同步操作将从 Gitee 极速下载/javascript-algorithms 强制同步,此操作会覆盖自 Fork 仓库以来所做的任何修改,且无法恢复!!!
确定后同步将在后台操作,完成时将刷新页面,请耐心等待。
Read this in other languages: Português
A red–black tree is a kind of self-balancing binary search tree in computer science. Each node of the binary tree has an extra bit, and that bit is often interpreted as the color (red or black) of the node. These color bits are used to ensure the tree remains approximately balanced during insertions and deletions.
Balance is preserved by painting each node of the tree with one of two colors in a way that satisfies certain properties, which collectively constrain how unbalanced the tree can become in the worst case. When the tree is modified, the new tree is subsequently rearranged and repainted to restore the coloring properties. The properties are designed in such a way that this rearranging and recoloring can be performed efficiently.
The balancing of the tree is not perfect, but it is good
enough to allow it to guarantee searching in O(log n) time,
where n is the total number of elements in the tree.
The insertion and deletion operations, along with the tree
rearrangement and recoloring, are also performed
in O(log n) time.
An example of a red–black tree:
In addition to the requirements imposed on a binary search tree the following must be satisfied by a red–black tree:
Some definitions: the number of black nodes from the root to a node is the node's black depth; the uniform number of black nodes in all paths from root to the leaves is called the black-height of the red–black tree.
These constraints enforce a critical property of red–black trees: the path from the root to the farthest leaf is no more than twice as long as the path from the root to the nearest leaf. The result is that the tree is roughly height-balanced. Since operations such as inserting, deleting, and finding values require worst-case time proportional to the height of the tree, this theoretical upper bound on the height allows red–black trees to be efficient in the worst case, unlike ordinary binary search trees.
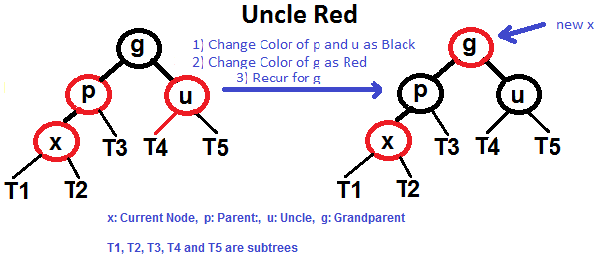
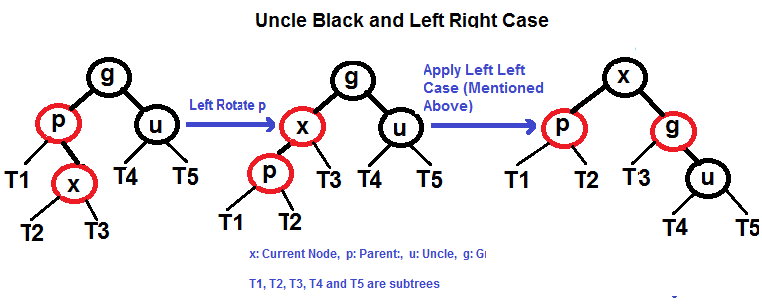
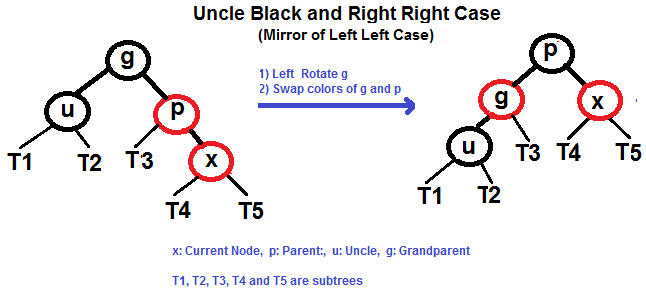
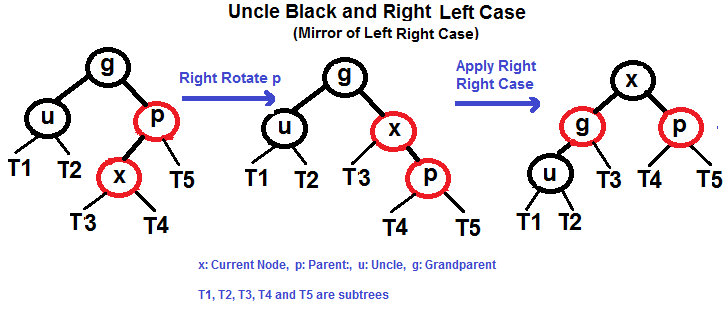
p is left child of g and x is left child of p)p is left child of g and x is right child of p)p is right child of g and x is right child of p)p is right child of g and x is left child of p)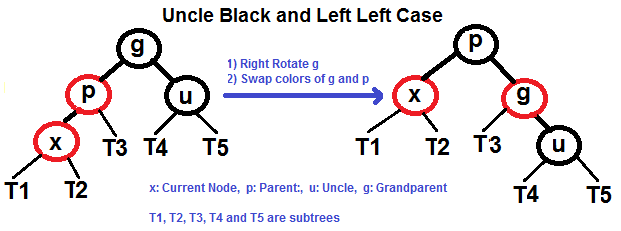
此处可能存在不合适展示的内容,页面不予展示。您可通过相关编辑功能自查并修改。
如您确认内容无涉及 不当用语 / 纯广告导流 / 暴力 / 低俗色情 / 侵权 / 盗版 / 虚假 / 无价值内容或违法国家有关法律法规的内容,可点击提交进行申诉,我们将尽快为您处理。