = 0.1, update_type = None, iter_times = 1407):
+ self.W1 = np.random.normal(size=(28 * 28, 256))
+ self.W2 = np.random.normal(size=(256, 64))
+ self.W3 = np.random.normal(size=(64, 10))
+
+
+ # 以下算子会在 forward 和 backward 中使用
+ self.matmul_1 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_1 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_2 = Matmul()
+ self.relu_2 = Relu()
+ self.matmul_3 = Matmul()
+ self.softmax = Softmax()
+ self.log = Log()
+
+ # 以下变量需要在 backward 中更新。 softmax_grad, log_grad 等为算子反向传播的梯度( loss 关于算子输入的偏导)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_1_grad = None
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = None, None
+ self.relu_2_grad = None
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = None, None
+ self.softmax_grad = None
+ self.log_grad = None
+
+ # 以下变量指定了梯度回传所用的优化方法,并完成了有关的初始化
+ self.update_type = update_type
+ self.learning_rate = learning_rate
+ self.iter_times = iter_times
+ if update_type == 'Momentum':
+ self.rho = 0.9
+ self.W1_delta = np.zeros(self.W1.shape)
+ self.W2_delta = np.zeros(self.W2.shape)
+ self.W3_delta = np.zeros(self.W3.shape)
+
+ elif update_type == 'Nesterov':
+ self.rho = 0.9
+ self.W1_delta = np.zeros(self.W1.shape)
+ self.W2_delta = np.zeros(self.W2.shape)
+ self.W3_delta = np.zeros(self.W3.shape)
+
+ elif update_type == 'Adam':
+ self.epsilon = 1e-7
+ self.beta1, self.beta2 = 0.9, 0.99
+ self.M1 = np.zeros(self.W1.shape)
+ self.M2 = np.zeros(self.W2.shape)
+ self.M3 = np.zeros(self.W3.shape)
+ self.G1, self.G2, self.G3 = .0, .0, .0
+
+ elif update_type == 'Inverse Time Decay':
+ self.beta = 0.1
+ self.t = 0
+
+ elif update_type == 'Exponential Decay':
+ self.beta = 0.96
+ self.t = 0
+
+ elif update_type == 'Natural Exponential Decay':
+ self.beta = 0.04
+ self.t = 0
+
+ elif update_type == 'Cosine Decay':
+ self.t = 0
+
+ elif update_type == 'AdaGrad':
+ self.epsilon = 1e-7
+
+ elif update_type == 'RMSprop':
+ self.beta = 0.9
+ self.epsilon = 1e-7
+ self.G1, self.G2, self.G3 = .0, .0, .0
+
+ elif update_type == 'AdaDelta':
+ self.beta = 0.9
+ self.epsilon = 1e-7
+ self.W1_delta = np.zeros(self.W1.shape)
+ self.W2_delta = np.zeros(self.W2.shape)
+ self.W3_delta = np.zeros(self.W3.shape)
+ self.X1, self.X2, self.X3 = .0, .0, .0
+ self.G1, self.G2, self.G3 = .0, .0, .0
+
+ def forward(self, x):
+ x = x.reshape(-1, 28 * 28)
+
+ # code6
+ if self.update_type == 'Nesterov':
+ # 在前向传播之前进行 Nesterov 算法的第一阶段
+ self.W1_delta = self.rho * self.W1_delta
+ self.W2_delta = self.rho * self.W2_delta
+ self.W3_delta = self.rho * self.W3_delta
+ self.W1 += self.W1_delta
+ self.W2 += self.W2_delta
+ self.W3 += self.W3_delta
+
+ x = self.matmul_1.forward(x, self.W1)
+ x = self.relu_1.forward(x)
+ x = self.matmul_2.forward(x, self.W2)
+ x = self.relu_2.forward(x)
+ x = self.matmul_3.forward(x, self.W3)
+ x = self.softmax.forward(x)
+ x = self.log.forward(x)
+
+ return x
+
+ def backward(self, y):
+ # for size in y.shape:
+ # y /= size
+
+
+ # code7
+ #self.log_grad = self.log.backward(-y)
+ self.log_grad = self.log.backward(y)
+ self.softmax_grad = self.softmax.backward(self.log_grad)
+ self.x3_grad, self.W3_grad = self.matmul_3.backward(self.softmax_grad)
+ self.relu_2_grad = self.relu_2.backward(self.x3_grad)
+ self.x2_grad, self.W2_grad = self.matmul_2.backward(self.relu_2_grad)
+ self.relu_1_grad = self.relu_1.backward(self.x2_grad)
+ self.x1_grad, self.W1_grad = self.matmul_1.backward(self.relu_1_grad)
+
+
+
+ def optimize(self, learning_rate):
+ if not self.update_type:
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+
+ elif self.update_type == 'Momentum':
+ self.W1_delta = self.rho * self.W1_delta - learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2_delta = self.rho * self.W2_delta - learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3_delta = self.rho * self.W3_delta - learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+ self.W1 += self.W1_delta
+ self.W2 += self.W2_delta
+ self.W3 += self.W3_delta
+
+ elif self.update_type == 'Nesterov':
+ # 在参数更新时进行 Nesterov 第二阶段
+ self.W1_delta -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2_delta -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3_delta -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+
+ elif self.update_type == 'Adam':
+ self.M1 = self.beta1 * self.M1 + (1 - self.beta1) * self.W1_grad
+ self.G1 = self.beta2 * self.G1 + (1 - self.beta2) * (self.W1_grad * self.W1_grad).sum()
+ _M1 = self.M1 / (1 - self.beta1)
+ _G1 = self.G1 / (1 - self.beta2)
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate / np.sqrt(_G1 + self.epsilon) * _M1
+
+ self.M2 = self.beta1 * self.M2 + (1 - self.beta1) * self.W2_grad
+ self.G2 = self.beta2 * self.G2 + (1 - self.beta2) * (self.W2_grad * self.W2_grad).sum()
+ _M2 = self.M2 / (1 - self.beta1)
+ _G2 = self.G2 / (1 - self.beta2)
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate / np.sqrt(_G2 + self.epsilon) * _M2
+
+ self.M3 = self.beta1 * self.M3 + (1 - self.beta1) * self.W3_grad
+ self.G3 = self.beta2 * self.G3 + (1 - self.beta2) * (self.W3_grad * self.W3_grad).sum()
+ _M3 = self.M3 / (1 - self.beta1)
+ _G3 = self.G3 / (1 - self.beta2)
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate / np.sqrt(_G3 + self.epsilon) * _M3
+
+ elif self.update_type == 'Inverse Time Decay':
+ learning_rate = self.learning_rate / (1.0 + self.beta * self.t)
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+ self.t += 1
+
+ elif self.update_type == 'Exponential Decay':
+ learning_rate = self.learning_rate * pow(self.beta, self.t)
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+ self.t += 1
+
+ elif self.update_type == 'Natural Exponential Decay':
+ learning_rate = self.learning_rate * np.exp(-self.beta * self.t)
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+ self.t += 1
+
+ elif self.update_type == 'Cosine Decay':
+ learning_rate = self.learning_rate / 2.0 * (1.0 + np.cos(self.t * np.pi / self.iter_times))
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate * self.W1_grad
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate * self.W2_grad
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate * self.W3_grad
+ self.t += 1
+
+ elif self.update_type == 'AdaGrad':
+ G = (self.W1_grad * self.W1_grad).sum()
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate / np.sqrt(G + self.epsilon) * self.W1_grad
+ G = (self.W2_grad * self.W2_grad).sum()
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate / np.sqrt(G + self.epsilon) * self.W2_grad
+ G = (self.W3_grad * self.W3_grad).sum()
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate / np.sqrt(G + self.epsilon) * self.W3_grad
+
+ elif self.update_type == 'RMSprop':
+ self.G1 = self.beta * self.G1 + (1 - self.beta) * (self.W1_grad * self.W1_grad).sum()
+ self.W1 -= learning_rate / np.sqrt(self.G1 + self.epsilon) * self.W1_grad
+ self.G2 = self.beta * self.G2 + (1 - self.beta) * (self.W2_grad * self.W2_grad).sum()
+ self.W2 -= learning_rate / np.sqrt(self.G2 + self.epsilon) * self.W2_grad
+ self.G3 = self.beta * self.G3 + (1 - self.beta) * (self.W3_grad * self.W3_grad).sum()
+ self.W3 -= learning_rate / np.sqrt(self.G3 + self.epsilon) * self.W3_grad
+
+ elif self.update_type == 'AdaDelta':
+ self.X1 = self.beta * self.X1 + (1 - self.beta) * (self.W1_delta * self.W1_delta).sum()
+ self.G1 = self.beta * self.G1 + (1 - self.beta) * (self.W1_grad * self.W1_grad).sum()
+ self.W1_delta = -np.sqrt(self.X1 + self.epsilon) / np.sqrt(self.G1 + self.epsilon) * self.W1_grad
+ self.W1 += self.W1_delta
+
+ self.X2 = self.beta * self.X2 + (1 - self.beta) * (self.W2_delta * self.W2_delta).sum()
+ self.G2 = self.beta * self.G2 + (1 - self.beta) * (self.W2_grad * self.W2_grad).sum()
+ self.W2_delta = -np.sqrt(self.X2 + self.epsilon) / np.sqrt(self.G2 + self.epsilon) * self.W2_grad
+ self.W2 += self.W2_delta
+
+ self.X3 = self.beta * self.X3 + (1 - self.beta) * (self.W3_delta * self.W3_delta).sum()
+ self.G3 = self.beta * self.G3 + (1 - self.beta) * (self.W3_grad * self.W3_grad).sum()
+ self.W3_delta = -np.sqrt(self.X3 + self.epsilon) / np.sqrt(self.G3 + self.epsilon) * self.W3_grad
+ self.W3 += self.W3_delta
+
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/numpy_mnist.py b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/numpy_mnist.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..4e2bf7a7f624444ede1e6b317d46b0052f1ac675
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/19307130062/numpy_mnist.py
@@ -0,0 +1,143 @@
+import numpy as np
+from numpy_fnn import NumpyModel, NumpyLoss
+from utils import download_mnist, batch, mini_batch, get_torch_initialization, plot_curve, one_hot
+
+def mini_batch(dataset, batch_size = 128, numpy = False):
+ if batch_size <= 0 or not isinstance(batch_size, int):
+ return None
+ # 1. 判断传入的 batch_size 是否合法,需要为正整数,不合法返回空
+
+ data, label = batch(dataset)[0]
+ # 2. 用 batch 方法将 torchvision 下的 MNIST 数据集转换为 numpy 的 array
+
+ datanum = len(data)
+ idx = np.arange(datanum)
+ np.random.shuffle(idx)
+ data, label = data[idx], label[idx]
+ # 3. 对 data 和 label 进行 random shuffle,具体来说,可以先对一个指示下标的数组做 random shuffle,然后用这个下标数组配合 slice 机制对 data 和 label 进行对应的 random shuffle,从而防止 data 和 label 错误匹配
+
+ batchnum = (datanum - 1) // batch_size + 1 # datanum 对 batch_size 下取整
+ batches = []
+ # 4. 计算 batch 数量,初始化 batches 列表
+
+ for i in range(batchnum):
+ batches.append((data[i * batch_size: min(datanum, (i + 1) * batch_size)], label[i * batch_size: min(datanum, (i + 1) * batch_size)]))
+ # 5. 通过 slice 机制选出第 i 个 batch 对应的 data 和 label 子集,放入 batches 列表中
+ return batches
+
+def numpy_run():
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel()
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+ epoch_number = 3
+ learning_rate = 0.1
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ # y_pred = model.forward(x.numpy()) # minibatch from pytorch
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x) # now x is a numpy array, so x.numpy() is not needed
+
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+
+
+def my_numpy_run(learning_rate = 0.01, epoch_number = 3, update_type = None):
+ train_dataset, test_dataset = download_mnist()
+
+ model = NumpyModel(learning_rate, update_type, iter_times = 1407)
+ numpy_loss = NumpyLoss()
+ model.W1, model.W2, model.W3 = get_torch_initialization()
+
+ train_loss = []
+
+
+ for epoch in range(epoch_number):
+ for x, y in mini_batch(train_dataset):
+ y = one_hot(y)
+
+ # y_pred = model.forward(x.numpy()) # minibatch from pytorch
+
+ y_pred = model.forward(x) # now x is a numpy array, so x.numpy() is not needed
+
+ loss = numpy_loss.get_loss(y_pred, y)
+
+ model.backward(numpy_loss.backward())
+ model.optimize(learning_rate)
+
+ train_loss.append(loss.item())
+
+ x, y = batch(test_dataset)[0]
+ accuracy = np.mean((model.forward(x).argmax(axis=1) == y))
+ print('[{}] Accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, accuracy))
+
+ return train_loss
+ # plot_curve(train_loss)
+
+def multi_test():
+ from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
+ cases = [ None,
+ 'Momentum',
+ 'Nesterov',
+ 'Adam',
+ 'Inverse Time Decay',
+ 'Exponential Decay',
+ 'Natural Exponential Decay',
+ 'Cosine Decay',
+ 'AdaGrad',
+ 'RMSprop',
+ 'AdaDelta',
+ ]
+
+ colors = ['#1f77b4',
+ '#ff7f0e',
+ '#2ca02c',
+ '#d62728',
+ '#9467bd',
+ '#8c564b',
+ '#e377c2',
+ '#7f7f7f',
+ '#bcbd22',
+ '#17becf',
+ '#1a55FF']
+
+ # Configure rcParams axes.prop_cycle to simultaneously cycle cases and colors.
+ # mpl.rcParams['axes.prop_cycle'] = cycler(markevery=cases, color=colors)
+ # Set the plot curve with markers and a title
+ plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (10.0, 4.0) # 设置figure_size尺寸
+ fig = plt.figure()
+ ax = fig.add_axes([0.1, 0.1, 0.6, 0.75])
+ plt.xlabel('step')
+ plt.ylabel('loss value')
+ for i in range(len(cases)):
+ print('Test ' + str(cases[i]) + ' :')
+ data = my_numpy_run(update_type = cases[i])
+ print('-------------\n')
+ ax.plot(range(len(data)), data, linewidth = 0.5, label = str(cases[i]))
+ ax.legend(bbox_to_anchor = (1.05, 1), loc = 'upper left', borderaxespad = 0.)
+
+ plt.savefig("5.4.png", format = 'png', dpi = 1000)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ numpy_run()
+ # my_numpy_run(learning_rate = 0.05, update_type = 'RMSprop')
+ # multi_test()
diff --git a/assignment-2/submission/19307130211/README.md b/assignment-2/submission/19307130211/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..bcbe1fc6a17e98a4a5fd9ec9df13c372ac4455da
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assignment-2/submission/19307130211/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,255 @@
+# Assignment2
+
+姓名:陈洋
+
+学号:19307130211
+
+
+
+### 1.算子推算:
+
+首先先推算得到FNN网络需要的算子,并编写相应代码。
+
+##### Matmul:
+
+对于Matmul的计算公式为:
+$$
+Y_{ij}=\sum_{1\leq k\leq d} W_{ik}\times X{kj}
+$$
+又因为[神经网络与深度学习-邱锡鹏](https://nndl.github.io/nndl-book.pdf)书中公式B.21
+
+得到
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial X}=\frac{\partial(W\times X)}{\partial X}=W^T\\\\
+\frac{\partial Y}{\partial X}=\frac{\partial(W\times X)}{\partial W}=X^T
+$$
+又因为链式法则,grad_y已知,所以:
+
+$grad\_x=grad\_y\times W^T $ 即`grad_x=np.matmul(grad_y,W.T) `
+
+$grad\_w=X^T\times grad\_y$ 即`grad_W=np.matmul(x.T,grad_y)`
+
+##### ReLU:
+
+对于ReLU的计算公式:
+$$
+Y_{ij}= \begin{cases} X{ij}, X{ij}\geq 0 \\\\ 0, X{ij}<0 \end{cases}
+$$
+所以
+$$
+\frac{\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X{ij}}= \begin{cases} 1, X{ij}\geq 0 \\\\ 0, X{ij}<0 \end{cases}
+$$
+又因为grad_y已知,所以得到:
+
+
+
+##### Log:
+
+Log 的计算公式为
+$$
+Y_{ij}=\ln(X_{ij}+\epsilon)
+$$
+所以
+$$
+\frac {\partial Y_{ij}}{\partial X_{ij}}= \frac {1}{(X_{ij}+\epsilon)}
+$$
+已知grad_y,所以:
+
+
+
+即对应于代码:
+
+~~~python
+mask=1/(x+self.epsilon) #求1/(X+e)
+grad_x=mask*grad_y
+~~~
+
+##### Softmax:
+
+softmax的计算公式为
+$$
+Y_{ij}=\frac{\exp\{X_{ij}\}}{\sum_{k=1}^d\exp\{X_{ik} \}}
+$$
+所以对应的代码为
+
+~~~python
+x_exp=np.exp(x) #先对X中每个元素求e^Xij,
+out=x_exp / np.sum(x_exp,axis=1,keepdims=True)#axis=1,压缩列,将矩阵的每一行相加,并保持x的维度
+~~~
+
+其导数的推导:
+
+对于每一行的softmax是单独的,所以这里一行为例,证明过程参考了[神经网络与深度学习-邱锡鹏](https://nndl.github.io/nndl-book.pdf)书中推导:
+
+
+
+所以对于每一行的softmax的Jacobs矩阵为:
+$$
+J=diag(Y_i)-Y_i\times Y_i^T
+$$
+所以对应的代码为
+
+~~~Python
+J=np.diag(temp)-np.outer(temp,temp)
+#每一行的导数为grad_Yi*J,所以grad_Xi计算代码如下:
+t=np.dot(grad_y[i],Jacobs[i])
+~~~
+
+### 2.网络的完善与实现
+
+通过对torch_mnist.py的阅读得到网络的结构:
+
+`input->全连接层->激活函数ReLU->全连接层->激活函数ReLU->全连接层->softmax->Log`
+
+所以其实只要按照同样的顺序调用之前实现好的算子,就可以完成实验的要求。
+
+##### 1.实验
+
+填写完代码后,初次运行numpy_mnist.py,结果如下:
+
+其中 epoch=3,learning_rate=0.1。
+
+~~~shell
+[0] Accuracy: 0.9487
+[1] Accuracy: 0.9647
+[2] Accuracy: 0.9690
+~~~
+
+
+
+##### 2.mini_batch 的实现
+
+mini_batch()函数源代码就是使用pytorch包里面的dataloader实现了对数据分组和打乱,所以我们实现的mini_batch()需要实现这两个功能。
+
+首先将data和label分别取出放在list中,通过numpy.random.choice()函数得到一个用来随机打乱的index。
+
+~~~python
+idx=np.random.choice(Num,Num,replace=False)
+~~~
+
+因为需要使用index作为索引,所以原先为list的数据需要使用np.array()进行转换,所以在训练过程中需要修改代码,如下。
+
+~~~python
+#y_pred = model.forward(x.numpy())
+y_pred = model.forward(x)
+~~~
+
+##### 3.对模型的进一步讨论
+
+增大epoch,使epoch=10,15,20:
+
+ +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+