From 92a779ff2a7fa566ec394d1c0e31b5ca9c00d801 Mon Sep 17 00:00:00 2001
From: cuiyangyang <14501257+cuiyangyang0729@user.noreply.gitee.com>
Date: Sun, 4 Jan 2026 02:09:23 +0000
Subject: [PATCH] add rt-thread-version/rt-thread-standard/tutorial/make-bsp.
Signed-off-by: cuiyangyang <14501257+cuiyangyang0729@user.noreply.gitee.com>
---
.../tutorial/make-bsp/MCX-A346 | 3219 +++++++++++++++++
1 file changed, 3219 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 rt-thread-version/rt-thread-standard/tutorial/make-bsp/MCX-A346
diff --git a/rt-thread-version/rt-thread-standard/tutorial/make-bsp/MCX-A346 b/rt-thread-version/rt-thread-standard/tutorial/make-bsp/MCX-A346
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..26a5eab
--- /dev/null
+++ b/rt-thread-version/rt-thread-standard/tutorial/make-bsp/MCX-A346
@@ -0,0 +1,3219 @@
+| **目录** | 作者 |
+| --- | :---: |
+| **零、实践指南说明** | **RT-Thread & ****NXP** |
+| **一、MCXA346上的UART实践** | 朱帅坤 |
+| **二、MCXA346上的GPIO实践** | 魏宁 |
+| **三、MCXA346上的RTC实践** | 黄子阳 |
+| **四、MCXA346上的ADC实践** | 柯九 |
+| **五、MCXA346上的HWTimer实践** | 张国庆 |
+| **六、MCXA346上的SPI实践** | 戴凌祥 |
+| | 吴长杰 |
+| **七、MCXA346上的PWM实践** | 陈子弈 |
+| **八、MCXA346上的 IIC(硬件) 实践** | 李金磊 |
+| | 王丰 |
+| **九、MCXA346上的CAN实践** | 吴艺彬 |
+| **FAQ** | **RT-Thread & ****NXP** |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# 零、实践指南说明
+## 硬件介绍
+1.开发板描述:
+
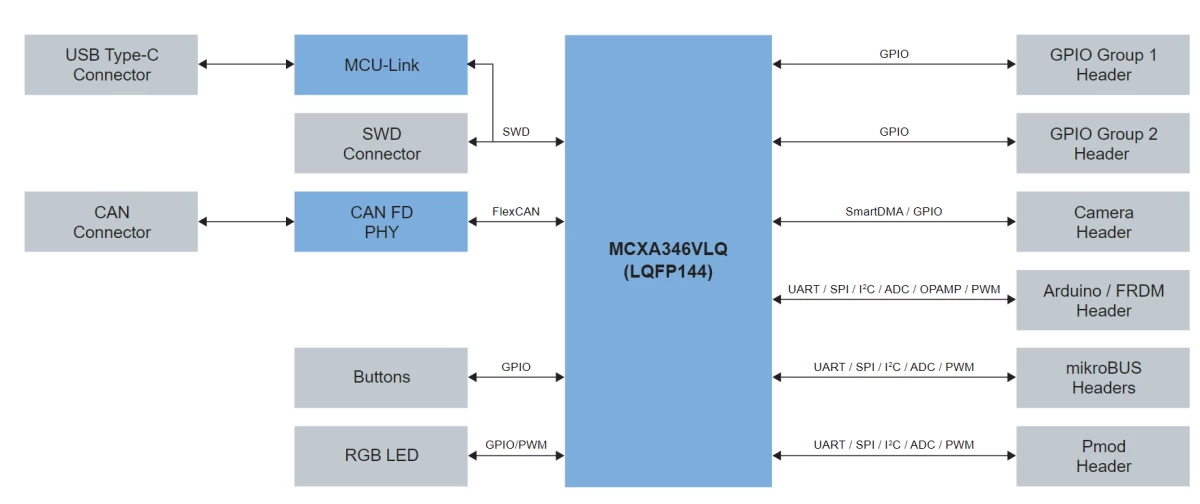
+FRDM-MCXA346是一款紧凑且可扩展的开发板,可让您快速基于FRDM-MCXA346微控制器单元(MCU)开展原型设计。它们提供行业标准的接口,可轻松访问MCU的I/O,配备集成的开放标准串行接口、外部闪存和板载MCU-Link调试器。
+
+2.开发板外观如下图所示:
+
+
+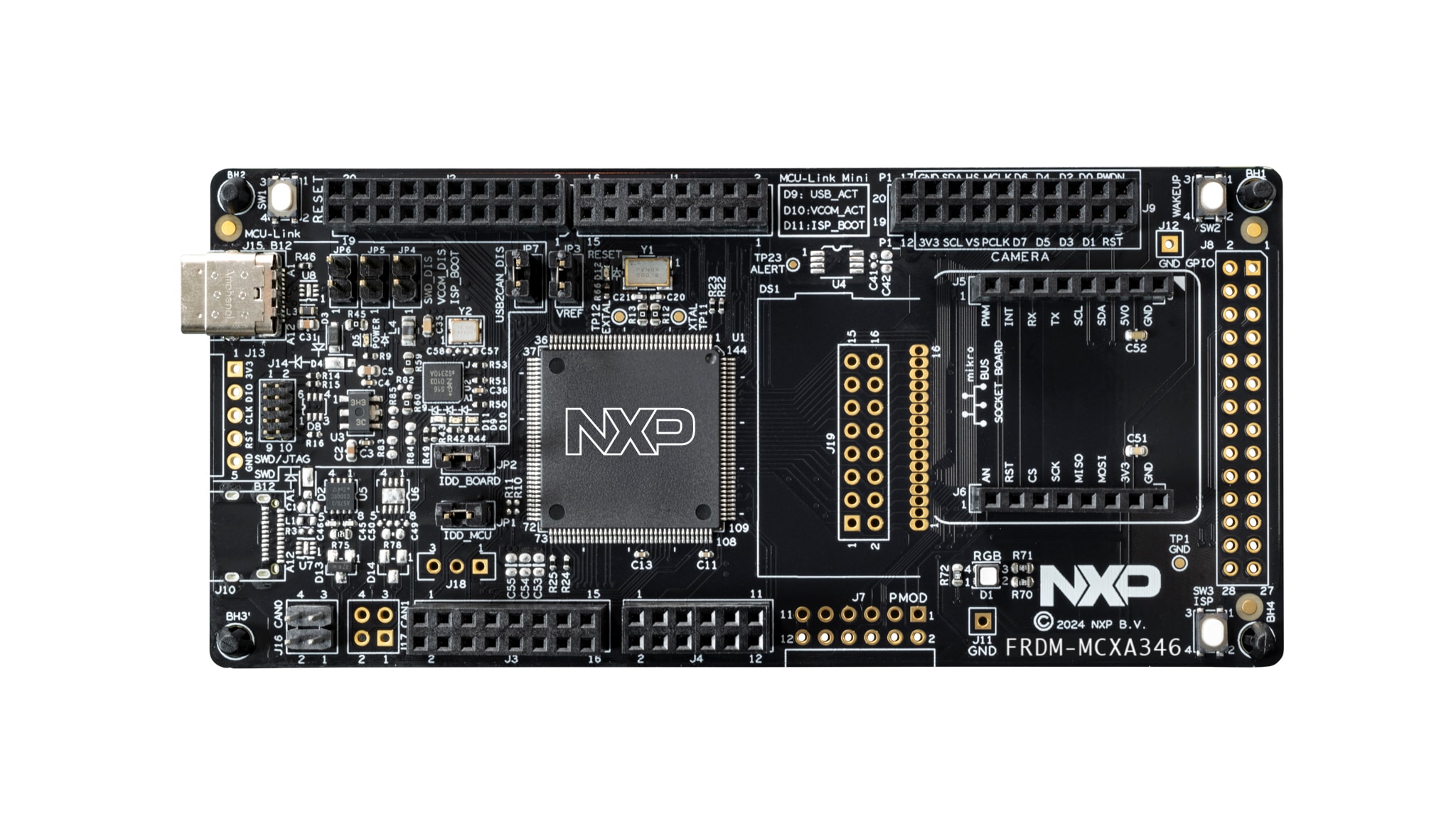3.该开发板常用 **板载资源** 如下:
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+4.特性
+
+
+
+微控制器
+
++ MCX A346 Arm® Cortex®-M33内核,运行频率高达180MHz
++ 高达1MB的闪存,高达256KB的RAM,带8KB的纠错码(ECC),支持乘法累加单元(MAU)和SmartDMA、控制器局域网灵活数据速率(CAN-FD)、低功耗通用异步收发器(LPUART)、低功耗串行外设接口(LPSPI)、低功耗内部集成电路(LPI2C)、DMA和低压差稳压器(LDO)
+
+连接
+
++ 高速通用串行总线(HS USB) Type-C连接器(板载MCU-Link调试器)
++ 控制器局域网(CAN)/I3C/串行外设接口(SPI)/I²C/UART连接器(Arduino,外设模块(PMOD)/微控制器总线(mikroBUS),未安装(DNP))
++ Wi-Fi连接器(Arduino,外设模块(PMOD)/微控制器总线(mikroBUS),未安装(DNP))
++ 摄像头连接器(SmartDMA)
+
+调试器
+
++ 板载MCU-Link调试器,带有CMSIS-DAP
++ JTAG/SWD/SWD连接器
+
+扩展选项
+
++ Arduino®接头
++ FRDM接头
++ Pmod™ *DNP
++ mikroBUS™
++ SmartDMA/摄像头接头
++ 通用输入/输出1 (GPIO1)接头
++ 通用输入/输出2 (GPIO2)接头
+
+用户接口
+
++ RGB用户LED
++ 复位按钮
++ 在系统编程(ISP)按钮
++ 唤醒按钮
+
+
+
+
+
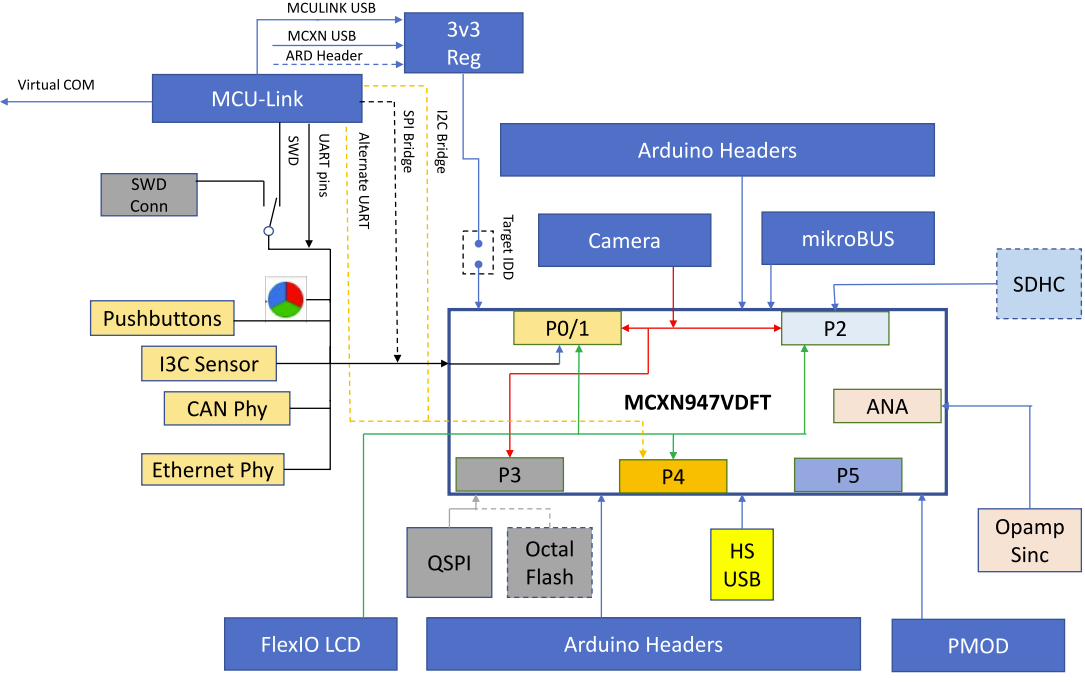
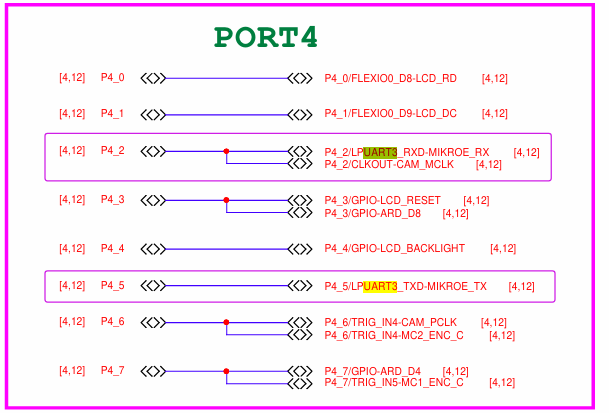
+# 一、MCXA346上的UART实践【朱帅坤】
+## NXP FRDM-MCXA346 通过串口使用esp8266
+### 1. LPUART 模块特点(MCXA346)
+MCXA346 集成 多达 4 个 LPUART(具体数量根据封装型号不同)。
+
+LPUART 主要特性:
+
++ 支持标准 UART:8/9/10 bit 数据位
++ 支持奇/偶/无校验
++ 支持 1 或 2 stop bits
++ 支持 DMA 发送/接收
++ 支持 中断模式 Rx/Tx
++ 支持 硬件流控 RTS/CTS(部分通道)
++ 支持可编程波特率(内部时钟、外部时钟都可)
++ 帧格式灵活配置
++ FIFO 缓冲(RX/TX FIFO 深度可配置)
++ LPUART 是 NXP Kinetis → i.MX RT → MCX 系列统一外设,代码在不同产品间可复用。
+
+### 1.硬件介绍
+##
+
+port连接mcu和mikro bus
+
+
+
+
+mikro_bus
+
+
+
+
+### 2.软件介绍
+#### (1) 初始化
+在pin_mux.c中添加串口3的初始化函数
+
+```c
+/* ------------------ UART3 TX (PORT4_5) ------------------ */
+const port_pin_config_t uart3_tx_config = {
+.pullSelect = kPORT_PullUp, /* 内部上拉 */
+.pullValueSelect = kPORT_LowPullResistor, /* 低阻上拉 */
+.slewRate = kPORT_FastSlewRate, /* 快速上升沿 */
+.passiveFilterEnable = kPORT_PassiveFilterDisable,
+.openDrainEnable = kPORT_OpenDrainDisable,
+.driveStrength = kPORT_LowDriveStrength,
+.driveStrength1 = kPORT_NormalDriveStrength,
+.mux = kPORT_MuxAlt3, /* UART3_TX 对应 ALT3 */
+.inputBuffer = kPORT_InputBufferEnable,
+.invertInput = kPORT_InputNormal,
+.lockRegister = kPORT_UnlockRegister};
+/* PORT4_5 is configured as LPUART3_TX */
+PORT_SetPinConfig(PORT4, 5U, &uart3_tx_config);
+/* ------------------ UART3 RX (PORT4_2) ------------------ */
+const port_pin_config_t uart3_rx_config = {
+.pullSelect = kPORT_PullUp,
+.pullValueSelect = kPORT_LowPullResistor,
+.slewRate = kPORT_FastSlewRate,
+.passiveFilterEnable = kPORT_PassiveFilterDisable,
+.openDrainEnable = kPORT_OpenDrainDisable,
+.driveStrength = kPORT_LowDriveStrength,
+.driveStrength1 = kPORT_NormalDriveStrength,
+.mux = kPORT_MuxAlt3, /* UART3_RX 对应 ALT3 */
+.inputBuffer = kPORT_InputBufferEnable,
+.invertInput = kPORT_InputNormal,
+.lockRegister = kPORT_UnlockRegister};
+/* PORT4_2 is configured as LPUART3_RX */
+PORT_SetPinConfig(PORT4, 2U, &uart3_rx_config);
+```
+
+在drv_uart.c中添加uart3 根据uart2 赋值粘贴
+
+```c
+#if defined(BSP_USING_UART3)
+struct rt_serial_device serial3;
+void LPUART3_IRQHandler(void)
+{
+ uart_isr(&serial3);
+}
+#endif
+#ifdef BSP_USING_UART3
+ {
+ &serial3,
+ LPUART3,
+ LPUART3_IRQn,
+ kCLOCK_Fro12M,
+#if (defined(CPU_MCXA346VLH) || defined(CPU_MCXA346VLL) || defined(CPU_MCXA346VLQ) || defined(CPU_MCXA346VPN))
+ kFRO_LF_DIV_to_LPUART3,
+#else
+ kFRO12M_to_LPUART3,
+#endif
+ kCLOCK_GateLPUART3,
+ kCLOCK_DivLPUART3,
+ "uart3",
+ },
+```
+
+在app中添加uart3测试代码
+
+```c
+#include
+#define TX_UART_NAME "uart3"
+static rt_device_t tx_serial = RT_NULL;
+/* 发送任务入口函数 */
+static void serial_tx_thread(void *parameter)
+{
+ char msg[] = "hello RT-Thread!\r\n";
+ while (1)
+ {
+ rt_device_write(tx_serial, 0, msg, sizeof(msg) - 1);
+ rt_thread_mdelay(500); /* 每 500ms 发一次 */
+ }
+}
+/* 初始化函数,在系统启动完成后自动运行 */
+int uart3_tx_init(void)
+{
+ /* 查找 uart3 设备 */
+ tx_serial = rt_device_find(TX_UART_NAME);
+ if (tx_serial == RT_NULL)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("Cannot find %s device!\n", TX_UART_NAME);
+ return -1;
+ }
+ /* 打开设备(仅发送,不需要接收) */
+ rt_device_open(tx_serial, RT_DEVICE_FLAG_WRONLY);
+ /* 创建线程 */
+ rt_thread_t tid = rt_thread_create(
+ "uart3_tx", /* 线程名 */
+ serial_tx_thread, /* 入口函数 */
+ RT_NULL, /* 参数 */
+ 1024, /* 栈大小 */
+ 20, /* 优先级 */
+ 10 /* 时间片 */
+ );
+ if (tid != RT_NULL)
+ rt_thread_startup(tid);
+ else
+ rt_kprintf("Create uart3_tx thread failed!\n");
+ return 0;
+}
+//INIT_APP_EXPORT(uart3_tx_init);
+/* 导出到 msh 命令列表中 */
+MSH_CMD_EXPORT(uart3_tx_init, uart3 device test);
+```
+
+#### (2) 添加AT功能
+AT 客户端,参考官方文档:
+
+[https://www.rt-thread.org/document/site/#/rt-thread-version/rt-thread-standard/application-note/components/at/an0014-at-client](https://www.rt-thread.org/document/site/#/rt-thread-version/rt-thread-standard/application-note/components/at/an0014-at-client)
+
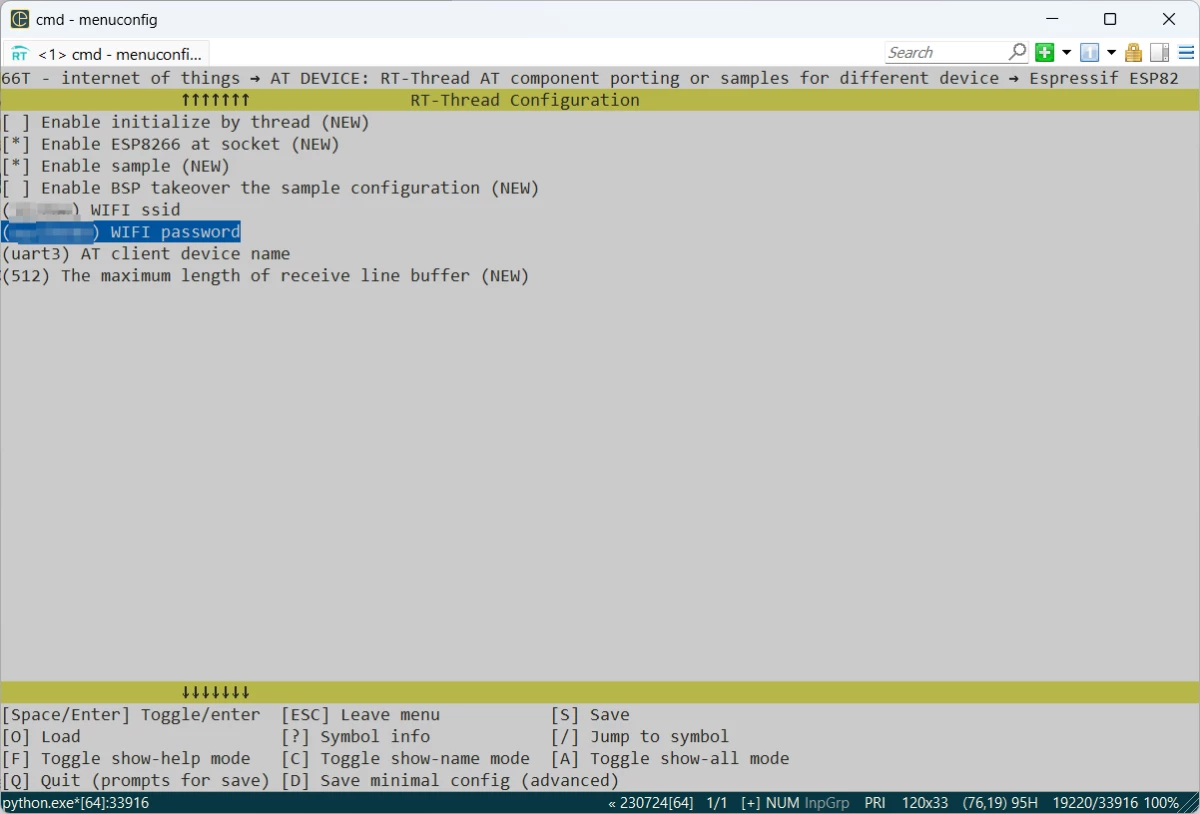
+开启 AT Client 功能:RT-Thread Components —-> Network —-> AT commands —> 开启 AT DEBUG,开启 AT Client 支持,目前 AT Client 支持多连接功能,后面需要手动初始化 AT Client。
+
+
+
+
+RT-Thread online packages —-> IoT - internet of things —-> AT Device配置开启 AT DEVICE 软件包支持
+
+
+
+
+### 3.实验效果
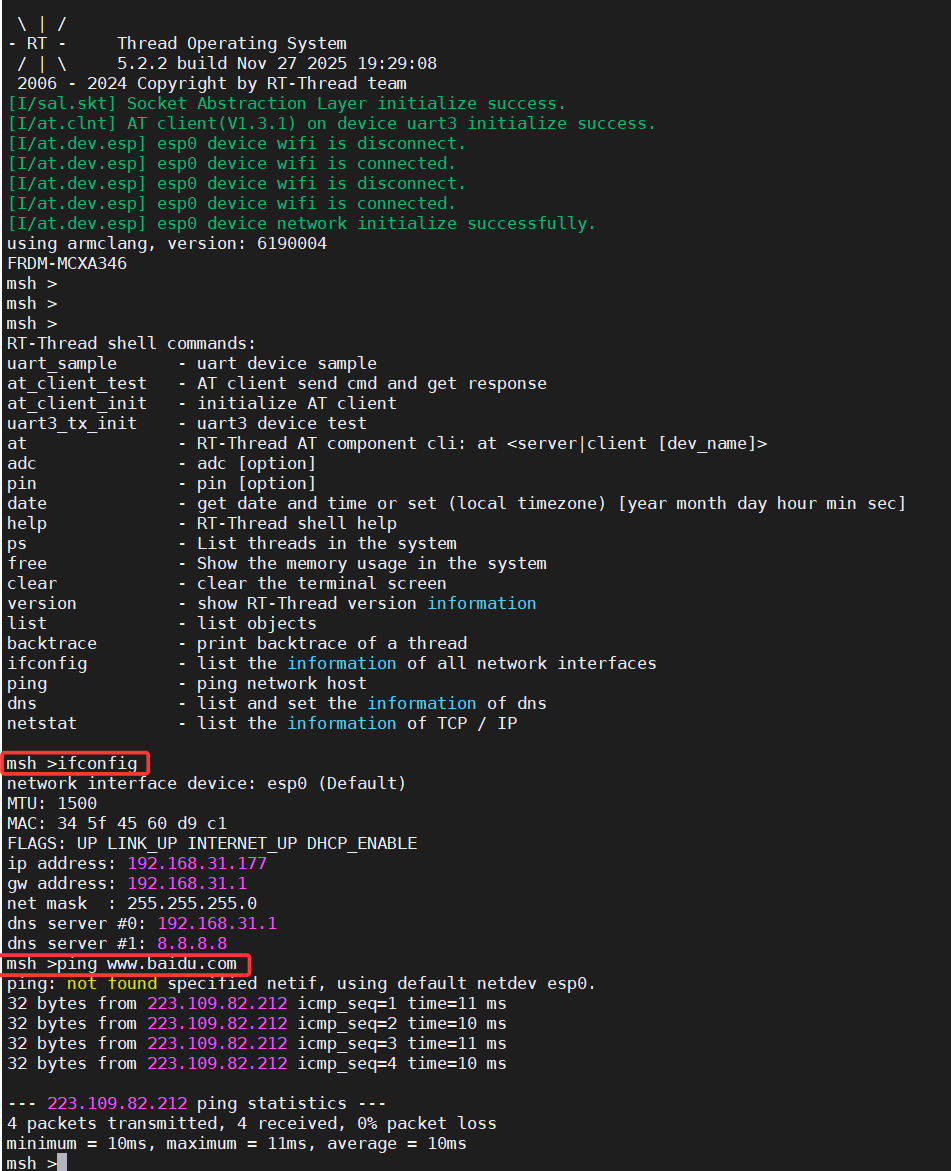
+通过串口连接esp8266,可以使用at_device来驱动,
+
+
+
+
+# 二、MCXA346上的GPIO实践【魏宁】
+## RT-Thread 基于 NXP FDRM-MCXA346 的GPIO功能实践指南
+
+
+### 1.睿赛德官方提供的基础教程
+```c
+FRDM-MCXA346是一款紧凑且可扩展的开发板,可让您快速基于FRDM-MCXA346微控制器单元(MCU)开展原型设计。它们提供行业标准的接口,可轻松访问MCU的I/O,配备集成的开放标准串行接口、外部闪存和板载MCU-Link调试器。NXP FRDM-MCXA346 上手指南:https://www.rt-thread.org/document/site/#/rt-thread-version/rt-thread-standard/tutorial/quick-start/frdm_mcxa346/quick-start
+```
+
+### 2.官方提供的教程中的部分细则
+[https://github.com/RT-Thread/rt-thread](https://github.com/RT-Thread/rt-thread) 到GitHub官网下载最新的源码
+
+rt-thread\bsp\nxp\mcxa\frdm-mcxa346 根据路径找到我们需要的源码
+
+到睿赛德开源网站找到Env工具,帮助我们得到完整代码
+
+
+
+
+第一次使用可以去官网查看使用教程:[https://www.rt-thread.org/document/site/#/rt-thread-version/rt-thread-standard/application-note/setup/standard-project/an0017-standard-project](https://www.rt-thread.org/document/site/#/rt-thread-version/rt-thread-standard/application-note/setup/standard-project/an0017-standard-project)
+
+第一次运行会让我们更新python环境,一定要更新,要不然会编译失败
+
+
+
+
+编译成功后,我们得到完整可执行文件
+
+
+### 3.GPIO部分的测试
+主要特性
+
+目标MCU: NXP MCX A346 (MCXA346VLQ),基于 Arm Cortex-M33 内核,最高运行频率 180 MHz
+
+调试接口: 板载 MCU-Link 调试探针,基于 LPC55S16 MCU
+
+通信接口:
+
+FlexCAN 接口:支持高速 CAN FD 收发器
+
+LPUART 接口:支持多个 UART 连接
+
+LPSPI 接口:支持 SPI 通信
+
+LPI2C 接口:支持 I2C 通信
+
+摄像头接口:支持基于 SmartDMA 的并行摄像头接口
+
+模拟功能:
+
+4个 16位 ADC 模块 (ADC0-ADC3)
+
+4个运算放大器模块 (OPAMP0-OPAMP3)
+
+扩展接口:
+
+Arduino 插座:4个连接器 (J1-J4)
+
+mikroBUS 插座:2个连接器 (J5-J6)
+
+Pmod 连接器:J7 (可选)
+
+GPIO 扩展连接器
+
+电源供电:
+
+通过 USB Type-C 连接器 J15 提供 5V 电源
+
+通过 CAN0 连接器 J16 提供 5V 电源(默认选项)
+
+支持 5-9V 外部电源输入
+
+时钟:
+
+MCX A346 MCU:8 MHz 时钟
+
+LPC55S16 MCU:16 MHz 时钟
+
+指示灯:
+
+电源指示灯 (绿色)
+
+复位指示灯 (红色)
+
+RGB LED (用户可控)
+
+MCU-Link 状态指示灯
+
+按键:
+
+复位按键 (SW1)
+
+唤醒按键 (SW2)
+
+ISP 按键 (SW3)
+
+该开发板常用 板载资源 如下:
+
+
+
+
+官方例程:
+
+
+
+
+官方例程视频演示:
+
+[https://t.bilibili.com/1146883652477517842?share_source=pc_native](https://t.bilibili.com/1146883652477517842?share_source=pc_native)
+
+GPIO和中断 测试演示:
+
+[https://t.bilibili.com/1146883828583759889?share_source=pc_native](https://t.bilibili.com/1146883828583759889?share_source=pc_native)
+
+
+
+### 4.GPIO和中断测试代码
+Gitee代码:[https://gitee.com/uraniumer/rtt/tree/master/](https://gitee.com/uraniumer/rtt/tree/master/)
+
+# 三、MCXA346上的RTC实践【黄子阳】
+
+
+## RT-Thread 基于 NXP FDRM-MCXA346 的软件 RTC 与 Alarm 功能实践指南
+## 一、前言
+在嵌入式开发中,RTC(Real-Time Clock,实时时钟) 是专门用于追踪、记录和输出 “实际时间”(年、月、日、时、分、秒,甚至毫秒、星期)的硬件模块或外设,其核心价值是让嵌入式系统具备 “时间感知能力”—— 即使主系统断电或休眠,RTC 也能持续运行并保持准确的时间,是需要时间戳、定时任务、周期性事件触发的场景(如智能表、数据记录仪、考勤机)的核心组件。
+
+### 1.1 硬件 RTC 特性
+硬件 RTC 是专门用于计时的独立硬件模块(可集成在 MCU 内或单独成芯片),是嵌入式系统中 “时间可靠性” 的核心选择,核心特点如下:
+
++ 独立运行:有专属晶振(32.768kHz 为主)和供电回路,不依赖主 CPU,主系统休眠或忙碌时仍能精准计时。
++ 断电不丢时:配备备用电池或超级电容,主电源断开后仍能持续运行,时间不重置。
++ 高精度低功耗:精度通常在 ±2ppm~±50ppm(每天偏差 0.17 秒~4.32 秒),休眠电流仅 0.5μA~10μA,续航能力强。
++ 支持硬件中断:可直接输出定时 / 闹钟中断,唤醒系统或触发任务,无需 CPU 轮询。
+
+### 1.2 软件 RTC 特性
+软件 RTC 是通过主 CPU 的定时器(Timer)和软件算法模拟的计时功能,无独立硬件,本质是 “用 CPU 资源换时间管理能力”,核心特点如下:
+
++ 无额外硬件成本:仅利用 MCU 内置的通用定时器,无需外接晶振、备用电源等组件。
++ 依赖主系统运行:主 CPU 休眠、复位或断电时,计时会停止或重置,无法保持时间。
++ 精度较低且易受干扰:计时精度依赖 CPU 定时器的晶振(通常为 MHz 级,需软件分频),受系统中断、任务调度影响大,偏差可能达秒级 / 分钟级。
++ 占用 CPU 资源:需要定时中断或轮询更新时间,会消耗部分 CPU 算力,不利于低功耗设计。
+
+### 1.3 本次实践背景
+NXP FDRM-MCXA346 开发板无独立硬件 RTC,因此本次实践通过 软件 RTC 方式实现时间管理,并进一步验证 Alarm 闹钟功能。
+
+
+
+
+
+## 二、环境配置与项目创建
+本次实践采用 “功能配置 + 代码编辑 + 编译下载” 的三段式工具链,具体工具如下:
+
++ env:负责 RT-Thread 功能项配置与工程生成
++ VSCode:负责代码编辑(可选,也可使用 Keil 内置编辑器)
++ MDK Keil:负责项目编译与程序下载
+
+
+
+### 2.1 源码拉取
+从 RT-Thread 官方 GitHub 仓库拉取最新源码,仓库地址:
+
+[https://github.com/RT-Thread/rt-thread](https://github.com/RT-Thread/rt-thread)
+
+
+
+
+
+## 三、项目配置(软件 RTC 功能使能)
+进入源码目录下的开发板对应 BSP 路径:rt-thread\bsp\nxp\mcx\mcxa\frdm-mcxa346
+
+在该路径下打开 env 工具
+
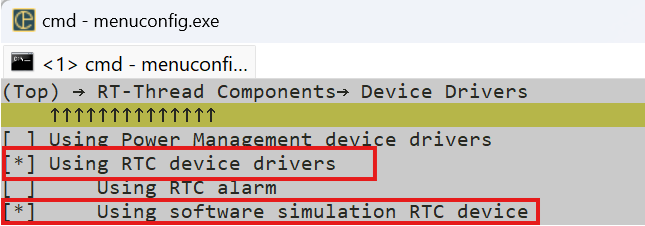
+在 env 中输入 menuconfig 进入图形化配置界面,按以下路径找到 RTC 配置项:
+
+RT-Thread Components → Device Drivers
+
+勾选以下两项,使能软件 RTC 功能:
+
++ [*] Using RTC device drivers(使能 RTC 设备驱动框架)
++ [*] Using software simulation RTC device(使能软件模拟 RTC 功能)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+配置完成后,按 ESC 键退出,退出时选择 “Save” 保存配置。
+
+
+
+## 四、编译与下载(软件 RTC 功能)
+### 4.1 项目编译
+在 env 工具中输入以下命令进行项目编译(-j16 中的 “16” 为 CPU 核心数,可根据自身电脑配置调整,如 4 核 CPU 可输入 -j4):
+
+```c
+scons -j16
+```
+
+
+
++ 编译成功标志:终端输出 “done building targets”。
+
+
+
+### 4.2 生成 MDK 工程
+编译完成后,在 env 中输入以下命令生成 MDK5 工程文件:
+
+
+
+```c
+scons --target=mdk5
+```
+
++ 生成成功标志:终端输出 “Keil-MDK project has generated successfully!”。
+
+
+
+### 4.3 程序下载
++ 进入 BSP 路径下的 project 目录,找到并打开 MDK 工程文件 project.uvprojx
++ 在 Keil 中点击 “Build” 按钮(或按 F7)重新编译工程,确保无报错
++ 将开发板通过 USB 连接电脑,选择对应的下载器,点击 “Download” 按钮(或按 F8)将程序下载到开发板
+
+
+
+## 五、软件 RTC 功能运行测试
+程序下载完成后,通过串口助手连接开发板的串口(波特率、数据位、停止位等参数需与代码配置一致,默认通常为 115200 8N1),进入 MSH 命令行界面,执行以下操作验证 RTC 功能:
+
+
+
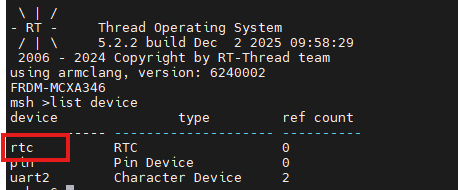
+### 5.1 查看 RTC 设备
+在 MSH 中输入以下命令,确认系统已识别到 RTC 设备:
+
+
+
+```c
+list device
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+
++ 预期结果:命令输出中包含 “rtc” 设备,说明软件 RTC 驱动加载成功。
+
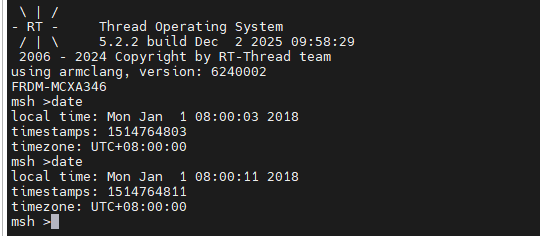
+### 5.2 时间获取与设置
+获取当前时间:在 MSH 中输入以下命令,查看系统当前时间(软件 RTC 初始时间可能为默认值,需手动设置):
+
+
+
+```c
+date
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+
+预期结果:终端输出当前时间(格式如 “2025-12-01 00:00:00”),且每秒自动更新。
+
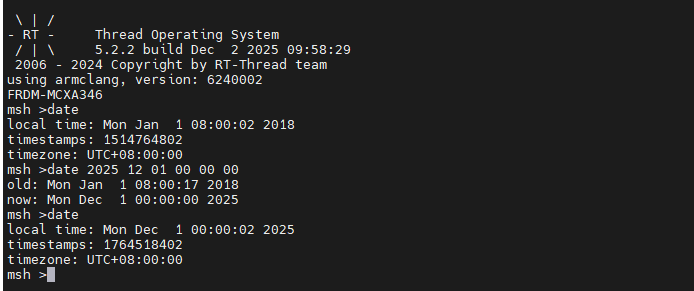
+设置系统时间:在 MSH 中输入以下命令,按 “年 月 日 时 分 秒” 的格式设置时间(示例:设置为 2025 年 12 月 1 日 10 时 30 分 0 秒):
+
+
+
+```c
+date 2025 12 1 10 30 0
+```
+
+
+
+
++ 预期结果:设置成功后,再次输入 date 命令,可看到时间已更新为设置值,并持续递增。
+
+## 六、Alarm 闹钟功能实践
+Alarm 闹钟功能基于 RTC 设备实现,通过设定闹钟时间触发中断,执行预设回调任务。RT-Thread 在软件层封装了 Alarm 组件,可实现 “无限个闹钟”(每个闹钟仅最后一次设定有效)。
+
+
+
+### 6.1 Alarm 组件配置
+进入 BSP 路径,打开 env 工具,输入 menuconfig 进入配置界面
+
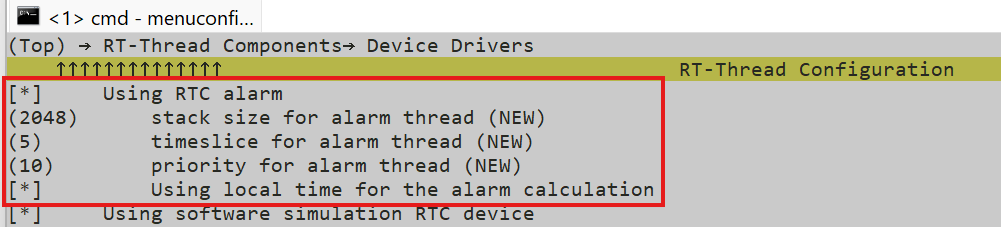
+按以下路径找到 Alarm 配置项:
+
+ RT-Thread Components → Device Drivers
+
+勾选并配置以下选项:
+
++ [*] Using RTC device drivers(已勾选,确保 RTC 功能使能)
++ [*] Using RTC alarm(使能 RTC Alarm 功能)
++ (2048) stack size for alarm thread (NEW)(设置 Alarm 线程栈大小,默认 2048 字节,可按需调整)
++ (5) timeslice for alarm thread (NEW)(设置 Alarm 线程时间片,默认 5 个系统滴答,可按需调整)
++ (10) priority for alarm thread (NEW)(设置 Alarm 线程优先级,默认 10,数值越小优先级越高,可按需调整)
++ [*] Using local time for the alarm calculation(使用本地时间计算闹钟触发时间)
++ [*] Using software simulation RTC device(已勾选,确保软件 RTC 功能使能)
+
+保存配置并退出 menuconfig。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### 6.2 Alarm 功能代码实现
+在 BSP 路径下的 applications 文件夹中,新建文件 alarm.c,并编写以下代码(实现 “每分钟触发一次闹钟,打印指定信息” 的功能):
+
+
+
+```c
+#include
+#include
+#include
+// 全局闹钟句柄(防重复创建)
+static struct rt_alarm *g_alarm = RT_NULL;
+// 闹钟回调函数(修改:每分钟打印指定内容)
+void user_alarm_callback(rt_alarm_t alarm, time_t timestamp)
+{
+ // 替换打印内容为要求的文本
+ rt_kprintf("Alarm start successfully!\n");
+}
+// 启动闹钟(MSH 命令)
+void alarm_sample(void)
+{
+ rt_device_t dev = rt_device_find("rtc");
+ struct rt_alarm_setup setup;
+ time_t now;
+ struct tm p_tm;
+ // 1. 防重复创建
+ if (g_alarm != RT_NULL)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("Alarm is already running!\n");
+ return;
+ }
+ // 2. 检查 RTC 设备
+ if (dev == RT_NULL)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("RTC device 'rtc' not found!\n");
+ return;
+ }
+ // 3. 计算「当前+1秒」的时间戳(确保不立即触发,等待到下一分钟)
+ now = time(NULL) + 1;
+ // 改用 localtime_r(适配系统时区)
+ localtime_r(&now, &p_tm);
+ // 4. 配置闹钟(每分钟触发)【修正注释:原"每秒触发"改为"每分钟触发"】
+ setup.flag = RT_ALARM_MINUTE;
+ setup.wktime = p_tm; // 直接赋值(struct tm 整体拷贝)
+ // 5. 创建并启动闹钟
+ g_alarm = rt_alarm_create(user_alarm_callback, &setup);
+ if (g_alarm != RT_NULL)
+ {
+ rt_alarm_start(g_alarm);
+ // 修改启动成功提示(仅说明启动,触发打印在回调中)
+ rt_kprintf("Alarm initialized successfully! Trigger every minute.\n");
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("Create alarm failed!\n");
+ }
+}
+// 停止闹钟(新增 MSH 命令)
+void alarm_stop(void)
+{
+ if (g_alarm != RT_NULL)
+ {
+ rt_alarm_delete(g_alarm);
+ g_alarm = RT_NULL;
+ rt_kprintf("Alarm stopped successfully!\n");
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("Alarm is not running!\n");
+ }
+}
+// 导出 MSH 命令(修正命令说明)
+MSH_CMD_EXPORT(alarm_sample, Start alarm (trigger every minute));
+MSH_CMD_EXPORT(alarm_stop, Stop the running alarm);
+
+```
+
+
+
+### 6.3 Alarm 功能编译与下载
+重复 “第四章 编译与下载” 的步骤:
+
++ 在 env 中执行 scons -j16 编译项目
++ 执行 scons —target=mdk5 更新工程
++ 在 Keil 中重新编译并下载程序到开发板
+
+### 6.4 Alarm 功能运行测试
+程序下载完成后,通过串口助手进入 MSH 命令行,执行以下操作验证 Alarm 功能:
+
+#### 6.4.1 查看 Alarm 线程
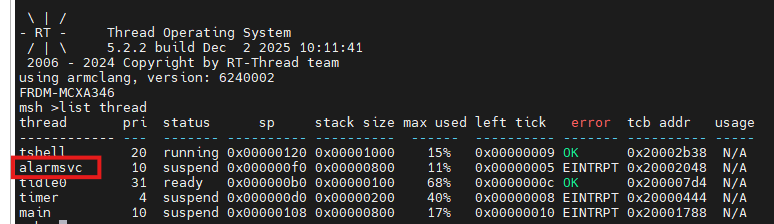
+在 MSH 中输入以下命令,确认 Alarm 线程已创建:
+
+```c
+list thread
+
+```
+
+
+
++ 预期结果:命令输出中包含 “alarm” 线程,初始状态为 “挂起”(未触发时线程休眠,触发时唤醒执行回调)。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 6.4.2 启动闹钟
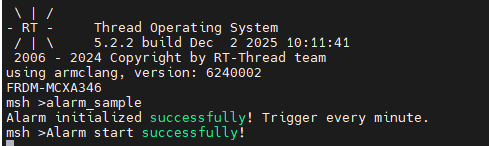
+在 MSH 中输入以下命令,启动 “每分钟触发一次” 的闹钟:
+
+```c
+alarm_sample
+```
+
+
+
+启动成功标志:终端输出 “Alarm initialized successfully! Trigger every minute.”。
+
+闹钟触发效果:从启动时间开始,每间隔 1 分钟,终端会自动打印 “Alarm start successfully!”。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 6.4.3 停止闹钟
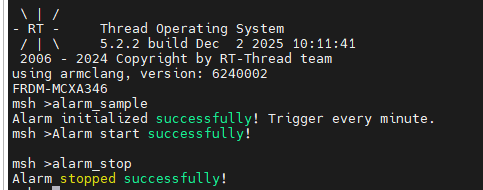
+在 MSH 中输入以下命令,停止当前运行的闹钟:
+
+
+
+```c
+alarm_stop
+
+```
+
++ 停止成功标志:终端输出 “Alarm stopped successfully!”,后续不再打印闹钟触发信息;若闹钟未启动,会输出 “Alarm is not running!”。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# 四、MCXA346上的ADC实践【柯九】
+## 1.准备工作
+### 1.1 ENV工具
+查看rtthread官网官方对MCXA346上手指南,按要求将MDK版本升至可支持该芯片的版本,源代码下载,
+
+rtthread官方使用env工具,
+
+第一次安装env工具一直失败,安装完成后首次启动装载支持包时报错,原因是python版本不兼容,个人电脑上之前已经安装过用于数据分析环境的Python环境
+
+第二次安装包报错是由于网络环境不佳,导致装载支持包时一直超时,
+
+配置 ENV 工具的 Python 依赖(pip)为阿里云镜像,下载速度会快很多!!!
+
+```c
+pip config set global.index-url https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/
+```
+
+
+
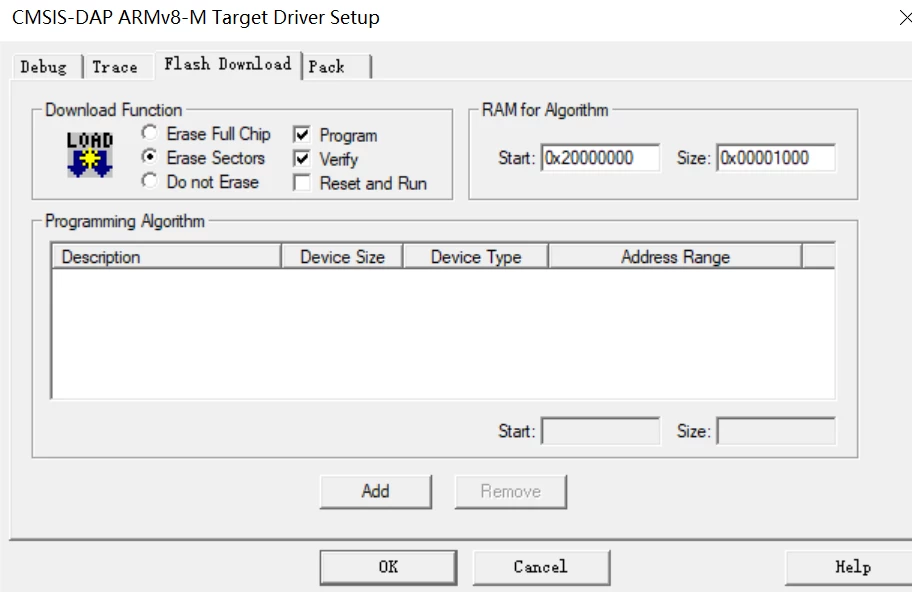
+### 1.2 下载报错
+官方历程编译后无报错,下载时发现一直显示“ Flash Download failed - “Cortex-M33””,排查后发现是Flash下载这里没有选择芯片,添加后就可以正常下载了,一般我会把Reset也勾上,或者下载完也可以按下Reset按键都可以。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## 2.ADC硬件相关
+参考链接:MCX A345 and MCX A346 Reference Manual
+
+MCX A346共有4个16位的ADC模块,分别为ADC0、ADC1、ADC2、ADC3.
+
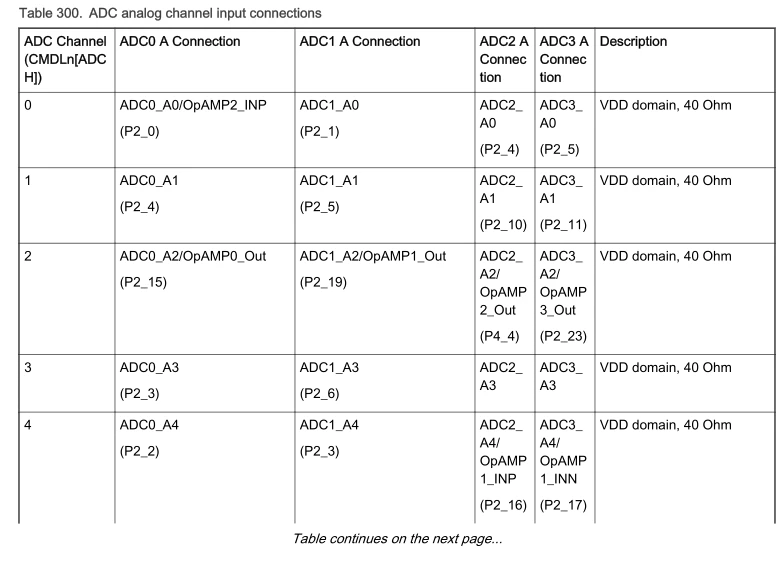
+下表列出部分引脚对照表.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### 2.1 ADC voltage reference options
+The ADC voltage reference can be selected by CFG[REFSEL] as follows:
+
+a. CFG[REFSEL] = 00, VREFH reference pin
+
+b. CFG[REFSEL] = 01, VREF1
+
+c. CFG[REFSEL] = 10, VDDA_ANA supply pin
+
+
+
+### 2.2 ADC trigger inputs
+ADC trigger sources get routed through the Input Multiplexing (INPUTMUX).
+
+解读:ADC的触发源(即让ADC开始采样的信号源)需要通过配置“输入多路复用器(INPUTMUX)”来选择.
+
+例如定时器溢出、外部引脚电平、软件指令等,这些信号源会触发ADC开始采样.这些触发源并不是直接连接到ADC的,而是通过“输入多路复用器(INPUTMUX)”这个模块来分配.
+
+
+
+### 2.3 ADC Synchronized Trigger
+对于MCX A346来说,它支持3种同步触发配置
+
+a. ADC0触发所有的其他ADC,实现四个ADC同步采样.
+
+b. ADC0触发ADC1—>ADC0和ADC1同步采样.
+
+c. ADC2触发ADC3—>ADC2和ADC3同步采样.
+
+
+
+## 3.ADC测试
+### 3.1 测试代码
+ENV中切换至目标工程目录下(frdm-mcxa346),
+
+
+
+1. 输入menuconfig.exe
+2. 选择 Hardware Drivers Config——>On-chip Peripheral Drivers—>Enable ADC Channel,界面上只能选择ADC0_CHANNEL22,选择ADC0_CHANNEL22后,保存退出
+3. scons —target=mdk5重新生成工程
+4. 编译无报错后,测试ADC0通道1,添加adc_test测试代码,在main函数中调用即可(main函数中是点灯程序,也可以删掉)
+
+```c
+#include
+/*adc related*/
+#define ADC_DEV_NAME "adc0"
+#define ADC_DEV_CHANNEL 1
+#define REFER_VOLTAGE 3300
+#define CONVERT_BITS (1 << 16)
+#define THREAD_PRIORITY 8
+#define THREAD_STACK_SIZE 512
+#define THREAD_TIMESLICE 5
+rt_adc_device_t adc_dev;
+void adc_test_thread_entry(void *parameter)
+{
+ rt_uint32_t value = 0, vol = 0;
+ while(1)
+ {
+ rt_thread_mdelay(1000);
+ value = rt_adc_read(adc_dev, ADC_DEV_CHANNEL);
+ /* 转换为对应电压值 */
+ vol = value * REFER_VOLTAGE / CONVERT_BITS;
+ rt_kprintf("the voltage is :%d.%02d \n", vol / 1000, vol % 1000);
+ }
+}
+void adc_test_init(void)
+{
+ rt_thread_t adc_tid;
+ adc_dev = (rt_adc_device_t)rt_device_find(ADC_DEV_NAME);
+ if(adc_dev != RT_NULL) {
+ rt_adc_enable(adc_dev, ADC_DEV_CHANNEL);
+ } else {
+ rt_kprintf("adc_test failed! can't find %s device!\n",ADC_DEV_NAME);
+ }
+ adc_tid = rt_thread_create("adc_tid",
+ adc_test_thread_entry, RT_NULL,
+ THREAD_STACK_SIZE,
+ THREAD_PRIORITY, THREAD_TIMESLICE);
+ if (adc_tid != RT_NULL) {
+ rt_thread_startup(adc_tid);
+ }
+}
+
+```
+
+```c
+#include
+#include "drv_pin.h"
+#include "adc_test.h"
+#define LED_PIN ((3*32)+18) /* Original LED pin */
+#define BUTTON_PIN ((1*32)+7) /* P1_7 button pin */
+static rt_bool_t led_state = RT_FALSE; /* Current LED state */
+/* Button interrupt callback function */
+void button_irq_callback(void *args)
+{
+ rt_kprintf("SW2 pressed\n");
+}
+int main(void)
+{
+#if defined(__CC_ARM)
+ rt_kprintf("using armcc, version: %d\n", __ARMCC_VERSION);
+#elif defined(__clang__)
+ rt_kprintf("using armclang, version: %d\n", __ARMCC_VERSION);
+#elif defined(__ICCARM__)
+ rt_kprintf("using iccarm, version: %d\n", __VER__);
+#elif defined(__GNUC__)
+ rt_kprintf("using gcc, version: %d.%d\n", __GNUC__, __GNUC_MINOR__);
+#endif
+ rt_kprintf("FRDM-MCXA346\r\n");
+ /* Configure LED pin as output */
+ rt_pin_mode(LED_PIN, PIN_MODE_OUTPUT);
+ rt_pin_write(LED_PIN, PIN_LOW);
+ /* Configure button pin as input with pull-up */
+ rt_pin_mode(BUTTON_PIN, PIN_MODE_INPUT_PULLUP);
+ /* Attach interrupt to button pin */
+ rt_pin_attach_irq(BUTTON_PIN, PIN_IRQ_MODE_FALLING, button_irq_callback, RT_NULL);
+ rt_pin_irq_enable(BUTTON_PIN, PIN_IRQ_ENABLE);
+ adc_test_init();
+ while (1)
+ {
+ /* Toggle LED state */
+ led_state = !led_state;
+ rt_pin_write(LED_PIN, led_state ? PIN_HIGH : PIN_LOW);
+ rt_thread_mdelay(500);
+ }
+}
+
+
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+#include
+
+/*adc related*/
+
+#define ADC_DEV_NAME "adc0"
+
+
+
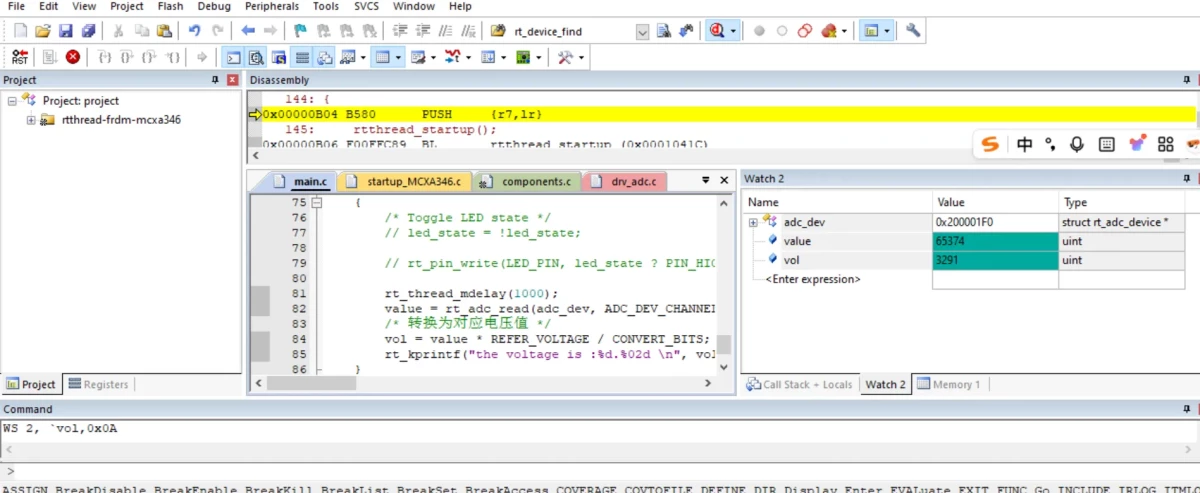
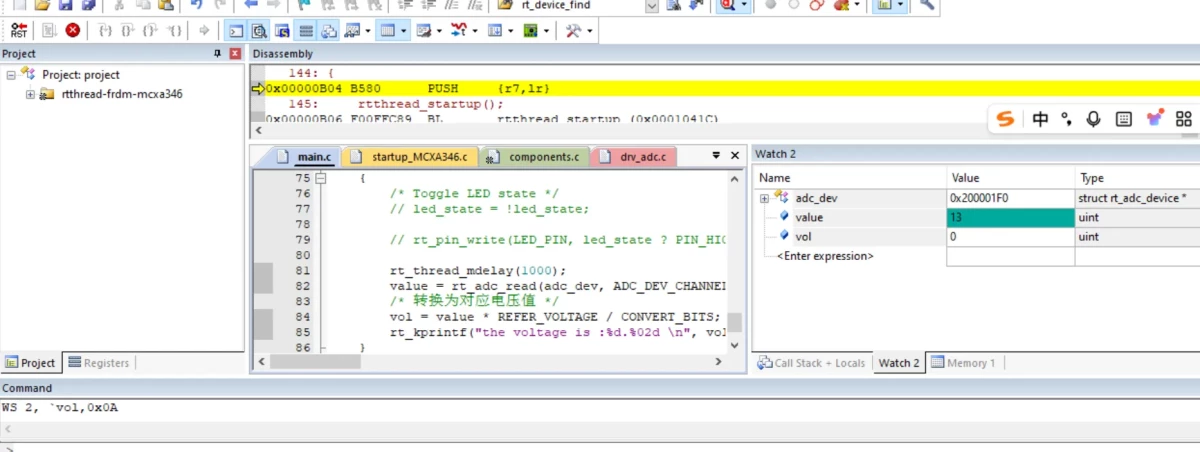
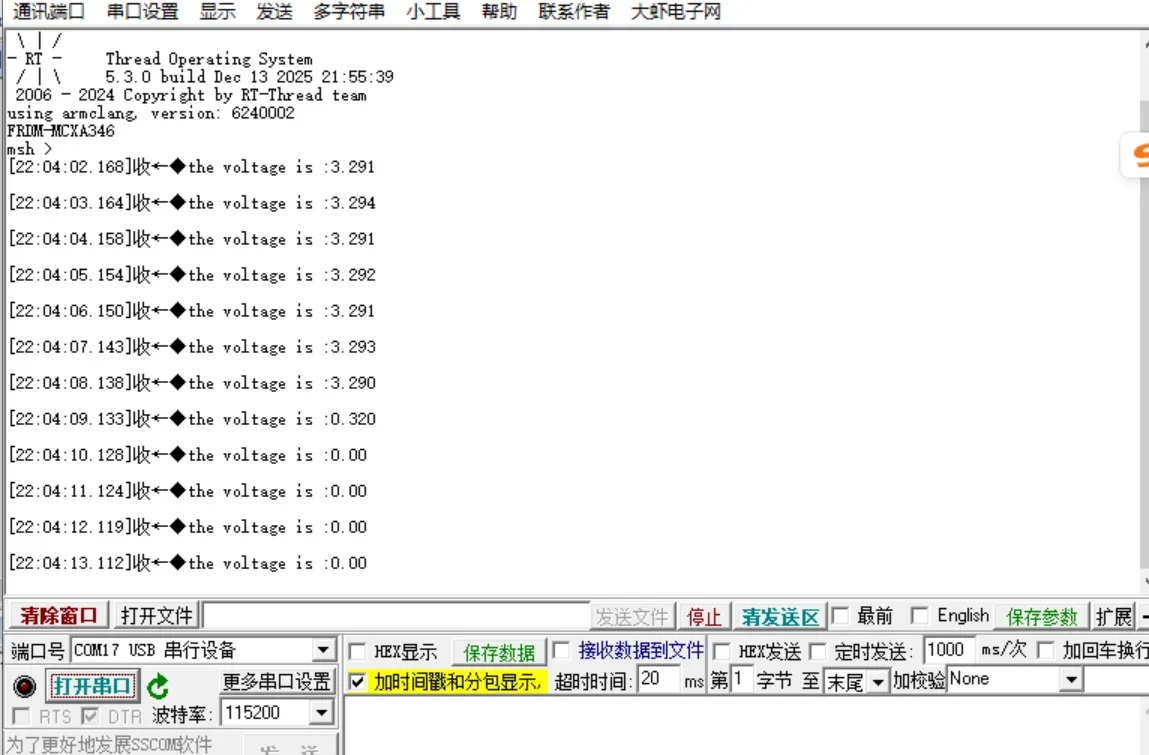
+### 3.2 结果验证
+将ADC0_CH1(P2_4)分别接在Jlink的3.3V和GND上测试,同步串口中打印转换后的电压值,单位是mv
+
+3.3V:
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+0V:
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+串口测试结果:
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### 3.3 问题记录
+#### 1. rt_device_find一直未找到ADC设备
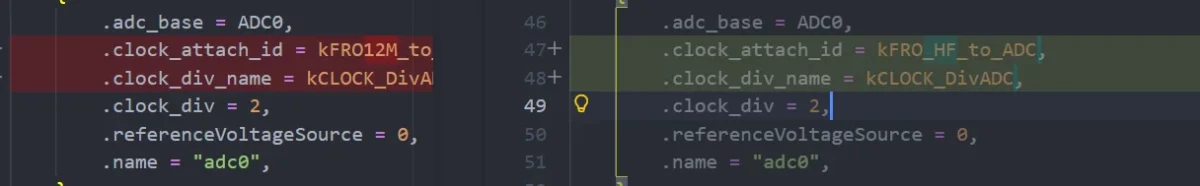
+原因:ENV工具使能ADC0_CHANNEL12后,测试时发现rt_device_find一直未找到ADc设备,排查发现是drv_adc文件中mcx_adc_obj中相关硬件参数配置被BSP_USING_ADC0宏定义,但ENV工具使能ADC后只宏定义了BSP_USING_ADC和BSP_USING_ADC0_CH22,需要rt_config.h中添加#define BSP_USING_ADC0
+
+#### 2. drv_adc.c中部分字段报错
+原因:MCXA346的宏定义不匹配,需要更改为实际对应的
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 3. ADC0_CHANNEL22测试时卡死
+原因:经排查发现卡死在rt_adc_enable中的LPADC_SetConvCommandConfig函数,是由于底层 ADC_CMDL_COUNT被宏定义为7U (数据手册1632页)限制了 commandId 的有效范围,channel=22 时映射的 commandId 超出了该范围导致触发assert 断言失败 ,程序进入死循环,修改adc_chl2cmd和adc_cmd2trig数组为实际的即可
+
+```c
+static uint8_t adc_chl2cmd[] = {
+ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,
+ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,
+ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,
+ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,
+ 1,2
+};
+static uint8_t adc_cmd2trig[] = {0,1,2,3,0,1,2};
+
+
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# 五、MCXA346上的HWTimer实践【张国庆】
+背景介绍
+
+MCXA346 基于Arm® Cortex®-M33内核,主频 180MHz, 738 CoreMark® (4.10 CoreMark®/MHz)
+
+特点如下:
+
+
+
++ 512KB Flash,128KB SRAM
++ 外设通信协议:2x LPSPI, 4x LPI2C, 6x LPUART,1x I3C,USB Full-speed (Device/Host) with on-chip FS PHY
++ 2x FlexPWM,Up to 2x Quadrature Encoder/Decoder (eQDC),2x AOI (AND/OR/Invert)
++ 4x 16-bit ADC,1 x 12-bit DAC,3 x High-speed Comparators
++ 5x 32-bit timers/counters (CTimer)
++ Up to 114 GPIOs
+
+本文将着重介绍 CTimer的功能以及使用方式。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## 环境搭建
+基于RT-thread env环境以及keil IDE环境对MCXA346进行开发。
+
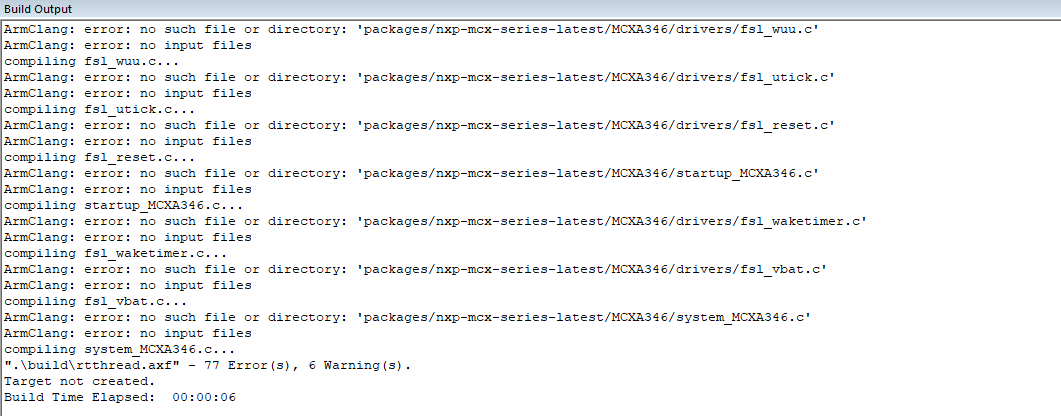
+首先初始化完外设以及keil的工程,直接编译有如下错误。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
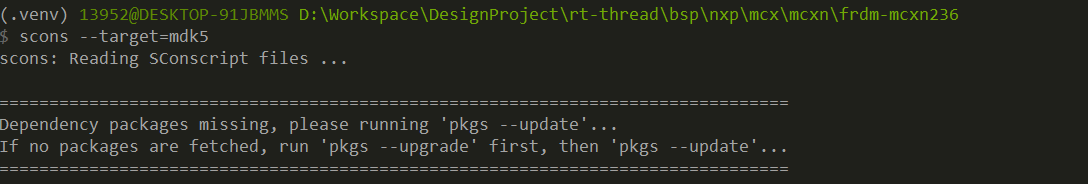
+在使用env环境的时候,需要注意nxp的package进行了更新,需要进行package的更新,不然就会有如下的报错。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
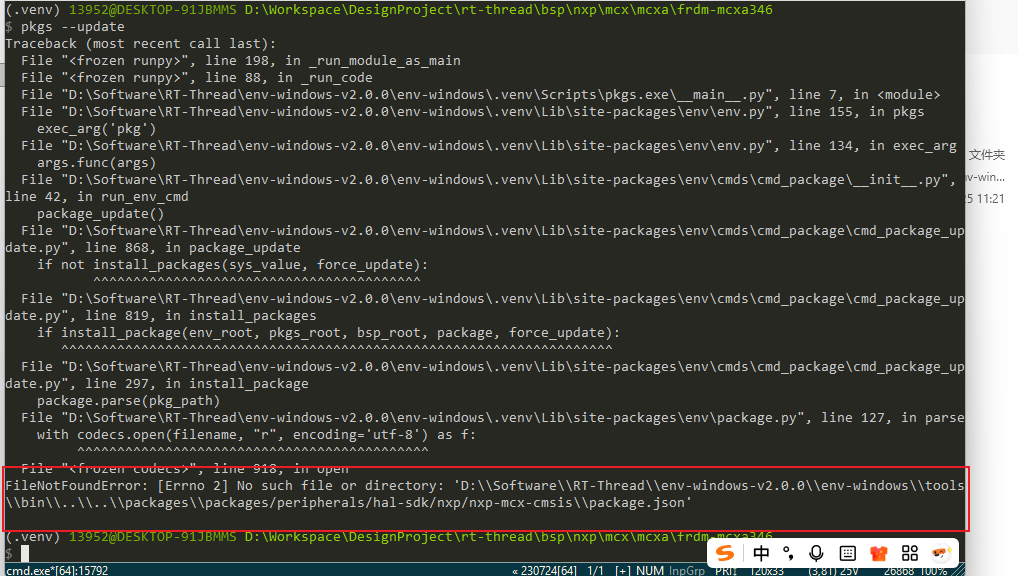
+在进行package的更新的时候,又发现报错:
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
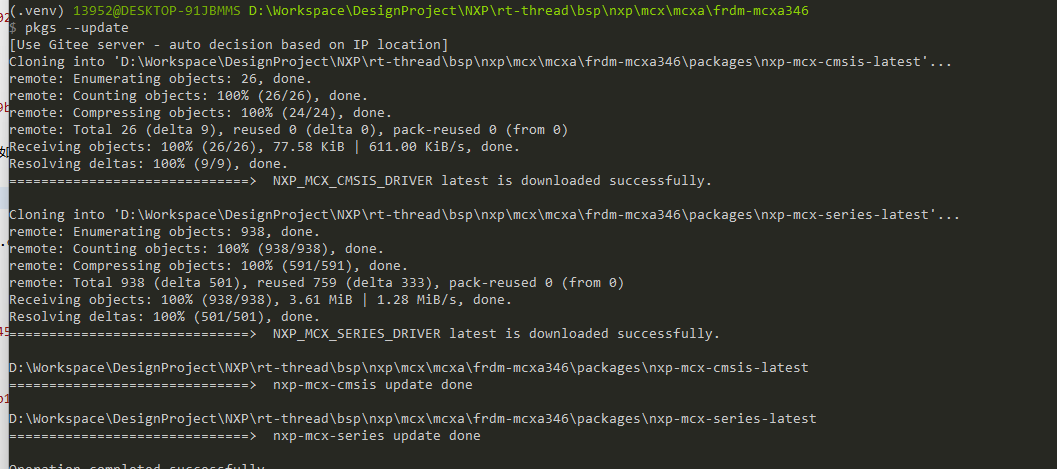
+原因是因为 RT-Thread仓库对NXP的BSP进行调整,将其挪到了其他仓库上面,而env 的环境又没有更新,所以就会出现如上问题,网上说可以用在线env去更新,
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
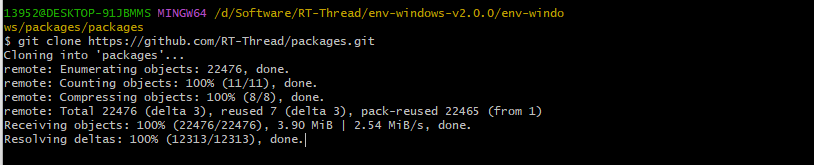
+当然也可以手动下载一下NXP的BSP,然后替换一下env下面的package目录即可。[https://github.com/RT-Thread/packages](https://github.com/RT-Thread/packages)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
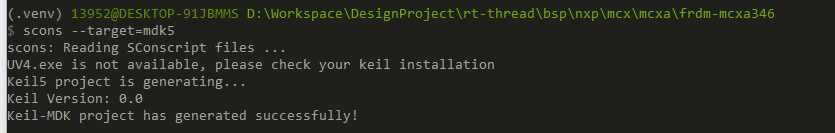
+之后再进行进行生成keil的工程的时候,就正常了。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+keil 可以正常编译通过。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## HW Timer功能介绍
+HW Timer的功能介绍如下:
+
+
+
++ MCX的HW Tinmer 频率为180MHZ,32bit 的预分频系数,
++ 支持计数和定时操作,支持4个输入信号捕获,运行脉冲宽度测量,支持边沿配置
++ 支持4个计数匹配操作,在计数匹配完成后支持持续操作,
++ 在计数复位后,支持自动重装载值
++ 支持在计数匹配之后,停止计数
++ 支持计数匹配之后,多种输出状态,高低状态以及翻转状态
++ 支持计数匹配之后,输出PWM波形,
+
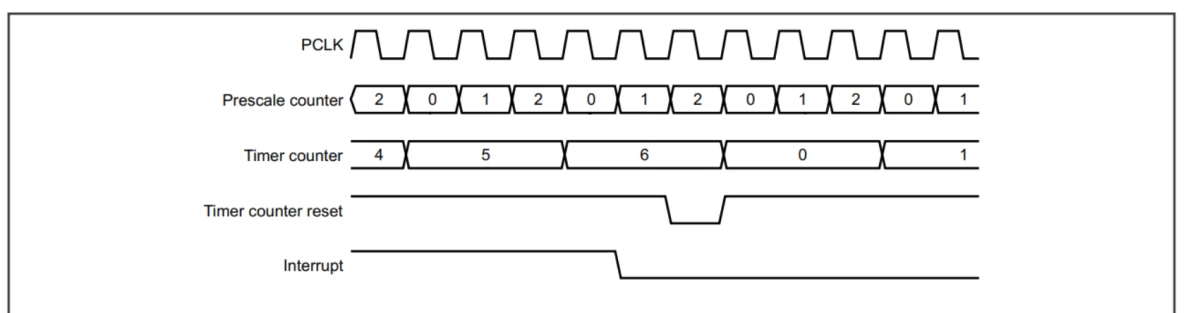
+下图为一个定时器配置为reset 且产生中断的一个时序图,预分频系数为2,匹配value为6。
+
+
+
++ 在计数达到6之后,产生中断,
++ 且在一个时钟之后,进行reset,继续计数
+
+
+
+
+
+
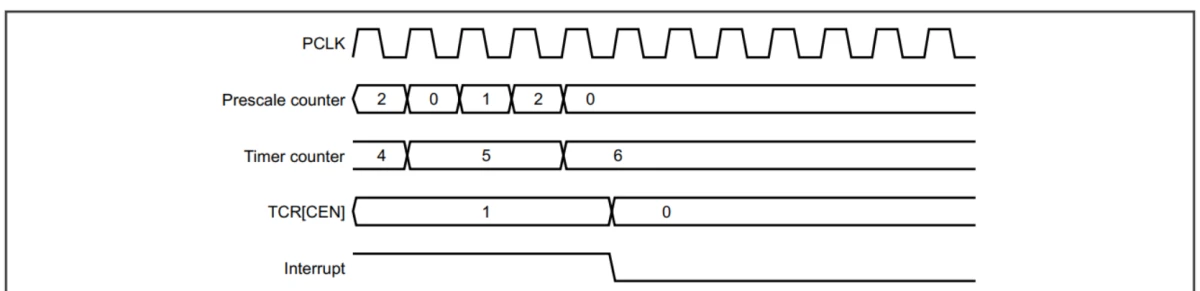
+当然也可以配置为停止模式,同样预分频系数为2,匹配value为6。
+
++ 在计数达到6之后,产生中断,
++ 没有进行reset,停止计时
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## 使用说明
+在MCXA346目录下面,大打开env环境,输入meuconfig,进行配置界面,选择Hardware Driver Config。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+继续选择onchip peripheral Drivers
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
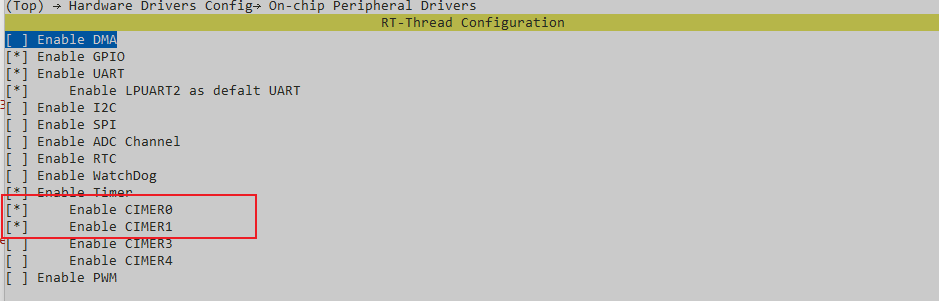
+最后配置CTimer0 和 CTimer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+至此,HW Timer配置完成,可以看到Keil 工程里面HW timer已经使能,且Ctimer0和Ctimer1使能。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+hw timr的使用流程如下:
+
+
+
++ 获取hw timer设备,需要指定timer name(前提是注册timer 设备,在env环境即配置好)
+
+测试hw timer的代码如下:
+
+```c
+#include
+#include
+#include "drv_pin.h"
+#include "pin_mux.h"
+#include "clock_config.h"
+#include "board.h"
+#include "fsl_inputmux.h"
+#include "fsl_gpio.h"
+#include
+#include "fsl_reset.h"
+#include "fsl_ctimer.h"
+#define HWTIMER_DEV_NAME "timer0" /* device name */
+#define THREAD_PRIORITY 25
+#define THREAD_STACK_SIZE 512
+#define THREAD_TIMESLICE 5
+static rt_thread_t tid1 = RT_NULL;
+rt_uint8_t timeout_flag = 0;
+static rt_err_t timeout_cb(rt_device_t dev, rt_size_t size)
+{
+ timeout_flag = 1;
+ return 0;
+}
+int test_hwtimer()
+{
+ rt_err_t ret = RT_EOK;
+ rt_hwtimerval_t timeout_s;
+ rt_device_t hw_dev = RT_NULL;
+ rt_hwtimer_mode_t mode;
+ rt_uint32_t freq = 1000000;
+ hw_dev = rt_device_find(HWTIMER_DEV_NAME);
+ rt_kprintf("find device success,device=%x\r\n",hw_dev);
+ if (hw_dev == RT_NULL)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("hwtimer sample run failed! can't find %s device!\n", HWTIMER_DEV_NAME);
+ return -RT_ERROR;
+ }
+ ret = rt_device_open(hw_dev, RT_DEVICE_OFLAG_RDWR);
+ rt_kprintf("open device success\r\n");
+ if (ret != RT_EOK)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("open %s device failed!\n", HWTIMER_DEV_NAME);
+ return ret;
+ }
+ rt_device_set_rx_indicate(hw_dev, timeout_cb);
+ rt_device_control(hw_dev, HWTIMER_CTRL_FREQ_SET, &freq);
+ mode = HWTIMER_MODE_PERIOD;
+ ret = rt_device_control(hw_dev, HWTIMER_CTRL_MODE_SET, &mode);
+ if (ret != RT_EOK)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("set mode failed! ret is :%d\n", ret);
+ return ret;
+ }
+ /* Example Set the timeout period of the timer */
+ timeout_s.sec = 3; /* secend */
+ timeout_s.usec = 0; /* microsecend */
+ if (rt_device_write(hw_dev, 0, &timeout_s, sizeof(timeout_s)) != sizeof(timeout_s))
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("set timeout value failed\n");
+ return -RT_ERROR;
+ }
+ rt_kprintf("init success\r\n");
+ while (1)
+ {
+ if(timeout_flag)
+ {
+ timeout_flag = 0;
+ rt_hwtimer_t *timer = (rt_hwtimer_t *)hw_dev;
+ rt_device_read(hw_dev, 0, &timeout_s, sizeof(timeout_s));
+ rt_kprintf("Read: Sec = %d, Usec = %d \r\n", timeout_s.sec, timeout_s.usec);
+ }
+ }
+ return ret;
+}
+MSH_CMD_EXPORT(test_hwtimer, hwtimer sample);
+static void thread1_entry(void *parameter)
+{
+ test_hwtimer();
+}
+int create_tester_hwtimer_thread(void)
+{
+ //* CTimer functional clock needs to be greater than or equal to SYSTEM_CLK */
+ CLOCK_SetClockDiv(kCLOCK_DivCTIMER0, 1u);
+ CLOCK_AttachClk(kFRO_HF_to_CTIMER0);
+ tid1 = rt_thread_create("thread1",
+ thread1_entry, RT_NULL,
+ THREAD_STACK_SIZE,
+ THREAD_PRIORITY, THREAD_TIMESLICE);
+ if (tid1 != RT_NULL)
+ rt_thread_startup(tid1);
+ return 0;
+}
+
+
+
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+同理可以测试timer2,产生100ms的中断,用于控制LED灯闪烁
+
+```c
+static rt_err_t timeout_cb2(rt_device_t dev, rt_size_t size)
+{;
+ timeout2_flag = 1;
+ return 0;
+}
+int test_hwtimer2()
+{
+ rt_err_t ret = RT_EOK;
+ rt_hwtimerval_t timeout_s;
+ rt_device_t hw_dev = RT_NULL;
+ rt_hwtimer_mode_t mode;
+ rt_uint32_t freq = 100000;
+ hw_dev = rt_device_find(HWTIMER_DEV2_NAME);
+ rt_kprintf("find device2 success,device=%x\r\n",hw_dev);
+ if (hw_dev == RT_NULL)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("hwtimer sample run failed! can't find %s device!\n", HWTIMER_DEV_NAME);
+ return -RT_ERROR;
+ }
+ ret = rt_device_open(hw_dev, RT_DEVICE_OFLAG_RDWR);
+ rt_kprintf("open device2 success\r\n");
+ if (ret != RT_EOK)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("open %s device failed!\n", HWTIMER_DEV_NAME);
+ return ret;
+ }
+ rt_device_set_rx_indicate(hw_dev, timeout_cb2);
+ rt_device_control(hw_dev, HWTIMER_CTRL_FREQ_SET, &freq);
+ mode = HWTIMER_MODE_PERIOD;
+ ret = rt_device_control(hw_dev, HWTIMER_CTRL_MODE_SET, &mode);
+ if (ret != RT_EOK)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("set mode failed! ret is :%d\n", ret);
+ return ret;
+ }
+ /* Example Set the timeout period of the timer */
+ timeout_s.sec = 0; /* secend */
+ timeout_s.usec = 100000; /* microsecend */
+ if (rt_device_write(hw_dev, 0, &timeout_s, sizeof(timeout_s)) != sizeof(timeout_s))
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("set timeout value failed\n");
+ return -RT_ERROR;
+ }
+ rt_kprintf("init device2 success\r\n");
+ while (1)
+ {
+ if(timeout2_flag)
+ {
+ timeout2_flag = 0;
+ /* Toggle LED state */
+ led_state = !led_state;
+ rt_pin_write(LED_PIN, led_state ? PIN_HIGH : PIN_LOW);
+ }
+ }
+ return ret;
+}
+
+
+```
+
+
+
+具体效果如下:
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+性能测试
+
+MCXA346的HW Tinmer 频率为180MHZ,可以设置频率为10MZ,根据其tick 值的变化,来分析 代码的执行效率。
+
+
+
+测试流程如下:
+
+
+
++ 频率为10MHZ,测量打印串口日志的执行时间,其相对较为耗时
++ 串口打印前记录timer tick,打印后记录其timer tick,
++ 打印差值,即其执行时间。
+
+测试代码如下:
+
+```c
+static rt_err_t timeout_cb(rt_device_t dev, rt_size_t size)
+{
+// rt_kprintf("this is hwtimer timeout callback fucntion!\n");
+// rt_kprintf("tick is :%d !\n", rt_tick_get());
+ timeout_flag = 1;
+ return 0;
+}
+int test_hwtimer()
+{
+ rt_err_t ret = RT_EOK;
+ rt_hwtimerval_t timeout_s;
+ rt_device_t hw_dev = RT_NULL;
+ rt_hwtimer_mode_t mode;
+ rt_uint32_t freq = 10000000;
+ hw_dev = rt_device_find(HWTIMER_DEV_NAME);
+ rt_kprintf("find device success,device=%x\r\n",hw_dev);
+ if (hw_dev == RT_NULL)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("hwtimer sample run failed! can't find %s device!\n", HWTIMER_DEV_NAME);
+ return -RT_ERROR;
+ }
+ ret = rt_device_open(hw_dev, RT_DEVICE_OFLAG_RDWR);
+ rt_kprintf("open device success\r\n");
+ if (ret != RT_EOK)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("open %s device failed!\n", HWTIMER_DEV_NAME);
+ return ret;
+ }
+ rt_device_set_rx_indicate(hw_dev, timeout_cb);
+ rt_device_control(hw_dev, HWTIMER_CTRL_FREQ_SET, &freq);
+ mode = HWTIMER_MODE_PERIOD;
+ ret = rt_device_control(hw_dev, HWTIMER_CTRL_MODE_SET, &mode);
+ if (ret != RT_EOK)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("set mode failed! ret is :%d\n", ret);
+ return ret;
+ }
+ /* Example Set the timeout period of the timer */
+ timeout_s.sec = 3; /* secend */
+ timeout_s.usec = 0; /* microsecend */
+ if (rt_device_write(hw_dev, 0, &timeout_s, sizeof(timeout_s)) != sizeof(timeout_s))
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("set timeout value failed\n");
+ return -RT_ERROR;
+ }
+ rt_kprintf("init success\r\n");
+ while (1)
+ {
+ //rt_thread_mdelay(3000);
+ if(timeout_flag)
+ {
+ timeout_flag = 0;
+ rt_hwtimer_t *timer = (rt_hwtimer_t *)hw_dev;
+ rt_device_read(hw_dev, 0, &timeout_s, sizeof(timeout_s));
+ rt_uint32_t timer_start = timer->ops->count_get(timer);
+ rt_kprintf("Read: Sec = %d, Usec = %d \r\n", timeout_s.sec, timeout_s.usec);
+ rt_uint32_t timer_end = timer->ops->count_get(timer);
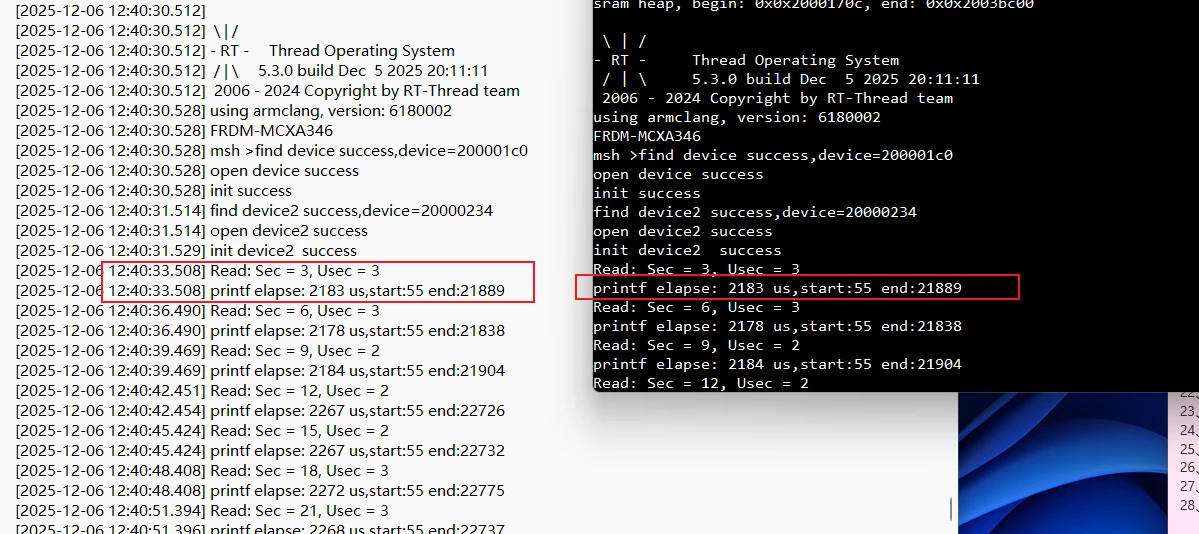
+ rt_kprintf("printf elapse: %d us,start:%d end:%d\n", (timer_end - timer_start)/10,timer_start,timer_end);
+ }
+ }
+ return ret;
+}
+
+
+```
+
+
+
++ 串口波特率为115200,其每秒发送的数据为11520 Byte,每个Byte发送的时间为:1/11520 * 1000 = 0.086ms,
++ 发送到串口的字节数为22字节,其时间需要:0.086 * 22 = 1.91ms,加上其他代码运行时间,与打印的2.183ms,基本相差不大
++ 分析timer的精度正确,可以用其高精度频率进行代码执行效率分析
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## 心得体会
++ MCXA346 的HW-Timer 功能还是相当强大,其timer 的频率相比其他厂商要高很多,满足日常的功能根本无压力
++ rtthread的 env工具也相当好用,界面配置外设启动,然后直接编写驱动代码即可,很方便入门小伙伴学习
++ 在使用hw timer的时候,其match 寄存器有4个,但是计数器只有1个,满足一个匹配就会归0或者产生中断,其他则无法继续匹配定时器,可能永远也无法达到,这个在使用的时候需要注意。
++ hw timer在使用的时候需要主要时钟的初始化,否则NXP MCU直接Hang住,都无法继续下载代码以及调试,需要进入ISP模式后才可以继续下载
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
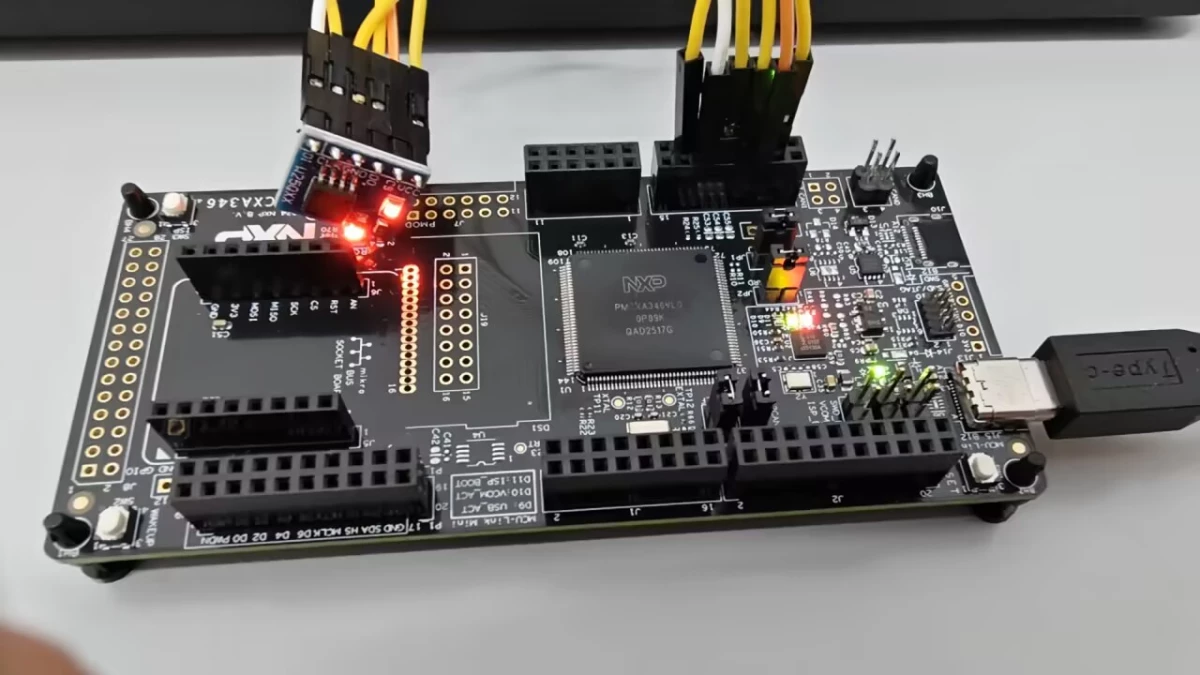
+# 六、MCXA346上的SPI实践【戴凌祥&吴长杰】
+## 基于RT-Thread的FRDM MCXA346在SPI-Flash上的实践【戴凌祥】
+
+
+## 一、硬件介绍
+
+
+
+
+
+### 板卡核心资源
++ MCX A346 Arm® Cortex®-M33内核,运行频率高达180MHz
++ 高达1MB的闪存,256KB的RAM
++ 板载MCU-Link调试器,带有CMSIS-DAP
++ 详细信息请移步到NXP官网[https://www.nxp.com.cn/design/design-center/development-boards-and-designs/FRDM-MCXA346](https://www.nxp.com.cn/design/design-center/development-boards-and-designs/FRDM-MCXA346)
+
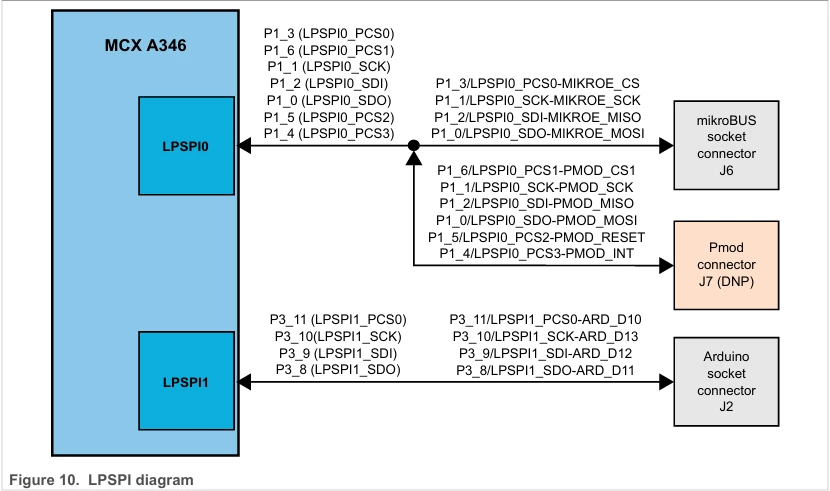
+### LPSPI硬件介绍
+LPSPI实际上还是SPI,只不过多了一个低功耗LP(Low Power),板卡的LPSPI引脚分配如图,有LPSPI0和LPSPI1:
+
+
+
+
+
+
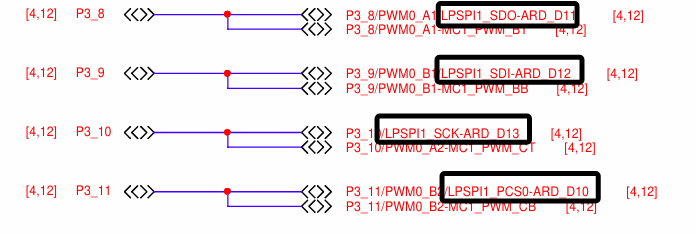
+本次实验采用LPSPI1,引脚如图:
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### W25Q64模块介绍
+W25Q64模块就是我们平常用的SPI_Flash,可以去淘宝上买现成的,这里不提供链接,直接在淘宝上搜索即可
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
++ P3_8接到W25Q64模块的DI引脚
++ P3_9接到W25Q64模块的DO引脚
++ P3_10接到W25Q64模块的CLK引脚
++ P3_11接到W25Q64模块的CS引脚
+
+### 实物接线图
+
+
+
+
+
+## 二、软件介绍
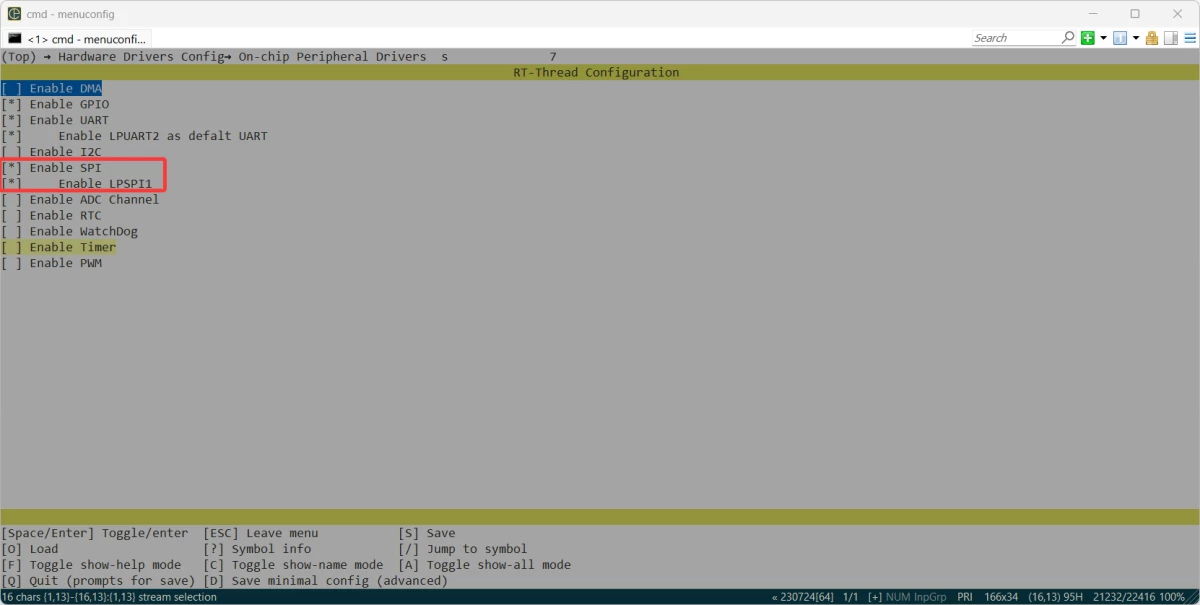
+### LPSPI1使能
+打开menuconfig,进入我们的Hardware Drivers Config,使能LPSPI1
+
+
+
+
+
+
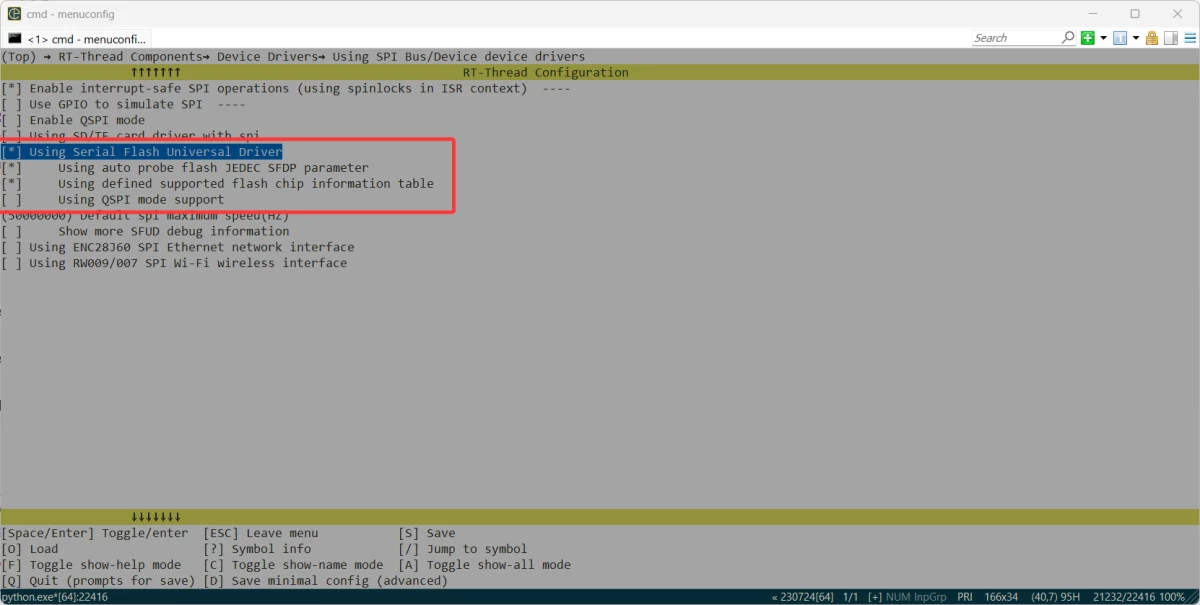
+### 启用SFUD
+SFUD(Serial Flash Universal Driver)串行 Flash 通用驱动库,这里为了重复编写Flash驱动,采用RT-Thread已经提供的支持SFUD
+
+
+
+
+
+
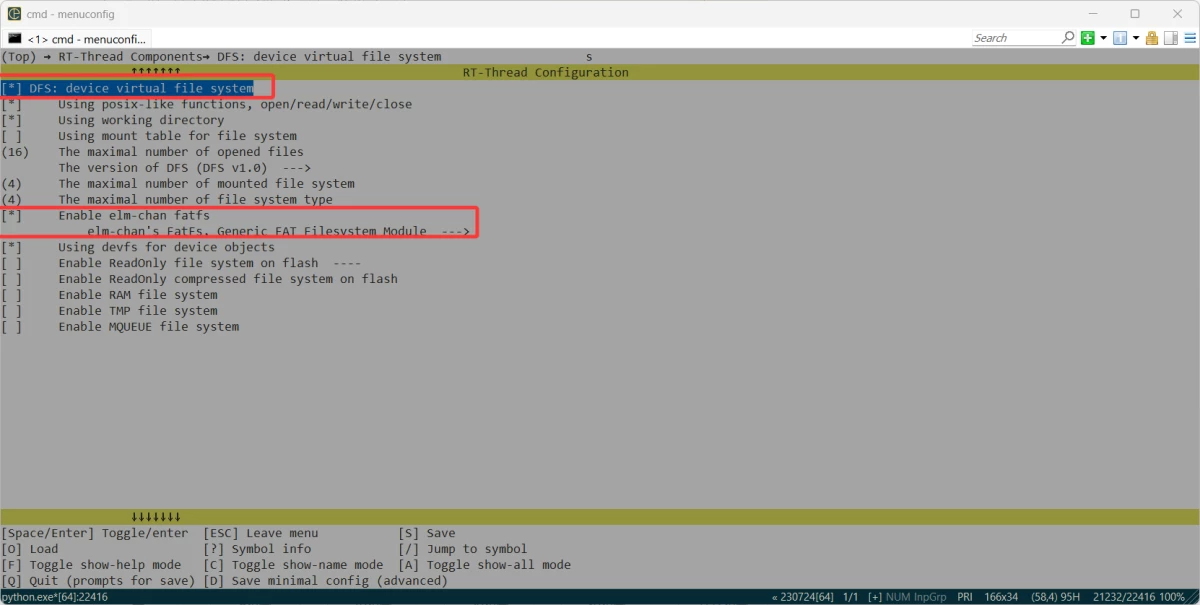
+### 启用DFS
+DFS(Device File System)虚拟文件系统,详细介绍可以去RT-Thread文档中心查看,这里提供链接:[[https://www.rt-thread.org/document/site/#/rt-thread-version/rt-thread-standard/programming-manual/filesystem/filesystem]](https://www.rt-thread.org/document/site/#/rt-thread-version/rt-thread-standard/programming-manual/filesystem/filesystem])
+
+
+
+
+
+
+到此,我们的menuconfig就配置完成了,执行以下命令以后,进入keil工程进行开发:
+
+```c
+pkgs --update
+scons --target=mdk5
+
+```
+
+
+
+### Keil代码编写
+W25Q64的片选脚是P3_11,这里采用偏移量的方法找到我们的P3_11,因为一个Port有32个引脚,P3_11在第3个Port,第3x32+11号引脚
+
+```c
+#define W25Q64_CS_PIN ((3*32)+11)
+static int rt_hw_spi_flash_init(void)
+{
+ if (rt_hw_spi_device_attach("spi1", "spi00", W25Q64_CS_PIN) != RT_EOK)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("Failed to attach SPI flash!\n");
+ return -RT_ERROR;
+ }
+ // 4. 初始化 SFUD
+ if (rt_sfud_flash_probe("W25Q64", "spi00") == RT_NULL)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("SFUD probe failed!\n");
+ return -RT_ERROR;
+ }
+ return RT_EOK;
+}
+INIT_COMPONENT_EXPORT(rt_hw_spi_flash_init);
+
+
+
+```
+
+
+
+初始化完成以后,我们还要进行文件系统的挂载,在主函数添加以下函数:
+
+```c
+dfs_mkfs("elm", "W25Q64");
+dfs_mount("W25Q64", "/", "elm", 0, 0);
+
+```
+
+
+
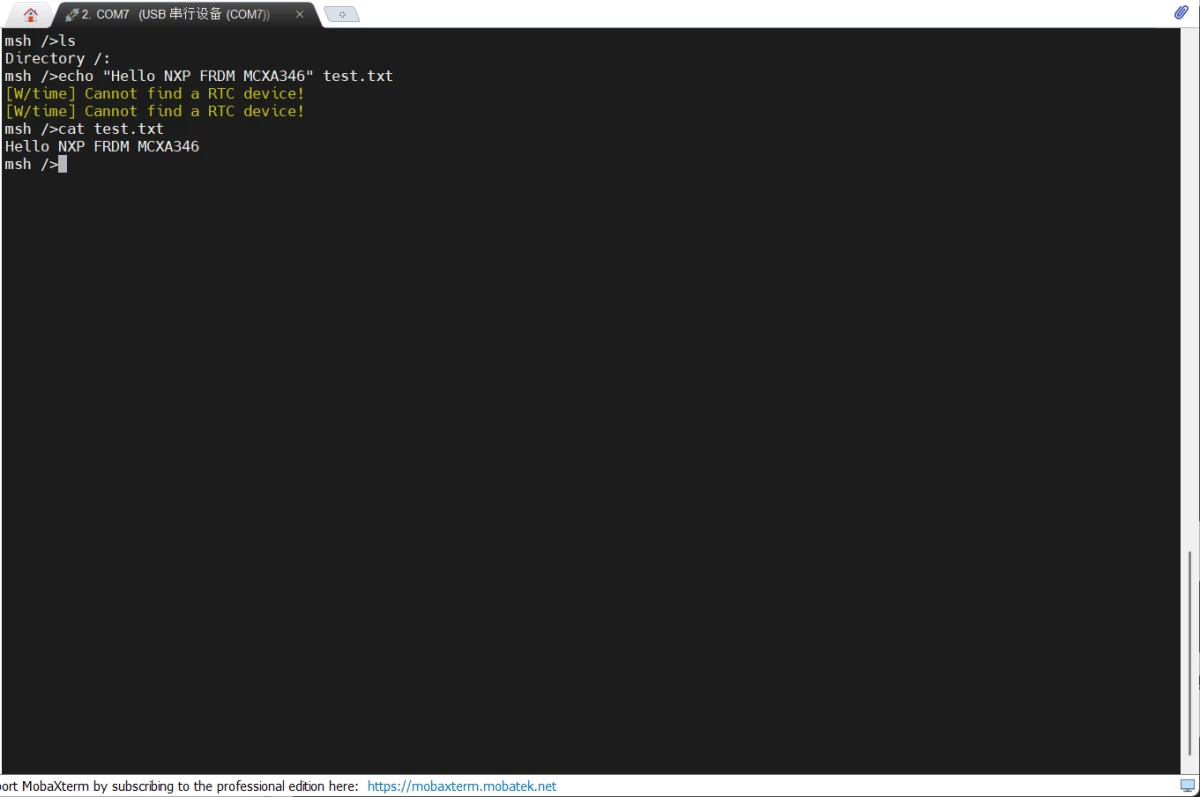
+但是我们要注意,dfs_mkfs只能在第一次使用没有文件系统的时候需要格式化,否则我们是不需要格式化的,不然会让你上次写入的数据丢失
+
+当然,我们也可以在RT-Thread的控制台进行格式化和挂载:
+
+```c
+msh />mkfs -t elm W25Q64
+[W/time] Cannot find a RTC device!
+msh />mount W25Q64 / elm
+mount device W25Q64(elm) onto / ... succeed!
+msh />
+
+```
+
+
+
+这里的Cannot find a RTC device!是因为文件写入需要记录时间,我这里没有注册RTC设备,但是这里也不影响我们的使用
+
+下面我们再来验证一下文件的读写:
+
+
+
+
+
+
+到此,我们的SPI Flash实践完成
+
+
+
+### 心得体会
+本次基于 FRDM-MCXA346 开发板的 LPSPI + W25Q64 SPI Flash 实践,我对 RT-Thread 在外设驱动、组件复用以及文件系统方面的整体设计有了更加直观和深入的理解。
+
+
+
++ 硬件层面,我熟悉了MCX A346 芯片 LPSPI 外设的引脚复用与资源分配方式
++ 软件层面,RT-Thread 提供的 SPI 框架、SFUD 组件和 DFS 文件系统 极大地降低了开发难度。通过 rt_hw_spi_device_attach 与 rt_sfud_flash_probe,可以快速完成 SPI Flash 的设备注册和识别,避免了重复编写底层 Flash 驱动代码,显著提升了开发效率。同时,借助 DFS,将底层的块设备抽象成文件系统,使 Flash 的使用方式更加直观,真正实现了“像操作文件一样操作存储器”。
+
+总体而言,本次实验不仅验证了 LPSPI + SPI Flash + SFUD + DFS 这一完整方案的可行性,也让我对 RT-Thread 的组件化设计理念和工程化思路有了更深的体会。
+
+源码链接:[https://github.com/Dailingxiang1/NXP-FRDM-MCXA346.git](https://github.com/Dailingxiang1/NXP-FRDM-MCXA346.git)
+
+
+
+## RT-Thread 基于 NXP FRDM-MCXA346 的 SPI-OLED 应用实践【吴长杰】
+## 一、硬件模块介绍
+###
+1.板载LPSPI接口介绍
+
+Low Power Serial Peripheral Interface (LPSPI)低功耗串行外围接口。在MCXA346开发板上可支持两个LPSPI,分别为 LPSPI0和 LPSPI1,支持SPI通信。其具有以下特性:
+(1)最小的 CPU 开销,支持 DMA 传输和接收请求的 FIFO 寄存器访问。
+(2)如果配置了深度睡眠模式并且有适当的时钟可用,操作将继续进行。
+(3)支持 32 位字长
+(4)可配置的时钟极性和相位
+(5)控制器模式下支持 4 个外围芯片选择
+(6)支持外设模式
+(7)4字传输和命令 FIFO
+(8)4字接收FIFO
+(9)控制器模式中的灵活定时参数,包括 SCK 频率和占空比,以及 PCS 和 SCK 边缘之间的延迟。
+(10)连续传输选项以保持 PCS 在多个帧之间保持有效
+(11)支持每个时钟边沿进行 1 位传输和接收的全双工传输
+(12)半双工传输支持以下功能:
+— 每个时钟边沿进行 1 位传输或接收
+— 每个时钟边沿进行 2 位传输或接收
+— 每个时钟边沿进行 4 位传输或接收
+(13)使用主机请求来控制 SPI 总线传输的开始选项
+(14)接收数据匹配逻辑,丢弃不匹配的数据并中断数据匹配
+
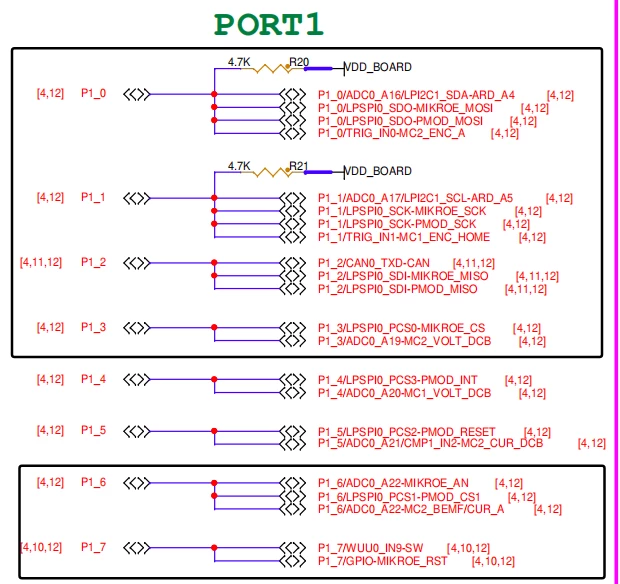
+### 2.LPSPI硬件介绍
+
+本次实验用到的接口为LPSIP1,其硬件原理图如下:
+MCU引脚配置
+
+
+
+
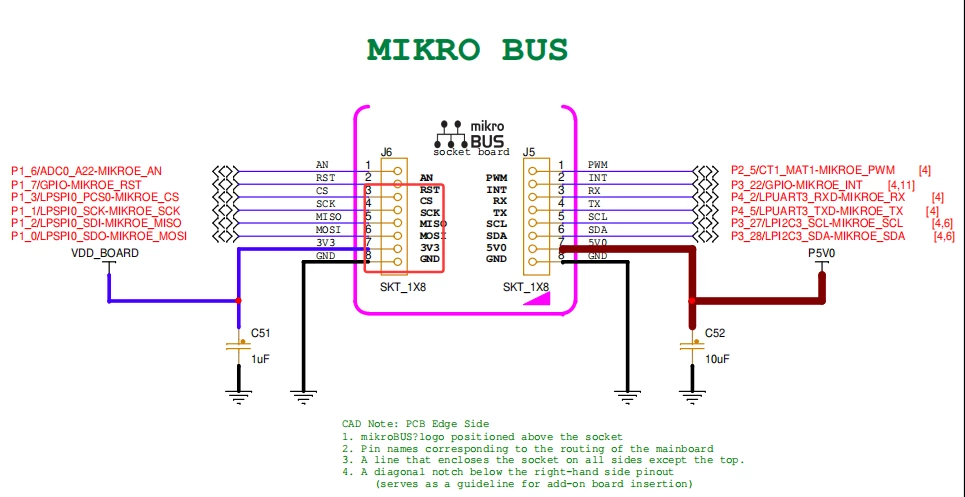
+通过port连接到mikro bus
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### 3.OLED引脚介绍
+
+1.GND 电源地
+2.VCC 电源正(3~5.5V)
+3.DO OLED的DO脚,在SPI和IC通信中为时钟管脚
+4.D1 OLED的D1脚,在SPI和 IIC通信中为数据管脚
+5.RES OLED的RES#脚,用来复位(低电平复位)
+6.DC OLED的D/C#E脚,数据和命令控制管脚
+7.CS OLED的CS#脚,片选管脚
+
+
+
+
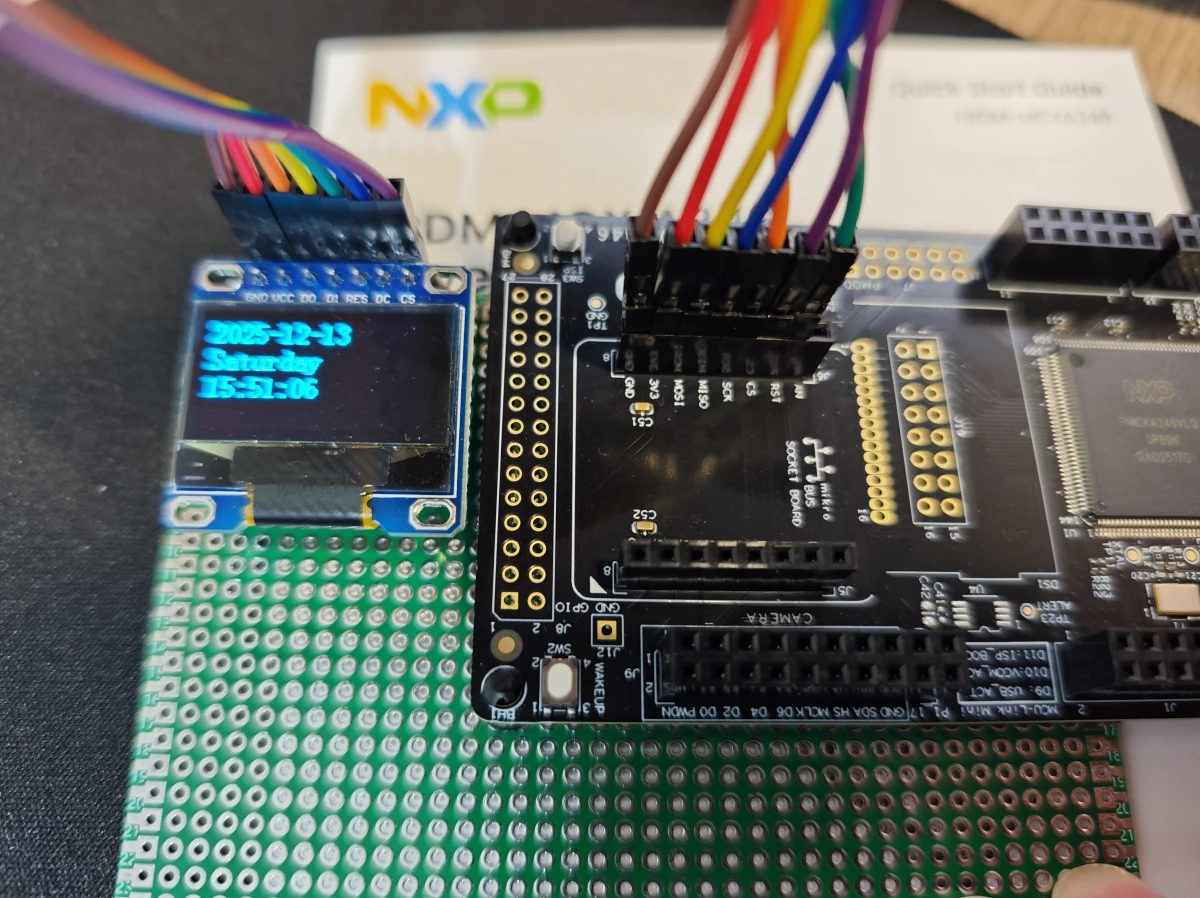
+### 4.外设接线
+
+oled接线如下:
+
+
+
+
+## 二、软件介绍
+###
+1.SPI接口使能
+
+在menuconfig配置中使能SPI,并使能LPSPI1,由于实验使用到了RTC,把RTC功能也使能上
+
+
+
+### 2.OLED代码移植修改
+####
+2.1代码移植
+
+将厂商提供的OLED文件夹移植到rtt工程中
+
+
+
+
+文件夹复制到工程后新建SConscript文件修改里面的内容,再执行scon指令时可自动将所有的.c,.h文件包含到keil工程中,修改内容如下:
+
+
+
+```c
+from building import *
+import os
+cwd = GetCurrentDir()
+CPPPATH = [cwd]
+src = Glob('*.c')
+group = DefineGroup('OLED', src, depend = [''], CPPPATH = CPPPATH)
+list = os.listdir(cwd)
+for item in list:
+ if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(cwd, item, 'SConscript')):
+ group = group + SConscript(os.path.join(item, 'SConscript'))
+Return('group')
+
+
+```
+
+####
+2.2代码修改
+
+1.修改oled.h的引脚宏定义
+
+```c
+//-----------------OLED引脚宏定义----------------
+#define BOARD_OLED_RST_PIN ((1*32)+7)
+#define BOARD_OLED_CLK_PIN ((1*32)+1)
+#define BOARD_OLED_DO_PIN ((1*32)+0)
+#define BOARD_OLED_CS_PIN ((1*32)+3)
+#define BOARD_OLED_DC_PIN ((1*32)+2)
+//-----------------OLED端口定义----------------
+#define OLED_SCLK_Clr() rt_pin_write(BOARD_OLED_CLK_PIN, PIN_LOW) //CLK
+#define OLED_SCLK_Set() rt_pin_write(BOARD_OLED_CLK_PIN, PIN_HIGH)
+#define OLED_SDIN_Clr() rt_pin_write(BOARD_OLED_DO_PIN, PIN_LOW) //D0
+#define OLED_SDIN_Set() rt_pin_write(BOARD_OLED_DO_PIN, PIN_HIGH)
+#define OLED_RST_Clr() rt_pin_write(BOARD_OLED_RST_PIN, PIN_LOW) //RES
+#define OLED_RST_Set() rt_pin_write(BOARD_OLED_RST_PIN, PIN_HIGH)
+#define OLED_DC_Clr() rt_pin_write(BOARD_OLED_DC_PIN, PIN_LOW) //DC
+#define OLED_DC_Set() rt_pin_write(BOARD_OLED_DC_PIN, PIN_HIGH)
+#define OLED_CS_Clr() rt_pin_write(BOARD_OLED_CS_PIN, PIN_LOW) //CS
+#define OLED_CS_Set() rt_pin_write(BOARD_OLED_CS_PIN, PIN_HIGH)
+
+
+
+```
+
+
+
+
+(2)修改oled初始化函数
+
+
+
+```c
+//OLED的初始化
+int oled_spi_device_init(void)
+{
+ int ret = 0;
+ struct rt_spi_device *spi_device = rt_malloc(sizeof(struct rt_spi_device));
+ if (!spi_device) return -1;
+ oled_gpio_init();
+ ret = rt_spi_bus_attach_device_cspin(spi_device, BOARD_OLED_DEVICE_NAME, "spi1", BOARD_OLED_CS_PIN, RT_NULL);
+ if (ret != RT_EOK) return -2;
+ OLED_RST_Set();
+ rt_thread_mdelay(100);
+ OLED_RST_Clr();//复位
+ rt_thread_mdelay(200);
+ OLED_RST_Set();
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0xAE,OLED_CMD);//--turn off oled panel
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0x00,OLED_CMD);//---set low column address
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0x10,OLED_CMD);//---set high column address
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0x40,OLED_CMD);//--set start line address Set Mapping RAM Display Start Line (0x00~0x3F)
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0x81,OLED_CMD);//--set contrast control register
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0xCF,OLED_CMD);// Set SEG Output Current Brightness
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0xA1,OLED_CMD);//--Set SEG/Column Mapping 0xa0左右反置 0xa1正常
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0xC8,OLED_CMD);//Set COM/Row Scan Direction 0xc0上下反置 0xc8正常
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0xA6,OLED_CMD);//--set normal display
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0xA8,OLED_CMD);//--set multiplex ratio(1 to 64)
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0x3f,OLED_CMD);//--1/64 duty
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0xD3,OLED_CMD);//-set display offset Shift Mapping RAM Counter (0x00~0x3F)
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0x00,OLED_CMD);//-not offset
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0xd5,OLED_CMD);//--set display clock divide ratio/oscillator frequency
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0x80,OLED_CMD);//--set divide ratio, Set Clock as 100 Frames/Sec
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0xD9,OLED_CMD);//--set pre-charge period
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0xF1,OLED_CMD);//Set Pre-Charge as 15 Clocks & Discharge as 1 Clock
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0xDA,OLED_CMD);//--set com pins hardware configuration
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0x12,OLED_CMD);
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0xDB,OLED_CMD);//--set vcomh
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0x40,OLED_CMD);//Set VCOM Deselect Level
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0x20,OLED_CMD);//-Set Page Addressing Mode (0x00/0x01/0x02)
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0x02,OLED_CMD);//
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0x8D,OLED_CMD);//--set Charge Pump enable/disable
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0x14,OLED_CMD);//--set(0x10) disable
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0xA4,OLED_CMD);// Disable Entire Display On (0xa4/0xa5)
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0xA6,OLED_CMD);// Disable Inverse Display On (0xa6/a7)
+ OLED_WR_Byte(0xAF,OLED_CMD);
+ OLED_Clear();
+ OLED_ColorTurn(0);//0正常显示,1 反色显示
+ OLED_DisplayTurn(0);//0正常显示 1 屏幕翻转显示
+ return 0;
+}
+INIT_APP_EXPORT(oled_spi_device_init);
+
+
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+3.main.c修改
+
+```c
+
+#include
+#include "drv_pin.h"
+#include "oled.h"
+#include "bmp.h"
+#define LED_PIN ((3*32)+18) /* Original LED pin */
+#define SW3_BUTTON_PIN ((0*32)+6) /* P0_6 button pin */
+static rt_bool_t led_state = RT_FALSE; /* Current LED state */
+//-----------------函数声明--------------------------
+void thread_led_entry(void *parameter);
+int thread_led_sample(void);
+void thread_get_rtc_time(void *parameter);
+int thread_rtc_sample(void);
+//---------------------------------------------------
+int main(void)
+{
+#if defined(__CC_ARM)
+ rt_kprintf("using armcc, version: %d\n", __ARMCC_VERSION);
+#elif defined(__clang__)
+ rt_kprintf("using armclang, version: %d\n", __ARMCC_VERSION);
+#elif defined(__ICCARM__)
+ rt_kprintf("using iccarm, version: %d\n", __VER__);
+#elif defined(__GNUC__)
+ rt_kprintf("using gcc, version: %d.%d\n", __GNUC__, __GNUC_MINOR__);
+#endif
+ rt_kprintf("FRDM-MCXA346-SPI-Test\r\n");
+ /* Configure LED pin as output */
+ rt_pin_mode(LED_PIN, PIN_MODE_OUTPUT);
+ rt_pin_write(LED_PIN, PIN_LOW);
+ thread_led_sample();
+ thread_rtc_sample();
+}
+void thread_led_entry(void *parameter)
+{
+ /* set LED1 pin mode to output */
+ rt_pin_mode(LED_PIN, PIN_MODE_OUTPUT);
+ while (1)
+ {
+ /* Toggle LED state */
+ led_state = !led_state;
+ rt_pin_write(LED_PIN, led_state ? PIN_HIGH : PIN_LOW);
+ rt_thread_mdelay(500);
+ }
+}
+int thread_led_sample(void)
+{
+ rt_thread_t led_thread;
+ led_thread = rt_thread_create("led_thread",
+ thread_led_entry,
+ RT_NULL,
+ 1024,
+ 15,
+ 20);
+ /* 如果获得线程控制块,启动这个线程 */
+ if (led_thread != RT_NULL)
+ rt_thread_startup(led_thread);
+ return RT_EOK;
+}
+void thread_get_rtc_time(void *parameter)
+{
+ time_t now = (time_t)0;
+ struct timeval tv = { 0 };
+ char date_buf[32];
+ char weekday_buf[32];
+ char time_buf[32];
+ struct tm tm_info;
+ static int colon_visible = 1;
+ static rt_tick_t last_tick = 0;
+ while(1)
+ {
+ gettimeofday(&tv, RT_NULL);
+ now = tv.tv_sec;
+ localtime_r(&now, &tm_info);
+ // 格式化日期: YYYY-MM-DD
+ strftime(date_buf, sizeof(date_buf), "%Y-%m-%d", &tm_info);
+ // 格式化完整星期
+ strftime(weekday_buf, sizeof(weekday_buf), "%A", &tm_info);
+ // 格式化时间(带闪烁的冒号)
+ if (rt_tick_get() - last_tick >= RT_TICK_PER_SECOND / 2)
+ {
+ last_tick = rt_tick_get();
+ colon_visible = !colon_visible;
+ }
+ if (colon_visible)
+ {
+ strftime(time_buf, sizeof(time_buf), "%H:%M:%S", &tm_info);
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ strftime(time_buf, sizeof(time_buf), "%H %M %S", &tm_info);
+ }
+ OLED_ShowString(0, 0, date_buf, 16);
+ OLED_ShowString(0, 16, weekday_buf, 16);
+ OLED_ShowString(0,32, time_buf, 16);
+ OLED_Refresh();
+ rt_thread_mdelay(100);
+ }
+}
+int thread_rtc_sample(void)
+{
+ rt_thread_t rtc_thread;
+ rtc_thread = rt_thread_create("rtc_thread",
+ thread_get_rtc_time,
+ RT_NULL,
+ 1024,
+ 15,
+ 20);
+ /* 如果获得线程控制块,启动这个线程 */
+ if (rtc_thread != RT_NULL)
+ rt_thread_startup(rtc_thread);
+ return RT_EOK;
+}
+
+
+```
+
+##
+下载验证
+
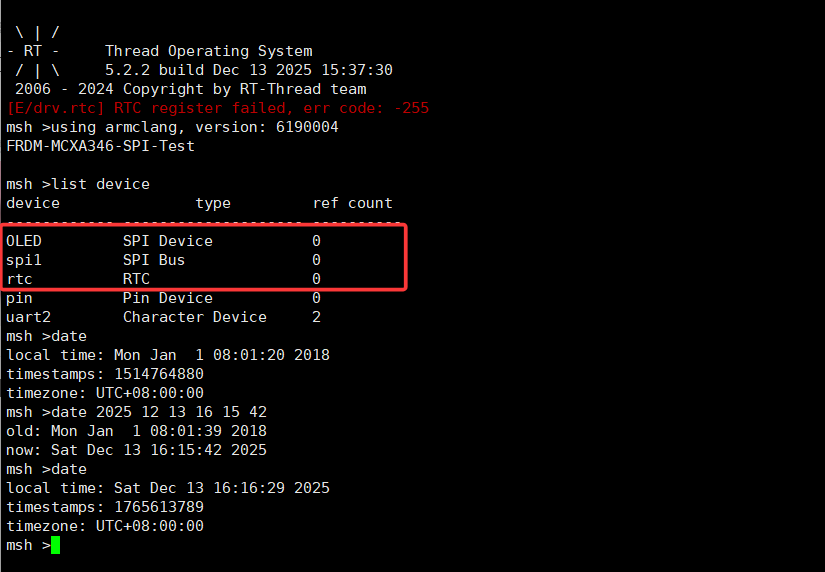
+1.使用list device查看msh注册的设备,oled,SPI,RTC均已经注册
+
+2.可使用date指令获取和修改当前rtc值
+
+
+
+
+3.运行演示
+B站链接:【rtthread基于NXP FRDM-MCXA346 LPSPI接口测验-哔哩哔哩】 [https://b23.tv/NQ5VtTP](https://b23.tv/NQ5VtTP)
+
+## 代码链接
+
+gittee链接:[https://gitee.com/tigreen/nxp-frdm-mcxa346.git](https://gitee.com/tigreen/nxp-frdm-mcxa346.git)
+
+
+
+## 总结
+
+NXP的FRDM-MCXA346开发板很小巧,开发方便,并且支持多种开发工具,兼容性很好,另外就是RTThread对该开发板的驱动兼容性很好,只需要调用对应的应用API即可进行开发使用,此外开发板的相关资料也不少,官方还提供教程文档,大大提升了开发进度。
+
+
+# 七、MCXA346上的PWM实践【陈子弈】
+## RT-Thread 基于 NXP FRDM-MCXA346 的 PWM 应用与呼吸灯实践教程
+## 一、PWM 的简单介绍
+脉冲宽度调制(英语:Pulse-width modulation,缩写:PWM),简称脉宽调制,是用脉冲来输出模拟信号的一种技术。一般变换后脉冲的周期固定,但脉冲的工作周期会依模拟信号的大小而改变。
+
+
+
+通过利用微处理器(本文基于 NXP FRDM-MCXA346)的数字输出对外设等控制的一种信号,它通过控制信号的脉冲宽度,实现对例如电流的精确控制。最常见的应用是用来调节亮度。
+
+
+
+## 二、PWM 的相关参数
++ 频率(Frequency, $f_{pwm}$)
+ - 定义:PWM 信号每秒重复的次数(Hz)。
+ - 关系式:f_pwm = timer_clock / (prescaler * (ARR + 1))
+ - 影响:决定输出周期与控制带宽。
++ 周期(Period, $T$)
+ - 定义:PWM 信号的一个完整周期,T = 1 / f_pwm。
+ - 单位:秒(s)、毫秒(ms)或微秒(μs)。
++ 占空比(Duty cycle, $D$)
+ - 定义:高电平时间与周期的比值,通常以百分比表示。
+ - 关系式:D = CCR / (ARR + 1)(CCR = 比较寄存器值)
+ - 设置:CCR = round(D * (ARR + 1))
++ 分辨率(Resolution)
+ - 描述:计数器能表示的不同占空比级数,通常为 ARR 的位宽。
+ - 计算:有效位数 ≈ log2(ARR + 1)。
++ 计时器时钟与预分频(timer_clock / prescaler)
+ - timer_clock:定时器输入时钟(来自系统时钟或总线时钟)。
+ - prescaler:将 timer_clock 降低以满足目标频率或提升计数范围。
+
+更多信息不再赘述,相信各位大佬一定有自己的见解。如果你第一次接触,也可在网络上搜索更多详解。
+
+
+
+## 三、关于 NXP FRDM-MCXA346
+NXP MCXA346 系列芯片被定位为 专为电机控制(如 PMSM、BLDC)优化的混合信号 MCU。这意味着其片上的 FlexPWM 不仅仅是一个通用的定时器,而是一个为高精度、快速控制回路设计的专业模块。
+
+
+
+该芯片在电机控制领域的优势主要体现在以下几个核心硬件协同上:
+
+
+
+### 1. FlexPWM
+FlexPWM 是该芯片的控制核心,专为高精度和快速响应设计,能够满足复杂电机控制算法对波形生成的严苛要求。
+
+
+
+### 2. 高级数学加速单元 (MAU) 协作
+MCXA346 内置了 MAU (Math Acceleration Unit),专门用于硬件加速电机控制中常用的数学运算(如三角函数、倒数、平方根等)。
+
+
+
++ 优势:MAU 可以极大地缩短控制算法(例如磁场定向控制 FOC)的执行时间,从而为 FlexPWM 留出更多的时间窗口来准备和加载新的 PWM 占空比,显著提升控制环路的频率和响应速度。
+
+## 四、实操部分
+我们这里通过示波器和呼吸灯现象来测试 PWM 输出
+
+### 一、首先,我们需要去官网下载相关环境
+#### 获取 SDK 与工具:
+这里给出官方的 Github:RT-Thread Releases。我们找到最新的版本来克隆。
+
+同时你需要 RT-Thread 的 env 工具(在官网下载,是一个压缩包,解压后双击 .bat 等待运行即可)。
+
+
+
+特别提醒:由于这一款 MCU 需要最新版本的 ARM 编译器,请务必提前更新你的 Arm-Keil 为最新版本(本教程环境:版本号为 5.43a,编译器版本号为 6.24)。
+
+
+
+#### 生成工程:
+解压后进入到 bsp\nxp\mcx\mcxa\frdm-mcxa346,在该路径打开 env 工具或是通过指令 cd 过去。
+
+输入 scons --target=mdk5(注意有空格)。如果是初次使用会提示缺少相关的包,按照文字提示输入 pkgs --update 下载依赖包,然后重新执行 scons --target=mdk5 就可以编译出 Keil 工程了。
+
+
+
+注意:路径不得有任何中文字符。
+
+
+
+#### 配置 Keil:
+打开 project.uvprojx 就是我们的工程了。
+
+在 Keil 官网 可以下载最新的芯片包。
+
+同时在“魔法棒”(Options for Target)里切换编译器版本到 6.24。并在 Utilities 界面点击 Settings -> Add,选中第一个 MCXA 的选项加入,然后按 OK 退出。
+
+
+
+#### 编译与烧录:
+尝试编译。板子开箱后上电会有一个默认程序,如果编译成功后有 6 个警告不影响。尝试烧录,即可烧录例程。
+
+
+
+### 二、FlexPWM 的配置与输出
+虽然目前还没有支持 RT-Thread Studio 图形化配置,但是我们可以通过 env 工具快速配置。
+
+
+
+1. 我们回到 env 环境工具中,输入 menuconfig,等待进入配置界面。
+2. 依次通过键盘上下方向键和回车选择:RT-Thread Components → Device Drivers → 选中 Using PWM device driver
+3. 通过 Backspace(或 ESC)键退回到主界面,进入:Hardware Drivers Config → Enable PWM → Enable eFlex PWM0(这里选择这个仅作示例)以及 Enable Timer → Enable Timer Enable CIMER0
+4. 按 ESC 退回界面,在保存界面保存并退出。
+5. 接下来可以编写代码。
+
+## 五、示例 PWM 代码
+```c
+// GPIO 口请根据盒内折页快速查阅 PWM 对应的可以复用的 GPIO,或者根据 NXP 官网的原理图快速定位
+#include
+#include "drv_pin.h"
+#include "fsl_common.h"
+#include "fsl_port.h"
+#include "fsl_pwm.h"
+#include "fsl_clock.h"
+#include "drv_pwm.h"
+/*
+ * 选定引脚:P3_0
+ * 对应芯片:PWM0_A0
+ * 即 Base=PWM0, Submodule=0, Channel=A
+ */
+#define PWM_BASE FLEXPWM0 /* PWM外设基地址:PWM0 */
+#define PWM_SUBMODULE kPWM_Module_0 /* 子模块:0 */
+#define PWM_CHANNEL kPWM_PwmA /* 通道:A (即 PWM0_A0) */
+#define PORT PORT3 /* 端口:PORT3 */
+#define PIN 0U /* 引脚号:0 */
+#define CLOCK_GATE kCLOCK_GateGPIO3 /* 端口时钟门控 */
+/*
+ * 在 NXP 芯片上,GPIO 需要切换到特定的 Alt 模式才能输出 PWM。
+ * 根据手册 https://www.nxp.com/doc/MCXAP144M240F60RM,PWM 功能通常是 Alt 5 。
+ */
+#define PIN_ALT kPORT_MuxAlt5
+#define PWM_CLK_FREQ CLOCK_GetFreq(kCLOCK_BusClk) /* 获取总线时钟频率 */
+/* 呼吸灯参数 */
+#define SPEED_MS 20 /* 每次变化的延时 (毫秒) */
+#define STEP_VALUE 2 /* 步进值:每次变化的幅度 */
+#define LED_PIN ((3*32)+19)
+#define BUTTON_PIN ((1*32)+7)
+static rt_bool_t led_state = RT_FALSE;
+void button_irq_callback(void *args)
+{
+ rt_kprintf("SW2 pressed\n");
+}
+//--------------------------PWM-----------------------------//
+/* 初始化 PWM 的底层函数 */
+void init_pwm_hardware(void)
+{
+ pwm_config_t pwmConfig;
+ pwm_signal_param_t pwmSignal[1];
+ status_t status;
+ /* 开启端口时钟 */
+ CLOCK_EnableClock(CLOCK_GATE);
+ /* 配置引脚复用:把 P3_0 切换到 Alt 模式 */
+ PORT_SetPinMux(PORT, PIN, PIN_ALT);
+ /* 获取默认配置 */
+ PWM_GetDefaultConfig(&pwmConfig);
+ /* 使用立即加载模式 */
+ pwmConfig.reloadLogic = kPWM_ReloadImmediate;
+ /* 初始化 PWM */
+ if (PWM_Init(PWM_BASE, PWM_SUBMODULE, &pwmConfig) == kStatus_Fail)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("Error: PWM Init failed\n");
+ return;
+ }
+ /* 配置具体的 PWM Channel 参数 */
+ pwmSignal[0].pwmChannel = PWM_CHANNEL;
+ pwmSignal[0].level = kPWM_HighTrue; /* 高电平点亮 */
+ pwmSignal[0].dutyCyclePercent = 0; /* 初始亮度 0 */
+ pwmSignal[0].deadtimeValue = 0;
+ pwmSignal[0].faultState = kPWM_PwmFaultState0;
+ pwmSignal[0].pwmchannelenable = true;
+ /* 设置 PWM 波形:频率 1kHz */
+ status = PWM_SetupPwm(PWM_BASE, PWM_SUBMODULE, pwmSignal, 1, kPWM_SignedCenterAligned, 1000U, PWM_CLK_FREQ);
+ if (status != kStatus_Success)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("Error: PWM Setup failed\n");
+ return;
+ }
+ PWM_SetPwmLdok(PWM_BASE, 1U << PWM_SUBMODULE, true);
+ /* 启动 PWM 定时器 */
+ PWM_StartTimer(PWM_BASE, 1U << PWM_SUBMODULE);
+ rt_kprintf("PWM Hardware Initialized on P3_0.\n");
+}
+//----------------------------------------------------------------//
+int main(void)
+{
+ rt_kprintf("Starting Breathing LED Demo on P3_0...\r\n");
+ /* 初始化底层 PWM */
+ init_pwm_hardware();
+ int duty_cycle = 0;
+ int direction = 1;
+#if defined(__CC_ARM)
+ rt_kprintf("using armcc, version: %d\n", __ARMCC_VERSION);
+#elif defined(__clang__)
+ rt_kprintf("using armclang, version: %d\n", __ARMCC_VERSION);
+#elif defined(__ICCARM__)
+ rt_kprintf("using iccarm, version: %d\n", __VER__);
+#elif defined(__GNUC__)
+ rt_kprintf("using gcc, version: %d.%d\n", __GNUC__, __GNUC_MINOR__);
+#endif
+ rt_kprintf("FRDM-MCXA346\r\n");
+ /* Configure LED pin as output */
+ // rt_pin_mode(LED_PIN, PIN_MODE_OUTPUT);
+ // rt_pin_write(LED_PIN, PIN_LOW);
+ /* Configure button pin as input with pull-up */
+ rt_pin_mode(BUTTON_PIN, PIN_MODE_INPUT_PULLUP);
+ /* Attach interrupt to button pin */
+ rt_pin_attach_irq(BUTTON_PIN, PIN_IRQ_MODE_FALLING, button_irq_callback, RT_NULL);
+ rt_pin_irq_enable(BUTTON_PIN, PIN_IRQ_ENABLE);
+ while (1)
+ {
+ /* Toggle LED state */
+ // led_state = !led_state;
+ // rt_pin_write(LED_PIN, led_state ? PIN_HIGH : PIN_LOW);
+ // rt_thread_mdelay(500);
+ duty_cycle += (direction * STEP_VALUE);
+ if (duty_cycle >= 100)
+ {
+ duty_cycle = 100;
+ direction = -1;
+ }
+ else if (duty_cycle <= 0)
+ {
+ duty_cycle = 0;
+ direction = 1;
+ }
+ /* 更新占空比 */
+ PWM_UpdatePwmDutycycle(PWM_BASE,
+ PWM_SUBMODULE,
+ PWM_CHANNEL,
+ kPWM_SignedCenterAligned,
+ (uint8_t)duty_cycle);
+ /* 必须设置 LDOK 才能生效 */
+ PWM_SetPwmLdok(PWM_BASE, 1U << PWM_SUBMODULE, true);
+ rt_thread_mdelay(SPEED_MS);
+ }
+}
+
+
+
+```
+
+
+
+# 八、MCXA346上的 IIC(硬件) 实践【李金磊&王丰】
+## 【FRDM-MCXA346 开发板】硬件IIC【李金磊】
+本文介绍了恩智浦 FRDM-MCXA346 开发板使能硬件 IIC 并完成工程测试的项目设计。
+
+
+
+## 项目介绍
++ 环境搭建:拉取 rt-thread 官方源码、下载并安装 rt-thread-env-tool 等;
++ 工程配置:使用 ENV 图形化功能配置工具,使能 IIC;
++ 工程编译:打包并编译工程,生成对应的 Keil 程序,完成工程编译;
++ 固件上传:关键驱动代码调试及固件上传;
++ 效果演示:串口登录 RT-Thread 终端并打印 IIC 设备地址。
+
+## 项目方案
+包括 menuconfig 工程配置、工程编译、RTC 驱动配置、固件上传等流程。
+
+
+
+## 环境搭建
+拉取 rt-thread 官方源码;[https://gitee.com/rtthread/rt-thread](https://gitee.com/rtthread/rt-thread)
+
+下载并安装 rt-thread-env-tool ;[https://gitee.com/rtthread/rt-thread](https://gitee.com/rtthread/rt-thread)
+
+详见: 【FRDM-MCXA346 开发板】介绍、环境搭建、工程测试 .[https://club.rt-thread.org/ask/article/0e048b18838029d1.html](https://club.rt-thread.org/ask/article/0e048b18838029d1.html)
+
+
+
+## 工程配置
+在前面完成环境搭建的基础上对 RTC 功能进行开启和配置。
+
+
+
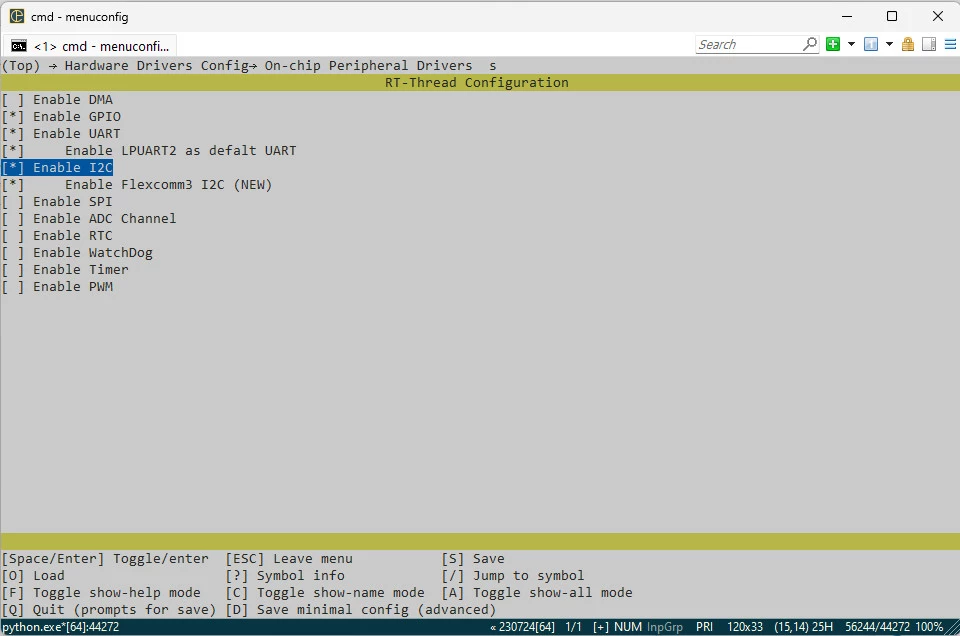
++ 进入目标开发板 BSP 路径 ...\rt-thread\bsp\nxp\mcx\mcxa\frdm-mcxa346 ;
++ 在空白处右键,选择 ConEmu Here 打开 Env 工具;
++ 执行 menuconfig 指令,进入图形化配置界面;
++ 依次进入 Hardware Drivers Config → On-chip Peripheral Drivers → Enable I2C ;
++ 回车,使能 IIC 功能;
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
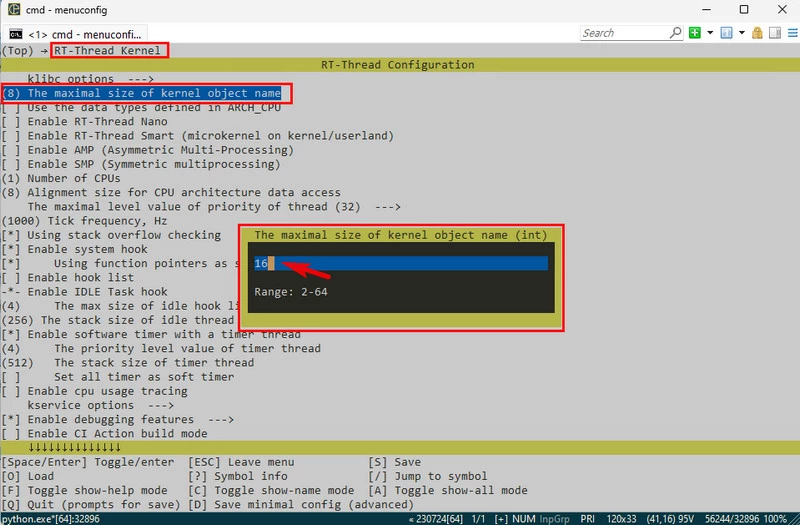
++ 进入 RT-Thread Kernel - (8) The maximal size of kernel object name 选项,将数值修改为 16;
+
+
+
+
+
+
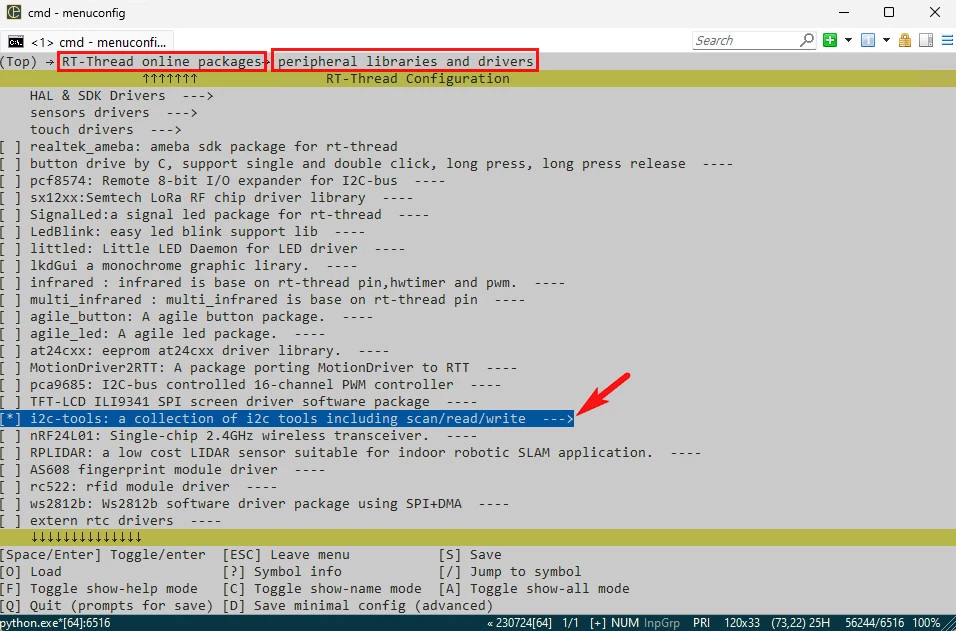
++ 进入 RT-Thread online packages - peripheral libraries and drivers - i2c-tools,使能 i2c-tools 软件包;
+
+
+
+
+
+
+按 Q 键保存并退出图形化配置界面;
+
+## 工程编译
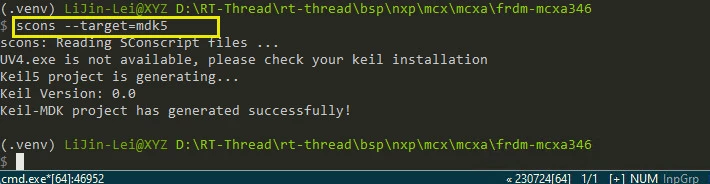
++ 运行指令 pkgs --update 使软件包配置生效;
++ 运行 scons --target=mdk5 指令,重新编译固件;
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## 固件上传
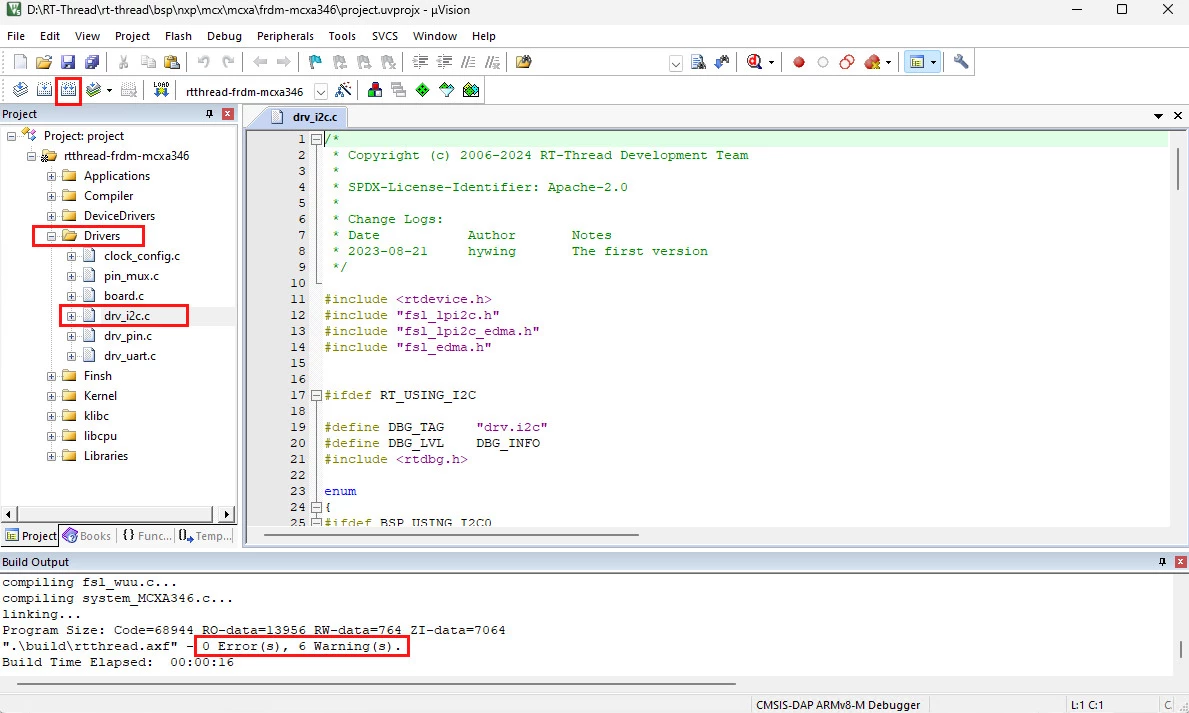
++ 双击 project.uvprojx 文件,使用 Keil 打开工程,可获取 IIC 驱动文件;
+
+
+
+
+
+
++ 重新构建工程,确保 0 报错。
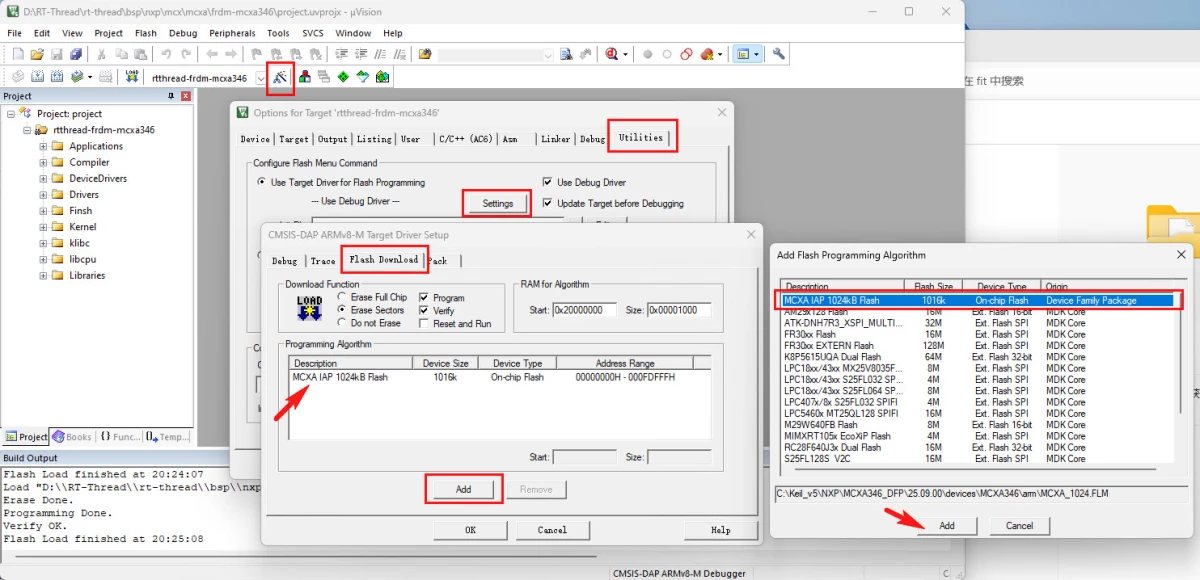
++ 点击魔术棒,配置调试器烧录选项,Utilities - Setting - Flash Download - Add 添加 MCXA IAP Flash ;
+
+
+
+
+
+
++ 点击 Download 按钮上传固件至开发板。
+
+## 测试 IIC
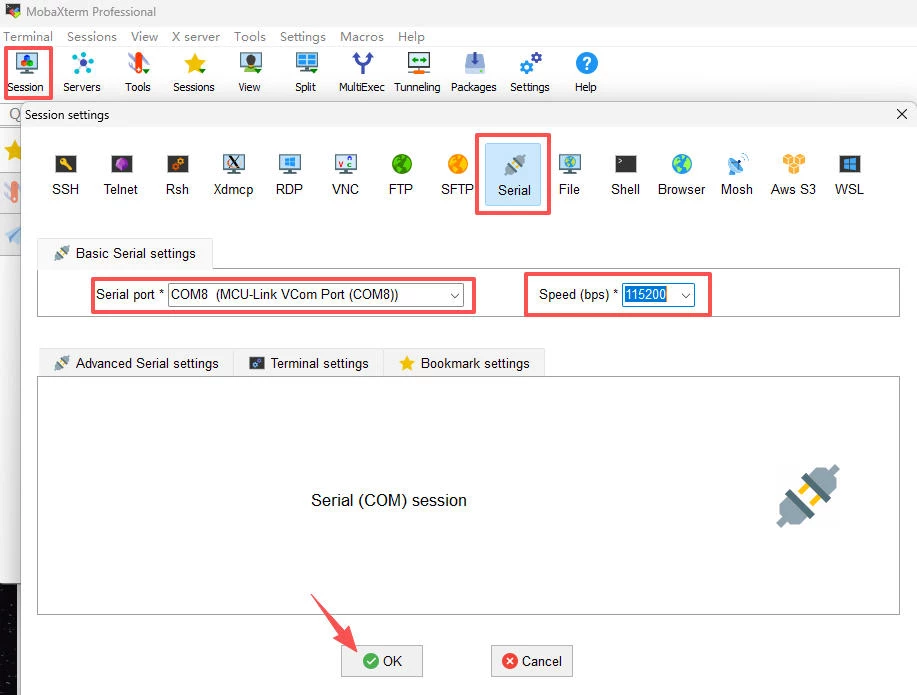
++ 运行 MobaXterm 软件,新建串口连接,配置设备端口和波特率 115200 bps
+
+
+
+
+
+
++ 连接后短按 RESET 键,输出 RT-Thread 固件信息;
++ 输入 help 指令获取 RT-Thread shell commands 信息;
++ 输入 i2c 获取相应的指令帮助,如 i2c scan i2c2 扫描 i2c 设备并获取地址;
+
+
+
+
+
+
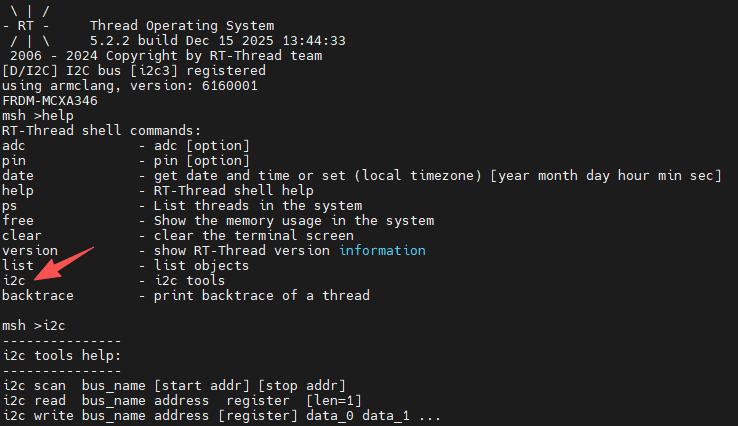
+## 工程测试
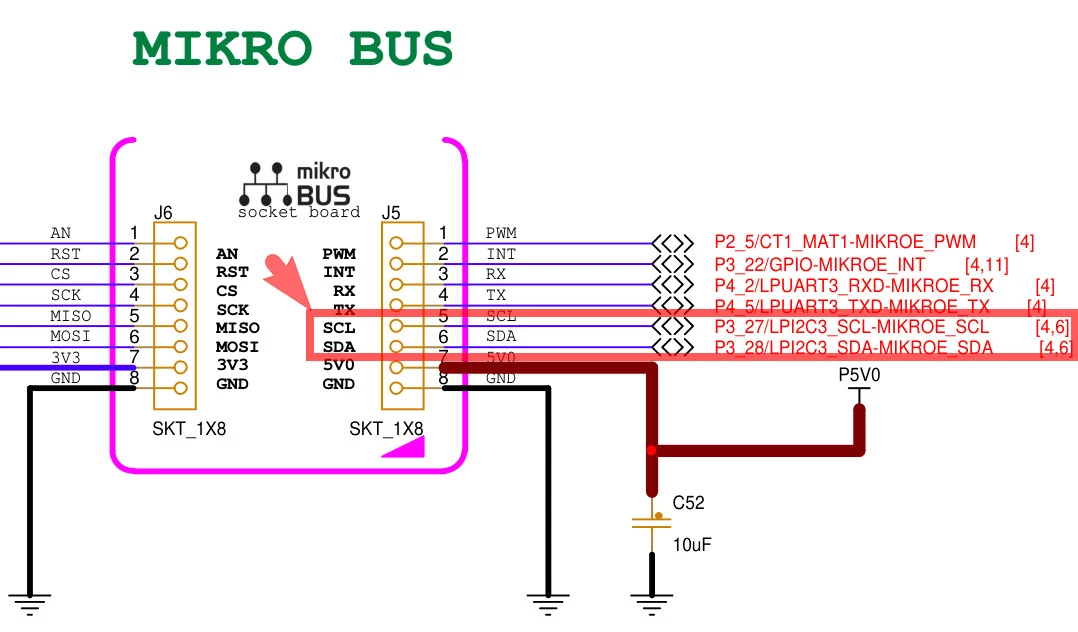
+### 硬件连接
+由原理图可知,板载 IIC3 对应接口位于 mikro BUS 的 SCL/SDA 引脚。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
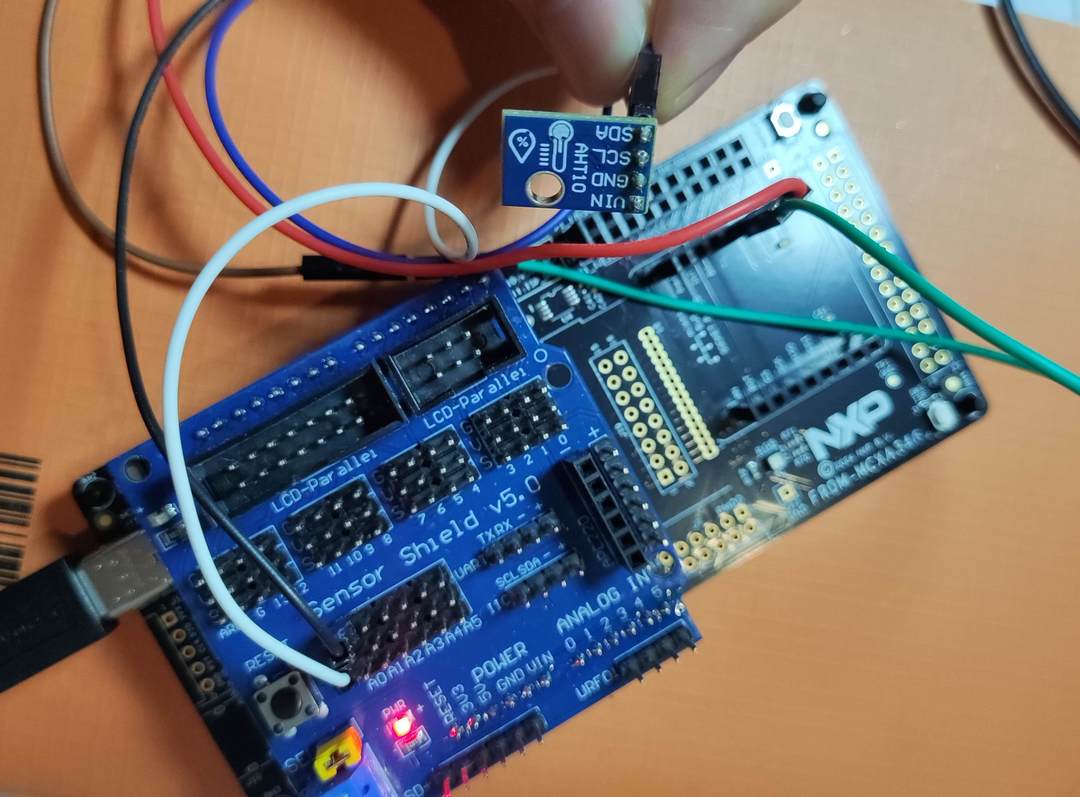
+将 IIC 通信设备连接至该引脚,如 AHT10、OLED、BMP280 等。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### 代码
+新建 ./Applications/iic_scan.c 文件,并添加如下代码
+
+```c
+#include
+#include
+// 扫描I2C设备函数
+static void i2c_scan(void)
+{
+ rt_uint8_t data;
+ struct rt_i2c_msg msg;
+ struct rt_i2c_bus_device *bus = rt_i2c_bus_device_find("i2c3");
+ if (!bus)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("Cannot find i2c3 bus!\n");
+ return;
+ }
+ rt_kprintf("Scanning I2C bus (i2c3) for devices...\n");
+ rt_kprintf(" 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F\n");
+ for (int i = 0; i < 0x80; i += 16)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("%02x: ", i);
+ for (int j = 0; j < 16; j++)
+ {
+ uint8_t addr = i + j;
+ // 跳过保留地址
+ if (addr == 0x00 || addr == 0x01 ||
+ addr == 0x02 || addr == 0x03 ||
+ addr >= 0x78) // 保留地址
+ {
+ rt_kprintf(" ");
+ continue;
+ }
+ msg.addr = addr;
+ msg.flags = RT_I2C_RD;
+ msg.buf = &data;
+ msg.len = 1;
+ if (rt_i2c_transfer(bus, &msg, 1) == 1)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("%02x ", addr);
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("-- ");
+ }
+ }
+ rt_kprintf("\n");
+ }
+}
+// MSH命令
+MSH_CMD_EXPORT(i2c_scan, scan i2c devices);
+
+
+
+```
+
+
+
+保存代码,重新编译固件并上传。
+
+
+
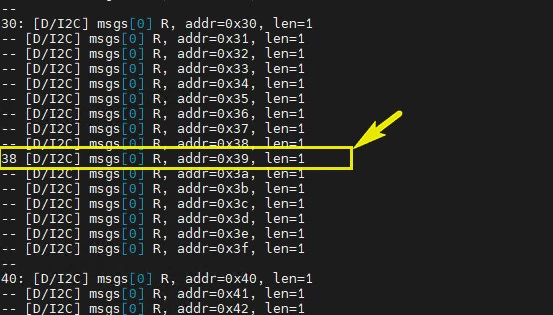
+### 效果
++ 使用 MobaXterm 软件新建串口连接,短按 RESET 键弹出固件信息;
++ 终端输入 iic_scan 打印设备对应的 iic 地址,如 0x38 ;
+
+
+
+
+
+
+总结
+
+本文介绍了恩智浦 FRDM-MCXA346 开发板使能硬件 IIC 并完成相关工程测试的项目设计,为相关产品的快速开发和应用设计提供了参考。
+
+
+
+## 【FRDM-MCXA346 开发板】硬件IIC测试【王丰】
+## 1. 测试目的
+本测试旨在验证NXP MCXA346开发板上RT-Thread系统中LPI2C3总线设备驱动的功能,确保I2C设备(MPU6050)能够正常初始化、读取数据并通过串口打印输出。
+
+
+
+## 2. 测试环境
+### 2.1 硬件环境
++ 开发板:NXP FRDM-MCXA346
++ MCU型号:MCXA346 (Cortex-M33)
++ I2C从设备:MPU6050 六轴陀螺仪加速度计
++ I2C总线:LPI2C3
++ 引脚连接:
+ - SCL:P3_27 (LPI2C3_SCL)
+ - SDA:P3_28 (LPI2C3_SDA)
++ 电源:3.3V供电
++ LED指示:P3_18 (红色LED)
++ 按键输入:P1_7
+
+### 2.2 软件环境
++ 操作系统:RT-Thread 5.x
++ 编译工具链:GCC ARM / Keil MDK / IAR EWARM
++ I2C驱动框架:RT-Thread设备驱动框架 (基于NXP LPI2C HAL)
++ 调试工具:串口终端 (115200 8N1)
+
+RT-Thread的I2C驱动采用分层架构,包括Driver层和HAL层,支持标准的设备驱动框架调用方式。
+
+
+
+### 2.3 MPU6050 配置参数
++ I2C地址:0x68 (AD0=GND) 或 0x69 (AD0=VCC)
++ 加速度量程:±4g (灵敏度 8192 LSB/g)
++ 陀螺仪量程:±1000 dps (灵敏度 32.8 LSB/dps)
++ 采样率:125Hz (1kHz / 8)
++ 数字低通滤波:44Hz
+
+## 3. 测试准备
+### 3.1 配置I2C设备
+在menuconfig中使能I2C设备驱动:
+
+```c
+RT-Thread Components → Device Drivers → Using I2C device drivers
+Hardware Drivers Config → On-chip Peripheral Drivers → Enable LPI2C3
+
+```
+
+
+
+NXP env配置
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### 3.2 初始化流程
+I2C设备的初始化需要完成以下步骤:
+
+
+
+1. 引脚复用配置(P3_27/P3_28 配置为 LPI2C3 功能)
+2. 注册I2C总线设备(驱动层自动注册为 i2c3)
+3. 配置I2C时钟频率(标准模式 100kHz)
+4. 扫描从设备(0x68/0x69 地址)
+5. 初始化MPU6050(配置量程、滤波器、采样率)
+
+### 3.3 代码准备
+```c
+/* 硬件引脚定义 */
+#define LED_PIN ((3*32)+18) /* P3_18 红色 LED */
+#define BUTTON_PIN ((1*32)+7) /* P1_7 按键 */
+#define I2C_BUS_NAME "i2c3" /* LPI2C3 总线 */
+/* I2C3 引脚定义 */
+#define I2C3_SCL_PIN ((3 * 32) + 27) /* P3_27 -> LPI2C3_SCL */
+#define I2C3_SDA_PIN ((3 * 32) + 28) /* P3_28 -> LPI2C3_SDA */
+/* MPU6050 灵敏度常量 */
+#define MPU6050_ACCEL_LSB_PER_G 8192 /* ±4g 量程 */
+#define MPU6050_GYRO_LSB_PER_DPS_X10 328 /* ±1000dps 量程 */
+#define MPU6050_TEMP_DIVISOR 340
+#define MPU6050_TEMP_OFFSET_CENTI 3653
+
+
+```
+
+## 4. 测试用例
+### 4.1 I2C总线状态检测
+测试目的:验证I2C总线引脚电平状态
+
+
+
+测试命令:
+
+```c
+msh> i2c3_dump
+
+```
+
+
+
+测试代码:
+
+```c
+static void i2c3_dump_pin_level(const char *tag)
+{
+ rt_pin_mode(I2C3_SCL_PIN, PIN_MODE_INPUT_PULLUP);
+ rt_pin_mode(I2C3_SDA_PIN, PIN_MODE_INPUT_PULLUP);
+ rt_hw_us_delay(10);
+ rt_kprintf("I2C3 pin level%s%s%s: SCL=%d SDA=%d\n",
+ (tag != RT_NULL) ? " [" : "",
+ (tag != RT_NULL) ? tag : "",
+ (tag != RT_NULL) ? "]" : "",
+ rt_pin_read(I2C3_SCL_PIN),
+ rt_pin_read(I2C3_SDA_PIN));
+}
+static void i2c3_dump(void)
+{
+ i2c3_dump_pin_level("cli");
+}
+MSH_CMD_EXPORT(i2c3_dump, dump I2C3 SCL/SDA levels);
+
+
+
+```
+
+预期输出:
+
+```c
+I2C3 pin level [cli]: SCL=1 SDA=1
+
+```
+
+
+
+### 4.2 I2C设备扫描
+测试目的:扫描I2C总线上的设备地址,识别MPU6050
+
+
+
+测试命令:
+
+```c
+msh> i2c3_scan
+
+```
+
+
+
+测试代码:
+
+```c
+static void i2c3_scan(void)
+{
+ struct rt_i2c_bus_device *bus;
+ int found = 0;
+ rt_kprintf("\n=== Scanning I2C3 Bus ===\n\n");
+ bus = rt_i2c_bus_device_find("i2c3");
+ if (!bus)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("Error: i2c3 not found!\n");
+ return;
+ }
+ const rt_uint8_t candidates[] = {0x68, 0x69};
+ for (rt_size_t i = 0; i < sizeof(candidates); i++)
+ {
+ rt_uint8_t addr = candidates[i];
+ rt_uint8_t id = i2c_read_byte(addr, 0x75); // WHO_AM_I 寄存器
+ if (id == 0x68 || id == 0x70)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("I2C device (MPU6050/6500) found at 0x%02X (WHO_AM_I=0x%02X)\n",
+ addr, id);
+ found++;
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("I2C 0x%02X not MPU6050 (WHO_AM_I=0x%02X)\n", addr, id);
+ }
+ rt_thread_mdelay(2);
+ }
+ rt_kprintf("\n=== Scan Complete ===\n");
+ rt_kprintf("Found %d device(s)\n\n", found);
+}
+MSH_CMD_EXPORT(i2c3_scan, scan i2c3 bus for devices);
+
+
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+预期输出:
+
+```c
+=== Scanning I2C3 Bus ===
+I2C device (MPU6050/6500) found at 0x68 (WHO_AM_I=0x68)
+=== Scan Complete ===
+Found 1 device(s)
+
+
+
+```
+
+
+
+### 4.3 MPU6050初始化
+测试目的:配置MPU6050寄存器
+
+
+
+测试命令:
+
+```c
+msh> mpu_init
+
+```
+
+
+
+测试代码:
+
+```c
+static rt_bool_t mpu6050_init_addr(rt_uint8_t addr)
+{
+ delay_ms(10);
+ // 读取WHO_AM_I寄存器验证设备
+ rt_uint8_t id = i2c_read_byte(addr, 0x75);
+ rt_kprintf("MPU6050 WHO_AM_I = 0x%02X (expect 0x68 or 0x70)\n", id);
+ if (!(id == 0x68 || id == 0x70))
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("MPU6050 WHO_AM_I mismatch!\n");
+ return RT_FALSE;
+ }
+ // 解除休眠 (PWR_MGMT_1 = 0x00)
+ rt_kprintf("MPU6050 wake up...\n");
+ if (i2c_write_byte(addr, 0x6B, 0x00) != RT_EOK)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("MPU6050 wake up failed!\n");
+ return RT_FALSE;
+ }
+ delay_ms(10);
+ // 采样分频 (SMPLRT_DIV = 7)
+ rt_kprintf("MPU6050 set sample rate divider...\n");
+ (void)i2c_write_byte(addr, 0x19, 0x07);
+ // 数字低通滤波 (CONFIG = 0x03)
+ rt_kprintf("MPU6050 set DLPF...\n");
+ (void)i2c_write_byte(addr, 0x1A, 0x03);
+ // 陀螺仪量程:±1000dps (GYRO_CONFIG = 0x10)
+ rt_kprintf("MPU6050 set gyro range to ±1000dps...\n");
+ if (i2c_write_byte(addr, 0x1B, 0x10) != RT_EOK)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("MPU6050 set gyro range failed!\n");
+ return RT_FALSE;
+ }
+ // 加速度量程:±4g (ACCEL_CONFIG = 0x08)
+ rt_kprintf("MPU6050 set accel range to ±4g...\n");
+ if (i2c_write_byte(addr, 0x1C, 0x08) != RT_EOK)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("MPU6050 set accel range failed!\n");
+ return RT_FALSE;
+ }
+ delay_ms(50);
+ // 验证配置
+ rt_uint8_t gyro_cfg = i2c_read_byte(addr, 0x1B);
+ rt_uint8_t accel_cfg = i2c_read_byte(addr, 0x1C);
+ rt_kprintf("MPU6050 GYRO_CONFIG = 0x%02X (expect 0x10)\n", gyro_cfg);
+ rt_kprintf("MPU6050 ACCEL_CONFIG = 0x%02X (expect 0x08)\n", accel_cfg);
+ if (gyro_cfg != 0x10 || accel_cfg != 0x08)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("MPU6050 config verify failed!\n");
+ return RT_FALSE;
+ }
+ mpu6050_addr = addr;
+ rt_kprintf("MPU6050 init success at 0x%02X\n", addr);
+ return RT_TRUE;
+}
+static void mpu_init(void)
+{
+ rt_uint8_t addr = 0x00;
+ if (i2c_found_num > 0)
+ {
+ addr = i2c_found_addrs[0];
+ }
+ if (addr == 0x00)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("MPU6050 not found\n");
+ return;
+ }
+ if (mpu6050_init_addr(addr))
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("MPU6050 init ok at 0x%02X\n", addr);
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("MPU6050 init fail at 0x%02X\n", addr);
+ }
+}
+MSH_CMD_EXPORT(mpu_init, init mpu6050 on I2C bus);
+
+
+```
+
+预期输出:
+
+```c
+MPU6050 WHO_AM_I = 0x68 (expect 0x68 or 0x70)
+MPU6050 wake up...
+MPU6050 set sample rate divider...
+MPU6050 set DLPF...
+MPU6050 set gyro range to ±1000dps...
+MPU6050 set accel range to ±4g...
+MPU6050 GYRO_CONFIG = 0x10 (expect 0x10)
+MPU6050 ACCEL_CONFIG = 0x08 (expect 0x08)
+MPU6050 init success at 0x68
+
+
+```
+
+
+
+### 4.4 MPU6050数据读取
+测试目的:读取加速度、陀螺仪、温度数据并串口打印
+
+
+
+测试命令:
+
+```c
+msh> mpu_read
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+测试代码:
+
+```c
+static rt_err_t mpu6050_read_all(rt_int16_t accel[3], rt_int16_t gyro[3], rt_int16_t *temp)
+{
+ if (mpu6050_addr == 0x00)
+ {
+ return -RT_ERROR;
+ }
+ // 从0x3B寄存器开始连续读取14字节
+ rt_uint8_t buf[14];
+ if (i2c_read_bytes(mpu6050_addr, 0x3B, buf, sizeof(buf)) != RT_EOK)
+ {
+ return -RT_ERROR;
+ }
+ // 解析数据(大端序)
+ accel[0] = (rt_int16_t)((buf[0] << 8) | buf[1]); // ACCEL_XOUT
+ accel[1] = (rt_int16_t)((buf[2] << 8) | buf[3]); // ACCEL_YOUT
+ accel[2] = (rt_int16_t)((buf[4] << 8) | buf[5]); // ACCEL_ZOUT
+ *temp = (rt_int16_t)((buf[6] << 8) | buf[7]); // TEMP_OUT
+ gyro[0] = (rt_int16_t)((buf[8] << 8) | buf[9]); // GYRO_XOUT
+ gyro[1] = (rt_int16_t)((buf[10] << 8) | buf[11]); // GYRO_YOUT
+ gyro[2] = (rt_int16_t)((buf[12] << 8) | buf[13]); // GYRO_ZOUT
+ return RT_EOK;
+}
+static void mpu_read(void)
+{
+ rt_int16_t accel[3] = {0};
+ rt_int16_t gyro[3] = {0};
+ rt_int16_t temp = 0;
+ if (mpu6050_read_all(accel, gyro, &temp) == RT_EOK)
+ {
+ // 打印原始值
+ rt_kprintf("MPU6050 Raw: A[%6d %6d %6d] G[%6d %6d %6d] T[%6d]\n",
+ accel[0], accel[1], accel[2],
+ gyro[0], gyro[1], gyro[2],
+ temp);
+ // 转换为物理单位
+ rt_int32_t ax_mg = ((rt_int32_t)accel[0] * 1000) / MPU6050_ACCEL_LSB_PER_G;
+ rt_int32_t ay_mg = ((rt_int32_t)accel[1] * 1000) / MPU6050_ACCEL_LSB_PER_G;
+ rt_int32_t az_mg = ((rt_int32_t)accel[2] * 1000) / MPU6050_ACCEL_LSB_PER_G;
+ rt_int32_t gx_mdps = ((rt_int32_t)gyro[0] * 10000) / MPU6050_GYRO_LSB_PER_DPS_X10;
+ rt_int32_t gy_mdps = ((rt_int32_t)gyro[1] * 10000) / MPU6050_GYRO_LSB_PER_DPS_X10;
+ rt_int32_t gz_mdps = ((rt_int32_t)gyro[2] * 10000) / MPU6050_GYRO_LSB_PER_DPS_X10;
+ rt_int32_t t_centi = ((rt_int32_t)temp * 100) / MPU6050_TEMP_DIVISOR + MPU6050_TEMP_OFFSET_CENTI;
+ // 打印物理值
+ rt_kprintf(" Phy: A[%4ld.%03ld %4ld.%03ld %4ld.%03ld]g ",
+ ax_mg / 1000, (ax_mg >= 0 ? ax_mg : -ax_mg) % 1000,
+ ay_mg / 1000, (ay_mg >= 0 ? ay_mg : -ay_mg) % 1000,
+ az_mg / 1000, (az_mg >= 0 ? az_mg : -az_mg) % 1000);
+ rt_kprintf("G[%4ld.%02ld %4ld.%02ld %4ld.%02ld]dps ",
+ gx_mdps / 100, (gx_mdps >= 0 ? gx_mdps : -gx_mdps) % 100,
+ gy_mdps / 100, (gy_mdps >= 0 ? gy_mdps : -gy_mdps) % 100,
+ gz_mdps / 100, (gz_mdps >= 0 ? gz_mdps : -gz_mdps) % 100);
+ rt_kprintf("T[%ld.%02ld]C\n",
+ t_centi / 100, t_centi % 100);
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("MPU6050 read failed\n");
+ }
+}
+MSH_CMD_EXPORT(mpu_read, read mpu6050 data);
+```
+
+
+
+预期输出:
+
+```c
+MPU6050 Raw: A[ -256 1024 16384] G[ 12 -34 56] T[ 8192]
+ Phy: A[ -0.031 0.125 2.000]g G[ 0.37 -1.04 1.71]dps T[24.09]C
+```
+
+
+
+4.5 I2C底层读写函数
+
+测试目的:提供I2C读写接口
+
+
+
+测试代码:
+
+```c
+static rt_err_t i2c_write_byte(rt_uint8_t dev_addr, rt_uint8_t reg_addr, rt_uint8_t data)
+{
+ struct rt_i2c_bus_device *bus = i2c_bus_get();
+ if (bus == RT_NULL)
+ {
+ return -RT_ERROR;
+ }
+ rt_uint8_t tx[2] = {reg_addr, data};
+ struct rt_i2c_msg msg;
+ msg.addr = dev_addr;
+ msg.flags = RT_I2C_WR;
+ msg.buf = tx;
+ msg.len = sizeof(tx);
+ rt_int32_t ret = rt_i2c_transfer(bus, &msg, 1);
+ if (ret != 1)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("I2C[%s] WR fail dev=0x%02X reg=0x%02X data=0x%02X ret=%d\n",
+ active_i2c_bus_name, dev_addr, reg_addr, data, ret);
+ return -RT_ERROR;
+ }
+ return RT_EOK;
+}
+static rt_err_t i2c_read_bytes(rt_uint8_t dev_addr, rt_uint8_t reg_addr, rt_uint8_t *buf, rt_uint8_t len)
+{
+ struct rt_i2c_bus_device *bus = i2c_bus_get();
+ if (bus == RT_NULL)
+ {
+ return -RT_ERROR;
+ }
+ if (buf == RT_NULL || len == 0)
+ {
+ return -RT_ERROR;
+ }
+ struct rt_i2c_msg msgs[2];
+ msgs[0].addr = dev_addr;
+ msgs[0].flags = RT_I2C_WR;
+ msgs[0].buf = ®_addr;
+ msgs[0].len = 1;
+ msgs[1].addr = dev_addr;
+ msgs[1].flags = RT_I2C_RD;
+ msgs[1].buf = buf;
+ msgs[1].len = len;
+ rt_int32_t ret = rt_i2c_transfer(bus, msgs, 2);
+ if (ret != 2)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("I2C[%s] RD fail dev=0x%02X reg=0x%02X len=%d ret=%d\n",
+ active_i2c_bus_name, dev_addr, reg_addr, len, ret);
+ return -RT_ERROR;
+ }
+ return RT_EOK;
+}
+static rt_uint8_t i2c_read_byte(rt_uint8_t dev_addr, rt_uint8_t reg_addr)
+{
+ rt_uint8_t v = 0;
+ if (i2c_read_bytes(dev_addr, reg_addr, &v, 1) != RT_EOK)
+ {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ return v;
+}
+```
+
+
+
+## 5. 测试步骤
+### 5.1 硬件连接
+1. 连接MPU6050到开发板:
++ VCC → 3.3V
++ GND → GND
++ SCL → P3_27
++ SDA → P3_28
++ AD0 → GND (地址0x68)
+2. 安装上拉电阻:
++ 4.7kΩ 从 VCC 到 SCL
++ 4.7kΩ 从 VCC 到 SDA
+
+### 5.2 编译下载
+1. 编译项目:
+
+```c
+scons --target=mdk5 # 生成 Keil 工程
+# 或
+scons # 直接编译
+```
+
+2. 下载固件到 MCXA346
+3. 打开串口终端(115200 8N1)
+
+
+
+### 5.3 执行测试
+按照以下顺序执行测试命令:
+
+```c
+# 1. 检查I2C引脚状态
+msh> i2c3_dump
+# 2. 扫描I2C设备
+msh> i2c3_scan
+# 3. 初始化MPU6050
+msh> mpu_init
+# 4. 读取传感器数据
+msh> mpu_read
+```
+
+
+
+### 5.4 自动运行
+在 main() 函数中自动执行初始化和数据读取:
+
+```c
+int main(void)
+{
+ rt_kprintf("FRDM-MCXA346\r\n");
+ i2c_set_active_bus(I2C_BUS_NAME);
+ // 检查总线状态
+ i2c3_dump_pin_level("boot");
+ if (rt_pin_read(I2C3_SDA_PIN) == PIN_LOW)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("I2C3 SDA is low, try bus recover\n");
+ if (!i2c3_bus_recover())
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("I2C3 recover failed (SDA still low)\n");
+ }
+ }
+ BOARD_InitPins();
+ rt_hw_us_delay(10);
+ // 自动扫描并初始化
+ i2c3_scan();
+ mpu_init();
+ // 循环读取数据
+ while (1)
+ {
+ mpu_read();
+ rt_thread_mdelay(500);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
+
+## 6. 预期结果
+### 6.1 功能验证
++ ✅ I2C3 设备成功注册
++ ✅ MPU6050 设备地址识别正确 (0x68)
++ ✅ WHO_AM_I 寄存器读取正确 (0x68)
++ ✅ 配置寄存器写入成功
++ ✅ 传感器数据读取成功
++ ✅ 串口正确打印原始值和物理值
+
+### 6.2 输出示例
+串口输出打印如下
+
+
+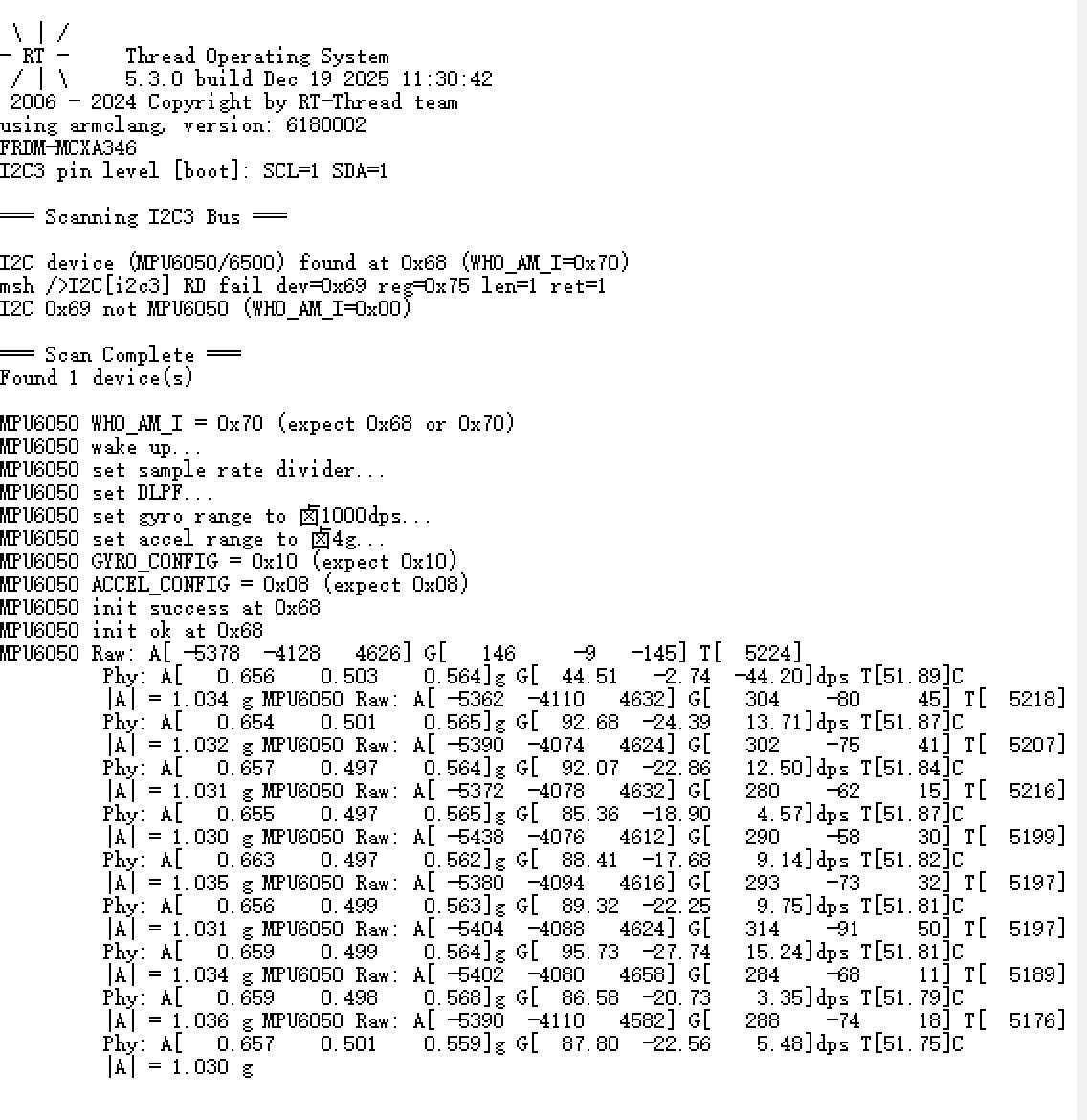
+
+
+
+7. 参考资料
+
++ : RT-Thread I2C使用教程
++ : RT-Thread 文档中心
++ : I2C使用指南-设计说明
++ : RT-Thread设备IIC驱动移植
+
+
+
+# 九、MCXA346上的CAN实践【吴艺彬】
+## 前言
+MCX A346 MCU有一个灵活的数据速率控制器局域网(FlexCAN)模块:CAN0。FRDM-MCXA346单板支持与CAN0模块通信。FlexCAN图显示FRDM-MCXA346的FlexCAN图。
+
+
+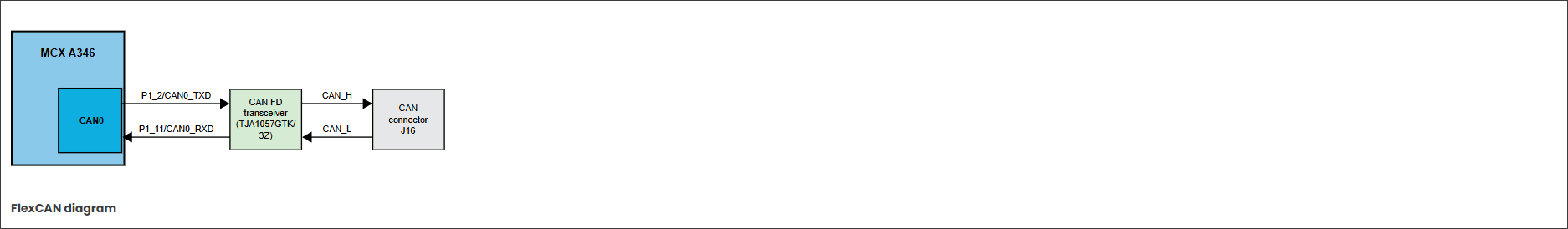
+
+
+
+
+
+当前适配的驱动只支持经典的can。
+
+
+
+## 准备工作
+搭建rt-thread的编程环境,可以参考
+
+[https://club.rt-thread.org/ask/article/dd4b615adc409793.html](https://club.rt-thread.org/ask/article/dd4b615adc409793.html)
+
+
+
+## 硬件连接
+
+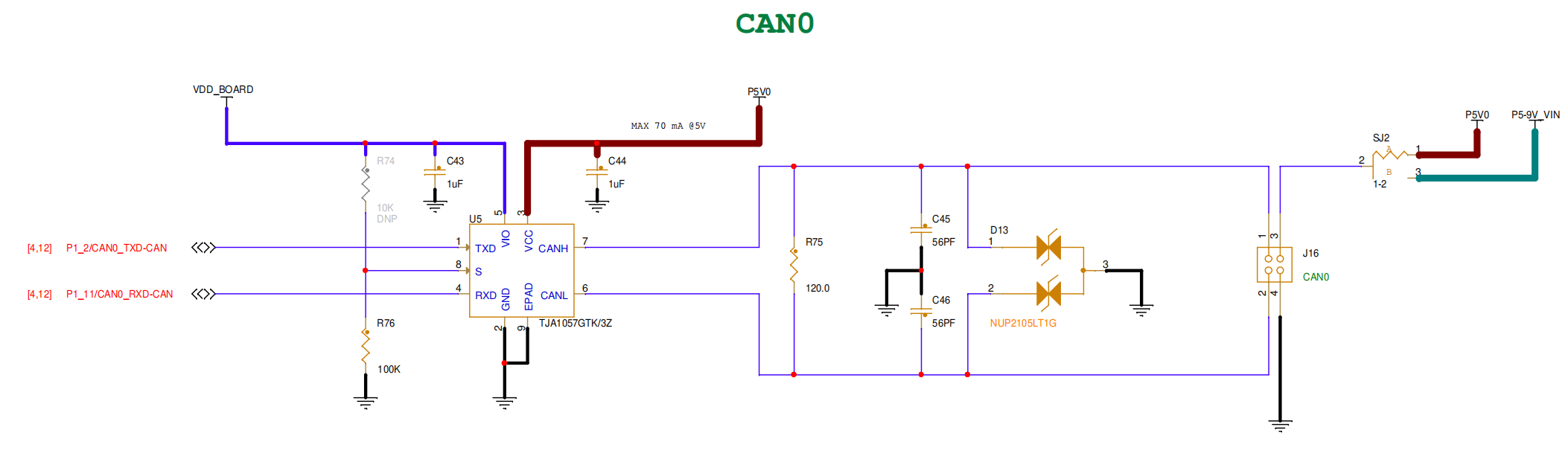
+
+
+
+由原理图可知,can所用到的引脚为P1_2(CAN_TX)、P1_11(CAN_RX)。
+
+
+
+## 配置过程
+### 拉取软件包
+进MCXA346的bsp目录下,打开env
+
+```c
+pkgs --update
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### 使能CAN
+
+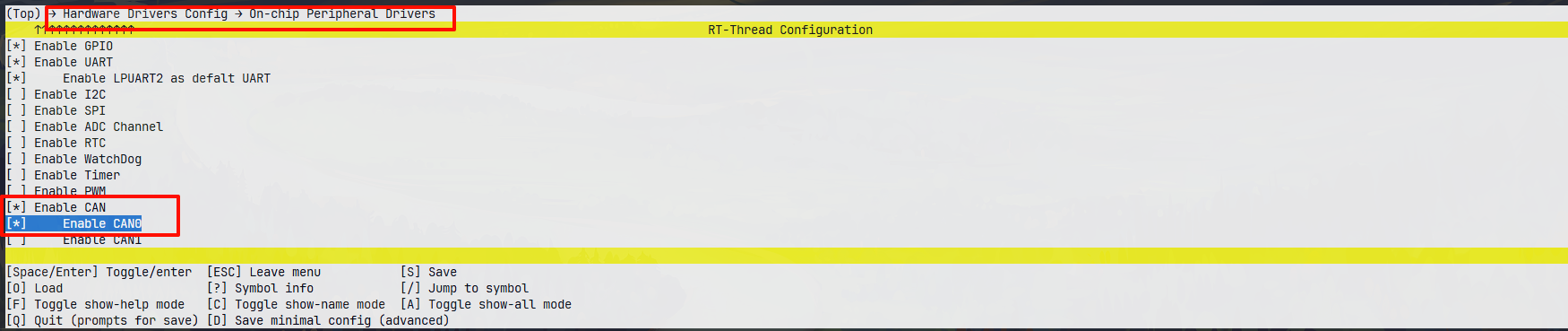
+
+
+
+### 配置CAN引脚
+添加在bsp/nxp/mcx/mcxa/frdm-mcxa346/board/MCUX_Config/board/pin_mux.c中的void BOARD_InitPins(void)函数中(默认已经添加)。
+
+```c
+static const reset_ip_name_t can_resets[] = FLEXCAN_RSTS_N;
+release_reset_array(can_resets, ARRAY_SIZE(can_resets));
+const port_pin_config_t port1_11_pin4_config = {/* Internal pull-up/down resistor is disabled */
+ .pullSelect = kPORT_PullDisable,
+ /* Low internal pull resistor value is selected. */
+ .pullValueSelect = kPORT_LowPullResistor,
+ /* Fast slew rate is configured */
+ .slewRate = kPORT_FastSlewRate,
+ /* Passive input filter is disabled */
+ .passiveFilterEnable = kPORT_PassiveFilterDisable,
+ /* Open drain output is disabled */
+ .openDrainEnable = kPORT_OpenDrainDisable,
+ /* Low drive strength is configured */
+ .driveStrength = kPORT_LowDriveStrength,
+ /* Normal drive strength is configured */
+ .driveStrength1 = kPORT_NormalDriveStrength,
+ /* Pin is configured as CAN0_RXD */
+ .mux = kPORT_MuxAlt11,
+ /* Digital input enabled */
+ .inputBuffer = kPORT_InputBufferEnable,
+ /* Digital input is not inverted */
+ .invertInput = kPORT_InputNormal,
+ /* Pin Control Register fields [15:0] are not locked */
+ .lockRegister = kPORT_UnlockRegister};
+/* PORT1_11 (pin 4) is configured as CAN0_RXD */
+PORT_SetPinConfig(PORT1, 11U, &port1_11_pin4_config);
+const port_pin_config_t port1_2_pin137_config = {/* Internal pull-up/down resistor is disabled */
+ .pullSelect = kPORT_PullDisable,
+ /* Low internal pull resistor value is selected. */
+ .pullValueSelect = kPORT_LowPullResistor,
+ /* Fast slew rate is configured */
+ .slewRate = kPORT_FastSlewRate,
+ /* Passive input filter is disabled */
+ .passiveFilterEnable = kPORT_PassiveFilterDisable,
+ /* Open drain output is disabled */
+ .openDrainEnable = kPORT_OpenDrainDisable,
+ /* Low drive strength is configured */
+ .driveStrength = kPORT_LowDriveStrength,
+ /* Normal drive strength is configured */
+ .driveStrength1 = kPORT_NormalDriveStrength,
+ /* Pin is configured as CAN0_TXD */
+ .mux = kPORT_MuxAlt11,
+ /* Digital input enabled */
+ .inputBuffer = kPORT_InputBufferEnable,
+ /* Digital input is not inverted */
+ .invertInput = kPORT_InputNormal,
+ /* Pin Control Register fields [15:0] are not locked */
+ .lockRegister = kPORT_UnlockRegister};
+/* PORT1_2 (pin 137) is configured as CAN0_TXD */
+PORT_SetPinConfig(PORT1, 2U, &port1_2_pin137_config);
+```
+
+
+
+### 生成工程
+```c
+scons --target=mdk5
+```
+
+### 示例代码
+```c
+#include
+#include
+#define CAN_DEV_NAME "can0" // The name of the CAN device
+static rt_device_t can_dev; // CAN device handle
+static struct rt_semaphore rx_sem; // Semaphore for message reception
+// Callback function for CAN reception
+static rt_err_t can_rx_callback(rt_device_t dev, rt_size_t size)
+{
+ // The CAN interrupt calls this callback when data is received.
+ // Release the semaphore to notify the receiving thread.
+ rt_sem_release(&rx_sem);
+ return RT_EOK;
+}
+static void can_rx_thread(void *parameter)
+{
+ rt_err_t res;
+ struct rt_can_msg rx_msg = {0};
+ // Set the receive callback function
+ rt_device_set_rx_indicate(can_dev, can_rx_callback);
+#ifdef RT_CAN_USING_HDR
+ // Example of configuring multiple hardware filters
+ struct rt_can_filter_item items[] =
+ {
+ // Filter 1: Match standard frames with IDs from 0x100 to 0x1FF. hdr_index will be -1.
+ RT_CAN_FILTER_ITEM_INIT(0x100, 0, 0, 0, 0x700, RT_NULL, RT_NULL),
+ // Filter 2: Match standard frames with IDs from 0x300 to 0x3FF. hdr_index will be -1.
+ RT_CAN_FILTER_ITEM_INIT(0x300, 0, 0, 0, 0x700, RT_NULL, RT_NULL),
+ // Filter 3: Exactly match standard frame with ID 0x211. hdr_index will be -1.
+ RT_CAN_FILTER_ITEM_INIT(0x211, 0, 0, 0, 0x7FF, RT_NULL, RT_NULL),
+ // Filter 4: Exactly match standard frame with ID 0x486 using a helper macro. hdr_index will be -1.
+ RT_CAN_FILTER_STD_INIT(0x486, RT_NULL, RT_NULL),
+ // Filter 5: Exactly match standard frame with ID 0x555 and explicitly assign it to filter bank #7.
+ // This uses direct struct initialization: {id, ide, rtr, mode, mask, hdr_bank}.
+ {0x555, 0, 0, 0, 0x7FF, 7}
+ };
+ // Create the filter configuration structure with 5 active filters.
+ struct rt_can_filter_config cfg = {sizeof(items)/sizeof(items[0]), 1, items};
+ // Set the hardware filters for the CAN device.
+ res = rt_device_control(can_dev, RT_CAN_CMD_SET_FILTER, &cfg);
+ RT_ASSERT(res == RT_EOK);
+#endif
+ // Some drivers might require an explicit start command.
+ // This is driver-specific.
+ rt_uint32_t cmd_arg = 1; // Argument to enable the controller
+ res = rt_device_control(can_dev, RT_CAN_CMD_START, &cmd_arg);
+ RT_ASSERT(res == RT_EOK);
+ while (1)
+ {
+ // Block and wait for the semaphore, which is released by the receive callback.
+ rt_sem_take(&rx_sem, RT_WAITING_FOREVER);
+ // Read one frame of data from the CAN device's general message queue.
+ rx_msg.hdr_index = -1;
+ rt_device_read(can_dev, 0, &rx_msg, sizeof(rx_msg));
+ // Print the received message's ID and data.
+ rt_kprintf("Received a message. ID: 0x%x, Data: ", rx_msg.id);
+ for (int i = 0; i < rx_msg.len; i++)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("%02x ", rx_msg.data[i]);
+ }
+ rt_kprintf("\n");
+ }
+}
+int can_sample(int argc, char *argv[])
+{
+ rt_err_t res;
+ rt_thread_t thread;
+ char can_name[RT_NAME_MAX];
+ // Allow specifying the CAN device name from the command line, e.g., "can_sample can2"
+ if (argc == 2)
+ {
+ rt_strncpy(can_name, argv[1], RT_NAME_MAX);
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ rt_strncpy(can_name, CAN_DEV_NAME, RT_NAME_MAX);
+ }
+ // Find the CAN device by name
+ can_dev = rt_device_find(can_name);
+ if (!can_dev)
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("find device %s failed!\n", can_name);
+ return -RT_ERROR;
+ }
+ // Initialize the receive semaphore
+ rt_sem_init(&rx_sem, "rx_sem", 0, RT_IPC_FLAG_FIFO);
+ // Open the CAN device in interrupt-driven TX/RX mode
+ res = rt_device_open(can_dev, RT_DEVICE_FLAG_INT_TX | RT_DEVICE_FLAG_INT_RX);
+ RT_ASSERT(res == RT_EOK);
+ // Create and start the data receiving thread
+ thread = rt_thread_create("can_rx", can_rx_thread, RT_NULL, 1024, 25, 10);
+ if (thread != RT_NULL)
+ {
+ rt_thread_startup(thread);
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("create can_rx thread failed!\n");
+ return -RT_ERROR;
+ }
+ rt_kprintf("CAN device %s opened successfully.\n", can_name);
+ // --- Demonstrate Blocking Send ---
+ struct rt_can_msg blocking_msg = {0};
+ blocking_msg.id = 0x78;
+ blocking_msg.ide = RT_CAN_STDID;
+ blocking_msg.rtr = RT_CAN_DTR;
+ blocking_msg.len = 8;
+ // The `nonblocking` flag is 0 by default for blocking mode.
+ for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++) blocking_msg.data[i] = i;
+ rt_kprintf("Attempting to send a message in BLOCKING mode...\n");
+ if (rt_device_write(can_dev, 0, &blocking_msg, sizeof(blocking_msg)) == sizeof(blocking_msg))
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("Blocking message sent successfully.\n");
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("Blocking message send failed.\n");
+ }
+ rt_thread_mdelay(100); // Wait a moment for clarity in the log
+ // --- Demonstrate Non-Blocking Send ---
+ struct rt_can_msg nonblocking_msg = {0};
+ nonblocking_msg.id = 0x79;
+ nonblocking_msg.ide = RT_CAN_STDID;
+ nonblocking_msg.rtr = RT_CAN_DTR;
+ nonblocking_msg.len = 4;
+ nonblocking_msg.data[0] = 0xDE;
+ nonblocking_msg.data[1] = 0xAD;
+ nonblocking_msg.data[2] = 0xBE;
+ nonblocking_msg.data[3] = 0xEF;
+ nonblocking_msg.nonblocking = 1; // <-- Key: Set the non-blocking flag
+ rt_kprintf("Attempting to send a message in NON-BLOCKING mode...\n");
+ if (rt_device_write(can_dev, 0, &nonblocking_msg, sizeof(nonblocking_msg)) == sizeof(nonblocking_msg))
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("Non-blocking message was accepted (sent or enqueued).\n");
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ rt_kprintf("Non-blocking send failed (buffer was full).\n");
+ }
+ return res;
+}
+// Export the function to the MSH command line
+MSH_CMD_EXPORT(can_sample, can device usage example);
+```
+
+### 运行结果
+
+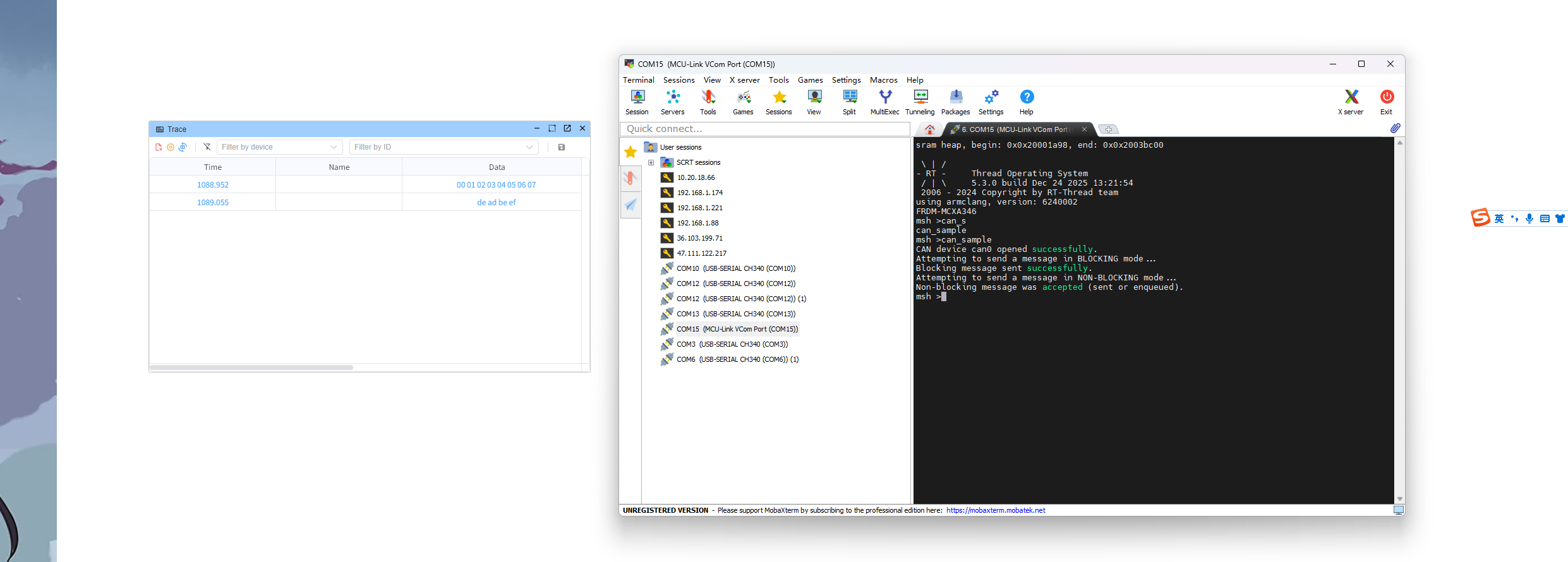
+
+#
+##
+
+
+# FAQ
+> 我有疑问:[https://club.rt-thread.org/](https://club.rt-thread.org/)
+>
+
--
Gitee