# openvino_notebooks
**Repository Path**: letsgomass/openvino_notebooks
## Basic Information
- **Project Name**: openvino_notebooks
- **Description**: 📚 A collection of Python notebooks for learning and experimenting with OpenVINO 👓
- **Primary Language**: Unknown
- **License**: Apache-2.0
- **Default Branch**: latest
- **Homepage**: None
- **GVP Project**: No
## Statistics
- **Stars**: 0
- **Forks**: 9
- **Created**: 2025-03-25
- **Last Updated**: 2025-03-27
## Categories & Tags
**Categories**: Uncategorized
**Tags**: None
## README
[English](README.md) | 简体中文 | [日本語](README_ja.md)
📚 OpenVINO™ Notebooks
[](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/blob/latest/LICENSE)
[](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/actions/workflows/treon_precommit.yml?query=event%3Apush)
[](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/actions/workflows/docker.yml?query=event%3Apush)
在这里,我们提供了一些可以运行的Jupyter* notebooks,用于学习和尝试使用OpenVINO™开发套件。这些notebooks旨在向各位开发者提供OpenVINO基础知识的介绍,并教会大家如何利用我们的API来优化深度学习推理。
🚀 您可以通过查看以下交互式的页面,对OpenVINO™ Notebooks的内容进行快速导览:
[OpenVINO™ Notebooks at GitHub Pages](https://openvinotoolkit.github.io/openvino_notebooks/)
[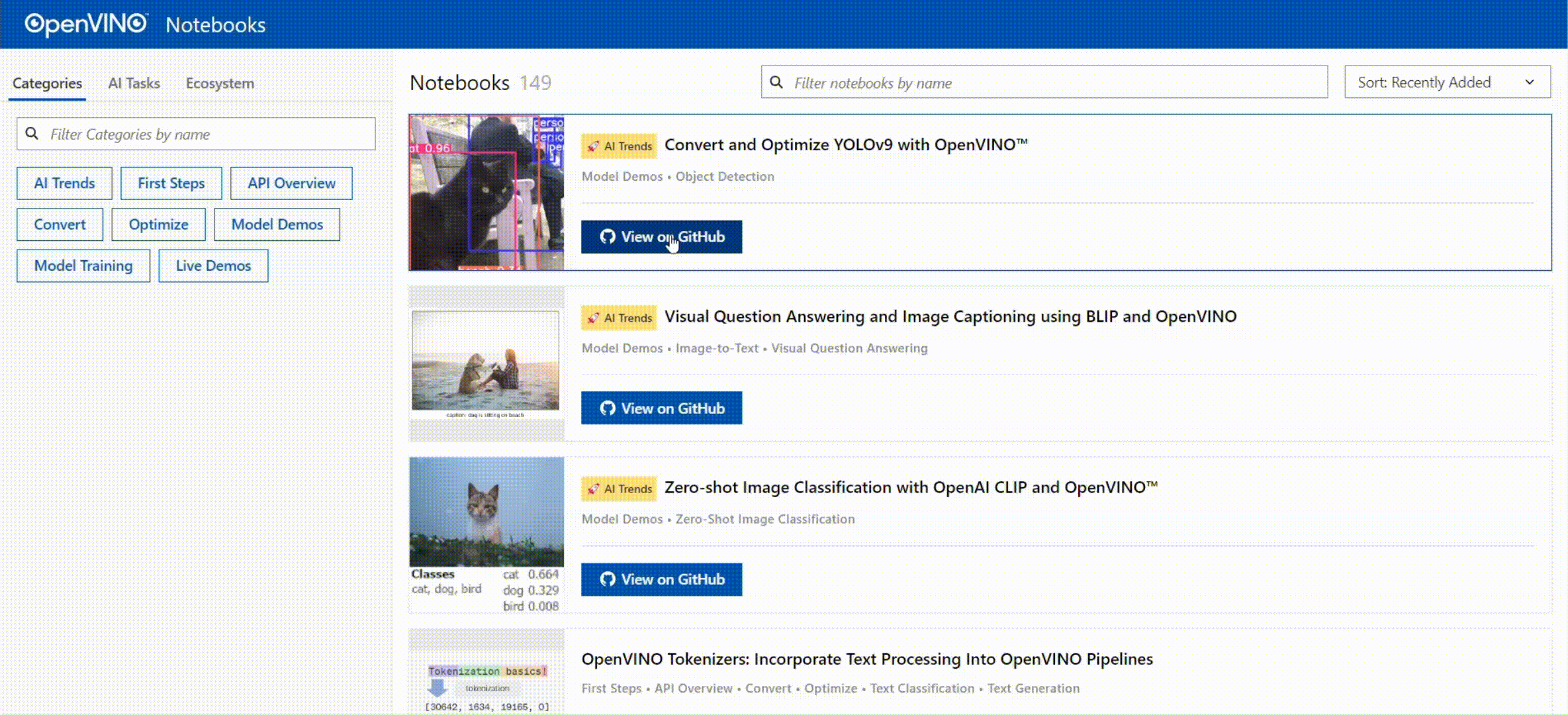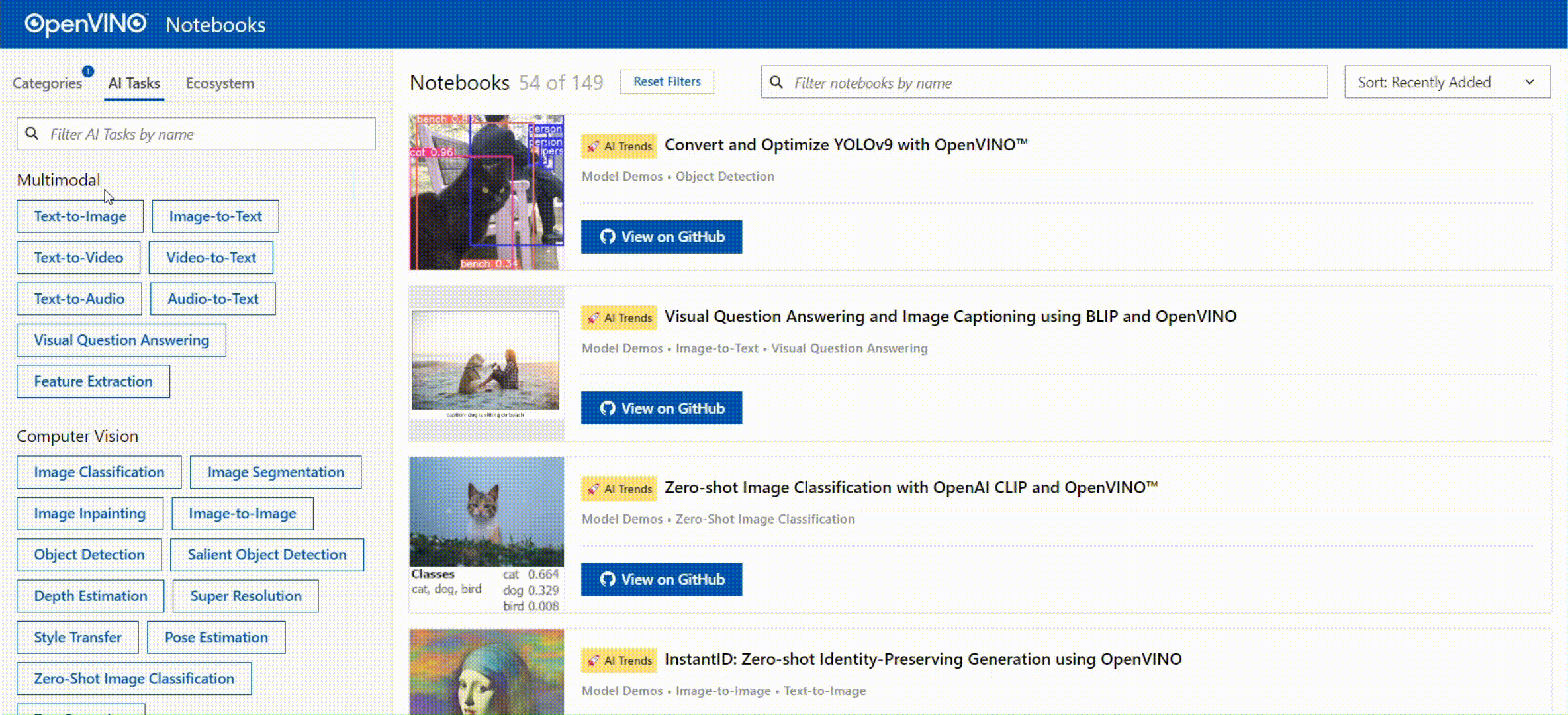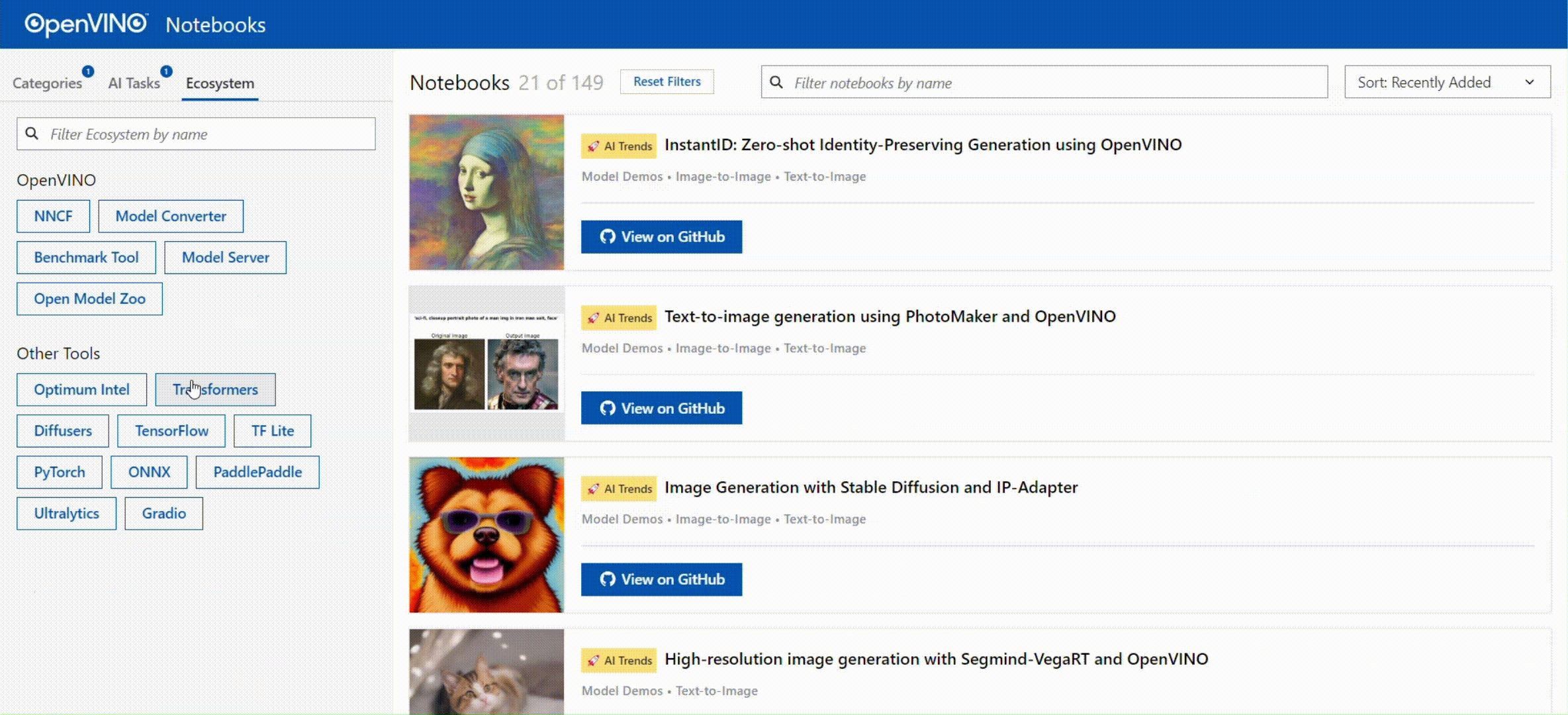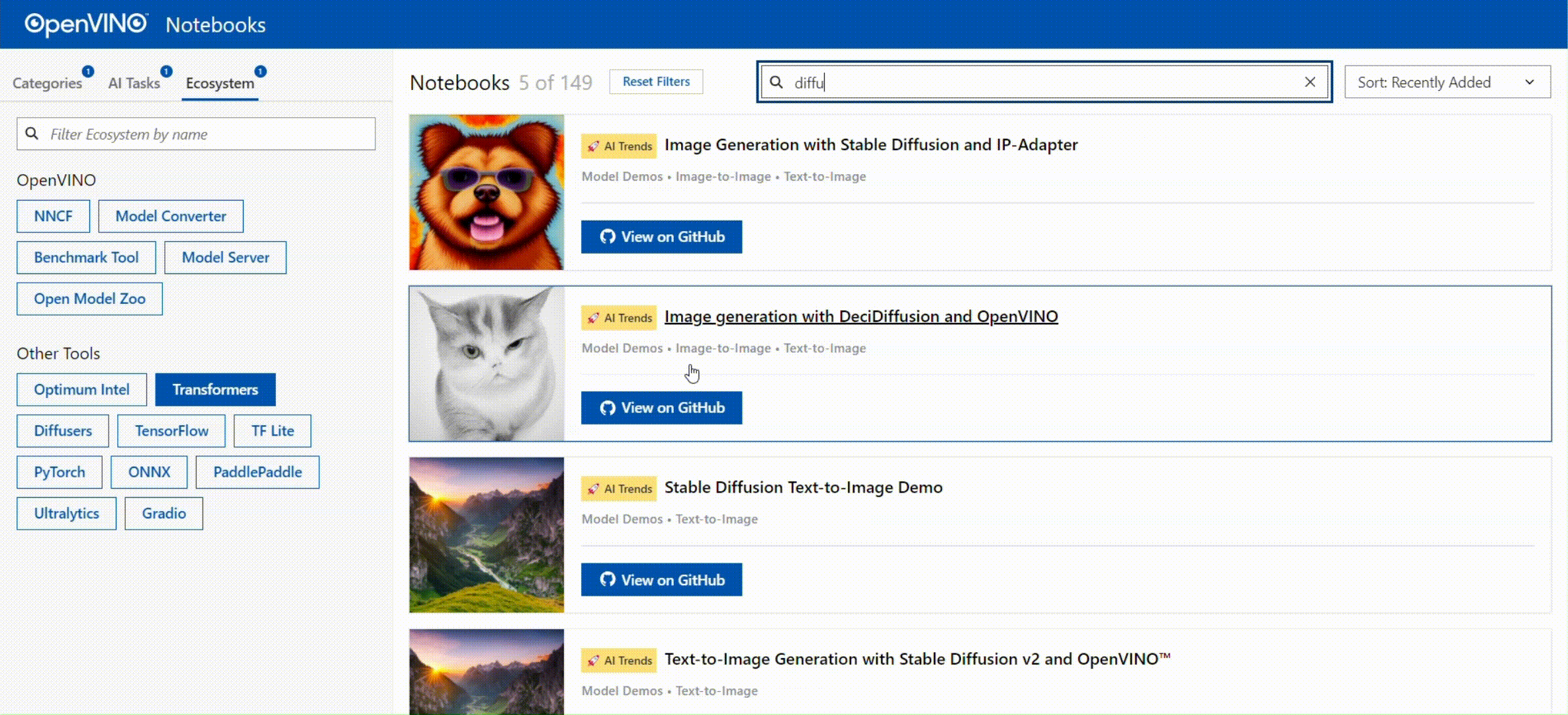](https://openvinotoolkit.github.io/openvino_notebooks/)
[]()
## 目录
- [目录](#目录)
- [📝 安装指南](#-安装指南)
- [🚀 开始](#-开始)
- [⚙️ 系统要求](#️-系统要求)
- [💻 运行Notebooks](#-运行notebooks)
- [启动单个Notebook](#启动单个notebook)
- [启动所有Notebooks](#启动所有notebooks)
- [🧹 清理](#-清理)
- [⚠️ 故障排除](#️-故障排除)
- [🧑💻 贡献者](#-贡献者)
- [❓ 常见问题解答](#-常见问题解答)
[]()
## 📝 安装指南
OpenVINO™ Notebooks需要预装Python和Git, 针对不同操作系统的安装参考以下英语指南:
| [Windows](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/wiki/Windows) | [Ubuntu](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/wiki/Ubuntu) | [macOS](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/wiki/macOS) | [Red Hat](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/wiki/Red-Hat-and-CentOS) | [CentOS](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/wiki/Red-Hat-and-CentOS) | [Azure ML](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/wiki/AzureML) | [Docker](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/wiki/Docker) | [Amazon SageMaker](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/wiki/SageMaker)|
| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | --------------------------------------------------------------------------- |--------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
[]()
## 🚀 开始
使用这个 [页面](https://openvinotoolkit.github.io/openvino_notebooks/)来探索notebooks, 选择一个跟你需求相关的开始试试吧。祝你好运!
**注意: 这个仓库的main分支已经升级了对于OpenVINO 2025.0 release的支持.** 请运行在你的 `openvino_env`虚拟环境中,运行 `pip install --upgrade -r requirements.txt` 升级到最新版本. 如果这是您第一次安装OpenVINO™ Notebooks,请参考以下的 [安装指南](#-installation-guide)。 如果您想使用上一个OpenVINO版本, 请切换至[2023.3 分支](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/tree/2023.3). 如果您想使用上一个长期维护 (LTS) 的OpenVINO版本,请切换到 [2022.3 分支](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/tree/2022.3)。
如果您有任何问题,可以开启一个 GitHub [讨论](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/discussions)。
如果你遇到了问题,请查看[故障排除](#-troubleshooting), [常见问题解答](#-faq) 或者创建一个GitHub [讨论](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/discussions)。
带有 和[colab 标签](https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg) 按键的Notebooks可以在无需安装的情况下运行。[Binder](https://mybinder.org/) 和[Google Colab](https://colab.research.google.com/)是基于有限资源的免费在线服务。 如果享有获得最佳性能体验,请遵循[安装指南](#-installation-guide)在本地运行Notebooks。
[]()
## ⚙️ 系统要求
这些notebooks可以运行在任何地方,包括你的笔记本电脑,云VM,或者一个Docker容器。下表列出了所支持的操作系统和Python版本。
| 支持的操作系统 | [Python Version (64-bit)](https://www.python.org/) |
| :--------------------------------------------------------- |:---------------------------------------------------|
| Ubuntu 20.04 LTS, 64-bit | 3.9 - 3.12 |
| Ubuntu 22.04 LTS, 64-bit | 3.9 - 3.12 |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8, 64-bit | 3.9 - 3.12 |
| CentOS 7, 64-bit | 3.9 - 3.12 |
| macOS 10.15.x versions or higher | 3.9 - 3.12 |
| Windows 10, 64-bit Pro, Enterprise or Education editions | 3.9 - 3.12 |
| Windows Server 2016 or higher | 3.9 - 3.12 |
[](#)
## 💻 运行Notebooks
### 启动单个Notebook
如果你希望启动单个的notebook(如:Monodepth notebook),运行以下命令:
```bash
jupyter vision-monodepth.ipynb
```
### 启动所有Notebooks
```bash
jupyter lab notebooks
```
在浏览器中,从Jupyter Lab侧边栏的文件浏览器中选择一个notebook文件,每个notebook文件都位于`notebooks` 目录中的子目录中。
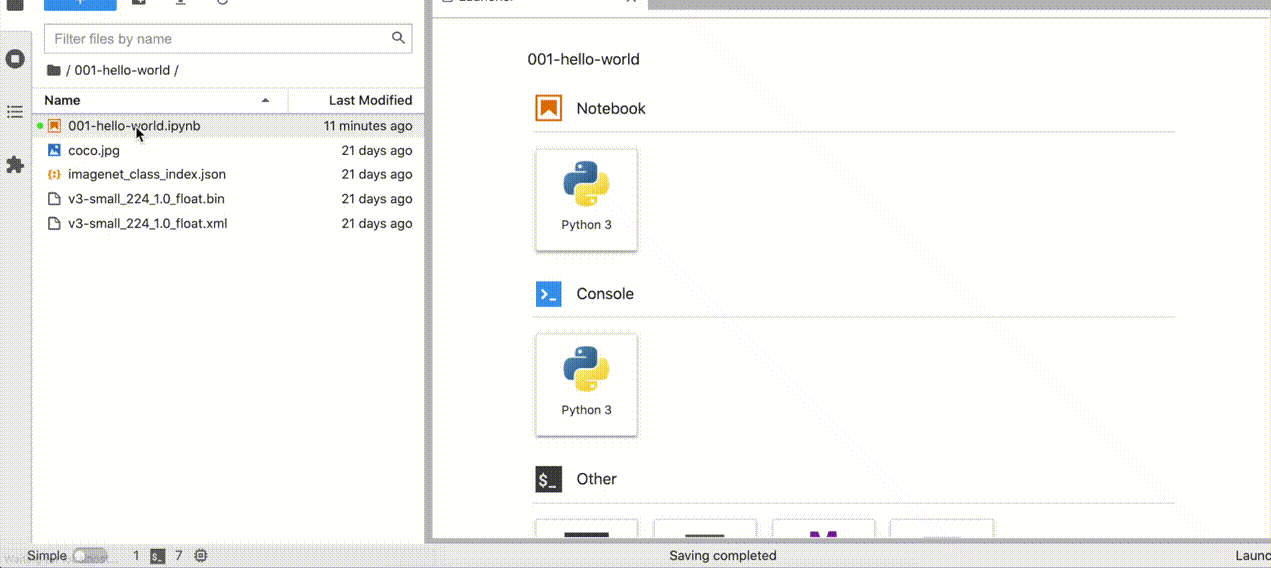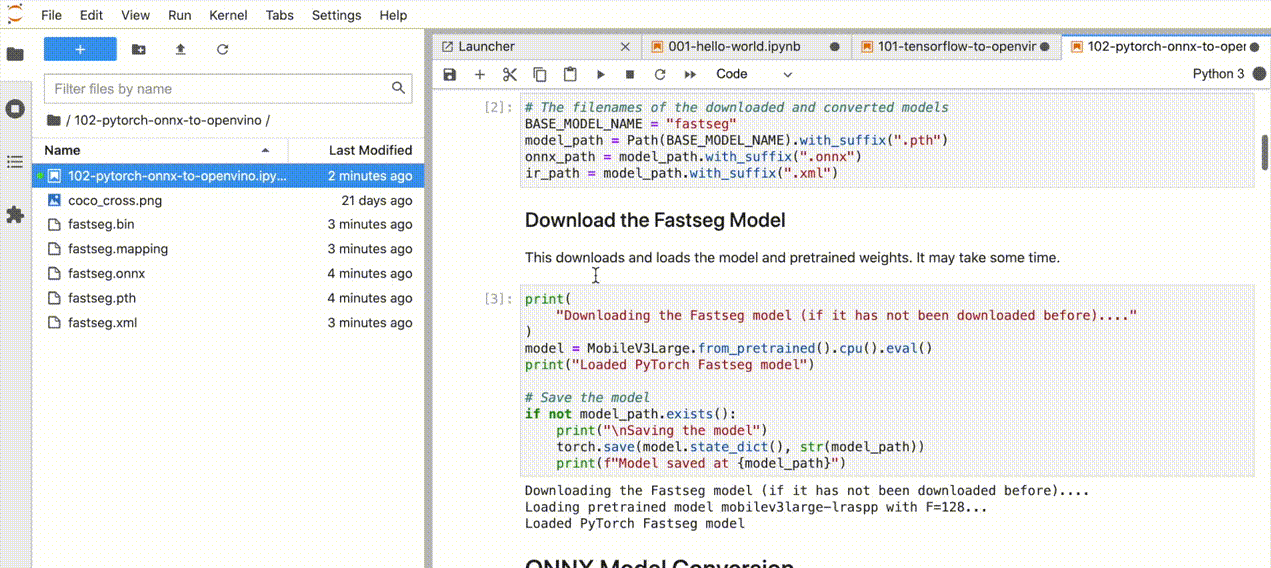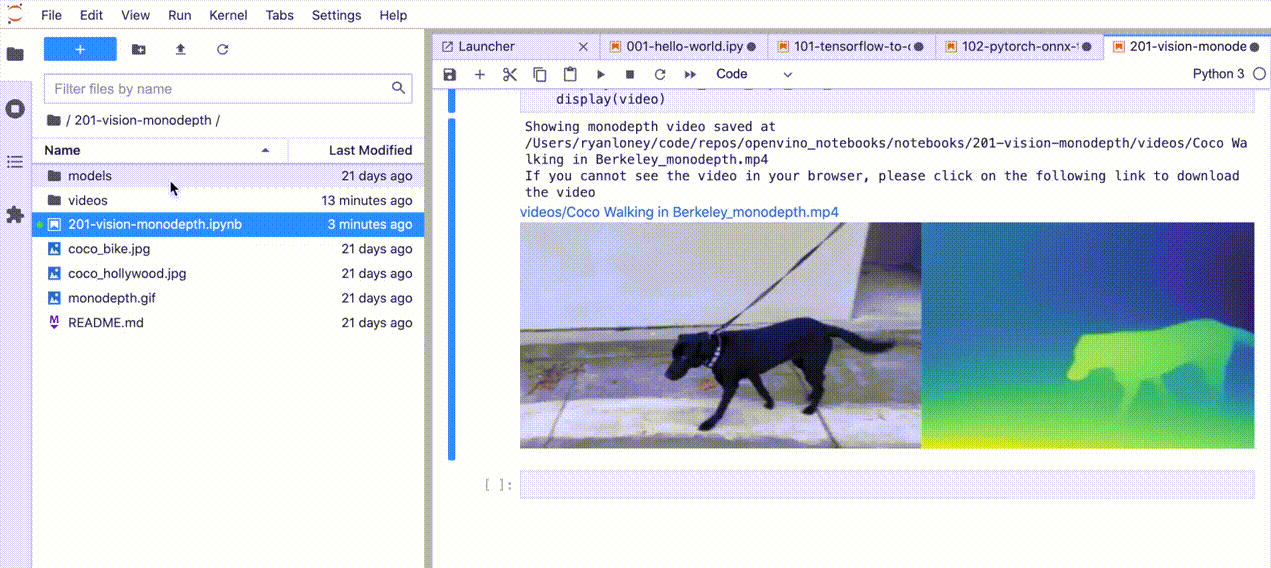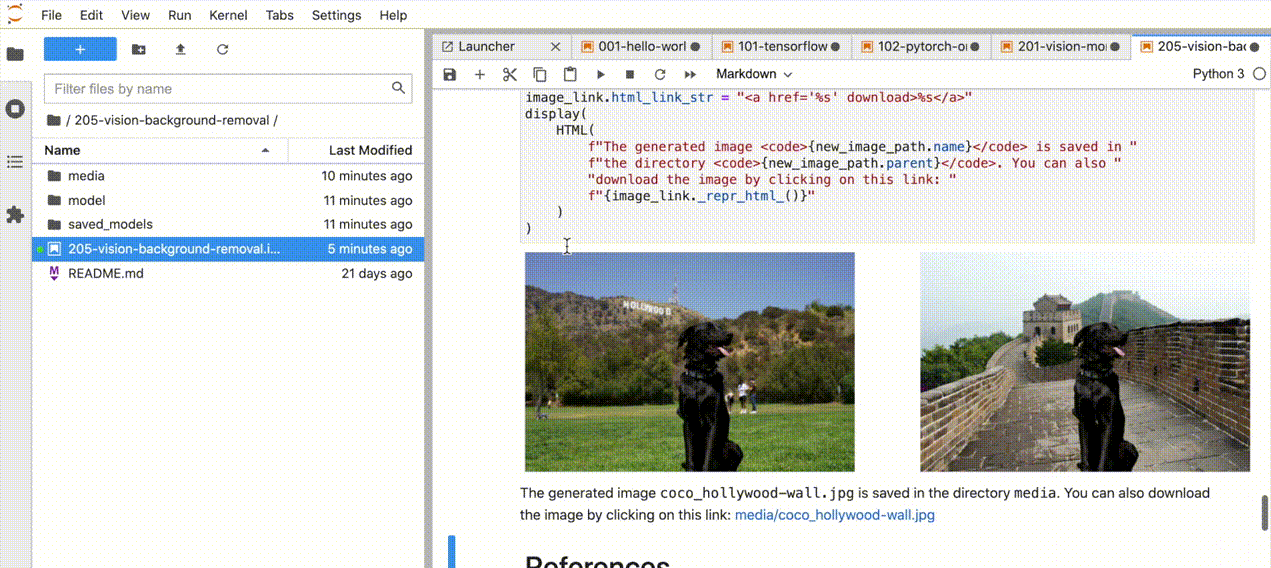 []()
## 🧹 清理
[]()
## 🧹 清理
1. 停止Jupyter Kernel
按 `Ctrl-c`结束 Jupyter session,会弹出一个提示框 `Shutdown this Jupyter server (y/[n])?`,您可以输入 `y` and 敲击 `Enter`回车。
2. 注销虚拟环境
注销虚拟环境:只需在激活了`openvino_env`的终端窗口中运行 `deactivate`即可。
重新激活环境:在Linux上运行 `source openvino_env/bin/activate` 或者在Windows上运行 `openvino_env\Scripts\activate` 即可,然后输入 `jupyter lab` 或 `jupyter notebook` 即可重新运行notebooks。
3. 删除虚拟环境 _(可选)_
直接删除 `openvino_env` 目录即可删除虚拟环境:
- On Linux and macOS:
```bash
rm -rf openvino_env
```
- On Windows:
```bash
rmdir /s openvino_env
```
- 从Jupyter中删除 `openvino_env` Kernel
```bash
jupyter kernelspec remove openvino_env
```
[]()
## ⚠️ 故障排除
如果以下方法无法解决您的问题,欢迎创建一个[讨论主题](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/discussions)
或[issue](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/issues)!
- 运行 `python check_install.py` 可以帮助检查一些常见的安装问题,该脚本位于openvino_notebooks 目录中。
记得运行该脚本之前先激活 `openvino_env` 虚拟环境。
- 如果出现 `ImportError` ,请检查是否安装了 Jupyter Kernel。如需手动设置kernel,从 Jupyter Lab 或 Jupyter Notebook 的_Kernel->Change Kernel_菜单中选择`openvino_env`内核。
- 如果OpenVINO是全局安装的,不要在执行了`setupvars.bat`或`setupvars.sh`的终端中运行安装命令。
- 对于Windows系统,我们建议使用_Command Prompt (`cmd.exe`),而不是_PowerShell。
[](#-contributors)
## 🧑💻 贡献者
 使用 [contributors-img](https://contrib.rocks)制作。
[]()
## ❓ 常见问题解答
* [OpenVINO支持哪些设备?](https://docs.openvino.ai/2024/openvino-workflow/running-inference/inference-devices-and-modes.html)
* [OpenVINO支持的第一代CPU是什么?](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/developer/tools/openvino-toolkit/system-requirements.html)
* [在使用OpenVINO部署现实世界解决方案方面有没有成功的案例?](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/internet-of-things/ai-in-production/success-stories.html)
---
\*其他名称和品牌可能被视为他人的财产。
使用 [contributors-img](https://contrib.rocks)制作。
[]()
## ❓ 常见问题解答
* [OpenVINO支持哪些设备?](https://docs.openvino.ai/2024/openvino-workflow/running-inference/inference-devices-and-modes.html)
* [OpenVINO支持的第一代CPU是什么?](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/developer/tools/openvino-toolkit/system-requirements.html)
* [在使用OpenVINO部署现实世界解决方案方面有没有成功的案例?](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/internet-of-things/ai-in-production/success-stories.html)
---
\*其他名称和品牌可能被视为他人的财产。

 []()
## 🧹 清理
[]()
## 🧹 清理
