# kinematics
**Repository Path**: splendid1020/kinematics
## Basic Information
- **Project Name**: kinematics
- **Description**: JavaScript 6DOF robot kinematics library
- **Primary Language**: JavaScript
- **License**: MIT
- **Default Branch**: master
- **Homepage**: None
- **GVP Project**: No
## Statistics
- **Stars**: 1
- **Forks**: 1
- **Created**: 2019-06-07
- **Last Updated**: 2022-08-09
## Categories & Tags
**Categories**: Uncategorized
**Tags**: None
## README
# kinematics.js
[](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/glumb/kinematics/master/LICENSE.md)
[](https://travis-ci.org/glumb/kinematics)
[](https://www.npmjs.com/package/kinematics)
[](https://codecov.io/github/glumb/kinematics)
6DOF robot kinematics in JavaScript.
## Install
```console
npm install kinematics --save
```
## Use
```js
const Kinematics = require('kinematics').default
const geometry = [
[1, 1, 0], // V0: 1x 1y
[0, 10, 0], // V1: 10y
[5, 0, 0], // V2: 5x
[3, 0, 0], // V3: 3x
[0, -3, 0], // V4: -3y
]
const RobotKin = new Kinematics(geometry)
let angles = [1.57, 1.2, 0, 0.3, 2.2, 1.1]
const pose = RobotKin.forward(...angles)[5]
angles = RobotKin.inverse(...pose)
```
## Geometry
The geometry array consists of 5 entries describing the links *V0-V5*. Each *Vn* is a tuple of 3 coordinates from *Jn* to *Jn+1*.
One constraint: The y,z of *V3* and x,z of *V4* must be 0 for the kinematics to work.


## API
**forward**
```js
RobotKin.forward(R0, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5)
```
returns
```
[
[ 0, 0, 0 ], //J0
[ 0.5, 1, -0.8 ], //J1
[ -0.2, -8.8, 0.3 ], //J2
[ 1.8, -5.6, -2.8 ], //J3
[ 3.0, -3.6, -4.7 ], //J4
[ 4.7, -1.3, -5.5, 1, 6, -2.8 ] //J5 + TCP Euler angles
]
```
**inverse**
*X,Y,Z* coordinates, *A,B,C* Euler angles in order 'abc'.
```js
RobotKin.inverse(X, Y, Z, A, B, C)
```
returns
```
[ 2, 1.6, 2.1, -3.5, 1, -1.5 ] //array of angles
[ 1, 2.3, 3.1, NaN, NaN, NaN ] //NaN for out of reach angles
```
## kinematic coupling
kinematics.js assumes a robot with a series of joints. Some robots may have different kinematics. The depicted robot has a hinge at *J1* and R1/R2 are at the same kinematic position. Therefore moving *R1* also changes the angle at *J2*. To account for that, *R2* has to move the same amount.

Using that information, you can use kinematics.js to calculate the initial angles and correct them according to your kinematics.
```js
let angles = RobotKin.inverse(...pose)
angles[2] += angles[1]
//set angles, do stuff 🤖
```
## TODO
- robot configuration
- comply with DH for TCP orientation?
- more kinematic chains
## Demo
See the kinematics in action: http://robot.glumb.de (Use Chrome or FF due to ES6 features)
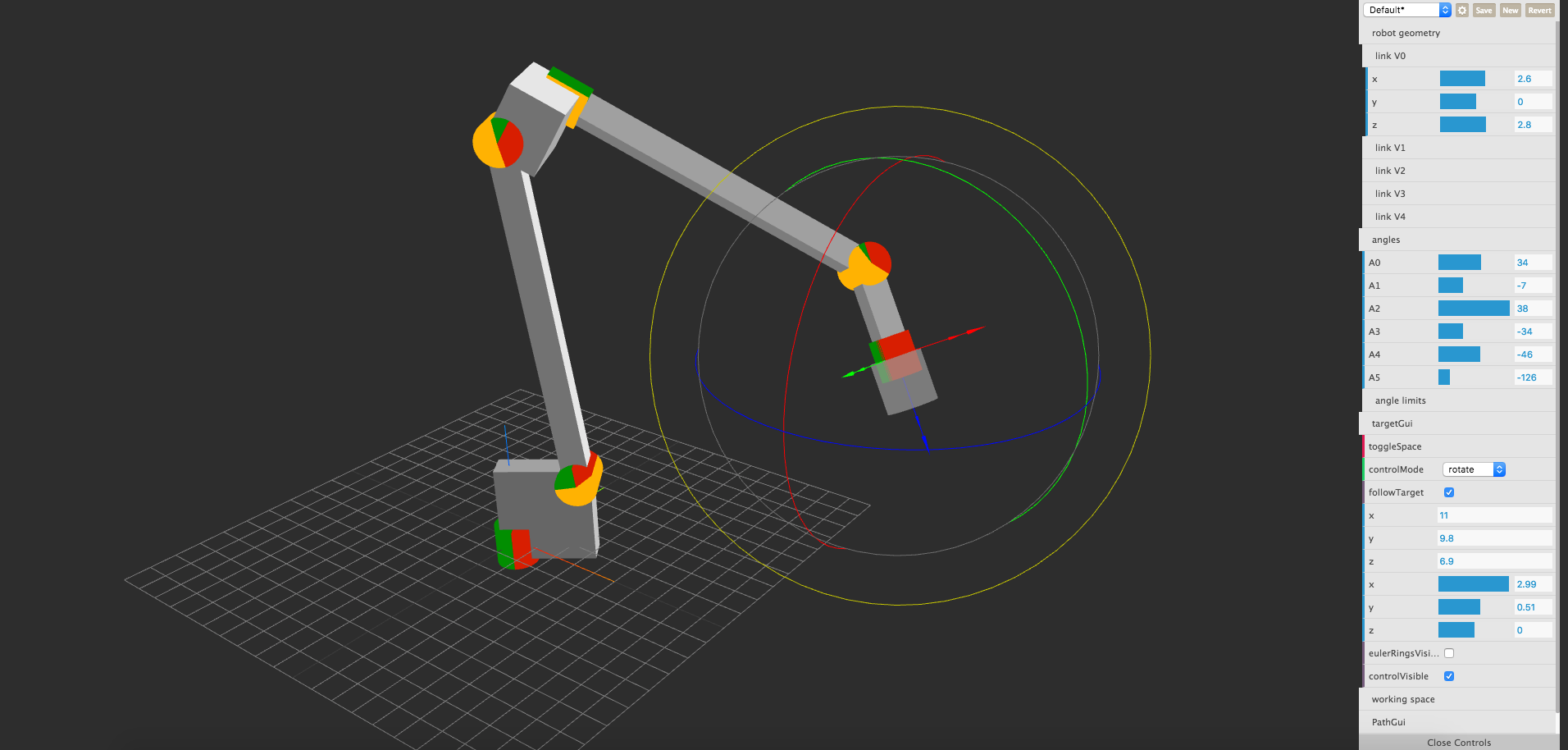
The gui is available in this repo:https://github.com/glumb/robot-gui

