# deepbots
**Repository Path**: helloliver/deepbots
## Basic Information
- **Project Name**: deepbots
- **Description**: No description available
- **Primary Language**: Unknown
- **License**: GPL-3.0
- **Default Branch**: master
- **Homepage**: None
- **GVP Project**: No
## Statistics
- **Stars**: 0
- **Forks**: 0
- **Created**: 2021-01-13
- **Last Updated**: 2021-01-13
## Categories & Tags
**Categories**: Uncategorized
**Tags**: None
## README
# deepbots
Deepbots is a simple framework which is used as "middleware" between the free
and open-source [Cyberbotics' Webots](https://cyberbotics.com/) robot simulator
and Reinforcement Learning algorithms. When it comes to Reinforcement Learning
the [OpenAI gym](https://gym.openai.com/) environment has been established as
the most used interface between the actual application and the RL algorithm.
Deepbots is a framework which follows the OpenAI gym environment interface
logic in order to be used by Webots applications.
## Installation
### Prerequisites
1. [Install Webots](https://cyberbotics.com/doc/guide/installing-webots)
- [Windows](https://cyberbotics.com/doc/guide/installation-procedure#installation-on-windows)
- [Linux](https://cyberbotics.com/doc/guide/installation-procedure#installation-on-linux)
- [macOS](https://cyberbotics.com/doc/guide/installation-procedure#installation-on-macos)
2. [Install Python version 3.X](https://www.python.org/downloads/) (please
refer to
[Using Python](https://cyberbotics.com/doc/guide/using-python#introduction)
to select the proper Python version for your system)
3. Follow the [Using Python](https://cyberbotics.com/doc/guide/using-python)
guide provided by Webots
4. Webots provides a basic code editor, but if you want to use
[PyCharm](https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/) as your IDE refer to
[using PyCharm IDE](https://cyberbotics.com/doc/guide/using-your-ide#pycharm)
provided by Webots
You will probably also need a backend library to implement the neural networks,
such as [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) or
[TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/). Deepbots interfaces with RL agents
using the OpenAI gym logic, so it can work with any backend library you choose
to implement the agent with and any agent that already works with gym.
### Install deepbots
Deepbots can be installed through the package installer
[pip](https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/) running the following command:
`pip install deepbots`
## Official resources
- On
[the deepbots-tutorials repository](https://github.com/aidudezzz/deepbots-tutorials)
you can find the official tutorials for deepbots
- On [the deepworlds repository](https://github.com/aidudezzz/deepworlds) you
can find examples of deepbots being used.
Feel free to contribute your
own!
## Citation
Conference paper (AIAI2020):
https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-49186-4_6
```bibtex
@InProceedings{10.1007/978-3-030-49186-4_6,
author="Kirtas, M.
and Tsampazis, K.
and Passalis, N.
and Tefas, A.",
editor="Maglogiannis, Ilias
and Iliadis, Lazaros
and Pimenidis, Elias",
title="Deepbots: A Webots-Based Deep Reinforcement Learning Framework for Robotics",
booktitle="Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations",
year="2020",
publisher="Springer International Publishing",
address="Cham",
pages="64--75",
abstract="Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) is increasingly used to train robots to perform complex and delicate tasks, while the development of realistic simulators contributes to the acceleration of research on DRL for robotics. However, it is still not straightforward to employ such simulators in the typical DRL pipeline, since their steep learning curve and the enormous amount of development required to interface with DRL methods significantly restrict their use by researchers. To overcome these limitations, in this work we present an open-source framework that combines an established interface used by DRL researchers, the OpenAI Gym interface, with the state-of-the-art Webots robot simulator in order to provide a standardized way to employ DRL in various robotics scenarios. Deepbots aims to enable researchers to easily develop DRL methods in Webots by handling all the low-level details and reducing the required development effort. The effectiveness of the proposed framework is demonstrated through code examples, as well as using three use cases of varying difficulty.",
isbn="978-3-030-49186-4"
}
```
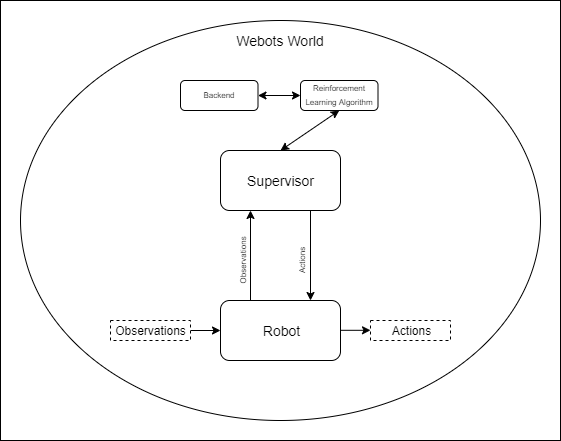
## How it works
First of all let's set up a simple glossary:
- `World`: Webots uses a tree structure to represent the different entities in
the scene. The World is the root entity which contains all the
entities/nodes. For example, the world contains the Supervisor and Robot
entities as well as other objects which might be included in the scene.
- `Supervisor`: The Supervisor is an entity which has access to all other
entities of the world, while having no physical presence in it. For example,
the Supervisor knows the exact position of all the entities of the world and
can manipulate them. Additionally, the Supervisor has the Supervisor
Controller as one of its child nodes.
- `Supervisor Controller`: The Supervisor Controller is a python script which
is responsible for the Supervisor. For example, in the Supervisor Controller
script the distance between two entities in the world can be calculated.
- `Robot`: The Robot is an entity that represents a robot in the world. It
might have sensors and other active components, like motors, etc. as child
entities. Also, one of its children is the Robot Controller. For example,
[epuck](https://cyberbotics.com/doc/guide/epuck) and
[TIAGo](https://cyberbotics.com/doc/guide/tiago-iron) are robots.
- `Robot Controller`: The Robot Controller is a python script which is
responsible for the Robot's movement and sensors. With the Robot Controller
it is possible to observe the world and act accordingly.
- `Environment`: The Environment is the interface as described by the OpenAI
gym. The Environment interface has the following methods:
- `get_observations()`: Return the observations of the robot. For example,
metrics from sensors, a camera image etc.
- step(action): Each timestep, the agent chooses an action, and the
environment returns the observation, the reward and the state of the
problem (done or not).
- `get_reward(action)`: The reward the agent receives as a result of their
action.
- `is_done()`: Whether it’s time to reset the environment. Most (but not all)
tasks are divided up into well-defined episodes, and done being True
indicates the episode has terminated. For example, if a robot has the task
to reach a goal, then the done condition might happen when the robot
"touches" the goal.
- `reset()`: Used to reset the world to the initial state.
In order to set up a task in Deepbots it is necessary to understand the
intention of the OpenAI gym environment. According to the OpenAI gym
documentation, the framework follows the classic “agent-environment loop”.
"Each timestep, the agent chooses an `action`, and the environment returns an
`observation` and a `reward`. The process gets started by calling `reset()`,
which returns an initial `observation`."

Deepbots follows this exact agent-environment loop with the only difference
being that the agent, which is responsible to choose an action, runs on the
Supervisor and the observations are acquired by the robot. The goal of the
deepbots framework is to hide this communication from the user, especially from
those who are familiar with the OpenAI gym environment. More specifically,
`SupervisorEnv` is the interface which is used by the Reinforcement Learning
algorithms and follows the OpenAI Gym environment logic. The Deepbots framework
provides different levels of abstraction according to the user's needs.
Moreover, a goal of the framework is to provide different wrappers for a wide
range of robots.
Deepbots also provides a default implementation of the `reset()` method,
leveraging Webots' built-in simulation reset functions, removing the need
for the user to implement reset procedures for simpler use-cases. It is
always possible to override this method and implement any custom reset
procedure, as needed.
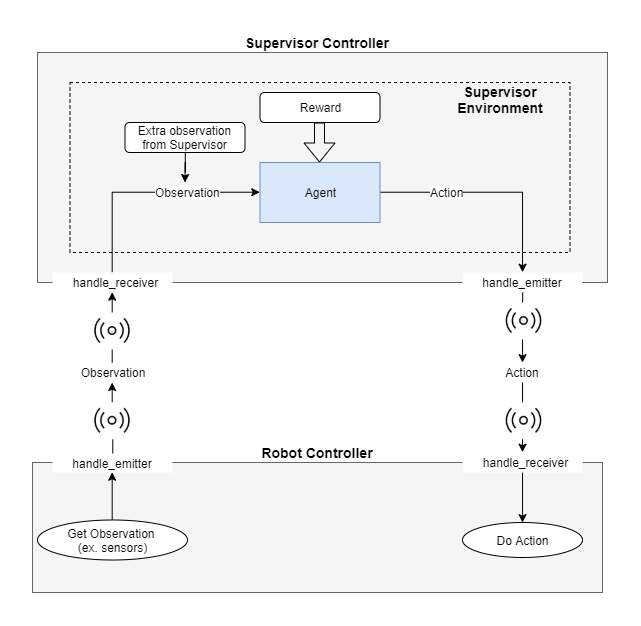
#### Emitter - receiver scheme
Currently, the communication between the `Supervisor` and the
`Robot` is achieved via an `emitter` and a `receiver`. Separating the `Supervisor`
from the `Robot`, deepbots can fit a variety of use-cases, e.g. multiple
`Robots` collecting experience and a `Supervisor` controlling them with a single
agent. The way Webots implements `emitter`/`receiver` communication requires messages
to be packed and unpacked, which introduces an overhead that becomes prohibiting in
use-cases where the observations are high-dimensional or long, such as camera images.
Deepbots provides another partially abstract class that combines the `Supervisor`
and the `Robot` into one controller and circumvents that issue, while being less
flexible, which is discussed [later](#combined-robot-supervisor-scheme).
On one hand, the `emitter` is an entity which is provided by Webots, that
broadcasts messages to the world. On the other hand, the `receiver` is an
entity that is used to receive messages from the `World`. Consequently, the
agent-environment loop is transformed accordingly. Firstly, the `Robot` uses its
sensors to retrieve the observation from the `World` and in turn uses the `emitter`
component to broadcast this observation. Secondly, the `Supervisor` receives the
observation via the `receiver` component and in turn, the agent uses it to choose
an action. It should be noted that the observation the agent uses might be
extended from the `Supervisor`. For example, a model might use LiDAR sensors
installed on the `Robot`, but also the Euclidean distance between the `Robot` and
an object. As it is expected, the `Robot` does not know the Euclidean distance,
only the `Supervisor` can calculate it, because it has access to all entities in
the `World`.
#### Combined Robot-Supervisor scheme
As mentioned earlier, in use-cases where the observation transmitted between
the `Robot` and the `Supervisor` is high-dimensional or long, e.g. high resolution
images taken from a camera, a significant overhead is introduced. This is circumvented
by inheriting and implementing the partially abstract `RobotSupervisor` that combines
the `Robot controller` and the `Supervisor Controller` into one, forgoing all
`emitter`/`receiver` communication. This new controller runs on the `Robot`, but
requires `Supervisor` privileges and is limited to one `Robot`, one `Supervisor`.
### Abstraction Levels
The deepbots framework has been created mostly for educational purposes. The
aim of the framework is to enable people to use Reinforcement Learning in
Webots. More specifically, we can consider deepbots as a wrapper of Webots
exposing an OpenAI gym style interface. For this reason there are multiple
levels of abstraction. For example, a user can choose if they want to use CSV
`emitter`/`receiver` or if they want to make an implementation from scratch.
In the top level of the abstraction hierarchy is the `SupervisorEnv` which is the
OpenAI gym interface. Below that level there are partially implemented classes
with common functionality. These implementations aim to hide the communication
between the `Supervisor` and the `Robot`, as described in the two different
schemes ealier. Similarly, in the `emitter`/`receiver` scheme the `Robot`
also has different abstraction levels. According to their needs, users can choose
either to process the messages received from the `Supervisor` themselves or
use the existing implementations.


