# hashed-wheel-timer
**Repository Path**: spring-x/hashed-wheel-timer
## Basic Information
- **Project Name**: hashed-wheel-timer
- **Description**: No description available
- **Primary Language**: Unknown
- **License**: EPL-1.0
- **Default Branch**: master
- **Homepage**: None
- **GVP Project**: No
## Statistics
- **Stars**: 0
- **Forks**: 0
- **Created**: 2024-06-24
- **Last Updated**: 2024-06-24
## Categories & Tags
**Categories**: Uncategorized
**Tags**: None
## README
# What is the Hashed Timer?
Hashed and Hierarchical Wheels were used as a base for Kernels and Network stacks, and
were described by the [freebsd](http://people.freebsd.org/~davide/asia/callout_paper.pdf),
[linux people](http://lwn.net/Articles/156329/),
[researchers](http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~nahum/w6998/papers/ton97-timing-wheels.pdf) and
in many other searches.
Many modern Java frameworks have their own implementations of Timing Wheels, for example,
[Netty](https://github.com/netty/netty/blob/4.1/common/src/main/java/io/netty/util/HashedWheelTimer.java),
[Agrona](https://github.com/real-logic/Agrona/blob/master/src/main/java/uk/co/real_logic/agrona/TimerWheel.java),
[Reactor](https://github.com/reactor/reactor-core/blob/master/src/main/java/reactor/core/timer/HashWheelTimer.java),
[Kafka](https://github.com/apache/kafka/blob/trunk/core/src/main/scala/kafka/utils/timer/Timer.scala),
[Seastar](https://github.com/scylladb/seastar/blob/master/core/timer-set.hh)
and many others. Of course, every implementation is adapted for the needs of the particular
framework.
The concept on the Timer Wheel is rather simple to understand: in order to keep
track of events on given resolution, an array of linked lists (alternatively -
sets or even arrays, YMMV) is preallocated. When event is scheduled, it's
address is found by dividing deadline time `t` by `resolution` and `wheel size`.
The registration is then assigned with `rounds` (how many times we should go
around the wheel in order for the time period to be elapsed).
For each scheduled resolution, a __bucket__ is created. There are `wheel size`
buckets, each one of which is holding `Registrations`. Timer is going through
each `bucket` from the first until the next one, and decrements `rounds` for
each registration. As soon as registration's `rounds` is reaching 0, the timeout
is triggered. After that it is either rescheduled (with same `offset` and amount
of `rounds` as initially) or removed from timer.
Hashed Wheel is often called __approximated timer__, since it acts on the
certain resolution, which allows it's optimisations. All the tasks scheduled for
the timer period lower than the resolution or "between" resolution steps will be
rounded to the "ceiling" (for example, given resolution 10 milliseconds, all the
tasks for 5,6,7 etc milliseconds will first fire after 10, and 15, 16, 17 will
first trigger after 20).
If you're a visual person, it might be useful for you to check out [these
slides](http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~cdgill/courses/cs6874/TimingWheels.ppt),
which help to understand the concept underlying the Hashed Wheel Timer better.
The early variant of this implementation was contributed to Project Reactor back in [2014](https://github.com/reactor/reactor/commit/53c0dcfab40b91838694843729c85c2effe7272b),
and now is extracted and adopted to be used as a standalone library with benchmarks,
`debounce`, `throttle` implementations, `ScheduledExecutorService` impl and
other bells and whistles.
For __buckets__, `ConcurrentHashSet` is used (this, however, does not have any
influence on the cancellation performance, it is still `O(1)` as cancellation is
handled during bucket iteration). Switching to the array didn't bring change
performance / throughput at all (however, reduced the memory footprint). Array
implementation is however harder to get right, as one would have to allow
multiple strategies for growth and shrinking of the underlying array.
Advancement would be to implement a hierarchical wheels, which would be quite
simple on top of this library.
# nanoTime
Internally, this library is using `nanoTime`, since it's a system timer (exactly
what the library needs) best used for measuring elapsed time, exactly as JDK
documentation states. One of the places to read about `nanoTime` is
[here](http://shipilev.net/blog/2014/nanotrusting-nanotime/).
# Waiting Strategies
Timer Wheel allows you to pick between the three wait strategies: `BusySpin`
(most resource- consuming), although resulting into the best precision. Timer
loop will never release control, and will spin forever waiting for new tasks.
`Yielding` strategy is some kind of a compromise, which yields control after
checking whether the deadline was reached or no. `Sleeping` strategy is
injecting a `Thread.sleep()` until the deadline. Moving from "system" timer
usually means you don't want to use `sleep` at all. Except maybe for testing.
# Usage
Library implements `ScheduledExecutorService`. The decision was made to
implement this interface instead of `Timer`, since what the library does has
more to do with scheduled executor service than.
# `debounce` and `throttle`
For convenience, library also provides
[debounce](http://rxmarbles.com/#debounce) and throttle for `Runnable`,
`Consumer` and `BiConsumer`, which allow you to wrap any runnable or consumer
into their debounced or throttled version. You can find more information about
debouncing and throttling by following the links above.
# Comparison with JDK ScheduledExecutorService
JDK Timers are great for the majority of cases. Benchmarks show that they're
working stably for "reasonable" amounts of events (tens of thousands).
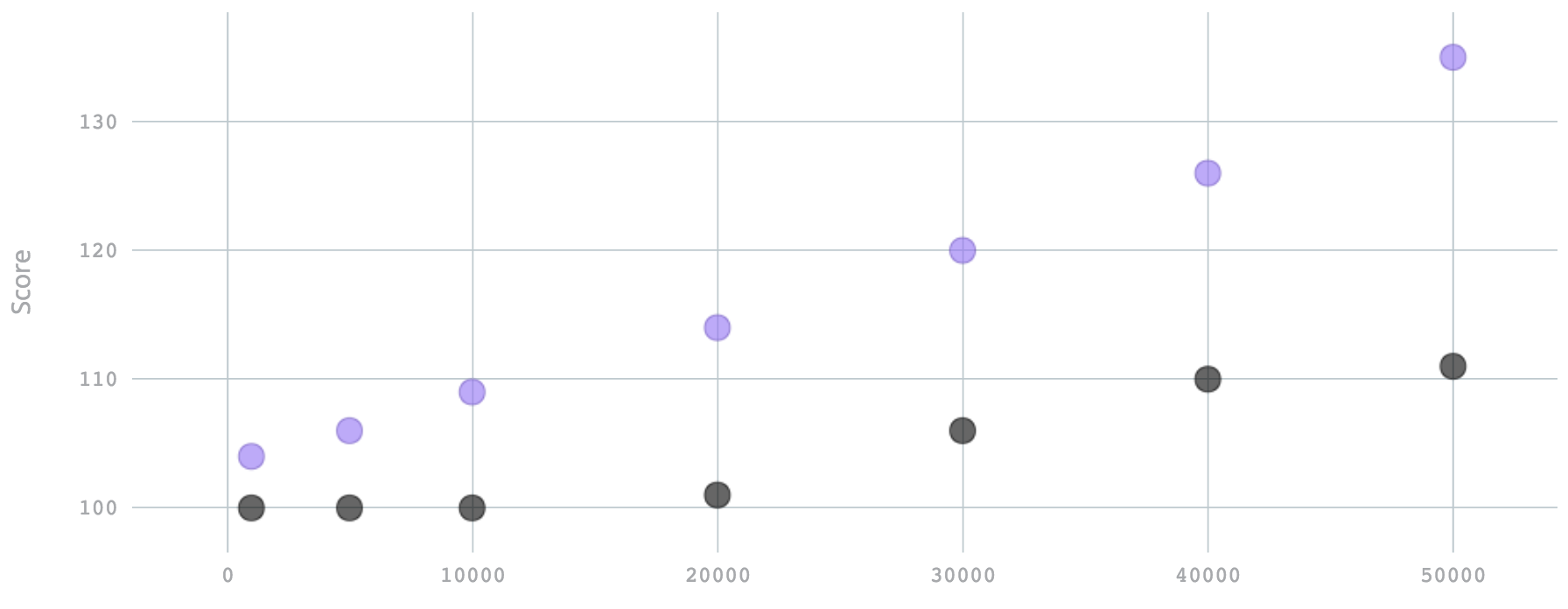
The following charts show the performance of JDK `ScheduledExecutorService`
(violet) vs `HashedWheelTimer` (black). The X is the amount of tasks submitted
sequentially, the Y `Score` axis is the latency until all the tasks were executed.
In the following chart, the Y axis is amount of tasks submitted sequentially,
although from 10 threads, where each next thread is starting with 10 millisecond
delay.
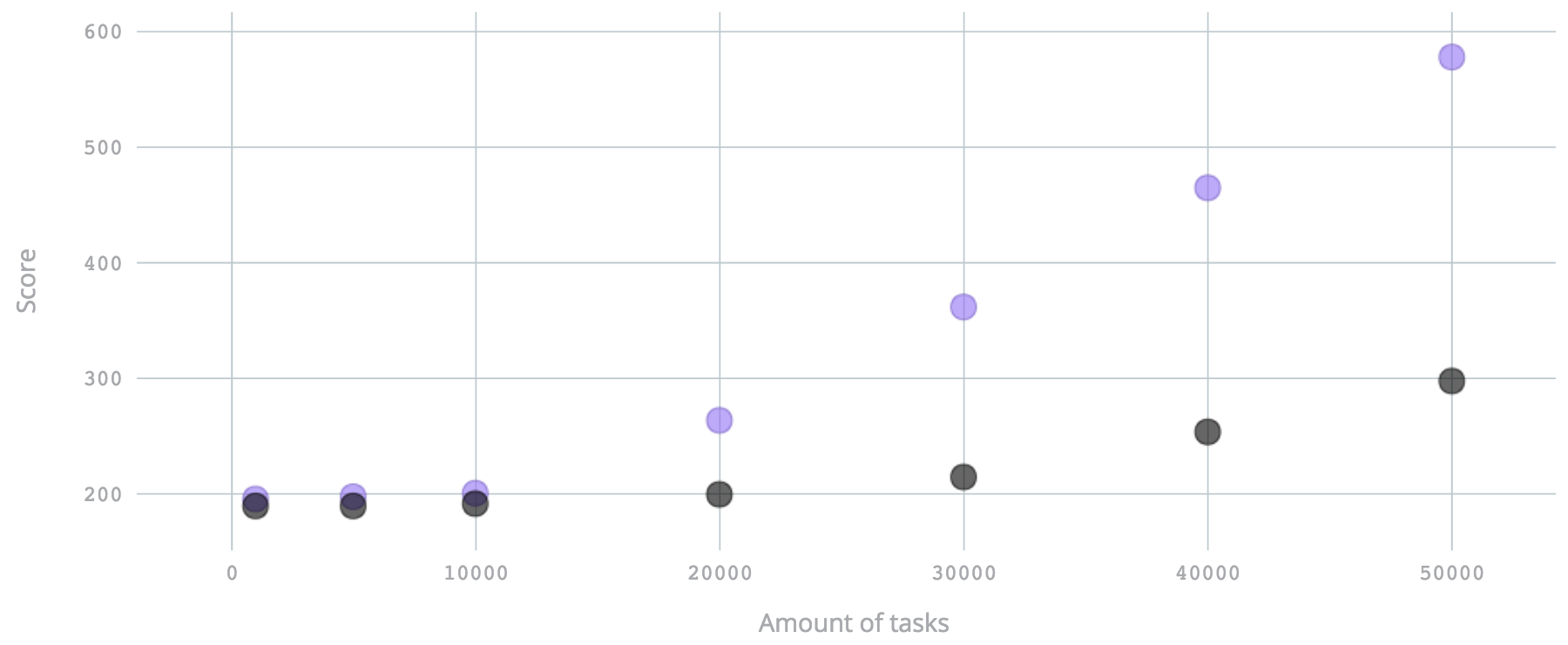
In both cases, 8 threads are used for workers. Changing amount of threads, hash
wheel size, adding more events to benchmarks doesn't significantly change the
picture.
You can see that `HashedWheelTimer` generally gives a flatter curve, which means
that given many fired events, it's precision is going to be better.
All benchmarks can be found
[here](https://github.com/ifesdjeen/hashed-wheel-timer/tree/master/bench). If
you think the benchmarks are suboptimal, incomplete, unrealistic or biased, just
fire an issue. It's always good to learn something new.
## Artifact
```xml
com.github.ifesdjeen
hashed-wheel-timer-core
1.0.0-RC1
```
Artifact is hosted on Sonatype OSS repository:
```xml
sonatype-releases
Sonatype Releases
https://oss.sonatype.org/content/repositories/releases
sonatype-snapshots
Sonatype Snapshot
https://oss.sonatype.org/content/repositories/snapshots
```
## License
Copyright © 2016 Alex P
Distributed under the Eclipse Public License either version 1.0 or (at
your option) any later version.