## 3 ZigZag Conversion
The string "PAYPALISHIRING" is written in a zigzag pattern on a given number of rows like this: (you may want to display this pattern in a fixed font for better legibility)
P A H N
A P L S I I G
Y I R
And then read line by line: "PAHNAPLSIIGYIR"
Write the code that will take a string and make this conversion given a number of rows:
string convert(string s, int numRows);
Example 1:
Input: s = "PAYPALISHIRING", numRows = 3
Output: "PAHNAPLSIIGYIR"
Example 2:
Input: s = "PAYPALISHIRING", numRows = 4
Output: "PINALSIGYAHRPI"
Explanation:
P I N
A L S I G
Y A H R
P I
Example 3:
Input: s = "A", numRows = 1
Output: "A"
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 1000s consists of English letters (lower-case and upper-case), ',' and '.'.1 <= numRows <= 1000Intuition
By iterating through the string from left to right, we can easily determine which row in the Zig-Zag pattern that a character belongs to.
Algorithm
We can use 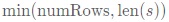 lists to represent the non-empty rows of the Zig-Zag Pattern.
lists to represent the non-empty rows of the Zig-Zag Pattern.
Iterate through s from left to right, appending each character to the appropriate row. The appropriate row can be tracked using two variables: the current row and the current direction.
The current direction changes only when we moved up to the topmost row or moved down to the bottommost row.
class Solution{
public:
string convert(string s,int numRows){
if (numRows == 1) return s;
vector<string> rows(min(numRows,int(s.size())));
int curRow = 0;
bool goingDown = false;
for (char c : s){
rows[curRow] += c;
if(curRow == 0 || curRow == numRows -1) goingDown = !goingDown;
curRow += goingDown?1:-1;
}
string ret;
for (string row:rows) ret += row;
return ret;
}
};
class Solution{
public String convert(String s, int numRows){
if(numRows == 1) return s;
List<StringBuilder> rows = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i< Math.min(numRows, s.length()); i++){
rows.add(new StringBuilder());
}
int curRow = 0;
boolean goingDown = false;
for (char c : s.toCharArray()){
rows.get(curRow).append(c);
if (curRow == 0 || curRow == numRows -1) goingDown =! goingDown;
curRow += goingDown ? 1 : -1;
}
StringBuilder ret = new StringBuilder();
for (StringBuilder row: rows) ret.append(row);
return ret.toString();
}
}
Complexity Analysis
Intuition
Visit the characters in the same order as reading the Zig-Zag pattern line by line.
Algorithm
Visit all characters in row 0 first, then row 1, then row 2, and so on...
For all whole numbers k,
(2*numRows - 2) -i.
class Solution{
public:
string convert(string s, int numRows){
if(numRows == 1) return s;
string ret;
int n = s.size();
int cycleLen = 2 * numRows -2;
for (int i =0; i<numRows ; i++){
for (int j =0 ; j+i < n; j+=cycleLen){
ret += s[j+i];
if (i!=0 && i!=numRows-1 && j+cycleLen-i <n){
ret += s[j+cycleLen -i];
}
}
}
return ret;
}
};
The distribution of the elements is period.
P A H N
A P L S I I G
Y I R
For example, the following has 4 periods(cycles):
P | A | H | N
A P | L S | I I | G
Y | I | R |
The size of every period is defined as "cycle"
cycle = (2*nRows - 2), except nRows == 1.
In this example, (2*nRows - 2) = 4.
In every period, every row has 2 elements, except the first row and the last row.
Suppose the current row is i, the index of the first element is j:
j = i + cycle*k, k = 0, 1, 2, ...
The index of the second element is secondJ:
secondJ = (j - i) + cycle - i
(j-i) is the start of current period, (j-i) + cycle is the start of next period.
class Solution{
public:
string convert(string s,int nRows){
if(nRows<=1) return s;
string result = "";
//the size of a cycle (period)
int cycle = 2* nRows -2;
for(int i =0 ;i< nRows; ++i){
for (int j =i ; j<s.length();j=j+cycle){
result = result + s[j];
int secondJ = (j - i) + cycle -i;
if(i != 0 && i != nRows-1 && secondJ < s.length())
result = result + s[secondJ];
}
}
return result;
}
};
此处可能存在不合适展示的内容,页面不予展示。您可通过相关编辑功能自查并修改。
如您确认内容无涉及 不当用语 / 纯广告导流 / 暴力 / 低俗色情 / 侵权 / 盗版 / 虚假 / 无价值内容或违法国家有关法律法规的内容,可点击提交进行申诉,我们将尽快为您处理。