The pytorch re-implement of the official EfficientDet with SOTA performance in real time, original paper link: https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.09070
The performance is very close to the paper's, it is still SOTA.
The speed/FPS test includes the time of post-processing with no jit/data precision trick.
| coefficient | pth_download | GPU Mem(MB) | FPS | Extreme FPS (Batchsize 32) | mAP 0.5:0.95(this repo) | mAP 0.5:0.95(paper) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D0 | efficientdet-d0.pth | 1049 | 36.20 | 163.14 | 33.1 | 33.8 |
| D1 | efficientdet-d1.pth | 1159 | 29.69 | 63.08 | 38.8 | 39.6 |
| D2 | efficientdet-d2.pth | 1321 | 26.50 | 40.99 | 42.1 | 43.0 |
| D3 | efficientdet-d3.pth | 1647 | 22.73 | - | 45.6 | 45.8 |
| D4 | efficientdet-d4.pth | 1903 | 14.75 | - | 48.8 | 49.4 |
| D5 | efficientdet-d5.pth | 2255 | 7.11 | - | 50.2 | 50.7 |
| D6 | efficientdet-d6.pth | 2985 | 5.30 | - | 50.7 | 51.7 |
| D7 | efficientdet-d7.pth | 3819 | 3.73 | - | 51.2 | 52.2 |
This pure-pytorch implement is up to 2 times faster than the official Tensorflow version without any trick.
Recorded on 2020-04-26,
official git version: https://github.com/google/automl/commit/006668f2af1744de0357ca3d400527feaa73c122
| coefficient | FPS(this repo, tested on RTX2080Ti) | FPS(official, tested on T4) | Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| D0 | 36.20 | 42.1 | 0.86X |
| D1 | 29.69 | 27.7 | 1.07X |
| D2 | 26.50 | 19.7 | 1.35X |
| D3 | 22.73 | 11.8 | 1.93X |
| D4 | 14.75 | 7.1 | 2.08X |
| D5 | 7.11 | 3.6 | 1.98X |
| D6 | 5.30 | 2.6 | 2.03X |
| D7 | 3.73 | - | - |
Test method (this repo):
Run this test on 2080Ti, Ubuntu 19.10 x64.
[2020-05-11] add boolean string convertion to make sure head_only works
[2020-05-10] replace nms with batched_nms to further improve mAP by 0.5~0.7, thanks Laughing-q.
[2020-05-04] fix coco category id mismatch bug, but it shouldn't affect training on custom dataset.
[2020-04-14] fixed loss function bug. please pull the latest code.
[2020-04-14] for those who needs help or can't get a good result after several epochs, check out this tutorial. You can run it on colab with GPU support.
[2020-04-10] warp the loss function within the training model, so that the memory usage will be balanced when training with multiple gpus, enabling training with bigger batchsize.
[2020-04-10] add D7 (D6 with larger input size and larger anchor scale) support and test its mAP
[2020-04-09] allow custom anchor scales and ratios
[2020-04-08] add D6 support and test its mAP
[2020-04-08] add training script and its doc; update eval script and simple inference script.
[2020-04-07] tested D0-D5 mAP, result seems nice, details can be found here
[2020-04-07] fix anchors strategies.
[2020-04-06] adapt anchor strategies.
[2020-04-05] create this repository.
# install requirements
pip install pycocotools numpy opencv-python tqdm tensorboard tensorboardX pyyaml webcolors
pip install torch==1.4.0
pip install torchvision==0.5.0
# run the simple inference script
python efficientdet_test.py
Training EfficientDet is a painful and time-consuming task. You shouldn't expect to get a good result within a day or two. Please be patient.
Check out this tutorial if you are new to this. You can run it on colab with GPU support.
# your dataset structure should be like this
datasets/
-your_project_name/
-train_set_name/
-*.jpg
-val_set_name/
-*.jpg
-annotations
-instances_{train_set_name}.json
-instances_{val_set_name}.json
# for example, coco2017
datasets/
-coco2017/
-train2017/
-000000000001.jpg
-000000000002.jpg
-000000000003.jpg
-val2017/
-000000000004.jpg
-000000000005.jpg
-000000000006.jpg
-annotations
-instances_train2017.json
-instances_val2017.json
# create a yml file {your_project_name}.yml under 'projects'folder
# modify it following 'coco.yml'
# for example
project_name: coco
train_set: train2017
val_set: val2017
num_gpus: 4 # 0 means using cpu, 1-N means using gpus
# mean and std in RGB order, actually this part should remain unchanged as long as your dataset is similar to coco.
mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
# this is coco anchors, change it if necessary
anchors_scales: '[2 ** 0, 2 ** (1.0 / 3.0), 2 ** (2.0 / 3.0)]'
anchors_ratios: '[(1.0, 1.0), (1.4, 0.7), (0.7, 1.4)]'
# objects from all labels from your dataset with the order from your annotations.
# its index must match your dataset's category_id.
# category_id is one_indexed,
# for example, index of 'car' here is 2, while category_id of is 3
obj_list: ['person', 'bicycle', 'car', ...]
# train efficientdet-d0 on coco from scratch
# with batchsize 12
# This takes time and requires change
# of hyperparameters every few hours.
# If you have months to kill, do it.
# It's not like someone going to achieve
# better score than the one in the paper.
# The first few epoches will be rather unstable,
# it's quite normal when you train from scratch.
python train.py -c 0 --batch_size 64 --optim sgd --lr 8e-2
# train efficientdet-d1 on a custom dataset
# with batchsize 8 and learning rate 1e-5
python train.py -c 1 -p your_project_name --batch_size 8 --lr 1e-5
# train efficientdet-d2 on a custom dataset with pretrained weights
# with batchsize 8 and learning rate 1e-5 for 10 epoches
python train.py -c 2 -p your_project_name --batch_size 8 --lr 1e-5 --num_epochs 10 \
--load_weights /path/to/your/weights/efficientdet-d2.pth
# with a coco-pretrained, you can even freeze the backbone and train heads only
# to speed up training and help convergence.
python train.py -c 2 -p your_project_name --batch_size 8 --lr 1e-5 --num_epochs 10 \
--load_weights /path/to/your/weights/efficientdet-d2.pth \
--head_only True
# while training, press Ctrl+c, the program will catch KeyboardInterrupt
# and stop training, save current checkpoint.
# let says you started a training session like this.
python train.py -c 2 -p your_project_name --batch_size 8 --lr 1e-5 \
--load_weights /path/to/your/weights/efficientdet-d2.pth \
--head_only True
# then you stopped it with a Ctrl+c, it exited with a checkpoint
# now you want to resume training from the last checkpoint
# simply set load_weights to 'last'
python train.py -c 2 -p your_project_name --batch_size 8 --lr 1e-5 \
--load_weights last \
--head_only True
# eval on your_project, efficientdet-d5
python coco_eval.py -p your_project_name -c 5 \
-w /path/to/your/weights
# when you get bad result, you need to debug the training result.
python train.py -c 2 -p your_project_name --batch_size 8 --lr 1e-5 --debug True
# then checkout test/ folder, there you can visualize the predicted boxes during training
# don't panic if you see countless of error boxes, it happens when the training is at early stage.
# But if you still can't see a normal box after several epoches, not even one in all image,
# then it's possible that either the anchors config is inappropriate or the ground truth is corrupted.
Q1. Why implement this while there are several efficientdet pytorch projects already.
A1: Because AFAIK none of them fully recovers the true algorithm of the official efficientdet, that's why their communities could not achieve or having a hard time to achieve the same score as the official efficientdet by training from scratch.
Q2: What exactly is the difference among this repository and the others?
A2: For example, these two are the most popular efficientdet-pytorch,
https://github.com/toandaominh1997/EfficientDet.Pytorch
https://github.com/signatrix/efficientdet
Here is the issues and why these are difficult to achieve the same score as the official one:
The first one:
The second one:
Pytorch's BatchNormalization is slightly different from TensorFlow, momentum_pytorch = 1 - momentum_tensorflow. Well I didn't realize this trap if I paid less attentions. signatrix/efficientdet succeeded the parameter from TensorFlow, so the BN will perform badly because running mean and the running variance is being dominated by the new input.
Mis-implement of Depthwise-Separable Conv2D. Depthwise-Separable Conv2D is Depthwise-Conv2D and Pointwise-Conv2D and BiasAdd ,there is only a BiasAdd after two Conv2D, while signatrix/efficientdet has a extra BiasAdd on Depthwise-Conv2D.
Misunderstand the first parameter of MaxPooling2D, the first parameter is kernel_size, instead of stride.
Missing BN after downchannel of the feature of the efficientnet output.
Using the wrong output feature of the efficientnet. This is big one. It takes whatever output that has the conv.stride of 2, but it's wrong. It should be the one whose next conv.stride is 2 or the final output of efficientnet.
Does not apply same padding on Conv2D and Pooling.
Missing swish activation after several operations.
Missing Conv/BN operations in BiFPN, Regressor and Classifier. This one is very tricky, if you don't dig deeper into the official implement, there are some same operations with different weights.
illustration of a minimal bifpn unit
P7_0 -------------------------> P7_2 -------->
|-------------| ↑
↓ |
P6_0 ---------> P6_1 ---------> P6_2 -------->
|-------------|--------------↑ ↑
↓ |
P5_0 ---------> P5_1 ---------> P5_2 -------->
|-------------|--------------↑ ↑
↓ |
P4_0 ---------> P4_1 ---------> P4_2 -------->
|-------------|--------------↑ ↑
|--------------↓ |
P3_0 -------------------------> P3_2 -------->
For example, P4 will downchannel to P4_0, then it goes P4_1, anyone may takes it for granted that P4_0 goes to P4_2 directly, right?
That's why they are wrong, P4 should downchannel again with a different weights to P4_0_another, then it goes to P4_2.
And finally some common issues, their anchor decoder and encoder are different from the original one, but it's not the main reason that it performs badly.
Also, Conv2dStaticSamePadding from EfficientNet-PyTorch does not perform like TensorFlow, the padding strategy is different. So I implement a real tensorflow-style Conv2dStaticSamePadding and MaxPool2dStaticSamePadding myself.
Despite of the above issues, they are great repositories that enlighten me, hence there is this repository.
This repository is mainly based on efficientdet, with the changing that makes sure that it performs as closer as possible as the paper.
Btw, debugging static-graph TensorFlow v1 is really painful. Don't try to export it with automation tools like tf-onnx or mmdnn, they will only cause more problems because of its custom/complex operations.
And even if you succeeded, like I did, you will have to deal with the crazy messed up machine-generated code under the same class that takes more time to refactor than translating it from scratch.
Q3: What should I do when I find a bug?
A3: Check out the update log if it's been fixed, then pull the latest code to try again. If it doesn't help, create a new issue and describe it in detail.
Conclusion: They are providing almost the same precision. Tips: set force_input_size=1920. Official repo uses original image size while this repo uses default network input size. If you try to compare these two repos, you must make sure the input size is consistent.
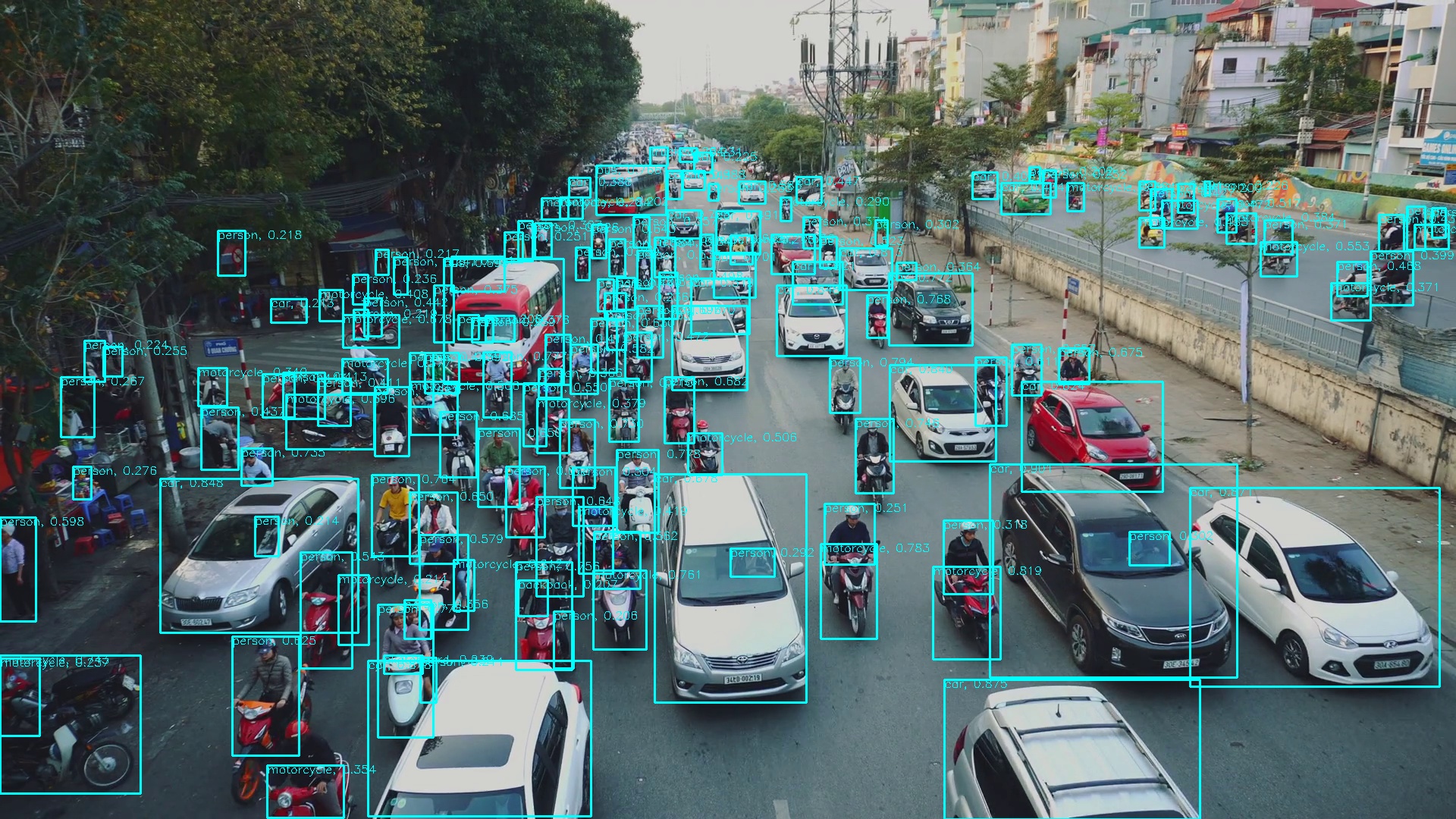
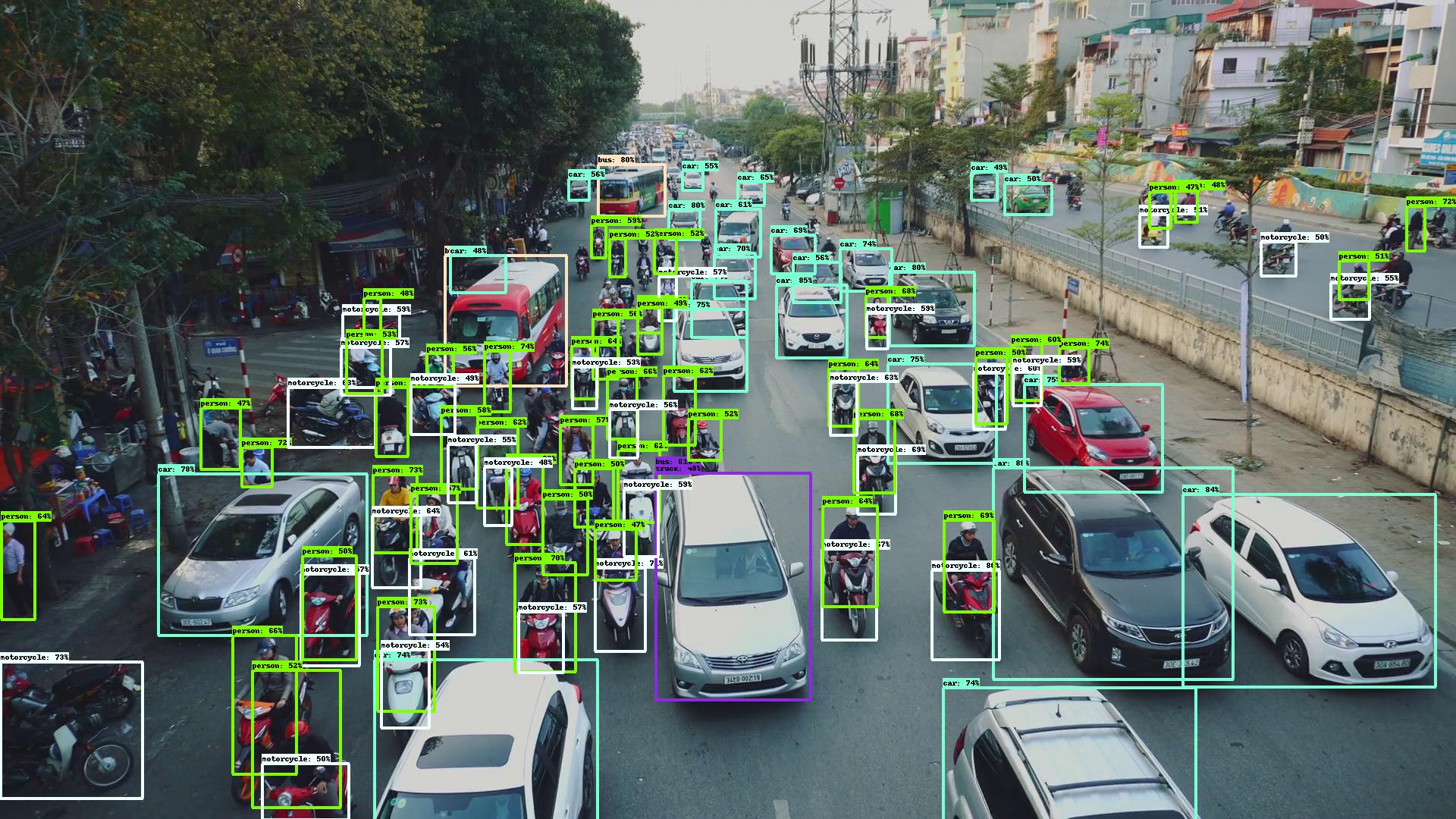
Appreciate the great work from the following repositories:
If you like this repository, or if you'd like to support the author for any reason, you can donate to the author. Feel free to send me your name or introducing pages, I will make sure your name(s) on the sponsors list.

Sincerely thank you for your generosity.
此处可能存在不合适展示的内容,页面不予展示。您可通过相关编辑功能自查并修改。
如您确认内容无涉及 不当用语 / 纯广告导流 / 暴力 / 低俗色情 / 侵权 / 盗版 / 虚假 / 无价值内容或违法国家有关法律法规的内容,可点击提交进行申诉,我们将尽快为您处理。