# esp32_nat_router
**Repository Path**: zwjin1210/esp32_nat_router
## Basic Information
- **Project Name**: esp32_nat_router
- **Description**: No description available
- **Primary Language**: Unknown
- **License**: Not specified
- **Default Branch**: master
- **Homepage**: None
- **GVP Project**: No
## Statistics
- **Stars**: 0
- **Forks**: 1
- **Created**: 2021-06-18
- **Last Updated**: 2025-04-04
## Categories & Tags
**Categories**: Uncategorized
**Tags**: None
## README
# ESP32 NAT Router
This is a firmware to use the ESP32 as WiFi NAT router. It can be used as
- Simple range extender for an existing WiFi network
- Setting up an additional WiFi network with different SSID/password for guests or IOT devices
It can achieve a bandwidth of more than 15mbps.
The code is based on the [Console Component](https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/api-guides/console.html#console) and the [esp-idf-nat-example](https://github.com/jonask1337/esp-idf-nat-example).
## Performance
All tests used `IPv4` and the `TCP` protocol.
| Board | Tools | Optimization | CPU Frequency | Throughput | Power |
| ----- | ----- | ------------ | ------------- | ---------- | ----- |
| `ESP32D0WDQ6` | `iperf3` | `0g` | `240MHz` | `16.0 MBits/s` | `1.6 W` |
| `ESP32D0WDQ6` | `iperf3` | `0s` | `240MHz` | `10.0 MBits/s` | `1.8 W` |
| `ESP32D0WDQ6` | `iperf3` | `0g` | `160MHz` | `15.2 MBits/s` | `1.4 W` |
| `ESP32D0WDQ6` | `iperf3` | `0s` | `160MHz` | `14.1 MBits/s` | `1.5 W` |
## First Boot
After first boot the ESP32 NAT Router will offer a WiFi network with an open AP and the ssid "ESP32_NAT_Router". Configuration can either be done via a simple web interface or via the serial console.
## Web Config Interface
The web interface allows for the configuration of all parameters. Connect you PC or smartphone to the WiFi SSID "ESP32_NAT_Router" and point your browser to "http://192.168.4.1". This page should appear:
 First enter the appropriate values for the uplink WiFi network, the "STA Settings". Leave password blank for open networks. Click "Connect". The ESP32 reboots and will connect to your WiFi router.
Now you can reconnect and reload the page and change the "Soft AP Settings". Click "Set" and again the ESP32 reboots. Now it is ready for forwarding traffic over the newly configured Soft AP. Be aware that these changes also affect the config interface, i.e. to do further configuration, connect to the ESP32 through one of the newly configured WiFi networks.
If you want to enter a '+' in the web interface you have to use HTTP-style hex encoding like "Mine%2bYours". This will result in a string "Mine+Yours". With this hex encoding you can enter any byte value you like, except for 0 (for C-internal reasons).
It you want to disable the web interface (e.g. for security reasons), go to the CLI and enter:
```
nvs_namespace esp32_nat
nvs_set lock str -v 1
```
After restart, no webserver is started any more. You can only re-enable it with:
```
nvs_namespace esp32_nat
nvs_set lock str -v 0
```
If you made a mistake and have lost all contact with the ESP you can still use the serial console to reconfigure it. All parameter settings are stored in NVS (non volatile storage), which is *not* erased by simple re-flashing the binaries. If you want to wipe it out, use "esptool.py -p /dev/ttyUSB0 erase_flash".
## Interpreting the on board LED
If the ESP32 is connected to the upstream AP then the on board LED should be on, otherwise off.
If there are devices connected to the ESP32 then the on board LED will keep blinking as many times as the number of devices connected.
For example:
One device connected to the ESP32, and the ESP32 is connected to upstream:
`*****.*****`
Two devices are connected to the ESP32, but the ESP32 is not connected to upstream:
`....*.*....`
# Command Line Interface
For configuration you have to use a serial console (Putty or GtkTerm with 115200 bps).
Use the "set_sta" and the "set_ap" command to configure the WiFi settings. Changes are stored persistently in NVS and are applied after next restart. Use "show" to display the current config. The NVS namespace for the parameters is "esp32_nat"
Enter the `help` command get a full list of all available commands:
```
help
Print the list of registered commands
free
Get the current size of free heap memory
heap
Get minimum size of free heap memory that was available during program execu
tion
version
Get version of chip and SDK
restart
Software reset of the chip
deep_sleep [-t ] [--io=] [--io_level=<0|1>]
Enter deep sleep mode. Two wakeup modes are supported: timer and GPIO. If no
wakeup option is specified, will sleep indefinitely.
-t, --time= Wake up time, ms
--io= If specified, wakeup using GPIO with given number
--io_level=<0|1> GPIO level to trigger wakeup
light_sleep [-t ] [--io=]... [--io_level=<0|1>]...
Enter light sleep mode. Two wakeup modes are supported: timer and GPIO. Mult
iple GPIO pins can be specified using pairs of 'io' and 'io_level' arguments
. Will also wake up on UART input.
-t, --time= Wake up time, ms
--io= If specified, wakeup using GPIO with given number
--io_level=<0|1> GPIO level to trigger wakeup
tasks
Get information about running tasks
nvs_set -v
Set key-value pair in selected namespace.
Examples:
nvs_set VarName i32 -v
123
nvs_set VarName str -v YourString
nvs_set VarName blob -v 0123456789abcdef
key of the value to be set
type can be: i8, u8, i16, u16 i32, u32 i64, u64, str, blob
-v, --value= value to be stored
nvs_get
Get key-value pair from selected namespace.
Example: nvs_get VarName i32
key of the value to be read
type can be: i8, u8, i16, u16 i32, u32 i64, u64, str, blob
nvs_erase
Erase key-value pair from current namespace
key of the value to be erased
nvs_namespace
Set current namespace
namespace of the partition to be selected
nvs_list [-n ] [-t ]
List stored key-value pairs stored in NVS.Namespace and type can be specified
to print only those key-value pairs.
Following command list variables stored inside 'nvs' partition, under namespace 'storage' with type uint32_t
Example: nvs_list nvs -n storage -t u32
partition name
-n, --namespace= namespace name
-t, --type= type can be: i8, u8, i16, u16 i32, u32 i64, u64, str, blob
nvs_erase_namespace
Erases specified namespace
namespace to be erased
set_sta
Set SSID and password of the STA interface
SSID
Password
set_sta_static
Set Static IP for the STA interface
IP
Subnet Mask
Gateway Address
set_ap
Set SSID and password of the SoftAP
SSID of AP
Password of AP
set_ap_ip
Set IP for the AP interface
IP
portmap [add|del] [TCP|UDP]
Add or delete a portmapping to the router
[add|del] add or delete portmapping
[TCP|UDP] TCP or UDP port
external port number
internal IP
internal port number
show
Get status and config of the router
```
If you want to enter non-ASCII or special characters (incl. ' ') you can use HTTP-style hex encoding (e.g. "My%20AccessPoint" results in a string "My AccessPoint").
## Flashing the prebuild Binaries
Install [esptool](https://github.com/espressif/esptool), go to the project directory, and enter:
```
esptool.py --chip esp32 --port /dev/ttyUSB0 \
--baud 115200 --before default_reset --after hard_reset write_flash \
-z --flash_mode dio --flash_freq 40m --flash_size detect \
0x1000 build/bootloader/bootloader.bin \
0x10000 build/esp32_nat_router.bin \
0x8000 build/partitions_example.bin
```
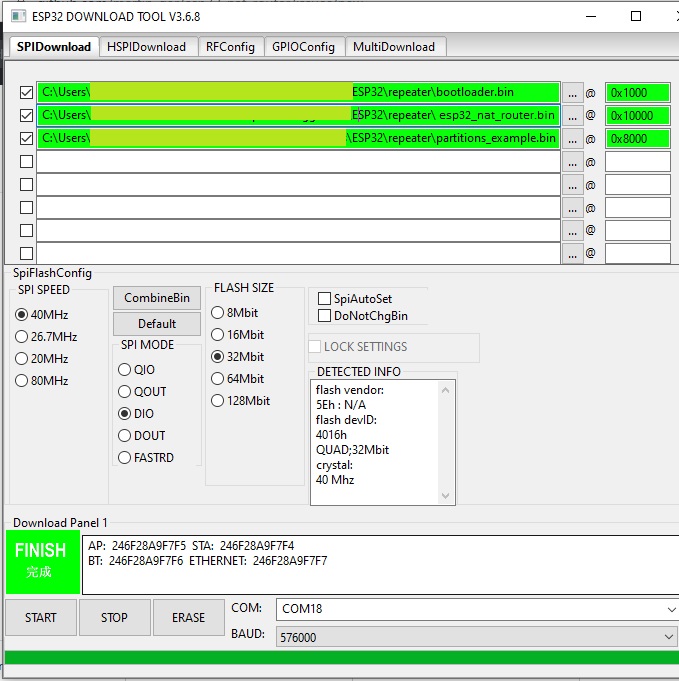
As an alternative you might use [Espressif's Flash Download Tools](https://www.espressif.com/en/products/hardware/esp32/resources) with the parameters given in the figure below (thanks to mahesh2000):
## Building the Binaries
The following are the steps required to compile this project:
1. Download and setup the ESP-IDF.
2. In the project directory run `make menuconfig` (or `idf.py menuconfig` for cmake).
1. *Component config -> LWIP > [x] Enable copy between Layer2 and Layer3 packets.
2. *Component config -> LWIP > [x] Enable IP forwarding.
3. *Component config -> LWIP > [x] Enable NAT (new/experimental).
3. Build the project and flash it to the ESP32.
A detailed instruction on how to build, configure and flash a ESP-IDF project can also be found the official ESP-IDF guide.
### DNS
As soon as the ESP32 STA has learned a DNS IP from its upstream DNS server on first connect, it passes that to newly connected clients.
Before that by default the DNS-Server which is offerd to clients connecting to the ESP32 AP is set to 8.8.8.8.
Replace the value of the *MY_DNS_IP_ADDR* with your desired DNS-Server IP address (in hex) if you want to use a different one.
## Troubleshooting
### Line Endings
The line endings in the Console Example are configured to match particular serial monitors. Therefore, if the following log output appears, consider using a different serial monitor (e.g. Putty for Windows or GtkTerm on Linux) or modify the example's UART configuration.
```
This is an example of ESP-IDF console component.
Type 'help' to get the list of commands.
Use UP/DOWN arrows to navigate through command history.
Press TAB when typing command name to auto-complete.
Your terminal application does not support escape sequences.
Line editing and history features are disabled.
On Windows, try using Putty instead.
esp32>
```
First enter the appropriate values for the uplink WiFi network, the "STA Settings". Leave password blank for open networks. Click "Connect". The ESP32 reboots and will connect to your WiFi router.
Now you can reconnect and reload the page and change the "Soft AP Settings". Click "Set" and again the ESP32 reboots. Now it is ready for forwarding traffic over the newly configured Soft AP. Be aware that these changes also affect the config interface, i.e. to do further configuration, connect to the ESP32 through one of the newly configured WiFi networks.
If you want to enter a '+' in the web interface you have to use HTTP-style hex encoding like "Mine%2bYours". This will result in a string "Mine+Yours". With this hex encoding you can enter any byte value you like, except for 0 (for C-internal reasons).
It you want to disable the web interface (e.g. for security reasons), go to the CLI and enter:
```
nvs_namespace esp32_nat
nvs_set lock str -v 1
```
After restart, no webserver is started any more. You can only re-enable it with:
```
nvs_namespace esp32_nat
nvs_set lock str -v 0
```
If you made a mistake and have lost all contact with the ESP you can still use the serial console to reconfigure it. All parameter settings are stored in NVS (non volatile storage), which is *not* erased by simple re-flashing the binaries. If you want to wipe it out, use "esptool.py -p /dev/ttyUSB0 erase_flash".
## Interpreting the on board LED
If the ESP32 is connected to the upstream AP then the on board LED should be on, otherwise off.
If there are devices connected to the ESP32 then the on board LED will keep blinking as many times as the number of devices connected.
For example:
One device connected to the ESP32, and the ESP32 is connected to upstream:
`*****.*****`
Two devices are connected to the ESP32, but the ESP32 is not connected to upstream:
`....*.*....`
# Command Line Interface
For configuration you have to use a serial console (Putty or GtkTerm with 115200 bps).
Use the "set_sta" and the "set_ap" command to configure the WiFi settings. Changes are stored persistently in NVS and are applied after next restart. Use "show" to display the current config. The NVS namespace for the parameters is "esp32_nat"
Enter the `help` command get a full list of all available commands:
```
help
Print the list of registered commands
free
Get the current size of free heap memory
heap
Get minimum size of free heap memory that was available during program execu
tion
version
Get version of chip and SDK
restart
Software reset of the chip
deep_sleep [-t ] [--io=] [--io_level=<0|1>]
Enter deep sleep mode. Two wakeup modes are supported: timer and GPIO. If no
wakeup option is specified, will sleep indefinitely.
-t, --time= Wake up time, ms
--io= If specified, wakeup using GPIO with given number
--io_level=<0|1> GPIO level to trigger wakeup
light_sleep [-t ] [--io=]... [--io_level=<0|1>]...
Enter light sleep mode. Two wakeup modes are supported: timer and GPIO. Mult
iple GPIO pins can be specified using pairs of 'io' and 'io_level' arguments
. Will also wake up on UART input.
-t, --time= Wake up time, ms
--io= If specified, wakeup using GPIO with given number
--io_level=<0|1> GPIO level to trigger wakeup
tasks
Get information about running tasks
nvs_set -v
Set key-value pair in selected namespace.
Examples:
nvs_set VarName i32 -v
123
nvs_set VarName str -v YourString
nvs_set VarName blob -v 0123456789abcdef
key of the value to be set
type can be: i8, u8, i16, u16 i32, u32 i64, u64, str, blob
-v, --value= value to be stored
nvs_get
Get key-value pair from selected namespace.
Example: nvs_get VarName i32
key of the value to be read
type can be: i8, u8, i16, u16 i32, u32 i64, u64, str, blob
nvs_erase
Erase key-value pair from current namespace
key of the value to be erased
nvs_namespace
Set current namespace
namespace of the partition to be selected
nvs_list [-n ] [-t ]
List stored key-value pairs stored in NVS.Namespace and type can be specified
to print only those key-value pairs.
Following command list variables stored inside 'nvs' partition, under namespace 'storage' with type uint32_t
Example: nvs_list nvs -n storage -t u32
partition name
-n, --namespace= namespace name
-t, --type= type can be: i8, u8, i16, u16 i32, u32 i64, u64, str, blob
nvs_erase_namespace
Erases specified namespace
namespace to be erased
set_sta
Set SSID and password of the STA interface
SSID
Password
set_sta_static
Set Static IP for the STA interface
IP
Subnet Mask
Gateway Address
set_ap
Set SSID and password of the SoftAP
SSID of AP
Password of AP
set_ap_ip
Set IP for the AP interface
IP
portmap [add|del] [TCP|UDP]
Add or delete a portmapping to the router
[add|del] add or delete portmapping
[TCP|UDP] TCP or UDP port
external port number
internal IP
internal port number
show
Get status and config of the router
```
If you want to enter non-ASCII or special characters (incl. ' ') you can use HTTP-style hex encoding (e.g. "My%20AccessPoint" results in a string "My AccessPoint").
## Flashing the prebuild Binaries
Install [esptool](https://github.com/espressif/esptool), go to the project directory, and enter:
```
esptool.py --chip esp32 --port /dev/ttyUSB0 \
--baud 115200 --before default_reset --after hard_reset write_flash \
-z --flash_mode dio --flash_freq 40m --flash_size detect \
0x1000 build/bootloader/bootloader.bin \
0x10000 build/esp32_nat_router.bin \
0x8000 build/partitions_example.bin
```
As an alternative you might use [Espressif's Flash Download Tools](https://www.espressif.com/en/products/hardware/esp32/resources) with the parameters given in the figure below (thanks to mahesh2000):

## Building the Binaries
The following are the steps required to compile this project:
1. Download and setup the ESP-IDF.
2. In the project directory run `make menuconfig` (or `idf.py menuconfig` for cmake).
1. *Component config -> LWIP > [x] Enable copy between Layer2 and Layer3 packets.
2. *Component config -> LWIP > [x] Enable IP forwarding.
3. *Component config -> LWIP > [x] Enable NAT (new/experimental).
3. Build the project and flash it to the ESP32.
A detailed instruction on how to build, configure and flash a ESP-IDF project can also be found the official ESP-IDF guide.
### DNS
As soon as the ESP32 STA has learned a DNS IP from its upstream DNS server on first connect, it passes that to newly connected clients.
Before that by default the DNS-Server which is offerd to clients connecting to the ESP32 AP is set to 8.8.8.8.
Replace the value of the *MY_DNS_IP_ADDR* with your desired DNS-Server IP address (in hex) if you want to use a different one.
## Troubleshooting
### Line Endings
The line endings in the Console Example are configured to match particular serial monitors. Therefore, if the following log output appears, consider using a different serial monitor (e.g. Putty for Windows or GtkTerm on Linux) or modify the example's UART configuration.
```
This is an example of ESP-IDF console component.
Type 'help' to get the list of commands.
Use UP/DOWN arrows to navigate through command history.
Press TAB when typing command name to auto-complete.
Your terminal application does not support escape sequences.
Line editing and history features are disabled.
On Windows, try using Putty instead.
esp32>
```